ΠΕΡΙΛΗΨΕΙΣ 7 Ο ΣΧΟΛΕΙΟ ΦΥΣΙΚΗΣ & ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΣΥΝΤΗΞΗΣ
|
|
|
- Μνημοσύνη Λόντος
- 8 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 ΕΝΩΣΗ EURATOM ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΕΡΙΛΗΨΕΙΣ 7 Ο ΣΧΟΛΕΙΟ ΦΥΣΙΚΗΣ & ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΣΥΝΤΗΞΗΣ Βόλοςς Απριιλίίου Παννεεπιισττήμιιο Θεεσσαλίίαςς (Αμφιθέατρα Μηχανολόγων & Χωροταξίας) ABSTRACTS 7 ΤΗ SCHOOL OF FUSION PHYSICS & TECHNOLOGY Voloss Aprri ill Univeerrssi itty off Theessssal ly (Auditoria Mechanical & Planning Engineering) ASSOCIATION EURATOM HELLENIC REPUBLIC
2 ii
3 FOREWORD The 7 th School of Fusion Science & Technology will be attended by students who have heard little about plasma and fusion, doctoral candidates who are working on problems related to fusion, postdoctoral researchers working on fusion topics for some years and by academic staff from universities in Greece who are coordinating research groups. Also, distinguished researchers from Europe and the USA will give invited talks. The joint attendance of such a school by all the above is creating additional needs and going beyond traditional schools. Thus, the programme committee developed a multi-level series of lectures with the aim to satisfy as many of the audience needs. The programme is divided in four units: School Classes, Invited Lectures, Advanced Seminars, Research Seminars which intercept in many respects but are apart in others. The School starts Monday morning in the Auditorium of Planning Engineering of the University of Thessaly with topics of interest to all. In the afternoon the students follow introductory topics while in the Auditorium of Mechanical Engineering the first advanced seminar on Gyrotrons takes place. The School continues on Tuesday morning while the second advanced seminar on Turbulence & Transport takes place in parallel. In the afternoon, the School classes continue while the 3 rd advanced Seminar on Heating & Current Drive takes place. On Wednesday This layout of parallel performance of the School and the Advanced Seminars will continue in the following days and the audiences of the School and the Seminars will be coming together only during the Invited Lectures delivered by distinguished researchers. After the morning classes of Wednesday, the afternoon will be free and in the evening the School Dinner will be held. On Thursday afternoon, the audience again separates and the students discuss with their teachers questions while the 4 th advanced seminar on Viscous Magnetohydrodynamics takes place. The audiences of the School and the Seminars meet during the invited plenary talks given by distinguished researchers, and during the breaks. Friday and Saturday are dedicated to topics of interest to all relating to advanced subjects of physics and technology of fusion and to current research works that are presented mainly by young researchers. Each year the School has certain state-of-art topics usually indicative of the activities of the Greek researchers. This year s topics are: Gyrotrons, Electro Cyclotron Resonance Heating, Turbulence & Transport, Viscous MHD Flows. These subjects will be the main objective of the advanced seminars. In this manner the Fusion School serves as a multi-disciplinary forum covering the interest of all. We hope that you will find this structure of the 7 th School rewarding and we look forward to your active participation that will warranty its success. In conclusion, the organizers of the Fusion Schools in Volos would like to express their sincere thanks to the European Commission for the continuous support. Volos 14 April 2008 The Programme Committee iii
4 ΠΡΟΛΟΓΟΣ Στο 7 ο Σχολείο Φυσικής & Τεχνολογίας Σύντηξης συμμετέχουν φοιτητές που έχουν ακούσει ελάχιστα για πλάσμα και σύντηξη, υποψήφιοι διδάκτορες που εργάζονται σε προβλήματα συνδεόμενα με σύντηξη, μεταδιδακτορικούς ερευνητές που ασχολούνται με θέματα σύντηξης αρκετά χρόνια, και ακαδημαϊκό προσωπικό ελληνικών πανεπιστημίων που διευθύνουν ερευνητικές ομάδες. Επίσης, θα κάνουν προσκεκλημένες ομιλίες διακεκριμένοι ερευνητές από την Ευρώπη και ΗΠΑ Η κοινή παρακολούθηση ενός τέτοιου Σχολείου από τους παραπάνω είναι φυσικό να δημιουργεί πρόσθετες ανάγκες και να ξεφεύγει από τα παραδοσιακά Σχολεία. Έτσι, η επιτροπή προγράμματος δημιούργησε μία πολυ-επίπεδη σειρά διαλέξεων με στόχο να ικανοποιήσει όσο το δυνατόν τις ανάγκες του ακροατηρίου. Το πρόγραμμα χωρίζεται σε τέσσερις ενότητες (Μαθήματα Σχολείου, Προσκεκλημένες Ομιλίες, Προχωρημένα Σεμινάρια, Ερευνητικές Εργασίες) που σε πολλά σημεία τέμνονται και άλλα απομακρύνονται. Το Σχολείο ξεκινά την Δευτέρα το πρωί στο Αμφιθέατρο Χωροταξίας του Πανεπιστημίου Θεσσαλίας με θέματα που ενδιαφέρουν όλους. Το απόγευμα οι φοιτητές παρακολουθούν εισαγωγικά θέματα ενώ παράλληλα στο Αμφιθέατρο Μηχανολόγων διεξάγεται το 1 ο προχωρημένο σεμινάριο στα Γυροτρόνια. Tο Σχολείο συνεχίζεται tην Τρίτη το πρωί ενώ στην αίθουσα σεμιναρίων διεξάγεται το 2 ο προχωρημένο σεμινάριο σε Τύρβη και Μεταφορά στο πλάσμα. Το απόγευμα συνεχίζονται τα μαθήματα και παράλληλα διεξάγεται το 3 ο προχωρημένο σεμινάριο στη Θέρμανση και Οδήγηση Ρευμάτων πλάσματος. Μετά τις πρωινές διαλέξεις της Τετάρτης, το απόγευμα είναι ελεύθερο ενώ το βράδυ θα παρατεθεί το καθιερωμένο Δείπνο. Το απόγευμα της Πέμπτης το ακροατήριο χωρίζεται πάλι και οι φοιτητές συζητούν με τους καθηγητές τους απορίες ενώ συγχρόνως διεξάγεται το 4 ο προχωρημένο σεμινάριο στην Ιξώδη Μαγνητο-υδροδυναμική. Τα ακροατήρια του Σχολείου και των Σεμιναρίων συναντώνται στις προσκεκλημένες ομιλίες που γίνονται από διακεκριμένους ερευνητές, και στα διαλείμματα. Η Παρασκευή και το Σάββατο είναι αφιερωμένα σε θέματα που ενδιαφέρουν όλους και αναφέρονται σε προχωρημένα θέματα φυσικής και τεχνολογίας της Σύντηξης και σε τρέχουσες ερευνητικές εργασίες που παρουσιάζονται κυρίως από νέους ερευνητές. Το Σχολείο κάθε χρόνο έχει κάποια θέματα αιχμής, ενδεικτικά συνήθως της δραστηριότητας πολλών Ελλήνων ερευνητών. Τα φετινά θέματα είναι: Gyrotrons, Electro Cyclotron Resonance Heating, Turbulence & Transport, Viscous MHD Flows. Τα θέματα αυτά θα είναι το κύριο αντικείμενο των προχωρημένων σεμιναρίων. Με τον τρόπο αυτό το Σχολείο Σύντηξης λειτουργεί ως ένας πολύ-επιστημονικός χώρος που καλύπτει τα ενδιαφέροντα όλων. Ελπίζουμε ότι θα βρείτε ενδιαφέρουσα αυτή την δομή του προγράμματος του 7 ου Σχολείου και προσδοκούμε στην ενεργή συμμετοχή σας που θα εξασφαλίσει την επιτυχία του. Κλείνοντας, οι οργανωτές των Σχολείων Σύντηξης στο Βόλο επιθυμούν να εκφράσουν τις θερμές ευχαριστίες τους στην Ευρωπαϊκή Επιτροπή για την συνεχή υποστήριξη. Βόλος 14 Απριλίου 2008 Η Επιτροπή Προγράμματος iv
5 CONTENTS - ΠΕΡΙΕΧΟΜΕΝΑ SCHOOL CLASSES (Given mainly in Greek, with some slides in English) SC01 Μ. Tsalas: Elements of electro-dynamics & Introduction to plasma p.01 SC02 Y. Kominis: Charged particle dynamics 01 SC03 Α. Αναστασιάδης: Charged particle interaction with nonlinear structures 01 SC04 Γ. Θρουμουλόπουλος: Introduction to magnetohydrodynamics 02 SC05 Π. Λαλούσης: Ideal and Resistive MHD: Numerical approach 02 SC06 Ι. Βομβορίδης: Kinetic theory 02 SC07 Λ. Βλάχος: Multiple fluid theory & Waves in plasmas 03 SC08 Κ. Χιτζανίδης: Kinetic instabilities 03 SC09 Ν. Πελεκάσης: Hydrodynamic & MHD stability 03 SC10 Ν. Βλάχος: Mathematical models and architecture of MHD codes 04 RESEARCH SEMINARS (Given in Greek, with slides in English and vice versa) S. Moustaizis: Physics and applications using compact plasma fusion devices p.05 I. Tigelis, G. Latsas, J.L. Vomvoridis: New results for beam-wave interaction in beam tunnels 05 RS01 S. Papastergiou: A blanket concept for DEMO and related MHD effects 05 RS02 P. Karditsas: Design and performance of the power plant helium cooled divertor 05 RS03 D. Strintzi: Gyrokinetic studies of ion heat transport at JET 06 RS04 S. Varoutis, D. Valougeorgis: Direct simulation of non-equilibrium flows related to fusion reactors 06 RS05 S. Misdanitis, D. Valougeorgis: Compressibility effects in flows under low, medium and high vacuum 06 RS06 S. Pantazis, D. Valougeorgis, A. Grecos: Numerical simulation of Brownian motion in a magnetic field 07 RS07 A. Grecos, D. Vavougios, Th. Grammenos: On Fokker-Planck type equations in stochastic transport 07 RS08 B. Weyssow: Smoothed particle hydrodynamic method with possible application to fusion plasmas 07 RS09 D. Apostolaki, G. Throumoulopoulos, H. Tasso: On tokamak equilibrium and stability with plasma flow parallel to the magnetic field 08 RS10 N. Pelekasis, D. Dimopoulos: Magnetic field effects on three-dimensional stability of natural convection flows in differentially heated cavities 08 RS11 D. Grigoriadis, S. Kassinos: MHD flows in complicated domains using the immersed boundary method 08 RS12 C. Dritselis, I. Sarris, N. Vlachos: Particle-turbulence interaction in MHD duct flows 09 RS13 S. Kakarantzas, I. Sarris, A. Grecos, N. Vlachos: MHD natural convection heat transfer of liquid metals in cylindrical annuli 09 RS14 Ι. Sarris, S. Kakarantzas, C. Dritselis, N. Vlachos: Heat transfer in turbulent MHD flows 09 RS15 K. Avramides, O. Dumbrajs, S. Kern, I. Pagonakis, J. Vomvoridis - Mode selection for a 170 GHz, 1 MW Gyrotron for ITER 10 RS16 Y. Kominis, K. Hizanidis, A. Ram: Quasilinear theory for momentum and spatial diffusion due to radio frequency waves in non-axisymmetric toroidal plasmas 10 v
6 RS17 H. Isliker: A self-organized criticality model for the magnetic topology in toroidal confinement devices 11 RS18 I. Sandberg: Intermittency in electromagnetic resistive ballooning turbulence 11 RS19 C. Tsironis, T. Samaras, L. Vlahos: Modelling the propagation of EC waves in hot anisotropic plasma with the FDTD method 11 RS20 G. Anastassiou, J. Vomvoridis: Post amplification of a Gaussian rf beam generated in a gyrotron via its interaction with a sheet electron beam 12 E.V. Votyakov - Liquid metal flow under an external inhomogeneous magnetic field. Wake of a magnetic obstacle 12 INVITED ADDRESSES (Slides will be made available on IA01 M. Tsalas, M. Watkins: Overview of the JET 2008 Experimental Program IA02 B. Weyssow, J. Pamela: EFDA: Structure and Workprogram IA03 A. Zurita: Challenges of the Euratom Fusion Programme INVITED LECTURES (Slides will be made available on IL01 Α.K. Ram: The case for Fusion energy IL02 A. Ram: Heating & current drive in fusion plasmas by radio frequency waves IL03 G. Ramponi: Physics analysis of ITER ECW systems for optimised performance IL04 A. Peeters: Introduction to micro-instabilities in toroidal plasmas IL05 D. Carati: Introduction to the theory and simulation of fluid and MHD turbulence IL06 S. Benkadda: Advances in understanding the complex nature of turbulent transport in magnetized fusion plasmas IL07 S. Alberti: Gyrotron physics and technology: From fusion to NMR spectroscopy IL08 B. Piosczyk: High power gyrotrons for fusion application: Basic design, status and goals IL09 S. Papastergiou: Design and analysis of in-vessel heat transfer devices for ITER/DEMO IL10 P. Karditsas: Design issues and implications for structural integrity of fusion power plant components ADVANCED SEMINARS (Slides will be made available on AS01 B. Piosczyk: Development of multi-mw gyrotron at FZK: present status & goals AS02 S. Illy: Particle-in-cell simulation tools for design and optimization of high power CW AS03 S. Alberti: Physics and technology of ITER-EC - upper launcher AS04 S. Benkadda - Multiscale dynamics of impurities transport in drift waves turbulence of edge tokamak plasmas AS05 A. Peeters - Gyrokinetic theory and simulations of turbulent transport AS06 A.K. Ram - Current issues in RF heating and current drive in tokamaks AS07 G. Ramponi - ECRH in ITER AS08 D. Carati - Development of large-eddy simulations for viscous MHD flows AS09 E. Votyakov - LM flows under external inhomogeneous magnetic field: wake of a magnetic obstacle AS10 N. Vlachos Problems in CFD modeling of MHD duct flows vi
7 SCHOOL CLASSES (Given mainly in Greek, with some slides in English) SC01 Μ. Τσάλας: Στοιχεία Ηλεκτροδυναμικής και Εισαγωγή στο Πλάσμα JET-UK & ΕΚΕΦΕ Δημόκριτος 1. Τι είναι η πυρηνική σύντηξη: Αντιδράσεις σύντηξης, Ηλιακές και στη Γη (ενεργός διατομή κτλ), Κριτήριο Lawson Πλάσμα 2. Τι είναι πλάσμα: Πλάσμα στη φύση, Παράμετροι πλάσματος (πυκνότητες, θερμοκρασίες κτλ), Η εξίσωση Saha, Μέθοδοι περιγραφής πλάσματος (μικρο vs μακροσκοπικές, κίνηση σωματιδίων, κινητική θεωρία, μαγνητοϋδροδυναμική, εξισώσεις Maxwell) 3. Δημιουργία πλάσματος στο εργαστήριο: Θερμικές μέθοδοι, Ηλεκτρικές μέθοδοι, Με ηλεκτρομαγνητικά κύματα, Με επιτάχυνση σωματιδίων 4. Βασικές παράμετροι πλάσματος: Μήκος και σφαίρα Debye - plasma parameter, Ηλεκτροστατικό δυναμικό-θωράκιση, Οιονεί ουδετερότητα, Συχνότητα πλάσματος, Μαγνητισμένο πλάσμα πλάσμα Beta 5. Συγκρούσεις Coulomb: Συχνότητα συγκρούσεων, Συγκρούσεις με ουδέτερα σωματίδια, Ηλεκτρική αντίσταση πλάσματος 6. Εισαγωγή στη μαγνητική συγκράτηση τοροειδή συστήματα SC02 Ι. Κομίνης: Δυναμική των τροχιών φορτισμένων σωματιδίων Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο 1. Τροχιές φορτισμένων σωματιδίων σε στατικά πεδία: Κίνηση σε στατικό ομογενές ηλεκτρικό πεδίο, Κίνηση σε στατικό ομογενές μαγνητικό πεδίο, Ολίσθηση E B, Κίνηση σε μη ομογενές στατικό ηλεκτρικό πεδίο, Κίνηση σε μη ομογενές στατικό μαγνητικό πεδίο (διαμήκης ανομοιογένεια, εγκάρσια ανομοιογένεια, καμπυλότητα πεδιακών γραμμών), Αδιαβατικές σταθερές 2. Αλληλεπίδραση φορτισμένων σωματιδίων με κύματα: Ομαλή και χαοτική κίνηση φορτισμένου σωματιδίου σε ομογενές στατικό μαγνητικό πεδίο υπό την επίδραση ηλεκτροστατικών κυμάτων (Χαμιλτονιανή περιγραφή της κίνησης φορτισμένου σωματιδίου, Κανονική θεωρία διαταραχών και υπολογισμός προσεγγιστικών σταθερών της κίνησης, Ο ρόλος των συντονισμών και το πρόβλημα των μικρών παρονομαστών, Επικάλυψη των συντονισμών και μετάβαση στο χάος), Περιπτώσεις (Διάδοση κύματος υπό διαφορετικές γωνίες ως προς το μαγνητικό πεδίο, Κυμάτων διακριτού και συνεχούς φάσματος) SC03 Α. Αναστασιάδης: Αλληλεπίδραση φορτίων με μη γραμμικές δομές-φύλλα ρεύματος Εθνικό Αστεροσκοπείο Αθηνών 1. Βασικές έννοιες: Τι είναι τα φύλλα ρεύματος; Σχηματισμός γεωμετρίες, Πως εμφανίζονται και που (παραδείγματα φυσικών συστημάτων); Παραδείγματα τροχιών φορτίων σε φύλλα ρεύματος 2. Φύλλα ρεύματος τύπου Harris και Χ-point: Γεωμετρία ηλεκτρομαγνητικού πεδίου, Εξίσωση κίνησης φορτίων, Νευτώνια και Χαμιλτονιανή προσέγγιση, Επιφάνεια Τομής Poincare, Είδος τροχιών (Περιοδικές, Ημι-περιοδικές, χαοτικές ), Ενεργειακές κατανομές φορτίων 3. ΜΥΔ Αριθμητικές Προσομοιώσεις: Επιλεγμένα αριθμητικά Αποτελέσματα 1
8 SC04 Γ. Θρουμουλόπουλος, Εισαγωγή στη Μαγνητοϋδροδυναμική Τμήμα Φυσικής, Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων 1. Βασικές έννοιες: Υδροδυναμική, Ιδανική Μαγνητοϋδροδυναμική, ΜΥΔ με ηλεκτρική απόσβεση (resistive) 2. Ισορροπία: Σφιγκτήρας-z (z-pinch), Εξίσωση Grad-Shafranov, Λύση Solovev, Ισορροπία με εσωτερικά φράγματα (internal barrier) 3. Ευστάθεια: Ενεργειακή αρχή των Bernstein, Frieman, Kruscal και Kulsrud., Ανάλυση ιδιοσυχνοτήτων, Αστάθεια σφιγκτήρα-z, Κατηγορίες ασταθειών (αστάθειες λόγω ρεύματος και πίεσης, τρόποι ταλάντωσης στα πλαίσια της ιδανικής ΜΥΔ και ΜΥΔ με ηλεκτρική απόσβεση, παραδείγματα) SC04 G. N. Throumoulopoulos, Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics, University of Ioannina Basic components of plasma confinement in fusion devices as the tokamak are equilibrium and stability. In equilibrium the pressure-gradient force acting on a plasma element is balanced by the magnetic force. Good confinement additionally requires stability for perturbations around an equilibrium state. The simplest model to study plasma confinement is magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). In the framework of MHD the plasma is described as a single fluid the physics of which is governed by electromagnetic interactions. In this talk the basic elements of the MHD model is first reviewed, then certain MHD equilibrium and linear stability issues of magnetically confined plasmas are presented. In addition, some current research problems in connection with the ITER project are briefly outlined. SC05 Παρ. Λαλούσης: ΜΥΔ χωρίς/με ηλεκτρική αντίσταση: Αριθμητική προσέγγιση Ινστιτούτο Τεχνολογίας & Έρευνας, Κρήτη Εισαγωγή στις εξισώσεις της ιδανικής, με ηλεκτρική αντίσταση, Hall, και δυο-ρευστών Μαγνητο-υδροδυναμικής, με χρονική εξέλιξη και σε πολλές διαστάσεις. Περιγραφή της αριθμητικής επίλυση αυτών των εξισώσεων, και αριθμητικά πειράματα για την καλύτερη κατανόηση του περιορισμού του πλάσματος. SC05 Par. Lalousis: Ideal and Resistive MHD: Numerical Approach Foundation for Research & Technoloy Hellas, Crete Ιntroduction to the equations of ideal, resistive, Hall, and two-fluid Magnetohydrodynamics, with time evolution and in multi-dimensions. Description of how to solve these equations numerically, and numerical experiments for the understanding of magnetic confinement. SC06 Ι. Βομβορίδης: Κινητική Θεωρία Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο 1. Η συνάρτηση κατανομής: Ροπές της συνάρτησης κατανομής, Βασικές συναρτήσεις κατανομής 2. Οι κινητικές εξισώσεις 3. Εφαρμογές κινητικής θεωρίας (Στατικές καταστάσεις ισορροπίας, Διάδοση κυμάτων (μικρού πλάτους) σε πλάσμα 4. Κύματα Langmuir σε μη μαγνητισμένο πλάσμα 5. Απόσβεση Landau 2
9 SC07 Λ. Βλάχος: Περιγραφή του πλάσματος από δύο ρευστά και Κύματα Αριστοτέλειο Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλονίκης 1. Εισαγωγή στη περιγραφή του πλάσματος από δύο ρευστά 2. Από τα δύο ρευστά στο ένα και στις εξισώσεις της Μαγνητο-υδροδυναμικής 3. Εισαγωγή στα κύματα: α) Ηλεκτρομαγνητικά κύματα στο κενό, β) Διάδοση ηλεκτρομαγνητικών κυμάτων σε αγωγούς, γ) Ακουστικές ταλαντώσεις 4. Κύματα σε μη μαγνητισμένο πλάσμα: α) Το πλάσμα ως διηλεκτρικό, β) Κύματα σε ψυχρό μη μαγνητισμένο πλάσμα 5. Κύματα από πλάσμα που περιγράφεται από δύο ρευστά: α) Ηλεκτροστατικά κύματα υψηλής συχνότητας, β) Εξισώσεις Vlassov-Maxwell, γ) Απόσβεση σε κύματα πλάσματος, δ) Ηλεκτροστατικά κύματα χαμηλής συχνότητας, ε) Ηλεκτρομαγνητικά κύματα υψηλής συχνότητας 6. Μαγνητοϋδροδυναμικά κύματα 7. Κύματα σε ανομοιογενές πλάσμα 8. Συμπεράσματα SC08 Κ. Χιτζανίδης, Κινητικές αστάθειες Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο 1. Σύντομη εισαγωγή στις διηλεκτρικές ιδιότητες του πλάσματος: Σχέσεις διασποράς, Κινητικός υπολογισμός του διηλεκτρικού τανυστή με και χωρίς την παρουσία εξωτερικού μαγνητικού πεδίου, Συναρτήσεις διασποράς πλάσματος (διαμήκης και εγκάρσια) 2. Αστάθειες σε χωρικά ομοιογενές πλάσμα: Κριτήριο του Penrose, Αστάθεια δέσμηςπλάσματος, Ιοντοακουστική αστάθεια, Αστάθειες κοντά σε αρμονικές της κυκλοτρονικής συχνότητας, Αστάθεια κώνου απωλειών, Ηλεκτρομαγνητικές αστάθειες. SC08 Κ. Hizanidis: Kinetic instabilities National Technical University of Athens 1. A short introduction to the dielectric properties of a plasma: Dispersion relations. Kinetic calculation of the dielectric tensor with and without external magnetic field. Plasma dispersion functions (longitudinal and transverse). 2. Instabilities in spatially homogeneous plasmas: Penrose criterion. Beam-plasma instability. Ion-acoustic wave instability. Instabilities near harmonics of the cyclotron frequencies. Loss-cone instability. Electromagnetic instabilities. SC09 Ν. Πελεκάσης: Υδροδυναμική και Μαγνητοϋδροδυναμική Ευστάθεια Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλίας 1. Στοιχειώδης θεωρία ευστάθειας και θεωρία διακλαδώσεων: Γραμμική και ελαφρώς μη γραμμική ανάλυση, Παραδείγματα από κλασσική υδροδυναμική ευστάθεια, Υπολογιστική κατασκευή διαγραμμάτων διακλάδωσης 2. Βασικές εξισώσεις Μαγνητοϋδροδυναμικής Μη γραμμική Μαγνητοϋδροδυναμική 3. Δυναμική σε χαμηλούς μαγνητικούς αριθμούς Reynolds: Μαγνητική απόσβεση Δημιουργία κίνησης, Οριακά στρώματα (Στρώματα Hartmann και πλαϊνά) 4. Ευστάθεια μαγνητοϋδροδυναμικών ροών: Ευστάθεια στρωμάτων Hartmann και πλαϊνών στρωμάτων, Ροή υγρών μετάλλων σε σωλήνες Εξαναγκασμένη και ελεύθερη αγωγή, Εφαρμογές στο σχεδιασμό αντιδραστήρων πλάσματος 3
10 SC10 Ν. Βλάχος, Μαθηματικά μοντέλα και αρχιτεκτονική κωδίκων υπολογιστικής ΜΥΔ Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλίας 1. Εξισώσεις Navier-Stokes για ροές σε οριακά στρώματα και με ανακυκλοφορία 2. Ολοκλήρωση εξισώσεων Navier-Stokes με πεπερασμένους όγκους 3. Αποσύζευξη του πεδίου ταχυτήτων από το πεδίο πίεσης 4. Αριθμητικές εξισώσεις για ροές σε οριακό στρώμα: Υπολογισμός ταχυτήτων και βαθμωτών μεγεθών, Εφαρμογές σε απλές ΜΥΔ ροές 5. Παραγωγή των αριθμητικών για ροές με ανακυκλοφορία: Διαγράμματα ροής υπολογισμού, Εφαρμογές σε απλές ΜΥΔ ροές 6. Μοντελοποίηση τύρβης, άνωσης και δυναμικής σωματιδίων 4
11 RESEARCH SEMINARS (Given in Greek, with slides in English and vice versa) S. Moustaizis - Physics and applications using compact plasma fusion devices University of Crete, Greece (Abstract not available at time of print) I.G. Tigelis, G.P. Latsas, J. L. Vomvoridis * - New results for beam-wave interaction in beam tunnels National & Kapodistrian University of Athens, Department of Physics, Greece, * National Technical U. of Athens, School of Electrical & Computer Engng, Greece Beam-loaded corrugated waveguides are used in several high-power microwaves applications. Specifically, they are employed in high-power generators like travelingwave tubes (TWT) and backward wave oscillators (BWO) to enable the beam-wave interaction or in gyrotrons to prevent the gyrotron interaction from occurring in the latter part of the beam tunnel rather than in the cavity. The successful design of such structures requires calculations of the propagation characteristics of the corrugated waveguide, of the beam-wave interaction and the characteristics of the developed modes. In this presentation, recent results for TM and TE waves in various geometries with and without losses will be presented and commented. RS01 S. Papastergiou - A blanket concept for DEMO and related MHD effects Associazione Euratom-ENEA, CR Frascati, Rome, Italy An analysis of the ENEA DCLL Blanket concept resulted in: (a) Simplified geometry, compatible with ports and relative ease of remote handling (b) Effective He flow in terms of heat transfer and pressure losses (c) Minimum e-m forces requiring a relatively simple support system, positioned in a way to reduce resultant stresses, and (d) MHD losses with low magnetic fields well within limits. The main elements of the analysis and the results obtained will be presented and discussed in this seminar. RS02 P. Karditsas - Design and performance of the power plant helium cooled divertor UKAEA Fusion, Culham Science Centre, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, UK The HETS and HEMP-HEMJ divertor concepts were proposed by ENEA and FZK, respectively. For HETS, previous studies identified the sharp edge bend as the feature that controls component performance. This seminar presents and summarizes results of thermal-fluid and structural analyses, with inlet shaping for optimised performance. Calculations were also performed on the HEMJ concept for the purposes of confirming CFD results independently produced by FZK. 5
12 RS03 D. Strintzi - Gyrokinetic studies of ion heat transport at JET National Technical University of Athens, Greece The anomalous character of ion heat transport in tokamaks is a long dated experimental observation. A comprehensive description of turbulent ion heat transport as driven by Ion Temperature Gradients (ITG) modes has been developed, and is at the bases of first principle predictions of ITER performance. Theoretical evidence has shown that the ITG has a threshold in the ion temperature profile, and that the ITG turbulence makes the ion temperature profiles stiff. For the first time, JET experiments have confirmed the theoretical predictions. With the help of gyrokinetic codes (GS2, GYRO, GKW, GENE), the low rotation ITG threshold pulses have been studied linearly and non-linearly. Very good agreement is found between the linear gyrokinetic threshold and the value found in the experiment. The stiffness level predicted by gyrokinetics is significantly smaller than observed in the low rotation plasmas and more in line with the values found in high rotation plasmas. RS04 S. Varoutis, D. Valougeorgis - Direct simulation of non-equilibrium flows related to fusion reactors Dept. of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, U. of Thessaly, Volos, Greece A Direct Simulation Monte Carlo (DSMC) code has been developed in order to describe efficiently vacuum gas flows in the whole range of the Knudsen number, including the transition regime, which is very important for ITER and other fusion machines as well. The DSMC method is a computational algorithm for simulating non-equilibrium gas behaviour. In brief, computational molecules move, reflect from solid boundaries and collide with each other so as to statistically mimic the behaviour of real molecules. Conservation of mass, momentum, and energy is enforced due to basic kinetic theory collision assumptions. A rigorous proof that DSMC produces a solution to the Boltzmann equation in the limit of vanishing discretization and stochastic errors is now available. The objective of the present work is to simulate parts of the vacuum system using the upgraded DSMC algorithm and in this frame work the DSMC code has been implemented to solve the flow of a rarefied gas through a tube of finite length. Results for the dimensionless flow rate and for the flow field (velocity, pressure and temperature) are presented under high, medium and low vacuum conditions and for various values of the length-to-radius. It is deduced that modifying geometry and rarefaction parameters has a significant impact on the magnitude of flow quantities. RS05 S. Misdanitis, D. Valougeorgis - Compressibility effects in flows under low medium and high vacuum Dept. of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, U. of Thessaly, Volos, Greece Compressibility versus rarefaction effects in non-equilibrium flows are investigated by solving the steady-state 1-D flow of a gas between two parallel moving plates, maintained at different temperatures. This is one of the classical problems in hydrodynamics and can be easily tackled in an analytical manner. However, the flow is far from equilibrium the corresponding kinetic approach is not trivial and requires the numerical solution of coupled nonlinear integro-differential equations in a computationally efficient manner. The coupled Couette and Fourier flows is solved by implementing the nonlinear Sakhov model in the whole range of the Knudsen number from the free molecular through the transition and slip regimes all the way up to the hydrodynamic limit. The computational scheme is based on an extension of the discrete velocity method, which has been successfully applied to the solution of linear kinetic equations. Results are provided for bulk flow quantities in terms of the three nondimensional parameters characterizing the flow, namely Knudsen number, Mach number and temperature ratio between the plates. A detailed study on the rarefaction and compressibility effects on the flow patterns is provided. Finally, the presence of a heat flux parallel to the plates, induced by the shear flow is also investigated. This is a cross effect, which is absent in the Navier-Stokes-Fourier solution. The validity of the results is confirmed in several ways including the recovery of the analytical solutions at the free molecular limit and slip regime. 6
13 RS06 S. Pantazis, D. Valougeorgis, A. Grecos - Numerical Simulation of Brownian motion in a magnetic field Dept. of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, U. of Thessaly, Volos, Greece The Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process, introduced by Langevin, is commonly used to model stochastic processes in physics problems including Brownian motion and externally driven harmonic oscillatory motion with damping. Following [1], an appropriate stochastic term is added to the governing Newton s second law equations and then the random movement of a charged particle in a plane normal to a uniform, stationary magnetic field may be described. The advantage of this approach is that closed form expressions predicting the motion of the charged particle for arbitrarily large time intervals may be obtained. Based on a simple test particle simulation algorithm a sequence of updates for position and velocity are estimated. Properties of the solution in the infinite dissipation limit have been explored and the spectral energy density function has been found. [1] D.S. Lemons and D.L. Kaufman, Brownian motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field, IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 27 (5), , 1999 RS07 A.P. Grecos, D. Vavougios, Th. Grammenos - On Fokker-Planck type equations in stochastic transport University of Thessaly, Association Euratom Hellenic Republic For the motion of a charged tagged particle in magnetised plasma, the effect of the bulk of the plasma is represented by a Langevin-type force, i.e. a friction term proportional to the velocity of the particle as well as a stochastic component. The case of a uniform external magnetic field is considered and a Gaussian process for the stochastic force is assumed. Because of the linearity of the system, the problem is exactly solvable. An exact Fokker-Planck type equation can be established for the probability density of the position and velocity of the particle. In case the correlation time for the random component of the force is finite, the coefficients of the equation are time-dependant. The derivation of this equation is sketched and its properties, its exact solution, and the validity of possible Markovian approximations are briefly discussed. RS08 B. Weyssow - Smoothed particle hydrodynamic method with possible application to fusion plasmas Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium The Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) is a gridless computational method used for simulating (compressible, free boundary) fluid flows. In this method the fluid volume is divided into a set of discrete fluid elements (the SPH particles) which are in interaction. These particles have a spatial distance, the smoothing length, usually denoted by "h", over which their properties are smoothed by a kernel function. Thus the spatial variation of any physical quantity is obtained by summing the relevant properties of the particles lying within two smoothing lengths of a particle at a given spatial position. The smoothing length is a fundamental quantity in SPH. When the smoothing length is too small, the SPH-particles behave almost all the time as free particles. On the contrary, when the smoothing length is too large, all SPH-particles are in interaction with all the particles of the system, leaving no possibility of motion. To achieve realistic simulations of hydrodynamic flows, it is therefore essential to understand the transition from the "solid" to the "liquid" and then to the "gas" state. 7
14 RS09 D. Apostolaki, G.N. Throumoulopoulos, H. Tasso * - On tokamak equilibrium and stability with plasma flow parallel to the magnetic field U. of Ioannina, Greece, * Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Garching, Germany Analytic solutions to a generalized Grad-Shafranov equation are derived describing steady states of a toroidal magnetically confined plasma with incompressible flow parallel to the magnetic field while pressure gradient, toroidal current density and flow are vanishing on the plasma boundary. The study includes configurations with either nested magnetic surfaces or non-nested magnetic surfaces in connection with negative current density on certain of the magnetic axes. Also, the linear stability of the equilibria constructed is examined for plasmas of constant density by applying a recent sufficient condition [Throumoulopoulos and Tasso, Phys. Plasmas 14, (2007)]. RS10 N.A. Pelekasis, D. Dimopoulos - Magnetic field effects on 3-d stability of natural convection flows in differentially heated cavities Dept. of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, U. of Thessaly, Volos, Greece Three dimensional stability analysis is conducted, of 2d steady state solutions obtained for free convection in a long square duct subject to a magnetic field with a temperature gradient perpendicular to the direction of gravity. For completeness sidewall conductivity is also accounted for. The base flow solution1 is characterized by two recirculation cells that extend along the longitudinal direction of the duct. Beyond a certain threshold value of Gr it loses stability to a 2d time periodic solution. The wave-number k for which neutral stability with respect to 3d periodic longitudinal disturbances is achieved, is sought for. The numerical methodology for eigenvalue calculations via the Arnoldi method is optimised and different options are tested. In the absence of magnetic field and at low Pr=0.032 the base flow is seen to be more unstable to three dimensional perturbations, smaller threshold value of Gr compared to 2d disturbances, leading to a stationary arrangement that is periodic in the longitudinal direction and dominated by small wavenumbers. The emergence of three-dimensional structures with the vortices aligned with the magnetic field, also developing periodically in the longitudinal direction, is investigated. In particular, the effect of increasing Hartman number is of interest in the context of a base configuration with the temperature gradient aligned with the direction of gravity, as indicated by relevant experiments2. [1] N. Pelekasis, Phys. Fluids. 18(3), 1-23 (2006) [2] U. Burr & U. Müller, J. Fluid Mech. 453, (2002) RS11 D.G.E. Grigoriadis, S.C. Kassinos - MHD flows in complicated domains using the immersed boundary method University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus The capability to accurately simulate the interaction of magnetic fields and magnetically conductive fluids in complex geometries is one of the key current issues in MHD flows. An efficient Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) methodology is presented which is appropriate for MHD simulations in geometrically complicated domains. The method is based on the immersed boundary (IB) method, which provides a reliable numerical tool for the calculation of hydrodynamic fields in arbitrarily shaped geometrical domains using Cartesian grids. The proposed extension of the IB method was developed to account for both the hydrodynamic field and the electric field involved in Lorentz forces. An efficient finite difference Cartesian grid solver is presented which uses the IB concept to dynamically mimic the existence of an arbitrarily shaped non-conducting immersed surface. Results are presented and compared for two and two and three-dimensional MHD flows around bodies in semi-confined and confined MHD flows. 8
15 RS12 C. Dritselis, I. Sarris, N. Vlachos - Particle-turbulence interaction in MHD duct flows Dept. of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, U. of Thessaly, Volos, Greece Μελετάται η αλληλεπίδραση σωματιδίων-τύρβης σε ροή υγρών μετάλλων υπό την επίδραση εξωτερικού ομοιόμορφου μαγνητικού πεδίου με τη χρήση άμεσης αριθμητικής προσομοίωσης (DNS). Το ενδιαφέρον εστιάζεται κυρίως στον τρόπο που τα σωματίδια επηρεάζονται από τις τυρβώδεις δομές της ροής κατά την κίνηση και εναπόθεσή τους στα μη-αγώγιμα τοιχώματα ενός καναλιού απείρων διαστάσεων. Ο μαγνητικός αριθμός Reynolds είναι μικρός και το επαγόμενο μαγνητικό πεδίο δεν λαμβάνεται υπόψη ως αμελητέο. Οι τροχιές των σωματιδίων καθορίζονται με σχήμα κατά Lagrange. Τα σωματίδια θεωρούνται αφόρτιστα και η κίνησή τους ελέγχεται από τη δύναμη οπισθέλκουσας. Οι συγκρούσεις μεταξύ σωματιδίων λαμβάνονται υπόψη και θεωρούνται πλήρως ελαστικές, ενώ αγνοείται η επίδραση τους πάνω την ορμή της συνεχούς φάσης. Έγινε παραμετρική μελέτη ως προς τη διεύθυνση και την ένταση του μαγνητικού πεδίου και το χρόνο απόκρισης των σωματιδίων. Από τη σύγκριση αντίστοιχων περιπτώσεων διφασικών ροών με και χωρίς το μαγνητικό πεδίο εξάγονται χρήσιμα συμπεράσματα για την επίδραση της δύναμης Lorentz πάνω στις τυρβώδεις δομές κοντά στα τοιχώματα, και επιπρόσθετα στην κίνηση και στη δυναμική συμπεριφορά των σωματιδίων. RS13 S. Kakarantzas, Ι. Sarris, A. Grecos, N. Vlachos - MHD natural convection heat transfer of liquid metals in cylindrical annuli Dept. of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, U. of Thessaly, Volos, Greece Γίνεται μελέτη με απευθείας αριθμητική προσομοίωση (DNS) της μη μόνιμης 3Δ ροής υγρού μετάλλου σε συγκεντρικούς κυλίνδρους. Εφαρμόζεται ομογενές εξωτερικό μαγνητικό πεδίο κάθετο στην αξονική διεύθυνση με ταυτόχρονη παρουσία ομοιόμορφων εσωτερικών πηγών θερμότητας. Τα κυλινδρικά τοιχώματα είναι σε θερμοκρασιακή διαφορά που προκαλεί φυσική συναγωγή, ενώ τα πάνω και κάτω τοιχώματα είναι αδιαβατικά. Όλα τα τοιχώματα θεωρούνται ηλεκτρικά μονωμένα. Η επίδραση της διαφοράς θερμοκρασίας και της έντασης των πηγών θερμότητας εκφράζεται μέσω του αδιάστατου εξωτερικού και εσωτερικού αριθμού Rayleigh, αντίστοιχα, και η ένταση του μαγνητικού πεδίου με τον αριθμό Hartmann. Τα αποτελέσματα δείχνουν την επίδραση των παραμέτρων στη ροή, και στην κατανομή θερμοκρασίας και μετάδοση θερμότητας. Ανάλογα με τις τιμές τους μπορούν να προκύψουν στρωτές ή τυρβώδεις ροές. Η παρουσία του μαγνητικού πεδίου προκαλεί αντίσταση στην κίνηση του ρευστού, μέσω της δύναμης Lorentz, ενώ παράλληλα η προοδευτική αύξησή του οδηγεί σε μείωση και για πολύ ισχυρές τιμές του, στην εξαφάνιση των διαταραχών που παρουσιάζονται στις περιπτώσεις της μη μόνιμης ροής. RS14 Ι.E. Sarris, S.C. Kakarantzas, C.D. Dritselis, N.S. Vlachos - Heat transfer in turbulent magnetohydrodynamic flows Dept. of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, U. of Thessaly, Volos, Greece Flow and heat transfer of electroconductive fluids in apparatus like liquid metal blankets for the fusion reactor is of technological importance and may be influenced by the presence of a magnetic field. The main objective is to study the effect of the external magnetic field on the turbulent heat transfer of liquid metals using direct numerical simulations. Except of the strength of the magnetic field, the effect of its direction on the heat transfer is also studied. It is known from general hydrodynamics that the so-called Reynolds analogy exists. In this analogy, the change in heat transfer rate is similar to the variation in friction. Our results show that the heat transfer can be roughly evaluated from changes of the friction factor. In particular, the increase of the strength of the magnetic field results in a decrease of the skin friction coefficient and a corresponding decrease of heat transfer. However, this analogy must be applied with caution to liquid metals, since it may be entirely distorted by the molecular thermal conduction. Except of the effect of the Prandtl number on heat transfer in liquid metals, phenomena connected with transition from fully turbulent 3D to quasi-2d flow because of the magnetic field may be also very important at high Hartmann numbers. 9
16 RS15 K.A. Avramides 1, O. Dumbrajs 2,3, S. Kern 4, I.G. Pagonakis 5, J.L. Vomvoridis 1 - Mode selection for a 170 GHz-1 MW Gyrotron for ITER 1 National Technical University of Athens, Greece, 2 Helsinki University of Technology, Finland, 3 University of Latvia, Riga, Latvia, 4 Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Germany, 5 École Polytechnique Fédéral de Lausanne, Switzerland Gyrotrons are the leading microwave sources for plasma heating and current drive in magnetic confinement fusion experiments [1], [2]. In a gyrotron, a helical electron beam, formed by a MIG-type electron gun and guided by an external magnetic field, delivers energy to a RF electromagnetic wave (i. e. a TE mode supported by the interaction cavity) through electron cyclotron resonance. The European development of a gyrotron for ITER is focused on a 170 GHz, 2 MW CW coaxial-cavity gyrotron [3]. However, a design of a 170 GHz, 1 MW CW conventional gyrotron, (i. e. a gyrotron employing a hollow-waveguide interaction cavity), has also been initiated as a fallback solution in case the ambitious coaxial concept does not reach the anticipated performance. To design a gyrotron, a set of suitable candidate operating modes must be specified first. The modes should meet the performance requirements and obey several physical and technological constraints related to the electron gun, the interaction cavity and to voltage depression. Using a pertinent systematic procedure, we have come up with such a group of TE modes for the 170 GHz, 1 MW CW conventional gyrotron. The results are presented, together with preliminary designs of the interaction cavity for the most promising operating modes. [1] M.V. Kartikeyan, E. Borie and M. Thumm, Gyrotrons High Power Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Springer-Verlag, [2] K. Sakamoto, Progress of high-power-gyrotron development for fusion research, Fusion Science and Technology 52, 145 (2007). [3] J.-P. Hogge et al., The European 2 MW, 170 GHz coaxial cavity gyrotron for ITER, Joint 32nd Int. Conf. Infrared Millimeter Waves and 15th Int. Conf. THz Electronics, Conference Digest 38, 3-7 Sept. 2007, Cardiff, UK. RS16 Y. Kominis, K. Hizanidis, A.K. Ram * - Quasilinear theory for momentum and spatial diffusion due to radio frequency waves in non-axisymmetric toroidal plasmas National Technical University of Athens, Greece, * Plasma Science & Fusion Center, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA We derive the relativistic quasilinear operator for the momentum and spatial diffusion of electrons due to their interaction with radio frequency (RF) waves in non-axisymmetric toroidal plasmas. The plasma equilibrium is expressed in terms of the magnetic flux coordinates of an axisymmetric plasma. The electron motion is treated fully relativistically and is expressed in guiding center coordinates using the action-angle variables of motion in an axisymmetric toroidal equilibrium. The non-axisymmetry in the equilibrium due to magnetic field perturbations and the effect of RF waves on electron motion are treated perturbatively. The magnetic field perturbations can be due to magnetic islands as in neoclassical tearing modes. The relativistic generalization is necessary so that the interaction of electrons with electron cyclotron (EC) waves is also described by the quasilinear operator. It is well-known that relativity needs to be included in a proper description of the damping of EC waves. Our study is a generalization of an earlier work by Kaufman [1] and is in contrast to the Kennel-Engelmann [2] description of quasilinear diffusion in a uniform plasma. We carry out the Lie perturbation technique to first order in the perturbation parameters. The generalized quasilinear evolution equation is accurate to second order in the perturbation parameters. The diffusion operator is time dependent and describes resonant and non-resonant momentum space diffusion, and non-resonant radial transport of electrons. The former leads to current generation in a plasma and the latter to the broadening of the current profile. The final results are expressed in a form that is suitable for numerical implementation. [1] A. N. Kaufmann, Phys. Fluids 15, 1063 (1972) [2] C. F. Kennel and F. Engelmann, Phys. Fluids 9, 2377 (1966) 10
17 RS17 H. Isliker - A self-organized criticality model for the magnetic topology in toroidal confinement devices Astronomy Lab., Dept. of Physics, University of Thessaloniki We introduce a Self-Organized Criticality (SOC) model in the form of a Cellular Automaton (CA) for the evolution of the magnetic field in toroidal confinement devices. The basic grid variable is the vector potential, and the magnetic field is determined as the curl of the vector potential, so that the magnetic field is compatible with MHD and Maxwell's equations. The current is calculated in accordance with MHD, as the curl of the magnetic field. The evolution rules of the CA are such as to mimic resistive magnetic reconnection in response to a current driven instability. The system starts from a simple tokamak equilibrium topology, expressed in terms of the vector potential, and it is continuously driven and finally reaches the SOC state. We present the basic characteristics of the SOC magnetic topology, such as typical shapes and evolution of the flux surfaces, the safety factor profile and the current distribution, etc., and we discuss in how far the SOC magnetic topology is realistic and potentially relevant for toroidal confinement devices. RS18 I. Sandberg - Intermittency in electromagnetic resistive ballooning turbulence National Technical University of Athens, Greece Turbulent fluctuations and the associated transport of heat and particles play a crucial role in magnetic fusion devices. Experimental observations reveal that even though the turbulence is essentially electrostatic, magnetic fluctuations can have a strong impact on the plasma dynamics. In this study we investigate the role of β-value on the intermittent events and on the multi-fractality of the fluctuations for the case of the electromagnetic resistive ballooning turbulence (RBM) using the global three-dimensional code EMEDGE3D. The intermittency effects that appear in the saturated level of RBM turbulence are studied by using various statistical methods. Beyond the determination of the basic statistical properties with the use of standard tools - such as the calculation of the probability density functions - we calculate the structure functions for all the fluctuating fields, averaged properly both in space and time. Using the extended self-similarity method we study the impact of the EM fluctuations and we show that finite β effects can determine the characteristic scales of the RMB turbulence and may increase the irregular redistribution of the energy in the turbulent cascade increasing intermittency. In order to extract the dominant features and characterize the coherent structures of the RBM turbulence we use the Singular Value Decomposition method, which permits the simultaneous analysis of the spatio-temporal data obtained by the EMEDGE3D simulations. RS19 C. Tsironis, T. Samaras and L. Vlahos - Modelling the propagation of EC waves in hot anisotropic plasma with the FDTD method Department of Physics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece In the problem of EC wave propagation in plasmas, the mainstream in theory and applications is oriented to frequency-domain asymptotic methods (see [1] and references therein), where the determination of the plasma response presents less difficulty. However, in many cases of interest, like e.g. mode conversion and off-axis heating, this approach breaks down and a full-wave analysis is necessary. In this work, we present a (novel) scattered-field FDTD algorithm for fully kinetic, anisotropic plasma (the total-field formalism for anisotropic medium has been derived in [2]). As an application, we study the perpendicular EC propagation and absorption in simplified geometry. In general, since FDTD is a time-domain technique, conversion from the frequency domain is required in order to be able to exploit the existing knowhow on the dielectric response. However, for a constant-frequency wave propagating in a stationary plasma, the FDTD method can be applied by directly implementing the frequency-domain dielectric tensor. [1] C. Tsironis, E. Poli and G.V. Pereverzev, Phys. Plasmas 13, (2006) [2] J. Schneider and S. Hudson, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 41, 994 (1993) 11
18 RS20 G.E. Anastassiou, J.L. Vomvoridis - Post amplification of a Gaussian rf beam generated in a gyrotron via its interaction with a sheet electron beam School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, National Technical University of Athens Gyrotron oscillators employ a weakly relativistic electron beam to produce coherent radiation in the range of millimetre and sub-millimetre wavelengths. In fusion applications and particularly for electron cyclotron heating, an output power of approximately 2 MW is accomplished in the range of 170 GHz, which is at least required for a gyro-device installed in ITER. To increase the output power of a conventional gyrotron, an alternative configuration very similar to the quasi-optical gyrotron (QOG) is proposed, in which a sheet electron beam immersed in a magnetostatic field intersects perpendicularly the rf beam produced by the gyrotron. This configuration results in the amplification of the initial Gaussian-shaped output of the gyrotrons to the power levels of several MW that are needed for an efficient fusion reactor. The problem is formulated for the motion of the sheet-beam electrons, treated as test particles, under the combined action of the magnetostatic field and the initial rf field. The equations of motion are solved numerically, the electronic efficiency is determined, and the additional radiation field produced due to the nonlinear perturbed electronic motion is calculated as well. To achieve that goal, a self-consistent iterative process is introduced, in which the radiation field in every step is calculated considering the electron trajectory of the previous step, and so forth. The latter scenario proceeds until convergence is eventually achieved for both the electronic motion and the produced radiation field. The direction of propagation of the total field is determined and the 3D pattern of the radiated power is also calculated integrated in all directions. The self-consistent process required to estimate the interaction properties is implemented successfully both in Matlab and C++ in a serial computer code. The obtained results strongly indicate that the initial output beam of a conventional gyrotron of approximately 2 MW can be effectively amplified into the range of approximately10 MW. Nevertheless, the serial codes are relatively slow and fail to generate massive results; therefore, a substantial effort has been invested in creating a parallel instance of the C++ code 1, which now gives the opportunity to solve large demanding simulations as it exploits a greater amount of CPU and memory resources. [Constructive contribution and private discussions with Dr. I. Pagonakis are kindly acknowledged] E.V. Votyakov - Liquid metal flow under an external inhomogeneous magnetic field. Wake of a magnetic obstacle University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus Effects of a heterogeneous magnetic field on a liquid metal flow might be of importance for a fusion reactor design. For instance, liquid metals can be used as a coolant in the fusion reactor. However, the behaviour of a liquid metal flow under an heterogeneous external magnetic field is much less understood in contrast to a under strong constant magnetic field. In the latter case, magnetic field simply results in a two-dimensionality of the flow, while in the former case, there might be observed so called M-shaped velocity profile, stagnant regions, and even different kinds of recirculation. These phenomena will be discussed in the course of the lecture. It will start from the didactic problem how to define a proper heterogeneous magnetic field for analytical and numerical calculations, then I discuss various 3D peculiarities of the flow, in particular it will be demonstrated that concept of twodimensionality of the flow is not anymore valid, and finally I will deduce a structure of the wake of a magnetic obstacle. The main results are presented in [1-3] [1] - [2] - [3]
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
[1] P Q. Fig. 3.1
![[1] P Q. Fig. 3.1 [1] P Q. Fig. 3.1](/thumbs/79/80362156.jpg) 1 (a) Define resistance....... [1] (b) The smallest conductor within a computer processing chip can be represented as a rectangular block that is one atom high, four atoms wide and twenty atoms long. One
1 (a) Define resistance....... [1] (b) The smallest conductor within a computer processing chip can be represented as a rectangular block that is one atom high, four atoms wide and twenty atoms long. One
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
ΑΛΛΗΛΕΠΙ ΡΑΣΗ ΜΟΡΦΩΝ ΛΥΓΙΣΜΟΥ ΣΤΙΣ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΕΣ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΕΣ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ Τοµέας οµοστατικής Εργαστήριο Μεταλλικών Κατασκευών ΑΛΛΗΛΕΠΙ ΡΑΣΗ ΜΟΡΦΩΝ ΛΥΓΙΣΜΟΥ ΣΤΙΣ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΕΣ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΕΣ ιπλωµατική Εργασία Ιωάννη Σ. Προµπονά
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ Τοµέας οµοστατικής Εργαστήριο Μεταλλικών Κατασκευών ΑΛΛΗΛΕΠΙ ΡΑΣΗ ΜΟΡΦΩΝ ΛΥΓΙΣΜΟΥ ΣΤΙΣ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΕΣ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΕΣ ιπλωµατική Εργασία Ιωάννη Σ. Προµπονά
Strain gauge and rosettes
 Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ. Μειέηε Υξόλνπ Απνζηείξσζεο Κνλζέξβαο κε Τπνινγηζηηθή Ρεπζηνδπλακηθή. Αζαλαζηάδνπ Βαξβάξα
 ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΔΚΠΑΙΓΔΤΣΙΚΟ ΙΓΡΤΜΑ ΘΔΑΛΟΝΙΚΗ ΥΟΛΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ & ΓΙΑΣΡΟΦΗ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ Μειέηε Υξόλνπ Απνζηείξσζεο Κνλζέξβαο κε Τπνινγηζηηθή Ρεπζηνδπλακηθή Αζαλαζηάδνπ Βαξβάξα
ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΔΚΠΑΙΓΔΤΣΙΚΟ ΙΓΡΤΜΑ ΘΔΑΛΟΝΙΚΗ ΥΟΛΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ & ΓΙΑΣΡΟΦΗ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ Μειέηε Υξόλνπ Απνζηείξσζεο Κνλζέξβαο κε Τπνινγηζηηθή Ρεπζηνδπλακηθή Αζαλαζηάδνπ Βαξβάξα
Η ΣΗΜΑΣΙΑ ΤΗΣ ΜΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΗΣ ΣΥΜΠΕΡΙΦΟΡΑΣ ΓΙΑ ΤΟΝ ΣΧΕ ΙΑΣΜΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Η ΣΗΜΑΣΙΑ ΤΗΣ ΜΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΗΣ ΣΥΜΠΕΡΙΦΟΡΑΣ ΓΙΑ ΤΟΝ ΣΧΕ ΙΑΣΜΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Μεταπτυχιακή Εργασία
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Η ΣΗΜΑΣΙΑ ΤΗΣ ΜΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΗΣ ΣΥΜΠΕΡΙΦΟΡΑΣ ΓΙΑ ΤΟΝ ΣΧΕ ΙΑΣΜΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Μεταπτυχιακή Εργασία
Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb.
 LUMP SUM Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Lump sum lump sum lump sum. lump sum fixed price lump sum lump
LUMP SUM Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Lump sum lump sum lump sum. lump sum fixed price lump sum lump
ΣΤΑΤΙΚΗ ΜΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΚΑΛΩ ΙΩΤΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ
 1 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ Σχολή Πολιτικών Μηχανικών ΠΜΣ οµοστατικός Σχεδιασµός και Ανάλυση Κατασκευών Εργαστήριο Μεταλλικών Κατασκευών Μεταπτυχιακή ιπλωµατική Εργασία ΣΤΑΤΙΚΗ ΜΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΚΑΛΩ
1 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ Σχολή Πολιτικών Μηχανικών ΠΜΣ οµοστατικός Σχεδιασµός και Ανάλυση Κατασκευών Εργαστήριο Μεταλλικών Κατασκευών Μεταπτυχιακή ιπλωµατική Εργασία ΣΤΑΤΙΚΗ ΜΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΚΑΛΩ
Μειέηε, θαηαζθεπή θαη πξνζνκνίσζε ηεο ιεηηνπξγίαο κηθξήο αλεκνγελλήηξηαο αμνληθήο ξνήο ΓΗΠΛΩΜΑΣΗΚΖ ΔΡΓΑΗΑ
 Μειέηε, θαηαζθεπή θαη πξνζνκνίσζε ηεο ιεηηνπξγίαο κηθξήο αλεκνγελλήηξηαο αμνληθήο ξνήο ΓΗΠΛΩΜΑΣΗΚΖ ΔΡΓΑΗΑ Κνηζακπφπνπινο Υ. Παλαγηψηεο Δπηβιέπσλ: Νηθφιανο Υαηδεαξγπξίνπ Καζεγεηήο Δ.Μ.Π Αζήλα, Μάξηηνο 2010
Μειέηε, θαηαζθεπή θαη πξνζνκνίσζε ηεο ιεηηνπξγίαο κηθξήο αλεκνγελλήηξηαο αμνληθήο ξνήο ΓΗΠΛΩΜΑΣΗΚΖ ΔΡΓΑΗΑ Κνηζακπφπνπινο Υ. Παλαγηψηεο Δπηβιέπσλ: Νηθφιανο Υαηδεαξγπξίνπ Καζεγεηήο Δ.Μ.Π Αζήλα, Μάξηηνο 2010
ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ
 ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ Τομέας Περιβαλλοντικής Υδραυλικής και Γεωπεριβαλλοντικής Μηχανικής (III) Εργαστήριο Γεωπεριβαλλοντικής Μηχανικής TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CRETE SCHOOL of
ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ Τομέας Περιβαλλοντικής Υδραυλικής και Γεωπεριβαλλοντικής Μηχανικής (III) Εργαστήριο Γεωπεριβαλλοντικής Μηχανικής TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CRETE SCHOOL of
ΙΕΥΘΥΝΤΗΣ: Καθηγητής Γ. ΧΡΥΣΟΛΟΥΡΗΣ Ι ΑΚΤΟΡΙΚΗ ΙΑΤΡΙΒΗ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΗΧΑΝΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΑΕΡΟΝΑΥΠΗΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ & ΑΥΤΟΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΥ / ΥΝΑΜΙΚΗΣ & ΘΕΩΡΙΑΣ ΜΗΧΑΝΩΝ ΙΕΥΘΥΝΤΗΣ: Καθηγητής Γ. ΧΡΥΣΟΛΟΥΡΗΣ Ι ΑΚΤΟΡΙΚΗ
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΗΧΑΝΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΑΕΡΟΝΑΥΠΗΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ & ΑΥΤΟΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΥ / ΥΝΑΜΙΚΗΣ & ΘΕΩΡΙΑΣ ΜΗΧΑΝΩΝ ΙΕΥΘΥΝΤΗΣ: Καθηγητής Γ. ΧΡΥΣΟΛΟΥΡΗΣ Ι ΑΚΤΟΡΙΚΗ
Written Examination. Antennas and Propagation (AA ) April 26, 2017.
 Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΣΟΜΟΙΩΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΔΥΝΑΜΙΚΗΣ ΤΟΥ ΕΔΑΦΙΚΟΥ ΝΕΡΟΥ ΣΤΗΝ ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΑΡΔΕΥΣΗΣ ΜΕ ΥΠΟΓΕΙΟΥΣ ΣΤΑΛΑΚΤΗΦΟΡΟΥΣ ΣΩΛΗΝΕΣ ΣΕ ΔΙΑΣΤΡΩΜΕΝΑ ΕΔΑΦΗ
 ΓΕΩΠΟΝΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΑΞΙΟΠΟΙΗΣΗΣ ΦΥΣΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΗΣ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΑΕΙΦΟΡΙΚΗ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΥΔΑΤΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ Δημήτριος Πάντζαλης Πτυχιούχος Γεωπόνος Α.Π.Θ.
ΓΕΩΠΟΝΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΑΞΙΟΠΟΙΗΣΗΣ ΦΥΣΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΗΣ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΑΕΙΦΟΡΙΚΗ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΥΔΑΤΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ Δημήτριος Πάντζαλης Πτυχιούχος Γεωπόνος Α.Π.Θ.
the total number of electrons passing through the lamp.
 1. A 12 V 36 W lamp is lit to normal brightness using a 12 V car battery of negligible internal resistance. The lamp is switched on for one hour (3600 s). For the time of 1 hour, calculate (i) the energy
1. A 12 V 36 W lamp is lit to normal brightness using a 12 V car battery of negligible internal resistance. The lamp is switched on for one hour (3600 s). For the time of 1 hour, calculate (i) the energy
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Study of In-vehicle Sound Field Creation by Simultaneous Equation Method
 Study of In-vehicle Sound Field Creation by Simultaneous Equation Method Kensaku FUJII Isao WAKABAYASI Tadashi UJINO Shigeki KATO Abstract FUJITSU TEN Limited has developed "TOYOTA remium Sound System"
Study of In-vehicle Sound Field Creation by Simultaneous Equation Method Kensaku FUJII Isao WAKABAYASI Tadashi UJINO Shigeki KATO Abstract FUJITSU TEN Limited has developed "TOYOTA remium Sound System"
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
Démographie spatiale/spatial Demography
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΙΑΣ Démographie spatiale/spatial Demography Session 1: Introduction to spatial demography Basic concepts Michail Agorastakis Department of Planning & Regional Development Άδειες Χρήσης
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΙΑΣ Démographie spatiale/spatial Demography Session 1: Introduction to spatial demography Basic concepts Michail Agorastakis Department of Planning & Regional Development Άδειες Χρήσης
(1) Describe the process by which mercury atoms become excited in a fluorescent tube (3)
 Q1. (a) A fluorescent tube is filled with mercury vapour at low pressure. In order to emit electromagnetic radiation the mercury atoms must first be excited. (i) What is meant by an excited atom? (1) (ii)
Q1. (a) A fluorescent tube is filled with mercury vapour at low pressure. In order to emit electromagnetic radiation the mercury atoms must first be excited. (i) What is meant by an excited atom? (1) (ii)
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACEG
 Lecture 4 Material behavior: Constitutive equations Field of the game Print version Lecture on Theory of lasticity and Plasticity of Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACG 4.1 Contents
Lecture 4 Material behavior: Constitutive equations Field of the game Print version Lecture on Theory of lasticity and Plasticity of Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACG 4.1 Contents
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Graded Refractive-Index
 Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Forced Pendulum Numerical approach
 Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΟΝ ΑΥΤΟΜΑΤΟ ΕΛΕΓΧΟ ΤΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Ανεµόµετρο AMD 1 Αισθητήρας AMD 2 11 ος όροφος Υπολογιστής
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΟΝ ΑΥΤΟΜΑΤΟ ΕΛΕΓΧΟ ΤΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Ανεµόµετρο AMD 1 Αισθητήρας AMD 2 11 ος όροφος Υπολογιστής
ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΟΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΝΟΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΚΑ ΑΥΤΟΝΟΜΟΥ ΝΗΣΙΟΥ ΜΕ Α.Π.Ε
 Τμήμα Ηλεκτρονικών Μηχανικών Τ.Ε. ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΟΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΝΟΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΚΑ ΑΥΤΟΝΟΜΟΥ ΝΗΣΙΟΥ ΜΕ Α.Π.Ε Πτυχιακή Εργασία Φοιτητής: Γεμενής Κωνσταντίνος ΑΜ: 30931 Επιβλέπων Καθηγητής Κοκκόσης Απόστολος Λέκτορας
Τμήμα Ηλεκτρονικών Μηχανικών Τ.Ε. ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΟΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΝΟΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΚΑ ΑΥΤΟΝΟΜΟΥ ΝΗΣΙΟΥ ΜΕ Α.Π.Ε Πτυχιακή Εργασία Φοιτητής: Γεμενής Κωνσταντίνος ΑΜ: 30931 Επιβλέπων Καθηγητής Κοκκόσης Απόστολος Λέκτορας
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
ΚΒΑΝΤΙΚΟΙ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΕΣ
 Ανώτατο Εκπαιδευτικό Ίδρυμα Πειραιά Τεχνολογικού Τομέα Τμήμα Ηλεκτρονικών Μηχανικών Τ.Ε. ΚΒΑΝΤΙΚΟΙ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΕΣ Πτυχιακή Εργασία Φοιτητής: ΜIΧΑΗΛ ΖΑΓΟΡΙΑΝΑΚΟΣ ΑΜ: 38133 Επιβλέπων Καθηγητής Καθηγητής Ε.
Ανώτατο Εκπαιδευτικό Ίδρυμα Πειραιά Τεχνολογικού Τομέα Τμήμα Ηλεκτρονικών Μηχανικών Τ.Ε. ΚΒΑΝΤΙΚΟΙ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΕΣ Πτυχιακή Εργασία Φοιτητής: ΜIΧΑΗΛ ΖΑΓΟΡΙΑΝΑΚΟΣ ΑΜ: 38133 Επιβλέπων Καθηγητής Καθηγητής Ε.
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ
 ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ Σχολή Πολιτικών Μηχανικών Τοµέας οµοστατικής ΑΛΛΗΛΕΠΙ ΡΑΣΗ ΑΣΤΟΧΙΑΣ ΑΠΟ ΛΥΓΙΣΜΟ ΚΑΙ ΠΛΑΣΤΙΚΟΠΟΙΗΣΗ ΣΕ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΑ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΑ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ Σχολή Πολιτικών Μηχανικών Τοµέας οµοστατικής ΑΛΛΗΛΕΠΙ ΡΑΣΗ ΑΣΤΟΧΙΑΣ ΑΠΟ ΛΥΓΙΣΜΟ ΚΑΙ ΠΛΑΣΤΙΚΟΠΟΙΗΣΗ ΣΕ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΑ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΑ ιπλωµατική εργασία: Λεµονάρη Μαρίνα Επιβλέπων καθηγητής:
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ Σχολή Πολιτικών Μηχανικών Τοµέας οµοστατικής ΑΛΛΗΛΕΠΙ ΡΑΣΗ ΑΣΤΟΧΙΑΣ ΑΠΟ ΛΥΓΙΣΜΟ ΚΑΙ ΠΛΑΣΤΙΚΟΠΟΙΗΣΗ ΣΕ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΑ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΑ ιπλωµατική εργασία: Λεµονάρη Μαρίνα Επιβλέπων καθηγητής:
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1
 Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ ΣΕΝΑΡΙΩΝ ΒΕΛΤΙΣΤΟΠΟΙΗΣΗΣ ΤΗΣ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΗΣ ΥΔΡΟΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ ΤΟΥ ΥΔΡΟΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΟΣ ΤΟΥ ΠΟΤΑΜΟΥ ΝΕΣΤΟΥ
 ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ ΣΕΝΑΡΙΩΝ ΒΕΛΤΙΣΤΟΠΟΙΗΣΗΣ ΤΗΣ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΗΣ ΥΔΡΟΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ ΤΟΥ ΥΔΡΟΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΟΣ ΤΟΥ ΠΟΤΑΜΟΥ ΝΕΣΤΟΥ ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ ΣΕΝΑΡΙΩΝ ΒΕΛΤΙΣΤΟΠΟΙΗΣΗΣ ΤΗΣ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΗΣ ΥΔΡΟΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ
ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ ΣΕΝΑΡΙΩΝ ΒΕΛΤΙΣΤΟΠΟΙΗΣΗΣ ΤΗΣ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΗΣ ΥΔΡΟΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ ΤΟΥ ΥΔΡΟΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΟΣ ΤΟΥ ΠΟΤΑΜΟΥ ΝΕΣΤΟΥ ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ ΣΕΝΑΡΙΩΝ ΒΕΛΤΙΣΤΟΠΟΙΗΣΗΣ ΤΗΣ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΗΣ ΥΔΡΟΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ
ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΑ ΥΠΟΣΤΥΛΩΜΑΤΑ ΥΠΟ ΘΛΙΨΗ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΜΨΗ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΑ ΥΠΟΣΤΥΛΩΜΑΤΑ ΥΠΟ ΘΛΙΨΗ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΣΥΓΚΡΙΣΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΤΙΚΩΝ ΛΥΣΕΩΝ ΚΑΝΟΝΙΣΤΙΚΩΝ ΙΑΤΑΞΕΩΝ ΚΑΙ
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ ΜΕΤΑΛΛΙΚΑ ΥΠΟΣΤΥΛΩΜΑΤΑ ΥΠΟ ΘΛΙΨΗ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΣΥΓΚΡΙΣΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΤΙΚΩΝ ΛΥΣΕΩΝ ΚΑΝΟΝΙΣΤΙΚΩΝ ΙΑΤΑΞΕΩΝ ΚΑΙ
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ "ΠΟΛΥΚΡΙΤΗΡΙΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΛΗΨΗΣ ΑΠΟΦΑΣΕΩΝ. Η ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΕΠΙΛΟΓΗΣ ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΥ ΥΓΕΙΑΣ "
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΚΑΛΑΜΑΤΑΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΟΝΑΔΩΝ ΥΓΕΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΡΟΝΟΙΑΣ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ "ΠΟΛΥΚΡΙΤΗΡΙΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΛΗΨΗΣ ΑΠΟΦΑΣΕΩΝ. Η ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΕΠΙΛΟΓΗΣ ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΥ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΚΑΛΑΜΑΤΑΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΟΝΑΔΩΝ ΥΓΕΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΡΟΝΟΙΑΣ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ "ΠΟΛΥΚΡΙΤΗΡΙΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΛΗΨΗΣ ΑΠΟΦΑΣΕΩΝ. Η ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΕΠΙΛΟΓΗΣ ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΥ
The kinetic and potential energies as T = 1 2. (m i η2 i k(η i+1 η i ) 2 ). (3) The Hooke s law F = Y ξ, (6) with a discrete analog
 Lecture 12: Introduction to Analytical Mechanics of Continuous Systems Lagrangian Density for Continuous Systems The kinetic and potential energies as T = 1 2 i η2 i (1 and V = 1 2 i+1 η i 2, i (2 where
Lecture 12: Introduction to Analytical Mechanics of Continuous Systems Lagrangian Density for Continuous Systems The kinetic and potential energies as T = 1 2 i η2 i (1 and V = 1 2 i+1 η i 2, i (2 where
5.4 The Poisson Distribution.
 The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
Capacitors - Capacitance, Charge and Potential Difference
 Capacitors - Capacitance, Charge and Potential Difference Capacitors store electric charge. This ability to store electric charge is known as capacitance. A simple capacitor consists of 2 parallel metal
Capacitors - Capacitance, Charge and Potential Difference Capacitors store electric charge. This ability to store electric charge is known as capacitance. A simple capacitor consists of 2 parallel metal
ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ. του φοιτητή του Τμήματος Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και. Τεχνολογίας Υπολογιστών της Πολυτεχνικής Σχολής του. Πανεπιστημίου Πατρών
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΜΕΤΑΤΡΟΠΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ του φοιτητή του
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΜΕΤΑΤΡΟΠΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ του φοιτητή του
Mean bond enthalpy Standard enthalpy of formation Bond N H N N N N H O O O
 Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ Διπλωματική Εργασία του φοιτητή του τμήματος Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Τεχνολογίας Ηλεκτρονικών
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ Διπλωματική Εργασία του φοιτητή του τμήματος Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Τεχνολογίας Ηλεκτρονικών
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ιπλωµατική Εργασία του φοιτητή του τµήµατος Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Τεχνολογίας Ηλεκτρονικών
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ιπλωµατική Εργασία του φοιτητή του τµήµατος Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών και Τεχνολογίας Ηλεκτρονικών
Αλληλεπίδραση Ανωδοµής-Βάθρων-Θεµελίωσης-Εδάφους σε Τοξωτή Οδική Μεταλλική Γέφυρα µε Σύµµικτο Κατάστρωµα
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ Σχολή Πολιτικών Μηχανικών Εργαστήριο Μεταλλικών Κατασκευών Αλληλεπίδραση Ανωδοµής-Βάθρων- Θεµελίωσης-Εδάφους σε Τοξωτή Οδική Μεταλλική Γέφυρα µε Σύµµικτο Κατάστρωµα ΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ Σχολή Πολιτικών Μηχανικών Εργαστήριο Μεταλλικών Κατασκευών Αλληλεπίδραση Ανωδοµής-Βάθρων- Θεµελίωσης-Εδάφους σε Τοξωτή Οδική Μεταλλική Γέφυρα µε Σύµµικτο Κατάστρωµα ΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ
«Χρήσεις γης, αξίες γης και κυκλοφοριακές ρυθμίσεις στο Δήμο Χαλκιδέων. Η μεταξύ τους σχέση και εξέλιξη.»
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΑΓΡΟΝΟΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΓΕΩΓΡΑΦΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΦΕΡΕΙΑΚΟΥ ΣΧΕΔΙΑΣΜΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ: «Χρήσεις γης, αξίες γης και κυκλοφοριακές ρυθμίσεις στο Δήμο Χαλκιδέων.
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΑΓΡΟΝΟΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΓΕΩΓΡΑΦΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΦΕΡΕΙΑΚΟΥ ΣΧΕΔΙΑΣΜΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ: «Χρήσεις γης, αξίες γης και κυκλοφοριακές ρυθμίσεις στο Δήμο Χαλκιδέων.
Εφαρµογή µεθόδων δυναµικής ανάλυσης σε κατασκευές µε γραµµική και µη γραµµική συµπεριφορά
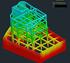 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΙΑΤΜΗΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥ ΩΝ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΣΧΕ ΙΑΣΜΟΣ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Εφαρµογή µεθόδων δυναµικής ανάλυσης σε κατασκευές µε γραµµική
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΙΑΤΜΗΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥ ΩΝ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΣΧΕ ΙΑΣΜΟΣ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΩΝ Εφαρµογή µεθόδων δυναµικής ανάλυσης σε κατασκευές µε γραµµική
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories
 Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
«ΑΓΡΟΤΟΥΡΙΣΜΟΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΟΠΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ: Ο ΡΟΛΟΣ ΤΩΝ ΝΕΩΝ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΠΡΟΩΘΗΣΗ ΤΩΝ ΓΥΝΑΙΚΕΙΩΝ ΣΥΝΕΤΑΙΡΙΣΜΩΝ»
 I ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΝΟΜΙΚΩΝ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ «ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΚΑΙ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑ» ΚΑΤΕΥΘΥΝΣΗ: ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΗ
I ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΝΟΜΙΚΩΝ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ «ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΚΑΙ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑ» ΚΑΤΕΥΘΥΝΣΗ: ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΗ
( ) 2 and compare to M.
 Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
Διπλωματική Εργασία. Μελέτη των μηχανικών ιδιοτήτων των stents που χρησιμοποιούνται στην Ιατρική. Αντωνίου Φάνης
 Διπλωματική Εργασία Μελέτη των μηχανικών ιδιοτήτων των stents που χρησιμοποιούνται στην Ιατρική Αντωνίου Φάνης Επιβλέπουσες: Θεοδώρα Παπαδοπούλου, Ομότιμη Καθηγήτρια ΕΜΠ Ζάννη-Βλαστού Ρόζα, Καθηγήτρια
Διπλωματική Εργασία Μελέτη των μηχανικών ιδιοτήτων των stents που χρησιμοποιούνται στην Ιατρική Αντωνίου Φάνης Επιβλέπουσες: Θεοδώρα Παπαδοπούλου, Ομότιμη Καθηγήτρια ΕΜΠ Ζάννη-Βλαστού Ρόζα, Καθηγήτρια
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님
 상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
GREECE BULGARIA 6 th JOINT MONITORING
 GREECE BULGARIA 6 th JOINT MONITORING COMMITTEE BANSKO 26-5-2015 «GREECE BULGARIA» Timeline 02 Future actions of the new GR-BG 20 Programme June 2015: Re - submission of the modified d Programme according
GREECE BULGARIA 6 th JOINT MONITORING COMMITTEE BANSKO 26-5-2015 «GREECE BULGARIA» Timeline 02 Future actions of the new GR-BG 20 Programme June 2015: Re - submission of the modified d Programme according
Computing the Gradient
 FMIA F. Moukalled L. Mangani M. Darwish An Advanced Introduction with OpenFOAM and Matlab This textbook explores both the theoretical oundation o the Finite Volume Method (FVM) and its applications in
FMIA F. Moukalled L. Mangani M. Darwish An Advanced Introduction with OpenFOAM and Matlab This textbook explores both the theoretical oundation o the Finite Volume Method (FVM) and its applications in
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΤΕΧΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ. Πτυχιακή εργασία
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΤΕΧΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΚΟΣΤΟΥΣ-ΟΦΕΛΟΥΣ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΔΙΕΙΣΔΥΣΗ ΤΩΝ ΑΝΑΝΕΩΣΙΜΩΝ ΠΗΓΩΝ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΥΠΡΟ ΜΕΧΡΙ ΤΟ 2030
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΤΕΧΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΚΟΣΤΟΥΣ-ΟΦΕΛΟΥΣ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΔΙΕΙΣΔΥΣΗ ΤΩΝ ΑΝΑΝΕΩΣΙΜΩΝ ΠΗΓΩΝ ΕΝΕΡΓΕΙΑΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΥΠΡΟ ΜΕΧΡΙ ΤΟ 2030
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ. Πτυχιακή εργασία EDQNM ΙΣΟΤΡΟΠΙΚΗΣ ΤΥΡΒΗΣ. Μιχάλης Πιερής
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία EDQNM ΙΣΟΤΡΟΠΙΚΗΣ ΤΥΡΒΗΣ Μιχάλης Πιερής Λεμεσός 2016 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία EDQNM ΙΣΟΤΡΟΠΙΚΗΣ ΤΥΡΒΗΣ Μιχάλης Πιερής Λεμεσός 2016 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ
ΔΗΜΟΚΡΙΤΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΡΑΚΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΑΓΩΓΗΣ
 ΔΗΜΟΚΡΙΤΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΡΑΚΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΑΓΩΓΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΠΡΟΣΧΟΛΙΚΗ ΗΛΙΚΙΑ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ Διαπολιτισμική Εκπαίδευση και Θρησκευτική Ετερότητα: εθνικές και θρησκευτικές
ΔΗΜΟΚΡΙΤΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΡΑΚΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΑΓΩΓΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΠΡΟΣΧΟΛΙΚΗ ΗΛΙΚΙΑ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ Διαπολιτισμική Εκπαίδευση και Θρησκευτική Ετερότητα: εθνικές και θρησκευτικές
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS
 VSB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS Lecture 1 Jiří Brožovský Office: LP H 406/3 Phone: 597 321 321 E-mail: jiri.brozovsky@vsb.cz WWW: http://fast10.vsb.cz/brozovsky/
VSB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS Lecture 1 Jiří Brožovský Office: LP H 406/3 Phone: 597 321 321 E-mail: jiri.brozovsky@vsb.cz WWW: http://fast10.vsb.cz/brozovsky/
Μετρήσεις ηλιοφάνειας στην Κύπρο
 Πτυχιακή εργασία Μετρήσεις ηλιοφάνειας στην Κύπρο Ιωσήφ Μικαίος Λεμεσός, Μάιος 2018 1 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΤΕΧΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ
Πτυχιακή εργασία Μετρήσεις ηλιοφάνειας στην Κύπρο Ιωσήφ Μικαίος Λεμεσός, Μάιος 2018 1 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΤΕΧΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ
Potential Dividers. 46 minutes. 46 marks. Page 1 of 11
 Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain. Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics
 A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
Πανεπιστήμιο Πειραιώς Τμήμα Πληροφορικής Πρόγραμμα Μεταπτυχιακών Σπουδών «Πληροφορική»
 Πανεπιστήμιο Πειραιώς Τμήμα Πληροφορικής Πρόγραμμα Μεταπτυχιακών Σπουδών «Πληροφορική» Μεταπτυχιακή Διατριβή Τίτλος Διατριβής Επίκαιρα Θέματα Ηλεκτρονικής Διακυβέρνησης Ονοματεπώνυμο Φοιτητή Σταμάτιος
Πανεπιστήμιο Πειραιώς Τμήμα Πληροφορικής Πρόγραμμα Μεταπτυχιακών Σπουδών «Πληροφορική» Μεταπτυχιακή Διατριβή Τίτλος Διατριβής Επίκαιρα Θέματα Ηλεκτρονικής Διακυβέρνησης Ονοματεπώνυμο Φοιτητή Σταμάτιος
AΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ
 AΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΕΙΔΙΚΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΡΟΣΤΑΣΙΑ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ ΚΑΙ ΒΙΩΣΙΜΗ ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ ΔΙΕΡΕΥΝΗΣΗ ΤΩΝ ΠΙΕΣΕΩΝ ΣΤΟ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝ
AΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΕΙΔΙΚΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΡΟΣΤΑΣΙΑ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ ΚΑΙ ΒΙΩΣΙΜΗ ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗ ΔΙΕΡΕΥΝΗΣΗ ΤΩΝ ΠΙΕΣΕΩΝ ΣΤΟ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝ
ΘΕΩΡΗΤΙΚΗ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΙΡΑΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΙΕΡΕΥΝΗΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΙΕΡΓΑΣΙΑΣ ΣΚΛΗΡΥΝΣΗΣ ΙΑ ΛΕΙΑΝΣΕΩΣ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΗΧΑΝΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΑΕΡΟΝΑΥΠΗΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΑΥΤΟΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΥ / ΥΝΑΜΙΚΗΣ & ΘΕΩΡΙΑΣ ΜΗΧΑΝΩΝ ΙΕΥΘΥΝΤΗΣ: Καθηγητής Γ. ΧΡΥΣΟΛΟΥΡΗΣ Ι ΑΚΤΟΡΙΚΗ
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΗΧΑΝΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΑΕΡΟΝΑΥΠΗΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΑΥΤΟΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΥ / ΥΝΑΜΙΚΗΣ & ΘΕΩΡΙΑΣ ΜΗΧΑΝΩΝ ΙΕΥΘΥΝΤΗΣ: Καθηγητής Γ. ΧΡΥΣΟΛΟΥΡΗΣ Ι ΑΚΤΟΡΙΚΗ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ. Πτυχιακή εργασία ΟΛΙΣΘΗΡΟΤΗΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΜΑΚΡΟΥΦΗ ΤΩΝ ΟΔΟΔΤΡΩΜΑΤΩΝ ΚΥΚΛΟΦΟΡΙΑΣ
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία ΟΛΙΣΘΗΡΟΤΗΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΜΑΚΡΟΥΦΗ ΤΩΝ ΟΔΟΔΤΡΩΜΑΤΩΝ ΚΥΚΛΟΦΟΡΙΑΣ Χριστοδούλου Αντρέας Λεμεσός 2014 2 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία ΟΛΙΣΘΗΡΟΤΗΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΜΑΚΡΟΥΦΗ ΤΩΝ ΟΔΟΔΤΡΩΜΑΤΩΝ ΚΥΚΛΟΦΟΡΙΑΣ Χριστοδούλου Αντρέας Λεμεσός 2014 2 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΙΣΧΥΟΣ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΙΣΧΥΟΣ Προοπτικές Εναρμόνισης της Ελληνικής Αγοράς Ηλεκτρικής Ενέργειας με τις Προδιαγραφές του Μοντέλου
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗΣ ΙΣΧΥΟΣ Προοπτικές Εναρμόνισης της Ελληνικής Αγοράς Ηλεκτρικής Ενέργειας με τις Προδιαγραφές του Μοντέλου
ΣΥΓΚΡΙΣΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΤΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΑΡΙΘΜΗΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΕΘΟ ΩΝ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΣΥΓΚΡΙΣΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΤΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΑΡΙΘΜΗΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΕΘΟ ΩΝ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΦΟΙΤΗΤΡΙΑ: Γ.ΦΕΒΡΑΝΟΓΛΟΥ ΕΠΙΒΛΕΠΩΝ ΚΑΘΗΓΗΤΗΣ: Χ.ΓΑΝΤΕΣ ΑΘΗΝΑ, ΟΚΤΩΒΡΙΟΣ 2000
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΟΜΟΣΤΑΤΙΚΗΣ ΣΥΓΚΡΙΣΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΤΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΑΡΙΘΜΗΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΕΘΟ ΩΝ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΦΟΙΤΗΤΡΙΑ: Γ.ΦΕΒΡΑΝΟΓΛΟΥ ΕΠΙΒΛΕΠΩΝ ΚΑΘΗΓΗΤΗΣ: Χ.ΓΑΝΤΕΣ ΑΘΗΝΑ, ΟΚΤΩΒΡΙΟΣ 2000
Μεταπτυχιακή διατριβή. Ανδρέας Παπαευσταθίου
 Σχολή Γεωτεχνικών Επιστημών και Διαχείρισης Περιβάλλοντος Μεταπτυχιακή διατριβή Κτίρια σχεδόν μηδενικής ενεργειακής κατανάλωσης :Αξιολόγηση συστημάτων θέρμανσης -ψύξης και ΑΠΕ σε οικιστικά κτίρια στην
Σχολή Γεωτεχνικών Επιστημών και Διαχείρισης Περιβάλλοντος Μεταπτυχιακή διατριβή Κτίρια σχεδόν μηδενικής ενεργειακής κατανάλωσης :Αξιολόγηση συστημάτων θέρμανσης -ψύξης και ΑΠΕ σε οικιστικά κτίρια στην
ΖΩΝΟΠΟΙΗΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΚΑΤΟΛΙΣΘΗΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΠΙΚΙΝΔΥΝΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΣΤΟ ΟΡΟΣ ΠΗΛΙΟ ΜΕ ΤΗ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΗ ΔΕΔΟΜΕΝΩΝ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΟΜΕΤΡΙΑΣ ΜΟΝΙΜΩΝ ΣΚΕΔΑΣΤΩΝ
 EΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΕΙΟ Τμήμα Μηχανικών Μεταλλείων-Μεταλλουργών ΖΩΝΟΠΟΙΗΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΚΑΤΟΛΙΣΘΗΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΠΙΚΙΝΔΥΝΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΜΕ ΤΗ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΗ ΔΕΔΟΜΕΝΩΝ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΟΜΕΤΡΙΑΣ ΜΟΝΙΜΩΝ ΣΚΕΔΑΣΤΩΝ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ Κιτσάκη Μαρίνα
EΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΕΙΟ Τμήμα Μηχανικών Μεταλλείων-Μεταλλουργών ΖΩΝΟΠΟΙΗΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΚΑΤΟΛΙΣΘΗΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΠΙΚΙΝΔΥΝΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΜΕ ΤΗ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΗ ΔΕΔΟΜΕΝΩΝ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΟΜΕΤΡΙΑΣ ΜΟΝΙΜΩΝ ΣΚΕΔΑΣΤΩΝ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ Κιτσάκη Μαρίνα
ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΕΥΤΕΡΟΒΑΘΜΙΑ ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΜΕΝΩΝ ΥΓΡΩΝ ΑΠΟΒΛΗΤΩΝ ΣΕ ΦΥΣΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΛΙΝΗΣ ΚΑΛΑΜΙΩΝ
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙ ΕΥΤΙΚΟ Ι ΡΥΜΑ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΦΥΣΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΕΥΤΕΡΟΒΑΘΜΙΑ ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΜΕΝΩΝ ΥΓΡΩΝ ΑΠΟΒΛΗΤΩΝ ΣΕ ΦΥΣΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΛΙΝΗΣ ΚΑΛΑΜΙΩΝ ΕΠΙΜΕΛΕΙΑ: ΑΡΜΕΝΑΚΑΣ ΜΑΡΙΝΟΣ ΧΑΝΙΑ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙ ΕΥΤΙΚΟ Ι ΡΥΜΑ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΦΥΣΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΕΥΤΕΡΟΒΑΘΜΙΑ ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΜΕΝΩΝ ΥΓΡΩΝ ΑΠΟΒΛΗΤΩΝ ΣΕ ΦΥΣΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΛΙΝΗΣ ΚΑΛΑΜΙΩΝ ΕΠΙΜΕΛΕΙΑ: ΑΡΜΕΝΑΚΑΣ ΜΑΡΙΝΟΣ ΧΑΝΙΑ
Σπανό Ιωάννη Α.Μ. 148
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΔΙΑΤΜΗΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΙΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΙΚΕΣ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΕΣ Ηλεκτροχημική εναπόθεση και μελέτη των ιδιοτήτων, λεπτών υμενίων μεταβατικών μετάλλων, για παραγωγή H2 Διπλωματική
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΔΙΑΤΜΗΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΙΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΙΚΕΣ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΕΣ Ηλεκτροχημική εναπόθεση και μελέτη των ιδιοτήτων, λεπτών υμενίων μεταβατικών μετάλλων, για παραγωγή H2 Διπλωματική
Parametrized Surfaces
 Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Calculating the propagation delay of coaxial cable
 Your source for quality GNSS Networking Solutions and Design Services! Page 1 of 5 Calculating the propagation delay of coaxial cable The delay of a cable or velocity factor is determined by the dielectric
Your source for quality GNSS Networking Solutions and Design Services! Page 1 of 5 Calculating the propagation delay of coaxial cable The delay of a cable or velocity factor is determined by the dielectric
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ
 ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ Μελέτη των υλικών των προετοιμασιών σε υφασμάτινο υπόστρωμα, φορητών έργων τέχνης (17ος-20ος αιώνας). Διερεύνηση της χρήσης της τεχνικής της Ηλεκτρονικής Μικροσκοπίας
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ Μελέτη των υλικών των προετοιμασιών σε υφασμάτινο υπόστρωμα, φορητών έργων τέχνης (17ος-20ος αιώνας). Διερεύνηση της χρήσης της τεχνικής της Ηλεκτρονικής Μικροσκοπίας
ΓΕΩΜΕΣΡΙΚΗ ΣΕΚΜΗΡΙΩΗ ΣΟΤ ΙΕΡΟΤ ΝΑΟΤ ΣΟΤ ΣΙΜΙΟΤ ΣΑΤΡΟΤ ΣΟ ΠΕΛΕΝΔΡΙ ΣΗ ΚΤΠΡΟΤ ΜΕ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΑΤΣΟΜΑΣΟΠΟΙΗΜΕΝΟΤ ΤΣΗΜΑΣΟ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΗ ΦΩΣΟΓΡΑΜΜΕΣΡΙΑ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΤΣΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΑΓΡΟΝΟΜΩΝ-ΣΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΣΟΜΕΑ ΣΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΙΑ ΕΡΓΑΣΗΡΙΟ ΦΩΣΟΓΡΑΜΜΕΣΡΙΑ ΓΕΩΜΕΣΡΙΚΗ ΣΕΚΜΗΡΙΩΗ ΣΟΤ ΙΕΡΟΤ ΝΑΟΤ ΣΟΤ ΣΙΜΙΟΤ ΣΑΤΡΟΤ ΣΟ ΠΕΛΕΝΔΡΙ ΣΗ ΚΤΠΡΟΤ ΜΕ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΑΤΣΟΜΑΣΟΠΟΙΗΜΕΝΟΤ
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΤΣΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΑΓΡΟΝΟΜΩΝ-ΣΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΣΟΜΕΑ ΣΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΙΑ ΕΡΓΑΣΗΡΙΟ ΦΩΣΟΓΡΑΜΜΕΣΡΙΑ ΓΕΩΜΕΣΡΙΚΗ ΣΕΚΜΗΡΙΩΗ ΣΟΤ ΙΕΡΟΤ ΝΑΟΤ ΣΟΤ ΣΙΜΙΟΤ ΣΑΤΡΟΤ ΣΟ ΠΕΛΕΝΔΡΙ ΣΗ ΚΤΠΡΟΤ ΜΕ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΑΤΣΟΜΑΣΟΠΟΙΗΜΕΝΟΤ
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
Lecture 26: Circular domains
 Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without eplicit written permission from the copyright owner. 1 Lecture 6: Circular domains
Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without eplicit written permission from the copyright owner. 1 Lecture 6: Circular domains
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Η αλληλεπίδραση ανάμεσα στην καθημερινή γλώσσα και την επιστημονική ορολογία: παράδειγμα από το πεδίο της Κοσμολογίας
 Η αλληλεπίδραση ανάμεσα στην καθημερινή γλώσσα και την επιστημονική ορολογία: παράδειγμα από το πεδίο της Κοσμολογίας ΠΕΡΙΛΗΨΗ Αριστείδης Κοσιονίδης Η κατανόηση των εννοιών ενός επιστημονικού πεδίου απαιτεί
Η αλληλεπίδραση ανάμεσα στην καθημερινή γλώσσα και την επιστημονική ορολογία: παράδειγμα από το πεδίο της Κοσμολογίας ΠΕΡΙΛΗΨΗ Αριστείδης Κοσιονίδης Η κατανόηση των εννοιών ενός επιστημονικού πεδίου απαιτεί
Appendix to On the stability of a compressible axisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe. By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee
 Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
