q-analogues of Triple Series Reduction Formulas due to Srivastava and Panda with General Terms
|
|
|
- Ήρα Βιτάλης
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Advances in Dynamical Systems and Applications ISSN , Volume 7, Numbe 1, pp ( analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas due to Sivastava and Panda with Geneal Tems Thomas Enst Uppsala Univesity Depatment of Mathematics PO Box 480, SE Uppsala, Sweden Abstact We find six double -analogues of the eduction fomulas by Sivastava and Panda fo tiple seies, with geneal tems These ae then spezialized to summations fo -Kampé de Féiet functions AMS Subject Classifications: 33D15, 33D05, 33C65 Keywods: Tiple seies, geneal tems, eduction fomula, Γ -function 1 Intoduction The histoy of the theme in this aticle goes many yeas back It deals with eualities between uite geneal tiple and double sums The coefficients consist of -shifted factoials, Γ -functions and -binomial coefficients Sivastava and Panda [10] collected these fomulas, peviously scatteed in the liteatue into 6 fomulas of a slightly diffeent chaacte than we pesent hee (fo 1 In Section 2 we find double -foms of these, by the 2 -Vandemonde summation fomulas, ie, 12 -foms These ae then specialized, in Section 3, to six summation fomulas fo -Kampé de Féiet functions We will use the (; l; λ opeato, which is exploed in detail in [6] We tun to the fist definitions Definition 11 The powe function is defined by a e a log( Let δ > 0 be an abitay small numbe We will use the following banch of the logaithm: π + δ < Im (log π + δ This defines a simply connected space in the complex plane The vaiables a, b, c, C denote cetain paametes The vaiables i, j, k, l, m, n, p, will denote natual numbes except fo cetain cases whee it will be clea fom Received July 1, 2010; Accepted Novembe 22, 2011 Communicated by Lance Littlejohn
2 42 Thomas Enst the context that i will denote the imaginay unit Let the -shifted factoial be defined by 1, n 0; n 1 a; n (1 a+m (11 n 1, 2, m0 Since poducts of -shifted factoials occu so often, to simplify them we shall feuently use the moe compact notation The opeato is defined by By (13 it follows that a 1,, a m ; n : C Z C Z a a + m a j ; n (12 j1 πi log (13 n 1 a; n (1 + a+m, (14 m0 Assume that (m, l 1, ie, m and l elatively pime The opeato m l : C Z C Z is defined by a a + 2πim l log (15 We will also need anothe genealization of the tilde opeato n 1 k 1 k ã; n ( i(a+m (16 m0 i0 This leads to the following -analogue of [11, p22, (2] Theoem 12 (See [4] a; kn k 1 a + m a ; n k + m ; n (17 k k m0 The following notation will be convenient: QE(x x
3 -analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas 43 Definition 13 (; l; λ; n l 1 λ + m λ ; n l + m ; n (18 l l m0 When λ is a vecto, we mean the coesponding poduct of vecto elements When λ is eplaced by a seuence of numbes sepaated by commas, we mean the coesponding poduct as in the case of -shifted factoials Definition 14 Let have dimensions Let (a, (b, (g i, (h i, (a, (b, (g i, (h i A, B, G i, H i, A, B, G i, H i 1 + B + B + H i + H i A A G i G i 0, i 1,, n Then the genealized -Kampé de Féiet function is defined by Φ A+A :G 1 +G 1 ;;Gn+G n B+B :H 1 +H 1 ;;Hn+H n m [ ] (a ˆ : (gˆ 1 ; ; (gˆ n (b ˆ : (hˆ 1 ; ; (hˆ n ; x (a : (g 1; ; (g n (b : (h 1; ; (h n (a; ˆ 0 m (a ( 0, m n j1 ( (g ˆ j ; j mj ((g j( j, m j x m j j (b; ˆ 0 m (b ( 0, m n j1 ( (h ˆ j ; j mj (h j ( j, m j 1; j mj ( 1 n j1 m j(1+h j +H j G j G j +B+B A A ( ( m n ( QE (B + B A A, 0 QE (1 + H j + H j G j G 2 j We assume that no factos in the denominato ae zeo We assume that j1 (a ( 0, m, (g j( j, m j, (b ( 0, m, (h j( j, m j contain factos of the fom ˆ a(k; k, (s; k, (s(k; k o QE (f( m ( mj 2, j (19 Definition 15 Let the Gauss -binomial coefficient be defined by ( n 1; n, k 0, 1,, n (110 k 1; k 1; n k Let the Γ -function be defined in the unit disk 0 < < 1 by Γ (x 1; x; (1 1 x (111
4 44 Thomas Enst 2 Cetain -summation Fomulas Sivastava [12] and Panda & Sivastava [10] have systematically collected and genealized a numbe of elated summation fomulas known fom the liteatue Ou task in this section is to find symmetic -analogues of these fomulas, which always occu in pais In cetain exceptional cases the convegence in the fomulas is not so good, we then eplace the euality sign by the sign fo fomal euality, We assume thoughout that M km + ln and {} is a seuence of bounded complex numbes Theoem 21 (Compae [10, (4 p 244] and [12, (9 p 28] ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N 1 β+; M ( 2 M xm y n 1 β; M NM 1 + α β; M 1 + α β N; M (21 Poof We have LHS Γ (α Γ (α ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β 1 β+; M ( 2 M 1 β; M ( α+β M+N Γ (α β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N 1 β; +M 1 α; N; 1; ( α+β M+N 1 β + M; 1 α; N; 1; xm y n 1 β; M α + β M; N 1 α; N xm y n 1 β; M NM 1 + α β; M 1 + α β N; M (22 The poof is complete
5 -analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas 45 Theoem 22 (Compae [10, (4 p 244] ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N 1 β+; M ( 2+(α β N+1 xm y n 1 β; M N(1 β 1 + α β; M 1 + α β N; M (23 Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β (( QE + (α β N Γ (α Γ (α β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N Γ (α 1 β; M 1 β+; M 1 β; +M 1 α; N; 1; 1 β + M; 1 α; N; 1; xm y n 1 β; M α + β M; N 1 α; N N(1 β+m xm y n 1 β; M N(1 β 1 + α β; M 1 + α β N; M (24 The poof is complete Theoem 23 (Compae [10, (5 p 244] and [12, (8 p 28] ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N 1 β+; M ( 2 1 α+; M xm y n 1 β; M 1 1 α + N; M (25
6 46 Thomas Enst Poof We have LHS Γ (α Γ (α ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β ( α+β+n Γ (α β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N 1 β+; M ( 2 1 α+; M 1 β; M 1 α; M 1 β; +M 1 α; +M N; 1; ( α+β+n 1 β + M; 1 α + M; N; 1; xm y n 1 β; M α + β; N 1 α; M 1 α + M; N xm y n 1 β; M 1 1 α + N; M (26 The poof is complete Theoem 24 (Compae [10, (5 p 244] ( 1 Γ (α 1 β+; M Γ (β 1 α+; M (( QE + (α β N β α; N Γ (α xm y n 1 β; M N(1 β+m 1 α; N 1 α + N; M (27
7 -analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas 47 Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β (( QE + (α β N Γ (α 1 β; +M N; Γ (α 1 α; +M 1; 1 β + M; N; Γ (α 1 α + M; 1; 1 β+; M 1 α+; M 1 β; M 1 α; M xm y n 1 β; M α + β; N N(1 β+m 1 α; M 1 + α + M; N β α; N Γ (α xm y n 1 β; M N(1 β+m 1 α; N 1 α + N; M (28 The poof is complete Theoem 25 (Compae [10, (6 p 244] and [12, (10 p 29] ( 1 Γ (α α ; M Γ (β β ; M β α; NΓ (α NM α N; M 1 α; N β; M QE (( 2 (29
8 48 Thomas Enst Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β Γ (α α; M Γ (α β; M ( α+β+n α; M Γ (α β; M β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N The poof is complete α ; M ( 2 β ; M α; M β; M N; 1; N 1 β M; N; 1 α M; 1; α + β; N 1; m 1; n 1 α M; N NM α N; M β; M Theoem 26 (Compae [10, (6 p 244] ( 1 Γ (α α ; M ( Γ (β β ; M β α; NΓ (α xm y n N(1 β α N; M 1 α; N β; M Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β Γ (α α; M Γ (α β; M α; M Γ (α β; M β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N 2+(α β N+1 α ; M ( β ; M α; M β; M N; 1; (α β+1 (210 (211 2+(α β N+1 1 β M; N; 1 α M; 1; α + β; N N(1 β M 1 α M; N α N; M N(1 β β; M (212
9 -analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas 49 The poof is complete Theoem 27 (Compae [10, (7 p 244] and [12, (11 p 29] ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N Poof We have LHS Γ (α Γ (α ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β β; M ( 2 β ; M ( 2 β; M α + β + N; M α + β; M ( α+β+m+n Γ (α β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N ( 2 β ; M N; α ; 1; N β; M 1 β M; 1 α; N; 1; β; M α + β + M; N 1 α; N β; M α + β + N; M α + β; M (213 (214 The poof is complete Remak 28 The convegence in fomula (213 is not so good Howeve, this fomula woks well in a numbe of special cases One example is 1, 85, α 53, β 5543, N 4, x 2, y 176 (215 In this case the diffeence LHS-RHS in (213 is fo 0 m 60, 0 n 60 Theoem 29 (Compae [10, (7 p 244] ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N (2+(1+α β M N β ; M N(1 β M β; M α + β + N; M α + β; M (216
10 50 Thomas Enst Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β Γ (α Γ (α β; M Γ (α β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N The poof is complete β ; M (1+α β M N ( 2+1 2M N; α ; 1; (1+α β M β; M 1 β M; 1 α; N; 1; N(1 β M β; M α + β + M; N 1 α; N N(1 β M β; M α + β + N; M α + β; M Theoem 210 (Compae [10, (8 p 244] and [12, (12 p 29] ( 1 Γ (α α ; M Γ (β β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β Γ (α Γ (α Γ (α QE xm y n α N; M 1 + α β; M 1 + α β N; M α ; M ( 2 α; M β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N (217 (( 2 β ; α; M N; 1; N α; M α + β M; N 1 M α; N (218 1 β; ( α+β M+N 1 α M; N; 1; α N; M 1 + α β; M 1 + α β N; M (219
11 -analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas 51 The poof is complete Theoem 211 (Compae [10, (8 p 244] ( 1 Γ (α ( 2+(1+α β+m N α ; M Γ (β 1; m 1; n β α; N Γ (α xm y n 1 β; M N(1 β 1 + α β; M 1 α; N 1 + α β N; M Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β Γ (α Γ (α Γ (α α; M β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N (220 α ; M ( 2+(1+α β+m N β ; α; M N; (1+α β+m 1; 1 β; 1 α M; N; 1; α; M N(1 β α + β M; N 1 M α; N The poof is complete α N; M N(1 β 1 + α β; M 1 + α β N; M (221 Remak 212 The convegence in fomula (220 is not so good Howeve, this fomula woks somehow in a numbe of special cases One example is 1, 99, α 43, β 5543, N 4, x 1, y 076 (222 In this case the diffeence LHS-RHS in (220 is fo 0 m 20, 0 n 20 Theoem 213 (Compae [10, (9 p 244] and [12, (13 p 29] ( 1 Γ (α ( 2+M Γ (β 1 α+; M β α; N Γ (α α + β + N; M 1 α; N 1 α + N, α + β; M (223
12 52 Thomas Enst Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β Γ (α Γ (α ( α+β+m+n Γ (α β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N The poof is complete 1 α; M ( 2+M 1 α+; M 1 β; 1 α; +M N; 1; ( α+β+m+n 1 β; 1 α + M; N; 1; 1 α; M α + β + M; N 1 α + M; N α + β + N; M 1 α + N, α + β; M Theoem 214 (Compae [10, (9 p 244] ( 1 Γ (α ( 2+(α β+1 N Γ (β 1 α+; M β α; N Γ (α NM α + β + N; M N(1 β 1 α; N 1 α + N, α + β; M Poof We have LHS ( 1 Γ (α Γ (β Γ (α Γ (α Γ (α β α; N Γ (α 1 α; N The poof is complete 1 α; M ( 2+(α β+1 N 1 α+; M 1 β; 1 α; +M N; 1; 1 β; 1 α + M; N; 1; 1 α; M N(1 β α + β + M; N 1 α + M; N xm y n N(1 β α + β + N; M 1 α + N, α + β; M (224 (225 (226
13 -analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas 53 3 Specializations Specializing the pevious fomulas leads to the following fomulas fo two vaiables, whee we have put θ(n; α, β; ; ( 1 ( 2 Γ (α Γ (β ; ω(n; α, β; β α; NΓ (α 1 α; N (31 We have assumed that B B G G in all fomulas The conditions fo A and E ae given sepaately in each case Theoem 31 (Compae [10, (16 p 246] We assume that A + 2l E [ ] (; l; 1 β+, (a : (b; (b θ(n; α, β; ; Φ A+2l:B E:G (e : (g; (g ; x l(n, y l(n [ ] (; l; 1 β, 1 + α β, (a : (b; (b ω(n; α, β; Φ A+4l:B (; l; 1 + α β N, (e : (g; (g ; x, y (32 Poof Put (a; m+n (b; m (b ; n (e; m+n (g; m (g ; n Nl(m+n (33 in (21 We have assumed that k l In the following poofs we use the value and assume that k l (a; m+n (b; m (b ; n (e; m+n (g; m (g ; n (34 Theoem 32 (Compae [10, (19 p 247] We assume that A E [ ] (; l; 1 β+, (a : (b; (b θ(n; α, β; ; Φ A+2l:B (; l; 1 α+, (e : (g; (g ; x, y [ ] ω(n; α, β; Φ A+2l:B (; l; 1 β, (a : (b; (b (; l; 1 α + N, (e : (g; (g ; x, y Poof Use (25 Theoem 33 (Compae [10, (20 p 247] We assume that A E [ ] (; l; α, (a : (b; (b θ(n; α, β; ; Φ A+2l:B (; l; β, (e : (g; (g ; x, y [ ] (; l; α N, (a : (b; (b ω(n; α, β; Φ A+2l:B (; l; β, (e : (g; (g ; x Nl, y Nl (35 (36
14 54 Thomas Enst Poof Use (29 Theoem 34 (Compae [10, (21 p 247] We assume that A E + 2l [ θ(n; α, β; ; (1+α β N Φ A:B ω(n; α, β; N(1 β Φ A+2l:B E+4l:G Poof Use (216 ] (a : (b; (b (; l; β, (e : (g; (g ; x l, y l [ (; l; β α + N, (a : (b; (b (; l; β, α + β, (e : (g; (g ; x Nl, y Nl (37 ] Theoem 35 (Compae [10, (22 p 248] We assume that A + 2l E θ(n; α, β; ; Φ A+2l:B E:G ω(n; α, β; Φ A+4l:B [ (; l; α, (a : (b; (b (e : (g; (g [ (; l; α N, 1 + α β, (a : (b; (b (; l; 1 + α β N, (e : (g; (g ] ; x, y ] ; x, y (38 Poof Use (218 Remak 36 In [9, (31 p 439] Kandu tied to deive a simila fomula Howeve, in this aticle the definitions ae insufficient Remak 37 Fomula (38 is a -analogue of [8] Theoem 38 (Compae [10, (23 p 248] We assume that A E + 2l [ θ(n; α, β; ; Φ A:B ω(n; α, β; Φ A+2l:B E+4l:G [ ] (a : (b; (b (; l; 1 α+, (e : (g; (g ; xl, y l (; l; α + β + N, (a : (b; (b (; l; 1 α + N, α + β, (e : (g; (g ] ; x, y (39 Poof Use (223 4 Conclusion We expect that these fomulas will be of geatest value when looking fo -analogues of eductions fo tiple -seies This is an investigation which has only stated, and hopefully will continue in the next yeas The connection with Γ -functions is uite inteesting, as is manifested in the book [7]
15 -analogues of Tiple Seies Reduction Fomulas 55 Refeences [1] T Enst, A method fo -calculus J nonlinea Math Physics 10 No4 (2003, [2] T Enst, Some esults fo -functions of many vaiables Rendiconti di Padova 112 (2004, [3] T Enst, A enaissance fo a -umbal calculus Poceedings of the Intenational Confeence Munich, Gemany July 2005 Wold Scientific, (2007 [4] T Enst, Some new fomulas involving Γ functions Rendiconti di Padova 118 (2007, [5] T Enst, The diffeent tongues of -calculus, Poceedings of Estonian Academy of Sciences 57 no 2 (2008, [6] T Enst, -analogues of geneal eduction fomulas by Buschman and Sivastava, togethe with the impotant (l; λ opeato eminding of MacRobet Demonstatio Mathematica XLIV (2011, [7] T Enst, A compehensive teatment of -calculus, Bikhäuse, 2012 [8] KC Gupta and A Sivastava, Cetain esults involving Kampé de Féiet s function Indian J Math 15 (1973, [9] D Kandu, Cetain expansions involving basic hypegeometic functions of two vaiables Indian J Pue Appl Math 18, no 5, (1987, [10] R Panda and HMSivastava, Some ecusion fomulas associated with multiple hypegeometic functions Bull Acad Polon Sci Se Sci Math Astonom Phys , no 3 (1975, [11] ED Rainville, Special functions Repint of 1960 fist edition (Chelsea Publishing Co, Bonx, NY, 1971 [12] H MSivastava, Cetain summation fomulas involving genealized hypegeometic functions Comment Math Univ St Paul 21, (1972/ ,
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
Analytical Expression for Hessian
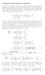 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Curvilinear Systems of Coordinates
 A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines
![Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines](/thumbs/51/28406191.jpg) Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
On a four-dimensional hyperbolic manifold with finite volume
 BULETINUL ACADEMIEI DE ŞTIINŢE A REPUBLICII MOLDOVA. MATEMATICA Numbers 2(72) 3(73), 2013, Pages 80 89 ISSN 1024 7696 On a four-dimensional hyperbolic manifold with finite volume I.S.Gutsul Abstract. In
BULETINUL ACADEMIEI DE ŞTIINŢE A REPUBLICII MOLDOVA. MATEMATICA Numbers 2(72) 3(73), 2013, Pages 80 89 ISSN 1024 7696 On a four-dimensional hyperbolic manifold with finite volume I.S.Gutsul Abstract. In
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
4.2 Differential Equations in Polar Coordinates
 Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Product of two generalized pseudo-differential operators involving fractional Fourier transform
 J. Pseudo-Diffe. Ope. Appl. 2011 2:355 365 DOI 10.1007/s11868-011-0034-5 Poduct of two genealized pseudo-diffeential opeatos involving factional Fouie tansfom Akhilesh Pasad Manish Kuma eceived: 21 Febuay
J. Pseudo-Diffe. Ope. Appl. 2011 2:355 365 DOI 10.1007/s11868-011-0034-5 Poduct of two genealized pseudo-diffeential opeatos involving factional Fouie tansfom Akhilesh Pasad Manish Kuma eceived: 21 Febuay
SCITECH Volume 13, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION Published online: March 29, 2018
 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
A NEW CLASS OF MODULAR EQUATIONS IN RAMANUJAN S ALTERNATIVE THEORY OF ELLIPTIC FUNCTIONS OF SIGNATURE 4 AND SOME NEW P-Q ETA-FUNCTION IDENTITIES
 A NEW CLASS OF MODULAR EQUATIONS IN RAMANUJAN S ALTERNATIVE THEORY OF ELLIPTIC FUNCTIONS OF SIGNATURE AND SOME NEW P-Q ETA-FUNCTION IDENTITIES S. Bhagava Chasheka Adiga M. S. Mahadeva Naika. Depatent of
A NEW CLASS OF MODULAR EQUATIONS IN RAMANUJAN S ALTERNATIVE THEORY OF ELLIPTIC FUNCTIONS OF SIGNATURE AND SOME NEW P-Q ETA-FUNCTION IDENTITIES S. Bhagava Chasheka Adiga M. S. Mahadeva Naika. Depatent of
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
TL-Moments and L-Moments Estimation for the Generalized Pareto Distribution
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 2009, no. 1, 43-52 TL-Moments L-Moments Estimation fo the Genealized Paeto Distibution Ibahim B. Abdul-Moniem Madina Highe Institute fo Management Technology Madina
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 2009, no. 1, 43-52 TL-Moments L-Moments Estimation fo the Genealized Paeto Distibution Ibahim B. Abdul-Moniem Madina Highe Institute fo Management Technology Madina
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Reminders: linear functions
 Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Mock Exam 7. 1 Hong Kong Educational Publishing Company. Section A 1. Reference: HKDSE Math M Q2 (a) (1 + kx) n 1M + 1A = (1) =
 Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics
 Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
ω ω ω ω ω ω+2 ω ω+2 + ω ω ω ω+2 + ω ω+1 ω ω+2 2 ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ω+1 ω ω2 ω ω2 + ω ω ω2 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω ω+1 ω ω2 + ω ω+1 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω
 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
The Laplacian in Spherical Polar Coordinates
 Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations
 Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
A summation formula ramified with hypergeometric function and involving recurrence relation
 South Asian Journal of Mathematics 017, Vol. 7 ( 1): 1 4 www.sajm-online.com ISSN 51-151 RESEARCH ARTICLE A summation formula ramified with hypergeometric function and involving recurrence relation Salahuddin
South Asian Journal of Mathematics 017, Vol. 7 ( 1): 1 4 www.sajm-online.com ISSN 51-151 RESEARCH ARTICLE A summation formula ramified with hypergeometric function and involving recurrence relation Salahuddin
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
The Neutrix Product of the Distributions r. x λ
 ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence
 International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 3, 143-149 A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence Santosh Kr. Saxena H. N. 419, Jawaharpuri, Badaun, U.P., India Presently working in
International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 3, 143-149 A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence Santosh Kr. Saxena H. N. 419, Jawaharpuri, Badaun, U.P., India Presently working in
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Homomorphism in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Automata
 International Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics Systems. ISSN 2248-9940 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 39-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijfms.htm Homomorphism in Intuitionistic
International Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics Systems. ISSN 2248-9940 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 39-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijfms.htm Homomorphism in Intuitionistic
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
( y) Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy. Equivalence Relation
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS
 SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
Commutative Monoids in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets
 Commutative Monoids in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets S K Mala #1, Dr. MM Shanmugapriya *2 1 PhD Scholar in Mathematics, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu- 641021 Assistant Professor of Mathematics,
Commutative Monoids in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets S K Mala #1, Dr. MM Shanmugapriya *2 1 PhD Scholar in Mathematics, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu- 641021 Assistant Professor of Mathematics,
DiracDelta. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2
![If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2 If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2](/thumbs/53/31933086.jpg) Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π 2, π 2
 Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)
![2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p) 2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)](/thumbs/40/21364883.jpg) Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
DIRECT PRODUCT AND WREATH PRODUCT OF TRANSFORMATION SEMIGROUPS
 GANIT J. Bangladesh Math. oc. IN 606-694) 0) -7 DIRECT PRODUCT AND WREATH PRODUCT OF TRANFORMATION EMIGROUP ubrata Majumdar, * Kalyan Kumar Dey and Mohd. Altab Hossain Department of Mathematics University
GANIT J. Bangladesh Math. oc. IN 606-694) 0) -7 DIRECT PRODUCT AND WREATH PRODUCT OF TRANFORMATION EMIGROUP ubrata Majumdar, * Kalyan Kumar Dey and Mohd. Altab Hossain Department of Mathematics University
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequality for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x, y, z X.
 Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines
 New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
1 3D Helmholtz Equation
 Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
On mixing generalized poison with Generalized Gamma distribution
 34 WALFORD I.E. CHUKWU(*) and DEVENDRA GUPTA (**) On mixing genealized poison with Genealized Gamma distibution CONTENTS: Intoduction Mixtue. Refeences. Summay. Riassunto. Key wods (*) Walfod I.E. Chukwu
34 WALFORD I.E. CHUKWU(*) and DEVENDRA GUPTA (**) On mixing genealized poison with Genealized Gamma distibution CONTENTS: Intoduction Mixtue. Refeences. Summay. Riassunto. Key wods (*) Walfod I.E. Chukwu
Tridiagonal matrices. Gérard MEURANT. October, 2008
 Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix
 The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
An Inventory of Continuous Distributions
 Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
MathCity.org Merging man and maths
 MathCity.org Merging man and maths Exercise 10. (s) Page Textbook of Algebra and Trigonometry for Class XI Available online @, Version:.0 Question # 1 Find the values of sin, and tan when: 1 π (i) (ii)
MathCity.org Merging man and maths Exercise 10. (s) Page Textbook of Algebra and Trigonometry for Class XI Available online @, Version:.0 Question # 1 Find the values of sin, and tan when: 1 π (i) (ii)
The k-bessel Function of the First Kind
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 7, 01, no. 38, 1859-186 The k-bessel Function of the First Kin Luis Guillermo Romero, Gustavo Abel Dorrego an Ruben Alejanro Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 7, 01, no. 38, 1859-186 The k-bessel Function of the First Kin Luis Guillermo Romero, Gustavo Abel Dorrego an Ruben Alejanro Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Bounding Nonsplitting Enumeration Degrees
 Bounding Nonsplitting Enumeration Degrees Thomas F. Kent Andrea Sorbi Università degli Studi di Siena Italia July 18, 2007 Goal: Introduce a form of Σ 0 2-permitting for the enumeration degrees. Till now,
Bounding Nonsplitting Enumeration Degrees Thomas F. Kent Andrea Sorbi Università degli Studi di Siena Italia July 18, 2007 Goal: Introduce a form of Σ 0 2-permitting for the enumeration degrees. Till now,
