Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων
|
|
|
- Μαρία Αντωνόπουλος
- 7 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων Όρια Πιστότητας (Confidence Limits) 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 1
2 Τα όρια πιστότητας -Confidence Limits (CL) Tα όρια πιστότητας μιας μέτρησης Μπορεί να αναφέρονται : 68%, 95%, 99% Μπορεί να είναι άνωτερο (Upper), κατώτερο (Lower), ή και τα δύο (twosided) x<u, x>l, L<x<U L U U 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 2
3 CL κατα την συχναζουσα πιθανότητα- Frequentist Μετρούμε μήκος με ένα μέτρο: σφάλμα gauss 0.1 (1σ) Για πραγματική τιμή x T μετρούμε x M με κατανομή gauss Το x M διαφερει απο το x T 0.1 στο 68% των μετρήσεων ΚΑΙ Το x Τ διαφερει απο το x Μ 0.1 στο 68% των μετρήσεων Μπορούμε να πούμε x M -0.1<x T <x M 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 3
4 Για πιο περίπλοκες κατανομές (όχι True X gauss)δεν είναι τόσο απλό Αλλά η αρχή είναι ίδια: --έστω οτι γνωρίζω απο ανεξάρτητη μέθοδο την κατανομή της μεταβλητής Χ, που περιλαμβάνει και την αληθή τιμή True X --απο τον estimator Θ και τις µετρήσεις µου υπολογίζω Θobs Οι ζώνες πιστότητας- Confidence Belts Measured X Construct Horizontally Read Vertically 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 4
5 To πρόβλημα της CL κατα την συχναζουσα πιθανότητα-frequentist Αρνητικά Lower και/ή Upper όρια για θετικές μετρούμενες ποσότητες : μέτρηση του βάρους (δοχείο-c+περιεχόμενο- M) με σφάλμα gauss. Mετρούμε R : R- σ< M+C < 68%, R-C-σ<Μ<R-C+σ@68% εστω: C=50, R=55, σ=10 => Έστω: C=50, R=31, σ=10 => Poisson: Signal + Background Background mean 2.50 Detect 3 events: Detect 0 events Total < 95% Signal<4.18@95% Total < 95% Signal < 95% Tα όρια είναι μαθηματικά σωστά αλλά χωρίς νόημα 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 5
6 Η προσέγγυση στο πρόβλημα με την πιθανότητας Βayes Μετρούµε ποσότητα x µε κατανοµή gauss και πραγµατική τιµή Χ ΔΕΝ υπολογίζουµε CL s Θεωρούµε οτι ΔΕΝ έχουµε καµµια γνώση της πραγµατικής τιµής και της µέτρησης P(Data Theory) είναι Gaussian P(Theory Data) είναι Gaussian P t x 0 L x 0 t P t /P x 0. x true Τα όρια που υπολογίζουμε είναι όπως και με την συχνάζουσα πιθανότητα για κατανομή gauss 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 6
7 Βayesian Confidence Intervals Έστω ότι παρατηρούμε 2 γεγονότα P(λ;2) P(2; λ)=e -λ λ 2 Κανονικοποιούμε Αν γνωρίζουμε ότι: background mean είναι 1.7, τότε γνωρίζουµε ότι λ>1.7 2 λ Πολλαπλασιάζουµε, κανονικοποιούµε και ερµηνεύουµε 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 7
8 Παράδειγμα για κατά Bayes CL Έστω ότι σύμφωνα με την μέτρησή μας η μάζα είναι: -0.5±0.2 gr Υπολογίζουμε την πιθανότητα η μάζα να ειναι 0 (2.5σ) 10% αυτής της πιθανότητας αντιστοιχεί σε 3.24σ (πίνακες για one-tailed gaussian integral - %probability) =>το 90% confidence upper limit ειναι: x0.2=0.15 gr Mε την υπόθεση οτι η πραγματική τιμή Χ μπορεί με ίση πιθανότητα να πάρει ΟΠΟΙΑΔΗΠΟΤΕ τιμή >0 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 8
9 Τι κάνουμε στην Φυσική? Feldman-Cousins Unified Method Στην ιδανική περίπτωση:επιλέγουµε στρατηγική, εξετάζουµε τα δεδοµένα, δινουµε τα αποτελέσµατα. Στην πράξη: εξετάζουµε τα δεδοµένα, επιλέγουµε στρατηγική, δίνουµε αποτελέσµατα Example: You have a background of 3.2 Observe 5 events? Quote one-sided upper limit ( =6.07@90%) Observe 25 events? Quote two-sided limits 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 9
10 Feldman-Cousins Unified Method TABLE V. 90% C.L. intervals for the Poisson signal mean 6 to 15., for total events observed n 0, for known mean background b ranging from n 0 b , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,13.52 PHYSICAL REVIEW D VOLUME 57, NUMBER 7 1 APRIL 1998 Unified approach to the classical statistical analysis of small signals 10
11 Maximum Likelihood and Confidence Levels ML estimator (large N) has variance given by MVB (Minimum Variance Bound) At peak Ln L is a parabola (L is a Gaussian) For large N Falls by ½ at Falls by 2 at a Read off 68%, 95% confidence regions 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 11
12 MVB (minimum variance bound) example N Gaussian measurements: estimate µ Ln L given by Differentiate twice wrt µ Take expectation value but it s a constant Invert and negate: 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 12
13 Another MVB example N Gaussian measurements: estimate σ Ln L still given by Differentiate twice wrt σ Take expectation value <(x i -µ) 2 >= σ 2 i Gives Invert and negate: 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 13
14 ln L is not a parabola ML for small N a a Argue: we could (invariance) transform to some a for which it is a parabola We could/should then get limits on a using standard L max -½ technique These would translate to limits on a These limits would be at the values of a for which L= L max -½ 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 14 So just do it directly
15 Multidimensional ML L is multidimensional Gaussian b For 2-d 39.3% lies within 1σ i.e. within region bounded by L=L max -½ For 68% need L=L max a Construct region(s) to test using numbers from integrated χ 2 distribution 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 15
Bayesian statistics. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ
 ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 651 APPENDIX B. BIBLIOGRAPHY 677 APPENDIX C. ANSWERS TO SELECTED EXERCISES 679
 APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
CE 530 Molecular Simulation
 C 53 olecular Siulation Lecture Histogra Reweighting ethods David. Kofke Departent of Cheical ngineering SUNY uffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu Histogra Reweighting ethod to cobine results taken at different
C 53 olecular Siulation Lecture Histogra Reweighting ethods David. Kofke Departent of Cheical ngineering SUNY uffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu Histogra Reweighting ethod to cobine results taken at different
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
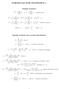 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Solution Series 9. i=1 x i and i=1 x i.
 Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
5.4 The Poisson Distribution.
 The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Probability and Random Processes (Part II)
 Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review
 Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Για να ελέγξουµε αν η κατανοµή µιας µεταβλητής είναι συµβατή µε την κανονική εφαρµόζουµε το test Kolmogorov-Smirnov.
 A. ΈΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΚΑΝΟΝΙΚΟΤΗΤΑΣ A 1. Έλεγχος κανονικότητας Kolmogorov-Smirnov. Για να ελέγξουµε αν η κατανοµή µιας µεταβλητής είναι συµβατή µε την κανονική εφαρµόζουµε το test Kolmogorov-Smirnov. Μηδενική υπόθεση:
A. ΈΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΚΑΝΟΝΙΚΟΤΗΤΑΣ A 1. Έλεγχος κανονικότητας Kolmogorov-Smirnov. Για να ελέγξουµε αν η κατανοµή µιας µεταβλητής είναι συµβατή µε την κανονική εφαρµόζουµε το test Kolmogorov-Smirnov. Μηδενική υπόθεση:
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet
 Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Exercise 2: The form of the generalized likelihood ratio
 Stats 2 Winter 28 Homework 9: Solutions Due Friday, March 6 Exercise 2: The form of the generalized likelihood ratio We want to test H : θ Θ against H : θ Θ, and compare the two following rules of rejection:
Stats 2 Winter 28 Homework 9: Solutions Due Friday, March 6 Exercise 2: The form of the generalized likelihood ratio We want to test H : θ Θ against H : θ Θ, and compare the two following rules of rejection:
Μαντζούνη, Πιπερίγκου, Χατζή. ΒΙΟΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ Εργαστήριο 5 ο
 Κατανομές Στατιστικών Συναρτήσεων Δύο δείγματα από κανονική κατανομή Έστω Χ= ( Χ, Χ,..., Χ ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) μεγέθους n και 1 n 1 1 Y = (Y, Y,...,Y ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) 1 n 1 Χ Y ( µ µ ) S σ Τ ( Χ,Y)
Κατανομές Στατιστικών Συναρτήσεων Δύο δείγματα από κανονική κατανομή Έστω Χ= ( Χ, Χ,..., Χ ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) μεγέθους n και 1 n 1 1 Y = (Y, Y,...,Y ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) 1 n 1 Χ Y ( µ µ ) S σ Τ ( Χ,Y)
Μενύχτα, Πιπερίγκου, Σαββάτης. ΒΙΟΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ Εργαστήριο 5 ο
 Κατανομές Στατιστικών Συναρτήσεων Δύο ανεξάρτητα δείγματα από κανονική κατανομή Έστω Χ= ( Χ, Χ,..., Χ ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) μεγέθους n και 1 n 1 1 Y = (Y, Y,..., Y ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) 1 n 1 Χ Y ( µ µ )
Κατανομές Στατιστικών Συναρτήσεων Δύο ανεξάρτητα δείγματα από κανονική κατανομή Έστω Χ= ( Χ, Χ,..., Χ ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) μεγέθους n και 1 n 1 1 Y = (Y, Y,..., Y ) τ.δ. από Ν( µ, σ ) 1 n 1 Χ Y ( µ µ )
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Pg The perimeter is P = 3x The area of a triangle is. where b is the base, h is the height. In our case b = x, then the area is
 Pg. 9. The perimeter is P = The area of a triangle is A = bh where b is the base, h is the height 0 h= btan 60 = b = b In our case b =, then the area is A = = 0. By Pythagorean theorem a + a = d a a =
Pg. 9. The perimeter is P = The area of a triangle is A = bh where b is the base, h is the height 0 h= btan 60 = b = b In our case b =, then the area is A = = 0. By Pythagorean theorem a + a = d a a =
An Inventory of Continuous Distributions
 Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
6. MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATION
 6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
9.09. # 1. Area inside the oval limaçon r = cos θ. To graph, start with θ = 0 so r = 6. Compute dr
 9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
Δείγμα (μεγάλο) από οποιαδήποτε κατανομή
 ΒΙΟΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ Εργαστήριο 4ο Κατανομές Στατιστικών Συναρτήσεων Δείγμα από κανονική κατανομή Έστω Χ= Χ Χ Χ τ.δ. από Ν µσ τότε ( 1,,..., n) (, ) Τ Χ Χ Ν Τ Χ σ σ Χ Τ Χ n Χ S µ S µ 1( ) = (0,1), ( ) = ( n 1)
ΒΙΟΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ Εργαστήριο 4ο Κατανομές Στατιστικών Συναρτήσεων Δείγμα από κανονική κατανομή Έστω Χ= Χ Χ Χ τ.δ. από Ν µσ τότε ( 1,,..., n) (, ) Τ Χ Χ Ν Τ Χ σ σ Χ Τ Χ n Χ S µ S µ 1( ) = (0,1), ( ) = ( n 1)
ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ΕΙΔΙΚΑ ΘΕΜΑΤΑ. Κεφάλαιο 13. Συμπεράσματα για τη σύγκριση δύο πληθυσμών
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΔΥΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΛΛΑΔΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ΠΑΤΡΑΣ Εργαστήριο Λήψης Αποφάσεων & Επιχειρησιακού Προγραμματισμού Καθηγητής Ι. Μητρόπουλος ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ΕΙΔΙΚΑ ΘΕΜΑΤΑ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΔΥΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΛΛΑΔΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ΠΑΤΡΑΣ Εργαστήριο Λήψης Αποφάσεων & Επιχειρησιακού Προγραμματισμού Καθηγητής Ι. Μητρόπουλος ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ΕΙΔΙΚΑ ΘΕΜΑΤΑ
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ
 ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ Γηπισκαηηθή Δξγαζία ηνπ Φνηηεηή ηνπ ηκήκαηνο Ζιεθηξνιόγσλ Μεραληθώλ θαη Σερλνινγίαο Ζιεθηξνληθώλ
ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ Γηπισκαηηθή Δξγαζία ηνπ Φνηηεηή ηνπ ηκήκαηνο Ζιεθηξνιόγσλ Μεραληθώλ θαη Σερλνινγίαο Ζιεθηξνληθώλ
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Queensland University of Technology Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies
 Queensland University of Technology Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies Lab Session #7 Example 5.2 (with 3SLS Extensions) Seemingly Unrelated Regression Estimation and 3SLS A survey of 206
Queensland University of Technology Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies Lab Session #7 Example 5.2 (with 3SLS Extensions) Seemingly Unrelated Regression Estimation and 3SLS A survey of 206
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων
 Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων 4ο Εξάμηνο2005-2006 Στατιστική Πιθανότητες-Κατανομές Διδάσκοντες : Χαρά Πετρίδου Δήµος Σαμψωνίδης 28/3/2005 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 1 28/3/2005 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 2 Πιθανότητες
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων 4ο Εξάμηνο2005-2006 Στατιστική Πιθανότητες-Κατανομές Διδάσκοντες : Χαρά Πετρίδου Δήµος Σαμψωνίδης 28/3/2005 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 1 28/3/2005 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 2 Πιθανότητες
Section 9.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
Άσκηση 10, σελ. 119. Για τη μεταβλητή x (άτυπος όγκος) έχουμε: x censored_x 1 F 3 F 3 F 4 F 10 F 13 F 13 F 16 F 16 F 24 F 26 F 27 F 28 F
 Άσκηση 0, σελ. 9 από το βιβλίο «Μοντέλα Αξιοπιστίας και Επιβίωσης» της Χ. Καρώνη (i) Αρχικά, εισάγουμε τα δεδομένα στο minitab δημιουργώντας δύο μεταβλητές: τη x για τον άτυπο όγκο και την y για τον τυπικό
Άσκηση 0, σελ. 9 από το βιβλίο «Μοντέλα Αξιοπιστίας και Επιβίωσης» της Χ. Καρώνη (i) Αρχικά, εισάγουμε τα δεδομένα στο minitab δημιουργώντας δύο μεταβλητές: τη x για τον άτυπο όγκο και την y για τον τυπικό
Παράδειγμα: Γούργουλης Βασίλειος, Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Τ.Ε.Φ.Α.Α. Δ.Π.Θ.
 Έλεγχος ύπαρξης στατιστικά σημαντικών διαφορών μεταξύ περισσότερων από δύο ανεξάρτητων δειγμάτων, που διαχωρίζονται βάσει ενός ανεξάρτητου παράγοντα (Ανάλυση διακύμανσης για ανεξάρτητα δείγματα ως προς
Έλεγχος ύπαρξης στατιστικά σημαντικών διαφορών μεταξύ περισσότερων από δύο ανεξάρτητων δειγμάτων, που διαχωρίζονται βάσει ενός ανεξάρτητου παράγοντα (Ανάλυση διακύμανσης για ανεξάρτητα δείγματα ως προς
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΟΣ ΣΥΝΔΕΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY 21 ος ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ Δεύτερος Γύρος - 30 Μαρτίου 2011
 Διάρκεια Διαγωνισμού: 3 ώρες Απαντήστε όλες τις ερωτήσεις Μέγιστο Βάρος (20 Μονάδες) Δίνεται ένα σύνολο από N σφαιρίδια τα οποία δεν έχουν όλα το ίδιο βάρος μεταξύ τους και ένα κουτί που αντέχει μέχρι
Διάρκεια Διαγωνισμού: 3 ώρες Απαντήστε όλες τις ερωτήσεις Μέγιστο Βάρος (20 Μονάδες) Δίνεται ένα σύνολο από N σφαιρίδια τα οποία δεν έχουν όλα το ίδιο βάρος μεταξύ τους και ένα κουτί που αντέχει μέχρι
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1
 Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise. Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University
 Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain. Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics
 A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ Ε ΟΜΕΝΩΝ. 5. Στατιστική συµπερασµατολογία για ποσοτικές µεταβλητές: Έλεγχοι υποθέσεων και διαστήµατα εµπιστοσύνης
 ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ Ε ΟΜΕΝΩΝ 5. Στατιστική συµπερασµατολογία για ποσοτικές µεταβλητές: Έλεγχοι υποθέσεων και διαστήµατα εµπιστοσύνης ιαστήµατα εµπιστοσύνης και έλεγχοι υποθέσεων για τη µέση τιµή Για µια ποσοτική µεταβλητή
ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ Ε ΟΜΕΝΩΝ 5. Στατιστική συµπερασµατολογία για ποσοτικές µεταβλητές: Έλεγχοι υποθέσεων και διαστήµατα εµπιστοσύνης ιαστήµατα εµπιστοσύνης και έλεγχοι υποθέσεων για τη µέση τιµή Για µια ποσοτική µεταβλητή
1.α ιαγνωστικοί Έλεγχοι. 2.α Ευαισθησία και Ειδικότητα (εισαγωγικές έννοιες) ΒΙΟΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΙΙ. Πολύ σηµαντικό το θεώρηµα του Bayes:
 ΠΜΣ ΕΠΑΓΓΕΛΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΙΚΗ ΥΓΕΙΑ, ΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΚΑΙ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΗ ΑΠΟΤΙΜΗΣΗ ΑΚ. ΕΤΟΣ 2006-2007, 3ο εξάµηνο ΒΙΟΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΙΙ ΜΑΘΗΜΑ 6 ΙΑΓΝΩΣΤΙΚΟΙ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΙ 1.β ιαγνωστικοί Έλεγχοι Πολύ σηµαντικό το θεώρηµα
ΠΜΣ ΕΠΑΓΓΕΛΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΙΚΗ ΥΓΕΙΑ, ΙΑΧΕΙΡΙΣΗ ΚΑΙ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΚΗ ΑΠΟΤΙΜΗΣΗ ΑΚ. ΕΤΟΣ 2006-2007, 3ο εξάµηνο ΒΙΟΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΙΙ ΜΑΘΗΜΑ 6 ΙΑΓΝΩΣΤΙΚΟΙ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΙ 1.β ιαγνωστικοί Έλεγχοι Πολύ σηµαντικό το θεώρηµα
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 24/3/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Όλοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα μικρότεροι του 10000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Όλοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα μικρότεροι του 10000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις
Δεδομένα (data) και Στατιστική (Statistics)
 Δεδομένα (data) και Στατιστική (Statistics) Η Στατιστική (Statistics) ασχολείται με την ανάλυση δεδομένων (data analysis): Πρόσφατες παιδαγωγικές εξελίξεις υποδεικνύουν ότι η Στατιστική πρέπει και να διδάσκεται
Δεδομένα (data) και Στατιστική (Statistics) Η Στατιστική (Statistics) ασχολείται με την ανάλυση δεδομένων (data analysis): Πρόσφατες παιδαγωγικές εξελίξεις υποδεικνύουν ότι η Στατιστική πρέπει και να διδάσκεται
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων
 Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων 4ο Εξάμηνο2004-2005 Διακριτική ικανότητα ανιχνευτή-υπόβαθρο- Υπολογισμός του σήματος Διδάσκοντες : Χαρά Πετρίδου Δημήτριος Σαμψωνίδης 18/4/2005 Υπολογ.Φυσική
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων 4ο Εξάμηνο2004-2005 Διακριτική ικανότητα ανιχνευτή-υπόβαθρο- Υπολογισμός του σήματος Διδάσκοντες : Χαρά Πετρίδου Δημήτριος Σαμψωνίδης 18/4/2005 Υπολογ.Φυσική
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ. Ψηφιακή Οικονομία. Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
χ 2 test ανεξαρτησίας
 χ 2 test ανεξαρτησίας Καθηγητής Ι. Κ. ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΥ demetri@econ.uoa.gr 7.2 Το χ 2 Τεστ Ανεξαρτησίας Tο χ 2 τεστ ανεξαρτησίας (όπως και η παλινδρόμηση) είναι στατιστικά εργαλεία για τον εντοπισμό σχέσεων μεταξύ
χ 2 test ανεξαρτησίας Καθηγητής Ι. Κ. ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΥ demetri@econ.uoa.gr 7.2 Το χ 2 Τεστ Ανεξαρτησίας Tο χ 2 τεστ ανεξαρτησίας (όπως και η παλινδρόμηση) είναι στατιστικά εργαλεία για τον εντοπισμό σχέσεων μεταξύ
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
ΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΟΒΙΟΛΟΓΙΑ, ΝΕΥΡΟΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΕΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗ
 A εξάμηνο 2009-2010 ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΟΒΙΟΛΟΓΙΑ, ΝΕΥΡΟΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΕΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗ Μεθοδολογία Έρευνας και Στατιστική ΑΝΤΩΝΙΟΣ ΧΡ. ΜΠΟΥΡΑΣ Χειμερινό Εξάμηνο 2009-2010 Ποιοτικές και Ποσοτικές
A εξάμηνο 2009-2010 ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΟΒΙΟΛΟΓΙΑ, ΝΕΥΡΟΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΕΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗ Μεθοδολογία Έρευνας και Στατιστική ΑΝΤΩΝΙΟΣ ΧΡ. ΜΠΟΥΡΑΣ Χειμερινό Εξάμηνο 2009-2010 Ποιοτικές και Ποσοτικές
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Right Rear Door. Let's now finish the door hinge saga with the right rear door
 Right Rear Door Let's now finish the door hinge saga with the right rear door You may have been already guessed my steps, so there is not much to describe in detail. Old upper one file:///c /Documents
Right Rear Door Let's now finish the door hinge saga with the right rear door You may have been already guessed my steps, so there is not much to describe in detail. Old upper one file:///c /Documents
1. Ηλεκτρικό μαύρο κουτί: Αισθητήρας μετατόπισης με βάση τη χωρητικότητα
 IPHO_42_2011_EXP1.DO Experimental ompetition: 14 July 2011 Problem 1 Page 1 of 5 1. Ηλεκτρικό μαύρο κουτί: Αισθητήρας μετατόπισης με βάση τη χωρητικότητα Για ένα πυκνωτή χωρητικότητας ο οποίος είναι μέρος
IPHO_42_2011_EXP1.DO Experimental ompetition: 14 July 2011 Problem 1 Page 1 of 5 1. Ηλεκτρικό μαύρο κουτί: Αισθητήρας μετατόπισης με βάση τη χωρητικότητα Για ένα πυκνωτή χωρητικότητας ο οποίος είναι μέρος
Solution to Review Problems for Midterm III
 Solution to Review Problems for Mierm III Mierm III: Friday, November 19 in class Topics:.8-.11, 4.1,4. 1. Find the derivative of the following functions and simplify your answers. (a) x(ln(4x)) +ln(5
Solution to Review Problems for Mierm III Mierm III: Friday, November 19 in class Topics:.8-.11, 4.1,4. 1. Find the derivative of the following functions and simplify your answers. (a) x(ln(4x)) +ln(5
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Mean bond enthalpy Standard enthalpy of formation Bond N H N N N N H O O O
 Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής
 Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής Να γραφεί πρόγραμμα το οποίο δέχεται ως είσοδο μια ακολουθία S από n (n 40) ακέραιους αριθμούς και επιστρέφει ως έξοδο δύο ακολουθίες από θετικούς ακέραιους
Πρόβλημα 1: Αναζήτηση Ελάχιστης/Μέγιστης Τιμής Να γραφεί πρόγραμμα το οποίο δέχεται ως είσοδο μια ακολουθία S από n (n 40) ακέραιους αριθμούς και επιστρέφει ως έξοδο δύο ακολουθίες από θετικούς ακέραιους
A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy. Equivalence Relation
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
τατιστική στην Εκπαίδευση II
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΣΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΣΗ τατιστική στην Εκπαίδευση II Λφση επαναληπτικής άσκησης Διδάσκων: Μιχάλης Λιναρδάκης ΠΑΙΔΑΓΩΓΙΚΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΗΜΟΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΑΓΩΓΗΣ Άδειες Χρήσης Το
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΣΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΣΗ τατιστική στην Εκπαίδευση II Λφση επαναληπτικής άσκησης Διδάσκων: Μιχάλης Λιναρδάκης ΠΑΙΔΑΓΩΓΙΚΟ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΗΜΟΤΙΚΗΣ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΣΗΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΩΝ ΑΓΩΓΗΣ Άδειες Χρήσης Το
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Exercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5
 Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
t-distribution t a (ν) s N μ = where X s s x = ν 2 FD ν 1 FD a/2 a/2 t-distribution normal distribution for ν>120
 t-ditribution t X x μ = where x = ν FD ν FD t a (ν) 0 t-ditribution normal ditribution for ν>0 a/ a/ -ta ta ΒΑΘΜΟΙ ΕΛΕΥΘΕΡΙΑΣ (freedom degree) Βαθμοί ελευθερίας (ν): ο αριθμός των ανεξάρτητων μετρήσεων
t-ditribution t X x μ = where x = ν FD ν FD t a (ν) 0 t-ditribution normal ditribution for ν>0 a/ a/ -ta ta ΒΑΘΜΟΙ ΕΛΕΥΘΕΡΙΑΣ (freedom degree) Βαθμοί ελευθερίας (ν): ο αριθμός των ανεξάρτητων μετρήσεων
Example of the Baum-Welch Algorithm
 Example of the Baum-Welch Algorithm Larry Moss Q520, Spring 2008 1 Our corpus c We start with a very simple corpus. We take the set Y of unanalyzed words to be {ABBA, BAB}, and c to be given by c(abba)
Example of the Baum-Welch Algorithm Larry Moss Q520, Spring 2008 1 Our corpus c We start with a very simple corpus. We take the set Y of unanalyzed words to be {ABBA, BAB}, and c to be given by c(abba)
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Similarly, we may define hyperbolic functions cosh α and sinh α from the unit hyperbola
 Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
Lecture 12: Pseudo likelihood approach
 Lecture 12: Pseudo likelihood approach Pseudo MLE Let X 1,...,X n be a random sample from a pdf in a family indexed by two parameters θ and π with likelihood l(θ,π). The method of pseudo MLE may be viewed
Lecture 12: Pseudo likelihood approach Pseudo MLE Let X 1,...,X n be a random sample from a pdf in a family indexed by two parameters θ and π with likelihood l(θ,π). The method of pseudo MLE may be viewed
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
519.22(07.07) 78 : ( ) /.. ; c (07.07) , , 2008
 .. ( ) 2008 519.22(07.07) 78 : ( ) /.. ;. : -, 2008. 38 c. ( ) STATISTICA.,. STATISTICA.,. 519.22(07.07),.., 2008.., 2008., 2008 2 ... 4 1...5...5 2...14...14 3...27...27 3 ,, -. " ", :,,,... STATISTICA.,,,.
.. ( ) 2008 519.22(07.07) 78 : ( ) /.. ;. : -, 2008. 38 c. ( ) STATISTICA.,. STATISTICA.,. 519.22(07.07),.., 2008.., 2008., 2008 2 ... 4 1...5...5 2...14...14 3...27...27 3 ,, -. " ", :,,,... STATISTICA.,,,.
PHOS π 0 analysis, for production, R AA, and Flow analysis, LHC11h
 PHOS π, ask PHOS π analysis, for production, R AA, and Flow analysis, Henrik Qvigstad henrik.qvigstad@fys.uio.no University of Oslo --5 PHOS π, ask ask he task we use, AliaskPiFlow was written prior, for
PHOS π, ask PHOS π analysis, for production, R AA, and Flow analysis, Henrik Qvigstad henrik.qvigstad@fys.uio.no University of Oslo --5 PHOS π, ask ask he task we use, AliaskPiFlow was written prior, for
: Monte Carlo EM 313, Louis (1982) EM, EM Newton-Raphson, /. EM, 2 Monte Carlo EM Newton-Raphson, Monte Carlo EM, Monte Carlo EM, /. 3, Monte Carlo EM
 2008 6 Chinese Journal of Applied Probability and Statistics Vol.24 No.3 Jun. 2008 Monte Carlo EM 1,2 ( 1,, 200241; 2,, 310018) EM, E,,. Monte Carlo EM, EM E Monte Carlo,. EM, Monte Carlo EM,,,,. Newton-Raphson.
2008 6 Chinese Journal of Applied Probability and Statistics Vol.24 No.3 Jun. 2008 Monte Carlo EM 1,2 ( 1,, 200241; 2,, 310018) EM, E,,. Monte Carlo EM, EM E Monte Carlo,. EM, Monte Carlo EM,,,,. Newton-Raphson.
«Χρήσεις γης, αξίες γης και κυκλοφοριακές ρυθμίσεις στο Δήμο Χαλκιδέων. Η μεταξύ τους σχέση και εξέλιξη.»
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΑΓΡΟΝΟΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΓΕΩΓΡΑΦΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΦΕΡΕΙΑΚΟΥ ΣΧΕΔΙΑΣΜΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ: «Χρήσεις γης, αξίες γης και κυκλοφοριακές ρυθμίσεις στο Δήμο Χαλκιδέων.
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΑΓΡΟΝΟΜΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΟΠΟΓΡΑΦΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΓΕΩΓΡΑΦΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΕΡΙΦΕΡΕΙΑΚΟΥ ΣΧΕΔΙΑΣΜΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ: «Χρήσεις γης, αξίες γης και κυκλοφοριακές ρυθμίσεις στο Δήμο Χαλκιδέων.
ΑΝΙΧΝΕΥΣΗ ΓΕΓΟΝΟΤΩΝ ΒΗΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΥ ΜΕ ΧΡΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΤΑΧΥΝΣΙΟΜΕΤΡΩΝ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ ΑΝΙΧΝΕΥΣΗ ΓΕΓΟΝΟΤΩΝ ΒΗΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΥ ΜΕ ΧΡΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΤΑΧΥΝΣΙΟΜΕΤΡΩΝ
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΜΕΤΣΟΒΙΟ ΠΟΛΥΤΕΧΝΕΙΟ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΩΝ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ ΑΝΙΧΝΕΥΣΗ ΓΕΓΟΝΟΤΩΝ ΒΗΜΑΤΙΣΜΟΥ ΜΕ ΧΡΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΤΑΧΥΝΣΙΟΜΕΤΡΩΝ
Ασκήσεις Εξετάσεων. Μεταπτυχιακό Πρόγραμμα Σπουδών στη. Διοίκηση των Επιχειρήσεων
 Ασκήσεις Εξετάσεων Μεταπτυχιακό Πρόγραμμα Σπουδών στη Διοίκηση των Επιχειρήσεων ΑΣΚΗΣΗ 1: Έλεγχος για τη μέση τιμή ενός πληθυσμού Η αντικαπνιστική νομοθεσία υποχρεώνει τους καπνιστές που εργάζονται σε
Ασκήσεις Εξετάσεων Μεταπτυχιακό Πρόγραμμα Σπουδών στη Διοίκηση των Επιχειρήσεων ΑΣΚΗΣΗ 1: Έλεγχος για τη μέση τιμή ενός πληθυσμού Η αντικαπνιστική νομοθεσία υποχρεώνει τους καπνιστές που εργάζονται σε
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
VBA Microsoft Excel. J. Comput. Chem. Jpn., Vol. 5, No. 1, pp (2006)
 J. Comput. Chem. Jpn., Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 29 38 (2006) Microsoft Excel, 184-8588 2-24-16 e-mail: yosimura@cc.tuat.ac.jp (Received: July 28, 2005; Accepted for publication: October 24, 2005; Published on
J. Comput. Chem. Jpn., Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 29 38 (2006) Microsoft Excel, 184-8588 2-24-16 e-mail: yosimura@cc.tuat.ac.jp (Received: July 28, 2005; Accepted for publication: October 24, 2005; Published on
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
( ) 2 and compare to M.
 Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
