Chapter 10: Time and Global States Introduction Clocks,events and process states Synchronizing physical clocks Logical time and logical clocks Global
|
|
|
- Αρσένιος Ταμτάκος
- 8 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Chapter 10: Time and Global States Introduction Clocks,events and process states Synchronizing physical clocks Logical time and logical clocks Global states Distributed debugging Summary
2 Time is an important issue in DS Time is a quantity we need to measure accurately E.g. e-commerce transaction involves events at a merchant s computer and at a bank computer. Thus, it is important for auditing purposes that these events are timestamped accurately. Algorithms depending on clock synchronization have been developed for several problems in distribution E.g. maintaining consistency of distributed data
3 There is no universe physical clock Physicist s view Newton s notation: absolute physical time Einstein s Relativity Theory People s approaches dealing with time Approximately synchronize Logical clocks
4 Model of a distributed system A collection of N processes p i, i = 1,2,.. N s i The state of p i E.g. variables Actions of p i Operations that transform p i s state Send or receive message between p j
5 Model of a distributed system e Event: occurrence of a single action (e.g., communication or processing action) i occur before in p i, e.g. e i e` (only if event e occurs before e` ) Total order of events in p i History of process p i history(p i ) = h i h i = <e i0, e i1, e i2, >
6 Clock skew and clock drift Each computer has its own clock Computer clocks tend not to be in perfect agreement Clock drift Crystal oscillate at different rate Clock drift can not be avoided Clock skew The instantaneous difference between the readings of any two clocks
7 Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) Computer clocks can be synchronized to external sources Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the international standard for timekeeping Broadcast UTC to the World E.g., by GPS or WWV
8 External & Internal synchronization C i : p i s clock I: an interval of real time External synchronization (to synchronize the clock with an external source of time) For a synchronization bound D > 0, and for a source S of UTC time, S(t)-C i (t) < D, for i = 1, 2, N and for all real times t in I Clocks C i are accurate to within the bound D
9 External & Internal synchronization (2) Internal synchronization (to synchronize the clocks of two computers) For a synchronization bound D > 0, C i (t)- C j (t) < D for i, j =1,2, N, and for all real times t in I Clocks C i agree within the bound D If accurate to within D, then agree within 2D
10 General synchronization issues (2) Clock failures Crash failure: stop ticking Arbitrary failure, e.g. Y2K bug
11 Synchronization in a synchronous system Protocol Sender: send M(t) Receiver: set time to t + T trans In a synchronous system, bounds are know min < T trans < max (constant) So, set T trans = (min+max) / 2 Receiver s clock = t + (min+max) / 2 Clock skew between sender and receiver (max min ) / 2 t t + min t +T trans t+max
12 Cristian s method of synchronizing clocks Applying circumstance Cristian observed that the round-trip times for messages exchanged between processes is relatively short Protocol Process p sends m r to request time and receives time t in message m t (t). It records the total T round to send message and receive reply (in the order ot milliseconds in LAN) Estimated time: t + T round /2 m r p m t Time server,s
13 Cristian s method of synchronizing clocks (2) Accuracy analysis If the minimum delay of a message transmission is min, then accuracy: ± (T round /2 min) t + min t +T round -min t t +T round /2 t +T round
14 The Berkeley algorithms Internal synchronization (developed for collections of computers running Berkeley UNIX) A coordinator computer (master) acts as coordinator. It periodically polls the other computers whose clocks are to be synchronized (called slaves) Protocol 1. The master polls the slaves clocks 2. The master estimates the slaves clocks by roundtrip time Similar to Christian s algorithm 3. Instead of considering only 1 slave, the master averages all the slaves clock values Advantage: Cancel out the individual clock s tendencies to run fast or slow
15 The Berkeley algorithms (2) 4. The master sends back to the slaves the amount that the slaves clocks should adjust by Positive or negative value Avoid further uncertainty due to the message transmission time Each slave adjusts its clock
16 Design aims of Network Time Protocol External synchronization Enable clients across the Internet to be synchronized accurately to UTC Reliability Can survive lengthy losses of connectivity Redundant server & redundant path between servers Scalability Enable clients to resynchronize sufficiently frequently to offset the rates of drift found in most computers Security Protect against interference with the time service
17 Network Time Protocol Architecture Note: Arrows denote synchronization control, numbers denote levels. Primary servers connected directly to a time source Secondary servers synchronized with primary servers, and so on Clocks belonging to higher levels may be less accurate (errors introduced at each level) Reconfigure when servers become unreachable
18 Synchronization measures NTP servers synchronize with one another in one of three modes: Multicast mode Intend for use on a high speed LAN Assuming a small delay Low accuracy but efficient Procedure-call mode Similar to Christian s (one server accepts requests from other computers which it processes by replying with its timestamp) Higher accuracy than multicast Symmetric mode A pair of servers operating in symmetric mode exchange messages with timing information The highest accuracy
19 Symmetric mode sync. implementation NTP servers retain 8 most recent pairs <o i,d i > The value o i of that corresponds to the minimum value d i is chosen to estimate o A NTP server exchanges with several peers in addition to with parent Peers with lower level numbers are favoured Peers with the lowest synchronization dispersion are favoured
20 Logical Time and Logical Clocks Lamport (1978) τόνισε ότι δεν µπορούµε να συγχρονίσουµε τέλεια ρολόγια σε ένα κατανεµηµένο σύστηµα, µπορούµε όµως να χρησιµοποιήσουµε ένα σύστηµα που να µοιάζει µε φυσική αιτιότητα (physical causality) για να ορίσουµε διάταξη σε γεγονότα που συµβαίνουν σε διαφορετικές διεργασίες
21 Happen-before relation HB1: If διεργασία p i : e i e`, then e e` HB2: For any message m, send(m) receive(m) HB3: IF e, e`and e`` είναι γεγονότα για τα οποία ισχύει ότι e e` and e` e``, τότε e e`` Causal ordering
22 Happen-before relation Δεν συσχετίζονται όλα τα γεγονότα µε τη σχέση Αυτά τα γεγονότα λέγονται παράλληλα γεγονότα a e Προβλήµατα Δεν είναι κατάλληλο για τις διαδικασίες συνεργασίας που δεν ανταλλάσουν µηνύµατα Capture potential causal ordering
23 Ιδέα Lamport επινόησε έναν απλό µηχανισµό µε τον οποίο η σχέση συνέβη-πριν (happenedbefore) µπορεί να συλληφθεί αριθµητικά, αυτό όνοµάζεται λογικό ρολόι Κάθε διεργασία έχει το δικό της λογικό ρολόι L i που χρησιµοποιεί σαν timestamp των γεγονότων. Εµείς χαρακτηρίζουµε το timestamp του γεγονότος e at p i by L i (e)
24 Lamport timestamps algorithm LC1 L i αυξάνεται κάθε φορά που ένα γεγονός συµβαίνει στην διεργασία p i : L i :=L i +1 LC2: (a) Οταν η διεργασία p i στέλνει µήνυµα m, µαζί µε το µήνυµα m βάζει και την τιµή t = L i (b) Οταν λαµβάνει το µήνυµα (m,t) µια διεργασία P j υπολογίζει το L j := max(l j, t) και µετά εκτελεί το LC1 πριν να βάλει timestamp στο γεγονός receive(m)
25 Lamport timestamps algorithm (2) e e` L(e) < L(e`) Το αντίθετο δεν είναι πάντα αλήθεια L(e) < L(e`) e e` or e e`
26 Totally ordered logical clocks Κάποια ζευγάρια των γεγονότων που παράγονται από διαφορετικές διαδικασίες, έχουν τα ίδια Lamport timestamps. Μπορούμε και τότε να δημιουργήσουμε μια συνολική διάταξη για τα γεγονότα ως εξής: Assumption T i : local timestamp of e that is an event occurring at p i T j : local timestamp of e` that is an event occurring at p j Define the timestamps of e, e` are (T i, i), (T j, j) Define < (T i, i) < (T j, j) if T i < T j, or T i = T j and i < j Χρήσιµο σε µερικές εφαρµογές (e.g. order processes to a critical section)
27 Διανυσµατικά Ρολόγια (Vector Clocks) Κάθε διεργασία p i έχει διάνυσµα vector clock V i VC1: Αρχικά, V i [j]=0, for i, j = 1,2, N VC2: Πριν η διεργασία p i timestamps ένα γεγονός, ορίζει V i [i] := V i [i] +1 VC3: p i ενσωµατώνει την τιµή t= V i σε κάθε µήνυµα που στέλνει VC4: Οταν η διεργασία p i λάβει το timestamp t σε ένα µήνυµα, ορίζει V i [j] :=max(v i [j], t[j]), for j=1,2,n
28 Vector Clocks - σηµασία Συγκρίνουµε vector timestamps ως εξής: V = V` iff V [j] = V`[j] for j = 1,2, N V <= V` iff V`[j]<=V`[j] for j = 1,2, N V < V` iff V`[j]< V`[j] for j = 1,2, N Otherwise V<>V V(e) < V(e`) e e`, V(e) <> V(e`) e e`
29 Vector Clocks - example
30 The problem of Global States Εξετάζουµε το πρόβληµα να διαπιστώσουµε αν µια συγκεκριµένη ιδιότητα είναι αληθής. Παραδείγµατα Distributed garbage collection Based on reference counting Should include the state of communication channels Distributed deadlock detection Look for waits-for relationship Distributed termination detection Look for state in which all processes are passive
31 Global states and consistent cuts The essential problem of Global states Absence of global time History of process p i h i = <e i0, e i1, e i 2 > Prefix of a process s history h i k = <e i0, e i1 e i k > Global history of processes set H = h 1 h 2 h N
32 The state (κατάσταση) of process p i s i k : η κατάσταση προτού το kth γεγονός συμβεί The state of channel between the p i and p j when transmit the massage A cut of a system execution A subset of its global history that is a union of prefixes of process histories. C = <h 1 c1, h 2 c2 h 3 c3 > A global state S = (s 1, s 2, s N ) s i corresponding to the cut of C is that of p i immediately after the last event processed by p i in the cut- e i ci
33 Global states and consistent cuts A cut C is consistent: For all events e C, f e f C < e 10, e 20 >, < e 12, e 22 >
34 Global states and consistent cuts A consistent global state: correspond to a consistent cut The s i corresponding to the cut C is that of p i immediately after the last event processed by p i in C Execution of a distributed system S 0 S 1 S 2
35 Global states and consistent cuts A run a total ordering of all the events in a global history that is consistent with each local history s ordering, i Not all runs pass through consistent global state A linearization (consistent) run an ordering of the events in a global history H that is consistent with this happened-before relation on H. Pass only consistent global state
36 Global states and consistent cuts S is reachable from a state S there is a linearization that pass through S and then S
37 The snapshot algorithm of Chandy and Lamport Σκοπός µας Να υπολογίσουµε consistent global state του κατανεµηµένου συστήµατος
38 The snapshot algorithm - assumptions Ούτε τα κανάλια, ούτε διαδικασίες αποτυγχάνουν Μονοκατευθυντικά κανάλια, FIFO παράδοση µηνυµάτων Πλήρης σύνδεση µεταξύ όλων των διεργασιών Κάθε διαδικασία µπορεί να ξεκινήσει µια παγκόσµια στιγµιότυπο (global snapshot) ανά πάσα χρονική στιγµή Οι διεργασίες µπορούν να συνεχίσουν την εκτέλεση και την αποστολή και λήψη µηνυµάτων, ενώ το κανονική στιγµιότυπο λαµβάνει χώρα
39 The snapshot algorithm - idea Οταν µια διεργασία καταγράψει µια κατάσταση S i, κάνε όλες τις διεργασίες να καταγράψουν τις καταστάσεις τους που έχουν προκληθεί από την S i
40 The snapshot algorithm - method Incoming channels, outgoing channels Process state + channel state Marker message Marker sending rule: µια διεργασία στέλνει ένα marker αφού έχει καταγράψει την κατάστασή της, και προτού στείλει άλλα µηνύµατα Marker receiving rule: µια διεργασία καταγράφει την κατάσταση της αν η κατάσταση της έχει αλλάξει από την τελευταία εγγραφή, διαφορετικά καταγράφει την κατάσταση των incoming channels
41 Marker receiving rule for process p i On p i s receipt of a marker message over channel c: if (p i has not yet recorded its state) it records its process state now; records the state of c as the empty set; turns on recording of messages arriving over other incoming channels; else p i records the state of c as the set of messages it has received over c since it saved its state. end if Marker sending rule for process p i After p i has recorded its state, for each outgoing channel c: p i sends one marker message over c (before it sends any other message over c).
42 The snapshot algorithm - example p 1 trade p 2 in widget which is 10$ per item Initial state p 1 has sent 50$ to p 2 to buy 5 widget, and p 2 has received the order
43 Execution of the processes in the example 1. Global state S 0 2. Global state S 1 3. Global state S 2 4. Global state S 3 <$1000, 0> p 1 c 2 (empty) p 2 <$50, 2000> c 1 (empty) <$900, 0> p 1 c (Order 10, $100), M 2 p 2 <$50, 2000> c 1 (empty) <$900, 0> p 1 c (Order 10, $100), M 2 p 2 <$50, 1995> c 1 (five widgets) M <$900, 5> p 1 c 2 (Order 10, $100) p 2 <$50, 1995> c 1 (empty) (M = marker message) The final recorded state P 1 :<$1000, 0>; p 2 :<$50,1995>;c 1 :<(five widgets)>;c 2 :<>
Ρολόγια και Συγχρονισμός
 Ρολόγια και Συγχρονισμός Κατανεμημένα Συστήματα 2015 2016 http://www.cslab.ece.ntua.gr/courses/distrib Συνοπτικά Πρέπει να ξέρουμε πότε έγινε τι Ιδανικά ακριβώς πότε έγινε τι Ή τουλάχιστον να διατάξουμε
Ρολόγια και Συγχρονισμός Κατανεμημένα Συστήματα 2015 2016 http://www.cslab.ece.ntua.gr/courses/distrib Συνοπτικά Πρέπει να ξέρουμε πότε έγινε τι Ιδανικά ακριβώς πότε έγινε τι Ή τουλάχιστον να διατάξουμε
Ρολόγια και Συγχρονισμός
 Ρολόγια και Συγχρονισμός Κατανεμημένα Συστήματα 2016-2017 http://www.cslab.ece.ntua.gr/courses/distrib Συνοπτικά Πρέπει να ξέρουμε πότε έγινε τι Ιδανικά ακριβώς πότε έγινε τι Ή τουλάχιστον να διατάξουμε
Ρολόγια και Συγχρονισμός Κατανεμημένα Συστήματα 2016-2017 http://www.cslab.ece.ntua.gr/courses/distrib Συνοπτικά Πρέπει να ξέρουμε πότε έγινε τι Ιδανικά ακριβώς πότε έγινε τι Ή τουλάχιστον να διατάξουμε
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ
 ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
(C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Connectionless transmission with datagrams. Connection-oriented transmission is like the telephone system You dial and are given a connection to the telephone of fthe person with whom you wish to communicate.
Connectionless transmission with datagrams. Connection-oriented transmission is like the telephone system You dial and are given a connection to the telephone of fthe person with whom you wish to communicate.
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Bayesian statistics. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Δίκτυα Επικοινωνιών ΙΙ: OSPF Configuration
 Δίκτυα Επικοινωνιών ΙΙ: OSPF Configuration Δρ. Απόστολος Γκάμας Διδάσκων 407/80 gkamas@uop.gr Δίκτυα Επικοινωνιών ΙΙ Διαφάνεια 1 1 Dynamic Routing Configuration Router (config) # router protocol [ keyword
Δίκτυα Επικοινωνιών ΙΙ: OSPF Configuration Δρ. Απόστολος Γκάμας Διδάσκων 407/80 gkamas@uop.gr Δίκτυα Επικοινωνιών ΙΙ Διαφάνεια 1 1 Dynamic Routing Configuration Router (config) # router protocol [ keyword
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
5.4 The Poisson Distribution.
 The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
[1] P Q. Fig. 3.1
![[1] P Q. Fig. 3.1 [1] P Q. Fig. 3.1](/thumbs/79/80362156.jpg) 1 (a) Define resistance....... [1] (b) The smallest conductor within a computer processing chip can be represented as a rectangular block that is one atom high, four atoms wide and twenty atoms long. One
1 (a) Define resistance....... [1] (b) The smallest conductor within a computer processing chip can be represented as a rectangular block that is one atom high, four atoms wide and twenty atoms long. One
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
the total number of electrons passing through the lamp.
 1. A 12 V 36 W lamp is lit to normal brightness using a 12 V car battery of negligible internal resistance. The lamp is switched on for one hour (3600 s). For the time of 1 hour, calculate (i) the energy
1. A 12 V 36 W lamp is lit to normal brightness using a 12 V car battery of negligible internal resistance. The lamp is switched on for one hour (3600 s). For the time of 1 hour, calculate (i) the energy
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Potential Dividers. 46 minutes. 46 marks. Page 1 of 11
 Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Ανοχή απέναντι σε Σφάλµατα Fault Tolerance
 Ανοχή απέναντι σε Σφάλµατα Fault Tolerance Μαρία Ι. Ανδρέου ΗΜΥ417, ΗΜΥ 663 Κατανεµηµένα Συστήµατα Χειµερινό Εξάµηνο 2006-2007 Τµήµα Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών & Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Βασικές
Ανοχή απέναντι σε Σφάλµατα Fault Tolerance Μαρία Ι. Ανδρέου ΗΜΥ417, ΗΜΥ 663 Κατανεµηµένα Συστήµατα Χειµερινό Εξάµηνο 2006-2007 Τµήµα Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών & Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Βασικές
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Study of In-vehicle Sound Field Creation by Simultaneous Equation Method
 Study of In-vehicle Sound Field Creation by Simultaneous Equation Method Kensaku FUJII Isao WAKABAYASI Tadashi UJINO Shigeki KATO Abstract FUJITSU TEN Limited has developed "TOYOTA remium Sound System"
Study of In-vehicle Sound Field Creation by Simultaneous Equation Method Kensaku FUJII Isao WAKABAYASI Tadashi UJINO Shigeki KATO Abstract FUJITSU TEN Limited has developed "TOYOTA remium Sound System"
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 24/3/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Όλοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα μικρότεροι του 10000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Όλοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα μικρότεροι του 10000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής
 Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής Να γραφεί πρόγραμμα το οποίο δέχεται ως είσοδο μια ακολουθία S από n (n 40) ακέραιους αριθμούς και επιστρέφει ως έξοδο δύο ακολουθίες από θετικούς ακέραιους
Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής Να γραφεί πρόγραμμα το οποίο δέχεται ως είσοδο μια ακολουθία S από n (n 40) ακέραιους αριθμούς και επιστρέφει ως έξοδο δύο ακολουθίες από θετικούς ακέραιους
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
ω ω ω ω ω ω+2 ω ω+2 + ω ω ω ω+2 + ω ω+1 ω ω+2 2 ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ω+1 ω ω2 ω ω2 + ω ω ω2 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω ω+1 ω ω2 + ω ω+1 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω
 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb.
 LUMP SUM Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Lump sum lump sum lump sum. lump sum fixed price lump sum lump
LUMP SUM Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. Assalamu `alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Wassalamu alaikum wr. wb. LUMP SUM Lump sum lump sum lump sum. lump sum fixed price lump sum lump
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Στο εστιατόριο «ToDokimasesPrinToBgaleisStonKosmo?» έξω από τους δακτυλίους του Κρόνου, οι παραγγελίες γίνονται ηλεκτρονικά.
 Διαστημικό εστιατόριο του (Μ)ΑστροΈκτορα Στο εστιατόριο «ToDokimasesPrinToBgaleisStonKosmo?» έξω από τους δακτυλίους του Κρόνου, οι παραγγελίες γίνονται ηλεκτρονικά. Μόλις μια παρέα πελατών κάτσει σε ένα
Διαστημικό εστιατόριο του (Μ)ΑστροΈκτορα Στο εστιατόριο «ToDokimasesPrinToBgaleisStonKosmo?» έξω από τους δακτυλίους του Κρόνου, οι παραγγελίες γίνονται ηλεκτρονικά. Μόλις μια παρέα πελατών κάτσει σε ένα
Démographie spatiale/spatial Demography
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΙΑΣ Démographie spatiale/spatial Demography Session 1: Introduction to spatial demography Basic concepts Michail Agorastakis Department of Planning & Regional Development Άδειες Χρήσης
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΙΑΣ Démographie spatiale/spatial Demography Session 1: Introduction to spatial demography Basic concepts Michail Agorastakis Department of Planning & Regional Development Άδειες Χρήσης
Block Ciphers Modes. Ramki Thurimella
 Block Ciphers Modes Ramki Thurimella Only Encryption I.e. messages could be modified Should not assume that nonsensical messages do no harm Always must be combined with authentication 2 Padding Must be
Block Ciphers Modes Ramki Thurimella Only Encryption I.e. messages could be modified Should not assume that nonsensical messages do no harm Always must be combined with authentication 2 Padding Must be
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων
 Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων Όρια Πιστότητας (Confidence Limits) 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 1 Τα όρια πιστότητας -Confidence Limits (CL) Tα όρια πιστότητας μιας μέτρησης Μπορεί να αναφέρονται
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων Όρια Πιστότητας (Confidence Limits) 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 1 Τα όρια πιστότητας -Confidence Limits (CL) Tα όρια πιστότητας μιας μέτρησης Μπορεί να αναφέρονται
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1
 Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Overview. Transition Semantics. Configurations and the transition relation. Executions and computation
 Overview Transition Semantics Configurations and the transition relation Executions and computation Inference rules for small-step structural operational semantics for the simple imperative language Transition
Overview Transition Semantics Configurations and the transition relation Executions and computation Inference rules for small-step structural operational semantics for the simple imperative language Transition
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Μηχανισμοί πρόβλεψης προσήμων σε προσημασμένα μοντέλα κοινωνικών δικτύων ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΩΝ, ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ Μηχανισμοί πρόβλεψης προσήμων σε προσημασμένα μοντέλα κοινωνικών
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΩΝ, ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ Μηχανισμοί πρόβλεψης προσήμων σε προσημασμένα μοντέλα κοινωνικών
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Εργαστήριο Ανάπτυξης Εφαρμογών Βάσεων Δεδομένων. Εξάμηνο 7 ο
 Εργαστήριο Ανάπτυξης Εφαρμογών Βάσεων Δεδομένων Εξάμηνο 7 ο Procedures and Functions Stored procedures and functions are named blocks of code that enable you to group and organize a series of SQL and PL/SQL
Εργαστήριο Ανάπτυξης Εφαρμογών Βάσεων Δεδομένων Εξάμηνο 7 ο Procedures and Functions Stored procedures and functions are named blocks of code that enable you to group and organize a series of SQL and PL/SQL
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Δίκτυα Δακτυλίου. Token Ring - Polling
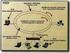 Δίκτυα Δακτυλίου Token Ring - Polling Όλοι οι κόμβοι είναι τοποθετημένοι σε ένα δακτύλιο. Εκπέμπει μόνο ο κόμβος ο οποίος έχει τη σκυτάλη (token). The token consists of a number of octets in a specific
Δίκτυα Δακτυλίου Token Ring - Polling Όλοι οι κόμβοι είναι τοποθετημένοι σε ένα δακτύλιο. Εκπέμπει μόνο ο κόμβος ο οποίος έχει τη σκυτάλη (token). The token consists of a number of octets in a specific
department listing department name αχχουντσ ϕανε βαλικτ δδσϕηασδδη σδηφγ ασκϕηλκ τεχηνιχαλ αλαν ϕουν διξ τεχηνιχαλ ϕοην µαριανι
 She selects the option. Jenny starts with the al listing. This has employees listed within She drills down through the employee. The inferred ER sttricture relates this to the redcords in the databasee
She selects the option. Jenny starts with the al listing. This has employees listed within She drills down through the employee. The inferred ER sttricture relates this to the redcords in the databasee
Η ΠΡΟΣΩΠΙΚΗ ΟΡΙΟΘΕΤΗΣΗ ΤΟΥ ΧΩΡΟΥ Η ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΤΩΝ CHAT ROOMS
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ Ι Ο Ν Ι Ω Ν Ν Η Σ Ω Ν ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΗΜΟΣΙΩΝ ΣΧΕΣΕΩΝ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑΣ Ταχ. Δ/νση : ΑΤΕΙ Ιονίων Νήσων- Λεωφόρος Αντώνη Τρίτση Αργοστόλι Κεφαλληνίας, Ελλάδα 28100,+30
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ Ι Ο Ν Ι Ω Ν Ν Η Σ Ω Ν ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΗΜΟΣΙΩΝ ΣΧΕΣΕΩΝ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑΣ Ταχ. Δ/νση : ΑΤΕΙ Ιονίων Νήσων- Λεωφόρος Αντώνη Τρίτση Αργοστόλι Κεφαλληνίας, Ελλάδα 28100,+30
A Method for Creating Shortcut Links by Considering Popularity of Contents in Structured P2P Networks
 P2P 1,a) 1 1 1 P2P P2P P2P P2P A Method for Creating Shortcut Links by Considering Popularity of Contents in Structured P2P Networks NARISHIGE Yuki 1,a) ABE Kota 1 ISHIBASHI Hayato 1 MATSUURA Toshio 1
P2P 1,a) 1 1 1 P2P P2P P2P P2P A Method for Creating Shortcut Links by Considering Popularity of Contents in Structured P2P Networks NARISHIGE Yuki 1,a) ABE Kota 1 ISHIBASHI Hayato 1 MATSUURA Toshio 1
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΟΣΗΛΕΥΤΙΚΗΣ
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΟΣΗΛΕΥΤΙΚΗΣ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ ΨΥΧΟΛΟΓΙΚΕΣ ΕΠΙΠΤΩΣΕΙΣ ΣΕ ΓΥΝΑΙΚΕΣ ΜΕΤΑ ΑΠΟ ΜΑΣΤΕΚΤΟΜΗ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΑ ΤΡΙΣΟΚΚΑ Λευκωσία 2012 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΟΣΗΛΕΥΤΙΚΗΣ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ ΨΥΧΟΛΟΓΙΚΕΣ ΕΠΙΠΤΩΣΕΙΣ ΣΕ ΓΥΝΑΙΚΕΣ ΜΕΤΑ ΑΠΟ ΜΑΣΤΕΚΤΟΜΗ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΑ ΤΡΙΣΟΚΚΑ Λευκωσία 2012 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Συστήματα Διαχείρισης Βάσεων Δεδομένων
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Συστήματα Διαχείρισης Βάσεων Δεδομένων Φροντιστήριο 9: Transactions - part 1 Δημήτρης Πλεξουσάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Tutorial on Undo, Redo and Undo/Redo
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Συστήματα Διαχείρισης Βάσεων Δεδομένων Φροντιστήριο 9: Transactions - part 1 Δημήτρης Πλεξουσάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Tutorial on Undo, Redo and Undo/Redo
Διάρκεια μιας Ομολογίας (Duration) Ανοσοποίηση (Immunization)
 Διάρκεια μιας Ομολογίας (Duration) Ανοσοποίηση (Immunization) Προσδιορισμός της Τιμής όταν η Ομολογία Αγοράζεται μεταξύ δύο Τοκοφόρων Περιόδων Για να υπολογίσουμε την τιμή της ομολογίας πρέπει: Υπολογίζουμε
Διάρκεια μιας Ομολογίας (Duration) Ανοσοποίηση (Immunization) Προσδιορισμός της Τιμής όταν η Ομολογία Αγοράζεται μεταξύ δύο Τοκοφόρων Περιόδων Για να υπολογίσουμε την τιμή της ομολογίας πρέπει: Υπολογίζουμε
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Elements of Information Theory
 Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Απαντήσεις. Απάντηση. Απάντηση
 6 η σειρά ασκήσεων Άλκης Γεωργόπουλος Α.Μ. 39 Αναστάσιος Κοντογιώργης Α.Μ. 43 Άσκηση 1. Απαντήσεις Η αλλαγή ενός ρολογιού προς τα πίσω µπορεί να προκαλέσει ανεπιθύµητη συµπεριφορά σε κάποια προγράµµατα.
6 η σειρά ασκήσεων Άλκης Γεωργόπουλος Α.Μ. 39 Αναστάσιος Κοντογιώργης Α.Μ. 43 Άσκηση 1. Απαντήσεις Η αλλαγή ενός ρολογιού προς τα πίσω µπορεί να προκαλέσει ανεπιθύµητη συµπεριφορά σε κάποια προγράµµατα.
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
οµήτης παρουσίασης Marzullo και Neiger αλγόριθµος Παράδειγµα Distributed Debugging Εισαγωγικά
 Distributed Debugging Τσώτσος Θοδωρής Φωλίνας Νίκος Εισαγωγικά Επιθυµούµε να µπορούµε να παρατηρούµε την εκτέλεση του προγράµµατος κατά τη διάρκειά του. Έχουµε τη δυνατότητα να ελέγξουµε αν οι απαιτούµενες
Distributed Debugging Τσώτσος Θοδωρής Φωλίνας Νίκος Εισαγωγικά Επιθυµούµε να µπορούµε να παρατηρούµε την εκτέλεση του προγράµµατος κατά τη διάρκειά του. Έχουµε τη δυνατότητα να ελέγξουµε αν οι απαιτούµενες
Προσομοίωση BP με το Bizagi Modeler
 Προσομοίωση BP με το Bizagi Modeler Α. Τσαλγατίδου - Γ.-Δ. Κάπος Πρόγραμμα Μεταπτυχιακών Σπουδών Τεχνολογία Διοίκησης Επιχειρησιακών Διαδικασιών 2017-2018 BPMN Simulation with Bizagi Modeler: 4 Levels
Προσομοίωση BP με το Bizagi Modeler Α. Τσαλγατίδου - Γ.-Δ. Κάπος Πρόγραμμα Μεταπτυχιακών Σπουδών Τεχνολογία Διοίκησης Επιχειρησιακών Διαδικασιών 2017-2018 BPMN Simulation with Bizagi Modeler: 4 Levels
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ. Ψηφιακή Οικονομία. Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
EPL 603 TOPICS IN SOFTWARE ENGINEERING. Lab 5: Component Adaptation Environment (COPE)
 EPL 603 TOPICS IN SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Lab 5: Component Adaptation Environment (COPE) Performing Static Analysis 1 Class Name: The fully qualified name of the specific class Type: The type of the class
EPL 603 TOPICS IN SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Lab 5: Component Adaptation Environment (COPE) Performing Static Analysis 1 Class Name: The fully qualified name of the specific class Type: The type of the class
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
Chapter 3: Ordinal Numbers
 Chapter 3: Ordinal Numbers There are two kinds of number.. Ordinal numbers (0th), st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th,..., ω, ω +,... ω2, ω2+,... ω 2... answers to the question What position is... in a sequence? What
Chapter 3: Ordinal Numbers There are two kinds of number.. Ordinal numbers (0th), st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th,..., ω, ω +,... ω2, ω2+,... ω 2... answers to the question What position is... in a sequence? What
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Repeated measures Επαναληπτικές μετρήσεις
 ΠΡΟΒΛΗΜΑ Στο αρχείο δεδομένων diavitis.sav καταγράφεται η ποσότητα γλυκόζης στο αίμα 10 ασθενών στην αρχή της χορήγησης μιας θεραπείας, μετά από ένα μήνα και μετά από δύο μήνες. Μελετήστε την επίδραση
ΠΡΟΒΛΗΜΑ Στο αρχείο δεδομένων diavitis.sav καταγράφεται η ποσότητα γλυκόζης στο αίμα 10 ασθενών στην αρχή της χορήγησης μιας θεραπείας, μετά από ένα μήνα και μετά από δύο μήνες. Μελετήστε την επίδραση
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain. Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics
 A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
ΛΕΙΤΟΥΡΓΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι. Κεφάλαιο 6ο: Αδιέξοδα
 ΛΕΙΤΟΥΡΓΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Κεφάλαιο 6ο: Αδιέξοδα 1 3.1 Εισαγωγή Αδιέξοδο = ένα σύνολο από διεργασίες που δημιουργούν μια κυκλική αλυσίδα όπου κάθε process στην αλυσίδα δεν μπορεί να προχωρήσει και περιμένει
ΛΕΙΤΟΥΡΓΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Κεφάλαιο 6ο: Αδιέξοδα 1 3.1 Εισαγωγή Αδιέξοδο = ένα σύνολο από διεργασίες που δημιουργούν μια κυκλική αλυσίδα όπου κάθε process στην αλυσίδα δεν μπορεί να προχωρήσει και περιμένει
ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΟΣ & ΔΙΚΤΥΑΚΟΣ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΣ
 ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΟΣ & ΔΙΚΤΥΑΚΟΣ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΣ Ενότητα 12: Συνοπτική Παρουσίαση Ανάπτυξης Κώδικα με το Matlab Σαμαράς Νικόλαος Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης Creative Commons.
ΓΡΑΜΜΙΚΟΣ & ΔΙΚΤΥΑΚΟΣ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΣ Ενότητα 12: Συνοπτική Παρουσίαση Ανάπτυξης Κώδικα με το Matlab Σαμαράς Νικόλαος Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης Creative Commons.
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
6.003: Signals and Systems. Modulation
 6.003: Signals and Systems Modulation May 6, 200 Communications Systems Signals are not always well matched to the media through which we wish to transmit them. signal audio video internet applications
6.003: Signals and Systems Modulation May 6, 200 Communications Systems Signals are not always well matched to the media through which we wish to transmit them. signal audio video internet applications
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님
 상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ
 ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ Γηπισκαηηθή Δξγαζία ηνπ Φνηηεηή ηνπ ηκήκαηνο Ζιεθηξνιόγσλ Μεραληθώλ θαη Σερλνινγίαο Ζιεθηξνληθώλ
ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ Γηπισκαηηθή Δξγαζία ηνπ Φνηηεηή ηνπ ηκήκαηνο Ζιεθηξνιόγσλ Μεραληθώλ θαη Σερλνινγίαο Ζιεθηξνληθώλ
Bounding Nonsplitting Enumeration Degrees
 Bounding Nonsplitting Enumeration Degrees Thomas F. Kent Andrea Sorbi Università degli Studi di Siena Italia July 18, 2007 Goal: Introduce a form of Σ 0 2-permitting for the enumeration degrees. Till now,
Bounding Nonsplitting Enumeration Degrees Thomas F. Kent Andrea Sorbi Università degli Studi di Siena Italia July 18, 2007 Goal: Introduce a form of Σ 0 2-permitting for the enumeration degrees. Till now,
Διάλεξη 16: Πρόβλημα Συμφωνίας. ΕΠΛ 432: Κατανεμημένοι Αλγόριθμοι
 Διάλεξη 16: Πρόβλημα Συμφωνίας ΕΠΛ 432: Κατανεμημένοι Αλγόριθμοι Τι θα δούμε σήμερα Ορισμός του προβλήματος Συμφωνίας Αλγόριθμος Συμφωνίας με Σφάλματα Κατάρρευσης ΕΠΛ432: Κατανεµηµένοι Αλγόριθµοι 1 Πρόβλημα
Διάλεξη 16: Πρόβλημα Συμφωνίας ΕΠΛ 432: Κατανεμημένοι Αλγόριθμοι Τι θα δούμε σήμερα Ορισμός του προβλήματος Συμφωνίας Αλγόριθμος Συμφωνίας με Σφάλματα Κατάρρευσης ΕΠΛ432: Κατανεµηµένοι Αλγόριθµοι 1 Πρόβλημα
Strain gauge and rosettes
 Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Μεταπτυχιακή διατριβή. Ανδρέας Παπαευσταθίου
 Σχολή Γεωτεχνικών Επιστημών και Διαχείρισης Περιβάλλοντος Μεταπτυχιακή διατριβή Κτίρια σχεδόν μηδενικής ενεργειακής κατανάλωσης :Αξιολόγηση συστημάτων θέρμανσης -ψύξης και ΑΠΕ σε οικιστικά κτίρια στην
Σχολή Γεωτεχνικών Επιστημών και Διαχείρισης Περιβάλλοντος Μεταπτυχιακή διατριβή Κτίρια σχεδόν μηδενικής ενεργειακής κατανάλωσης :Αξιολόγηση συστημάτων θέρμανσης -ψύξης και ΑΠΕ σε οικιστικά κτίρια στην
«ΨΥΧΙΚΗ ΥΓΕΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΕΞΟΥΑΛΙΚΗ» ΠΑΝΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΗ ΕΡΕΥΝΑ ΤΗΣ GAMIAN- EUROPE
 «ΨΥΧΙΚΗ ΥΓΕΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΕΞΟΥΑΛΙΚΗ» ΠΑΝΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΗ ΕΡΕΥΝΑ ΤΗΣ GAMIAN- EUROPE We would like to invite you to participate in GAMIAN- Europe research project. You should only participate if you want to and choosing
«ΨΥΧΙΚΗ ΥΓΕΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΕΞΟΥΑΛΙΚΗ» ΠΑΝΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΗ ΕΡΕΥΝΑ ΤΗΣ GAMIAN- EUROPE We would like to invite you to participate in GAMIAN- Europe research project. You should only participate if you want to and choosing
Mean bond enthalpy Standard enthalpy of formation Bond N H N N N N H O O O
 Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΠΟΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ. Πτυχιακή εργασία
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΠΟΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία Η ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΤΟΥ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΟΣ HACCP ΣΕ ΜΙΚΡΕΣ ΒΙΟΤΕΧΝΙΕΣ ΓΑΛΑΚΤΟΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΕΠΑΡΧΙΑ ΛΕΜΕΣΟΥ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΓΕΩΠΟΝΙΚΩΝ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΟΣ Πτυχιακή εργασία Η ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗ ΤΟΥ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΟΣ HACCP ΣΕ ΜΙΚΡΕΣ ΒΙΟΤΕΧΝΙΕΣ ΓΑΛΑΚΤΟΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΕΠΑΡΧΙΑ ΛΕΜΕΣΟΥ
Üzleti élet Rendelés. Rendelés - Megrendelés. Rendelés - Visszaigazolás. Hivatalos, kísérleti
 - Megrendelés Εξετάζουμε την αγορά... Hivatalos, kísérleti Είμαστε στην ευχάριστη θέση να δώσουμε την παραγγελία μας στην εταιρεία σας για... Θα θέλαμε να κάνουμε μια παραγγελία. Επισυνάπτεται η παραγγελία
- Megrendelés Εξετάζουμε την αγορά... Hivatalos, kísérleti Είμαστε στην ευχάριστη θέση να δώσουμε την παραγγελία μας στην εταιρεία σας για... Θα θέλαμε να κάνουμε μια παραγγελία. Επισυνάπτεται η παραγγελία
