ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION. Solution Manual
|
|
|
- Ἰεζάβελ Σπυρόπουλος
- 5 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu , India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
2 2
3 Contents Electomagnetic Radiation 5 2 Antenna Chaacteistics 9 3 Wie Antennas 45 4 Apetue Antennas 59 5 Antenna Aas 83 6 Special Antennas 97 7 Antenna Measuements 05 8 Radio Wave Popagation 07 3
4 4 CONTENTS
5 Chapte Electomagnetic Radiation Solution. The unit vectos in spheical coodinates, viz., a, a θ, and a φ epessed in tems of a, a, and a z as see Eample.7, can be a = a sin θ cos φ + a sin θ sin φ + a z cos θ a θ = a cos θ cos φ + a cos θ sin φ a z sin θ a φ = a sin φ + a cos φ Taking the dot poduct of each of the unit vectos with itself, a a = sin 2 θ cos 2 φ + sin 2 θ sin 2 φ + cos 2 θ = a θ a θ = cos 2 θ cos 2 φ + cos 2 θ sin 2 φ + sin 2 θ = a φ a φ = sin 2 φ + cos 2 φ = Taking the dot poducts with each othe, a a θ = sin θ cos θ cos 2 φ + sin θ cos θ sin 2 φ sin θ cos θ = 0 a θ a φ = cos θ cos φ sin φ + cos θ sin φ cos φ = 0 a a φ = sin θ cos φ sin φ + sin θ sin φ cos φ = 0 Theefoe, the spheical coodinate sstem is othogonal. Solution.2 In ectangula coodinate sstem, the gadient opeato is given b Taking the cul of φ, Epanding the deteminant, 2 φ φ = a z 2 φ z dφ φ = a d + a dφ d + a dφ z dz a a a z φ = z dφ dφ dφ d d dz 2 φ + a z 2 φ 2 φ + a z z 2 φ = 0 5
6 6 CHAPTER. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION Solution.3 The cul of a vecto in ectangula coodinates is given b a a a z A = z A A A z Epanding the deteminant, Az A = a A z Taking the divegence, 2 A z A = 2 A + z A + a z A z A + a z A 2 A z 2 A z 2 A + z 2 A = 0 z Solution.4 In ectangula coodinates a a a z A = z A A A z Az A = a A A + a z z A z A + a z A Now we can epand A as A = { A a A A z z A } z { Az +a z A A z A } { A +a z z A z Az A } z { 2 } A = a + 2 A z z 2 A 2 2 A 2 z { 2 } A +a + 2 A z z 2 A 2 2 A 2 z { 2 } A +a z z + 2 A z 2 A z 2 2 A z 2 { 2 A = a + 2 A z z + 2 A 2 2 A 2 2 A 2 2 A 2 z { 2 A +a + 2 A z z + 2 A 2 2 A 2 2 A 2 2 A 2 z } }
7 7 { 2 } A +a z z + 2 A z + 2 A z 2 z 2 A z 2 2 A z 2 2 A z 2 z A = a + A + A z z A +a + A + A z z A +a z z + A + A z z a 2 A a 2 A a z 2 A z = A 2 A Solution.5 In a souce-fee egion the Mawell s equations educe to Taking the cul of the fist equation, E = jωµh H = jωɛe E = 0 H = 0 E = jωµ H Epanding the L.H.S. using the vecto identit and substituting the epession fo H on the R.H.S fom the second equation, Since E = 0 and ω 2 µɛ = k 2, we get E 2 E = jωµjωɛe 2 E + k 2 E = 0 Similal, taking and cul of the second equation, H = jωɛ E Epanding the L.H.S. using the vecto identit and substituting the epession fo E on the R.H.S fom the fist equation, H 2 H = jωɛ jωµh Since H = 0, we get 2 H + k 2 H = 0 Solution.6 Fom Eqns.3 to.34, we can conclude that V = V 0 e jk / epesents a wave with a velocit v = ω/k. Since both ω and k ae positive numbes, the
8 8 CHAPTER. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION velocit is positive. Theefoe, V epesents a wave tavelling in the positive diection. Solution.7 a The equiphase suface is a sphee of adius with cente at the oigin. b Equiphase suface is a plane =constant. Solution.8 Fom Eqn.53, we have Substituting into Eqn.57 A z = µ I 0dl e jk A = a φ µ I 0dl e jk sin θ θ µ I 0dl e jk cos θ Pefoming the indicated diffeentiation, µ A = a φ I 0dl jke jk sin θ + e jk Substituting in and eaanging, we get = a φ H = 0 H θ = 0 µ I 0dl e jk sin θjk + H = µ A H φ = jk I 0dl sin θ e jk + jk sin θ Solution.9 Substituting the epession fo H φ fom Eqn.6 into Eqn.63 E = jωɛ 2 sin θ a θ a θ sin θjk I 0dl sin θ sin θjk I 0dl sin θ { e jk Pefoming the indicated diffeentiation, E = a jωɛ 2 2 sin θ cos θjk I 0dl sin θ a θ jk I 0dl sin 2 { θ e jk { + jk e jk { + } jk } + } jk } jke jk jk e jk jk e jk jk 2
9 9 Substituting ωɛ = k/η and simplifing E = η a cos θjk I 0dl e jk { + } jk 2π jk { +a θ jk I 0dl sin θ jk e jk This can be witten in component fom as E = η I 0dl cos θ 2π E θ = jη ki 0dl sin θ E φ = 0 e jk e jk + jk k 2 + jk + jk k 2 } Solution.0 Fom Eqn.53, the magnetic vecto potential due to a z diected cuent element is, µ A = a z I 0dl e jk whee, = z 2 The cul of A in ectangula coodinates is given b Az A = a A A + a z z A z A + a z A Since A and A ae zeo, Diffeentiating A z with espect to, A z A = a a A z A z = µ I 0dl e jk We now compute Similal, e jk = = e jk jk e jk z 2 e jk 2 jk e jk = e jk jk z 2
10 0 CHAPTER. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION and hence A z = µ I 0dl e jk jk Theefoe, the magnetic field components ae, H = A z µ = I 0dl H = A z µ = I 0dl H z = 0 e jk e jk jk jk Using the tansfomation fom ectangula to spheical coodinates see Appendi F, H = sin θ cos φh + sin θ sin φh H θ = cos θ cos φh + cos θ sin φh H φ = sin φh + cos φh Substituting the epessions fo H and H and using the elationships = sin θ cos φ and = sin θ sin φ, H = I 0dl e jk = 0 H θ = I 0dl e jk = 0 H φ = I 0dl e jk = jk I 0dl sin θ jk {sin θ cos φ sin θ sin φ sin θ sin φ sin θ cos φ} jk {cos θ cos φ sin θ sin φ cos θ sin φ sin θ cos φ} jk sin φ sin θ sin φ cos φ sin θ cos φ e jk + jk These ae the same as given b Eqns.59 to.6. The electic field is computed using, E = jωɛ H = Hz a jωɛ H H + a z z H z H + a z H Since H z = 0, E = H a jωɛ z + a H z + a H z H We now compute the patial deivates of H and H with espect to,, and z. H = I 0dl e jk + jk e jk jk + e jk jk
11 Similal, H H = I 0dl + e jk = I 0dl + e jk jk e jk + e jk 3 e jk jk + e jk 3 jk jk jk jk Using = sin θ cos φ 2 + sin θ sin φ 2 = 2 sin 2 θ, we can wite H H = I 0dl + e jk jk jk + 2 sin 2 θ 2 sin2 θ + sin2 θ 2 Futhe, we can wite the deivatives of H and H with espect to z as H z H z = I 0dl e jk z e jk 3 e jk = I 0dl e jk z 3 jk z jk jk jk + e jk z + e jk jk z 3 jk z 3 which can be witten as, H = I 0dl e jk jk cos θ sin θ sin φ jk z + e jk sin θ sin φ H z e jk = I 0dl e jk jk sin θ sin φ cos θ e jk jk cos θ sin θ cos φ sin θ cos φ cos θ jk The electic field is given b E = H a jωɛ z + a H z + a H z H jk cos θ 2 + e jk cos θ sin θ cos φ 2
12 2 CHAPTER. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION = I { 0dl e jk a jk cos θ sin θ cos φ jk jωɛ e jk jk sin θ cos φ cos θ + e jk cos θ sin θ cos φ 2 e jk +a jk cos θ sin θ sin φ jk e jk jk sin θ sin φ cos θ + e jk cos θ sin θ sin φ 2 e jk a z jk + 2 sin 2 θ + jk } 2 sin2 θ + sin2 θ 2 The components of the electic field in spheical coodinates can be witten as E = sin θ cos φe + sin θ sin φe + cos θe z E θ = cos θ cos φe + cos θ sin φe sin θe z E φ = sin φe + cos φe Substituting the epessions fo E, E and E z, and simplifing E = I 0dl e jk { sin θ cos φ jk jωɛ sin θ cos φ cos θ jk + sin θ sin φ jk sin θ sin φ cos θ cos θ sin θ cos φ + sin θ cos φ cos θ sin θ sin φ jk cos θ jk jk cos θ + sin θ sin φ 2 cos θ jk + 2 sin 2 θ + jk } 2 sin2 θ + sin2 θ 2 = I 0dl e jk { jk + 2 sin 2 θ cos θ + jωɛ jk sin 2 θ cos θ + jk + } 2 sin2 θ cos θ = I 0dl k e jk + 2π ωɛ jk cos θ = η I 0dl cos θ e jk + 2π jk 2 jk + sin 2 θ cos θ + 2 sin2 θ cos θ cos θ jk + sin 2 θ cos θ
13 3 E θ = I 0dl e jk { cos θ cos φ jk jωɛ sin θ cos φ cos θ jk + cos θ sin φ jk sin θ sin φ cos θ cos θ sin θ cos φ + sin θ cos φ cos θ sin θ sin φ jk cos θ jk jk cos θ + sin θ sin φ 2 + sin θ jk + 2 sin 2 θ + jk } 2 sin2 θ + sin2 θ 2 = I 0dl e jk { jk + 2 cos 2 θ sin θ + jωɛ + jk sin 3 θ jk + sin θ + + } 2 sin3 θ = I 0dl sin θ e jk jk jωɛ = I 0dl sin θ = I 0dl sin θ = jη I 0dl sin θ e jk jωɛ e jk jωɛ e jk jk jk 2 + jk jk k 2 2 jk + cos 2 θ sin θ + 2 cos2 θ sin θ jk + sin 3 θ jk + 2 jk jk + E φ = I 0dl e jk { sin φ jk jωɛ sin θ cos φ cos θ jk + sin θ cos φ + cos φ jk cos θ sin θ sin φ sin θ sin φ cos θ jk + sin θ sin φ = 0 cos θ sin θ cos φ jk cos θ 2 jk } cos θ These ae the epessions fo the components of the electic field in spheical coodinate sstem as given b Eqns
14 4 CHAPTER. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION Solution. Substituting ω = 2πf and f = v/λ, Using k = 2π/λ, and v = / µɛ, we get ωµ = 2π v λ µ ωµ = k µɛ µ = k µ ɛ = kη Solution.2 The electic and magnetic fields in the fa-field egion of a Hetzian dipole can be witten as E θ = E 0 sin θ e jk H φ = E 0 η sin θ e jk whee E 0 is a comple constant. Taking the cul of the electic field, a a θ sin θa φ E = 2 sin θ θ φ 0 E 0 sin θ e jk 0 Since the electic field is independent of φ, diffeentiation with espect to φ ields a zeo. Thus, the deteminant can be epanded to get, { } E = sin θa 2 φ sin θ E 0 sin θe jk Diffeentiating with espect, Similal, H = = 2 sin θ E = a φ je 0 k sin θ e jk ωµ e jk = ja φ E 0 sin θ η E 0 = jωµ a φ η = jωµh a a θ sin θa φ θ φ 0 0 sin θ E 0 η 2 sin θ a E 0 e jk 2 sin θ cos θ η sin θ e jk sin θ e jk E 0 e jk = a 2 cos θ + a η 2 θ j E 0 e jk sin θk η 2 sin θ a E 0 θ η sin2 θ jke jk
15 At lage distances, we can ignoe the tem containing / 2 and using the elationship k/η = ωɛ, we can wite H = jωɛ { = jωɛe a θ E 0 sin θ e jk } 5 Solution.3 Assuming fa field condition, fom Eqn.69, E θ = jη ki 0dl sin θ E θ = η ki 0dl sin θ e jk In the - plane θ = 90. Substituting dl= m, I 0 = 0 A, f= MHz which coesponds to λ = 300 m, and k = 2π/λ = 2π/300 and η = Ω we get Theefoe, we get E θ = π = =6279 m = 0 3 Solution.4 The magnetic vecto potential fo a diected Hetzian dipole is given b Epessing a is spheical coodinates, The magnetic field is given b µ 0 A = a I 0dl e jk A = µ 0 I 0dl e jk a sin θ sin φ + a θ cos θ sin φ + a φ cos φ H = µ A = a a θ sin θa φ µ 2 sin θ θ φ A A θ sin θa φ { I 0 dl = a 2 sin θ cos φ e jk cos θ sin φ e jk sin θ θ φ a θ sin θ cos φ e jk sin θ sin φ e jk φ + sin θa φ cos θ sin φ e jk } sin θ sin φ e jk θ I 0 dl = {a 2 cos θ cos φ e jk cos θ cos φ e jk sin θ
16 6 CHAPTER. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION a θ jk sin θ cos φ e jk + sin θa φ = I 0dl e jk = a θ jki 0 dl jk cos θ sin φ e jk sin θ cos φ e jk cos θ sin φ e jk } {a θ cos φjk + a φ cos θ sin φjk + } cos φe jk + jki 0 dl a φ cos θ sin φe jk jk + jk The electic field is given b, E = jωɛ H = a a θ sin θa φ jωɛ 2 sin θ θ φ 0 H θ sin θh φ = jki 0dl jωɛ 2 sin θ { a sin θ cos θ sin φ e jk + cos φ e jk + θ jk φ jk a θ sin θ cos θ sin φ e jk + jk + sin θa φ cos φ e jk + } jk = k I 0 dl ωɛ 2 sin θ {a cos 2 θ sin φ e jk + + sin φ e jk + jk jk +a θ sin θ cos θ sin φ + sin θa φ jke jk { jke jk + jk The components of the electic field ae, E = η I 0dl + jk + e jk jk 2 2 sin θ sin φ sin2 θ e jk = η I 0dl sin θ sin φe jk E θ = η I 0dl jk 2 sin θ = η jki 0dl E φ = η jki 0dl + jk sin θ cos θ sin φe jk cos θ sin φe jk cos φe jk } + e jk jk 2 } + jk + jk k 2 + jk k 2 + jk k 2
17 7 Solution.5 The electic field, E z at 0, 00, 0 is the same as E θ = 00, θ = π, φ = 2, and fom Eqn.65 π 2 E θ = jη ki 0dl e jk + jk k 2 Compaing it = 2 cos6π 0 6 t with it = I 0 cosωt we get, I 0 = 2 A, ω = 6π 0 6 and k = ω = 6π 06 = ad/m. Fom the data given in the poblem, we have v dl = 0.5 m and = 00 m. Theefoe, Since a z E z θ=90 = a θ E θ, e j E θ = j j = j0.088e j j = j j0.592 = j E θ = V/m E z = = V/m If the dipole is oiented along diection, the field also gets oiented along the diection. Theefoe, E = V/m
18 8 CHAPTER. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small spheres separated by a distance s. The charge on one sphere changes with time and is described by
 5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics
 Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
VEKTORANALYS. CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (kroklinjiga koordinatsytem) Kursvecka 4. Kapitel 10 Sidor
 VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines
![Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines](/thumbs/51/28406191.jpg) Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
4.2 Differential Equations in Polar Coordinates
 Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Curvilinear Systems of Coordinates
 A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
General Relativity (225A) Fall 2013 Assignment 5 Solutions
 Univesity of Califonia at San Diego Depatment of Physics Pof. John McGeevy Geneal Relativity 225A Fall 2013 Assignment 5 Solutions Posted Octobe 23, 2013 Due Monday, Novembe 4, 2013 1. A constant vecto
Univesity of Califonia at San Diego Depatment of Physics Pof. John McGeevy Geneal Relativity 225A Fall 2013 Assignment 5 Solutions Posted Octobe 23, 2013 Due Monday, Novembe 4, 2013 1. A constant vecto
The Laplacian in Spherical Polar Coordinates
 Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Problems in curvilinear coordinates
 Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Analytical Expression for Hessian
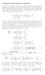 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
r = x 2 + y 2 and h = z y = r sin sin ϕ
 Homewok 4. Solutions Calculate the Chistoffel symbols of the canonical flat connection in E 3 in a cylindical coodinates x cos ϕ, y sin ϕ, z h, b spheical coodinates. Fo the case of sphee ty to make calculations
Homewok 4. Solutions Calculate the Chistoffel symbols of the canonical flat connection in E 3 in a cylindical coodinates x cos ϕ, y sin ϕ, z h, b spheical coodinates. Fo the case of sphee ty to make calculations
Written Examination. Antennas and Propagation (AA ) April 26, 2017.
 Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2
 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, irrotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE + V Φ + i x. Ψ y = Φ. and. Ψ x
 STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
dx x ψ, we should find a similar expression for rθφ L ψ. From L = R P and our knowledge of momentum operators, it follows that + e y z d
 PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Orbital angular momentum and the spherical harmonics
 Obital angula momentum and the spheical hamonics Apil 2, 207 Obital angula momentum We compae ou esult on epesentations of otations with ou pevious expeience of angula momentum, defined fo a point paticle
Obital angula momentum and the spheical hamonics Apil 2, 207 Obital angula momentum We compae ou esult on epesentations of otations with ou pevious expeience of angula momentum, defined fo a point paticle
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation format: Markus Zahn, 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation format: Markus Zahn, 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
 Problem 7.19 Ignoring reflection at the air soil boundary, if the amplitude of a 3-GHz incident wave is 10 V/m at the surface of a wet soil medium, at what depth will it be down to 1 mv/m? Wet soil is
Problem 7.19 Ignoring reflection at the air soil boundary, if the amplitude of a 3-GHz incident wave is 10 V/m at the surface of a wet soil medium, at what depth will it be down to 1 mv/m? Wet soil is
Physics 505 Fall 2005 Practice Midterm Solutions. The midterm will be a 120 minute open book, open notes exam. Do all three problems.
 Physics 55 Fll 25 Pctice Midtem Solutions The midtem will e 2 minute open ook, open notes exm. Do ll thee polems.. A two-dimensionl polem is defined y semi-cicul wedge with φ nd ρ. Fo the Diichlet polem,
Physics 55 Fll 25 Pctice Midtem Solutions The midtem will e 2 minute open ook, open notes exm. Do ll thee polems.. A two-dimensionl polem is defined y semi-cicul wedge with φ nd ρ. Fo the Diichlet polem,
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
3.7 Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions for P-Flow
 .0 - Maine Hydodynaics, Sping 005 Lectue 10.0 - Maine Hydodynaics Lectue 10 3.7 Govening Equations and Bounday Conditions fo P-Flow 3.7.1 Govening Equations fo P-Flow (a Continuity φ = 0 ( 1 (b Benoulli
.0 - Maine Hydodynaics, Sping 005 Lectue 10.0 - Maine Hydodynaics Lectue 10 3.7 Govening Equations and Bounday Conditions fo P-Flow 3.7.1 Govening Equations fo P-Flow (a Continuity φ = 0 ( 1 (b Benoulli
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Theoretical Competition: 12 July 2011 Question 1 Page 1 of 2
 Theoetical Competition: July Question Page of. Ένα πρόβλημα τριών σωμάτων και το LISA μ M O m EIKONA Ομοεπίπεδες τροχιές των τριών σωμάτων. Δύο μάζες Μ και m κινούνται σε κυκλικές τροχιές με ακτίνες και,
Theoetical Competition: July Question Page of. Ένα πρόβλημα τριών σωμάτων και το LISA μ M O m EIKONA Ομοεπίπεδες τροχιές των τριών σωμάτων. Δύο μάζες Μ και m κινούνται σε κυκλικές τροχιές με ακτίνες και,
Chapter 7a. Elements of Elasticity, Thermal Stresses
 Chapte 7a lements of lasticit, Themal Stesses Mechanics of mateials method: 1. Defomation; guesswok, intuition, smmet, pio knowledge, epeiment, etc.. Stain; eact o appoimate solution fom defomation. Stess;
Chapte 7a lements of lasticit, Themal Stesses Mechanics of mateials method: 1. Defomation; guesswok, intuition, smmet, pio knowledge, epeiment, etc.. Stain; eact o appoimate solution fom defomation. Stess;
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1- Uzunluğu b olan (b > λ) tek kutuplu bir tel anten xy düzlemindeki iletken plakaya dik olan z ekseninde bulunmakta olup I
 1- Uzunluğu b olan (b > λ) tek kutuplu bi tel anten xy düzlemindeki iletken plakaya dik olan z ekseninde bulunmakta olup I sabit akımı taşımaktadı. a) ( θφ,, ) noktasındaki elektik alanı hesaplayın. 1-
1- Uzunluğu b olan (b > λ) tek kutuplu bi tel anten xy düzlemindeki iletken plakaya dik olan z ekseninde bulunmakta olup I sabit akımı taşımaktadı. a) ( θφ,, ) noktasındaki elektik alanı hesaplayın. 1-
Appendix to On the stability of a compressible axisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe. By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee
 Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Exercise, May 23, 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1
 Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
Topic 4. Linear Wire and Small Circular Loop Antennas. Tamer Abuelfadl
 Topic 4 Linear Wire and Small Circular Loop Antennas Tamer Abuelfadl Electronics and Electrical Communications Department Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Tamer Abuelfadl (EEC, Cairo University)
Topic 4 Linear Wire and Small Circular Loop Antennas Tamer Abuelfadl Electronics and Electrical Communications Department Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Tamer Abuelfadl (EEC, Cairo University)
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Course Reader for CHEN 7100/7106. Transport Phenomena I
 Couse Reade fo CHEN 7100/7106 Tanspot Phenomena I Pof. W. R. Ashust Aubun Univesity Depatment of Chemical Engineeing c 2012 Name: Contents Peface i 0.1 Nomenclatue........................................
Couse Reade fo CHEN 7100/7106 Tanspot Phenomena I Pof. W. R. Ashust Aubun Univesity Depatment of Chemical Engineeing c 2012 Name: Contents Peface i 0.1 Nomenclatue........................................
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
九十七學年第一學期 PHYS2310 電磁學期中考試題 ( 共兩頁 )
 九十七學年第一學期 PHY 電磁學期中考試題 ( 共兩頁 ) [Giffiths Ch.-] 補考 8// :am :am, 教師 : 張存續記得寫上學號, 班別及姓名等 請依題號順序每頁答一題 Useful fomulas V ˆ ˆ V V = + θ+ V φ ˆ an θ sinθ φ v = ( v) (sin ) + θvθ + v sinθ θ sinθ φ φ. (8%,%) cos
九十七學年第一學期 PHY 電磁學期中考試題 ( 共兩頁 ) [Giffiths Ch.-] 補考 8// :am :am, 教師 : 張存續記得寫上學號, 班別及姓名等 請依題號順序每頁答一題 Useful fomulas V ˆ ˆ V V = + θ+ V φ ˆ an θ sinθ φ v = ( v) (sin ) + θvθ + v sinθ θ sinθ φ φ. (8%,%) cos
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
Mock Exam 7. 1 Hong Kong Educational Publishing Company. Section A 1. Reference: HKDSE Math M Q2 (a) (1 + kx) n 1M + 1A = (1) =
 Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
( y) Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) 21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations
 Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (2, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = 1+9 = 3.
 Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = ˆx( 1)+ŷ( 1 ( 1))+ẑ(0 ( 3)) = ˆx+ẑ3, A = 1+9 = 3.16, â = A A = ˆx+ẑ3 3.16
Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = ˆx( 1)+ŷ( 1 ( 1))+ẑ(0 ( 3)) = ˆx+ẑ3, A = 1+9 = 3.16, â = A A = ˆx+ẑ3 3.16
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Spherical Coordinates
 Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
1 3D Helmholtz Equation
 Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Space-Time Symmetries
 Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Jackson 2.25 Homework Problem Solution Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell
 Jackson 2.25 Hoework Proble Solution Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell PROBLEM: Two conducting planes at zero potential eet along the z axis, aking an angle β between the, as
Jackson 2.25 Hoework Proble Solution Dr. Christopher S. Baird University of Massachusetts Lowell PROBLEM: Two conducting planes at zero potential eet along the z axis, aking an angle β between the, as
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Trigonometry 1.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
 Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
Strain and stress tensors in spherical coordinates
 Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Risk! " #$%&'() *!'+,'''## -. / # $
 Risk! " #$%&'(!'+,'''## -. / 0! " # $ +/ #%&''&(+(( &'',$ #-&''&$ #(./0&'',$( ( (! #( &''/$ #$ 3 #4&'',$ #- &'',$ #5&''6(&''&7&'',$ / ( /8 9 :&' " 4; < # $ 3 " ( #$ = = #$ #$ ( 3 - > # $ 3 = = " 3 3, 6?3
Risk! " #$%&'(!'+,'''## -. / 0! " # $ +/ #%&''&(+(( &'',$ #-&''&$ #(./0&'',$( ( (! #( &''/$ #$ 3 #4&'',$ #- &'',$ #5&''6(&''&7&'',$ / ( /8 9 :&' " 4; < # $ 3 " ( #$ = = #$ #$ ( 3 - > # $ 3 = = " 3 3, 6?3
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Section 8.2 Graphs of Polar Equations
 Section 8. Graphs of Polar Equations Graphing Polar Equations The graph of a polar equation r = f(θ), or more generally F(r,θ) = 0, consists of all points P that have at least one polar representation
Section 8. Graphs of Polar Equations Graphing Polar Equations The graph of a polar equation r = f(θ), or more generally F(r,θ) = 0, consists of all points P that have at least one polar representation
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
CHAPTER (2) Electric Charges, Electric Charge Densities and Electric Field Intensity
 CHAPTE () Electric Chrges, Electric Chrge Densities nd Electric Field Intensity Chrge Configurtion ) Point Chrge: The concept of the point chrge is used when the dimensions of n electric chrge distriution
CHAPTE () Electric Chrges, Electric Chrge Densities nd Electric Field Intensity Chrge Configurtion ) Point Chrge: The concept of the point chrge is used when the dimensions of n electric chrge distriution
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
Orbital angular momentum and the spherical harmonics
 Orbital angular momentum and the spherical harmonics March 8, 03 Orbital angular momentum We compare our result on representations of rotations with our previous experience of angular momentum, defined
Orbital angular momentum and the spherical harmonics March 8, 03 Orbital angular momentum We compare our result on representations of rotations with our previous experience of angular momentum, defined
Exercise 1.1. Verify that if we apply GS to the coordinate basis Gauss form ds 2 = E(u, v)du 2 + 2F (u, v)dudv + G(u, v)dv 2
 Math 209 Riemannian Geometry Jeongmin Shon Problem. Let M 2 R 3 be embedded surface. Then the induced metric on M 2 is obtained by taking the standard inner product on R 3 and restricting it to the tangent
Math 209 Riemannian Geometry Jeongmin Shon Problem. Let M 2 R 3 be embedded surface. Then the induced metric on M 2 is obtained by taking the standard inner product on R 3 and restricting it to the tangent
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
Similarly, we may define hyperbolic functions cosh α and sinh α from the unit hyperbola
 Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
Parametrized Surfaces
 Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
9.09. # 1. Area inside the oval limaçon r = cos θ. To graph, start with θ = 0 so r = 6. Compute dr
 9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
The Neutrix Product of the Distributions r. x λ
 ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
Forced Pendulum Numerical approach
 Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Logsine integrals. Notes by G.J.O. Jameson. log sin θ dθ = π log 2,
 Logsine integrals Notes by G.J.O. Jameson The basic logsine integrals are: log sin θ dθ = log( sin θ) dθ = log cos θ dθ = π log, () log( cos θ) dθ =. () The equivalence of () and () is obvious. To prove
Logsine integrals Notes by G.J.O. Jameson The basic logsine integrals are: log sin θ dθ = log( sin θ) dθ = log cos θ dθ = π log, () log( cos θ) dθ =. () The equivalence of () and () is obvious. To prove
Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation
 Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation Praveen. C praveen@math.tifrbng.res.in Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Center for Applicable Mathematics Bangalore 560065 http://math.tifrbng.res.in/~praveen
Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation Praveen. C praveen@math.tifrbng.res.in Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Center for Applicable Mathematics Bangalore 560065 http://math.tifrbng.res.in/~praveen
