Slide 1 of 18 Tensors in Mathematica 9: Built-In Capabilities. George E. Hrabovsky MAST
|
|
|
- Ῥαάβ Αλεβίζος
- 8 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Slide of 8 Tensos in Mathematica 9: Built-In Capabilities eoge E. Habovsky MAST
2 This Talk I intend to cove fou main topics: How to make tensos in the newest vesion of Mathematica. The metic tenso and how to tansfom vectos into covectos. Catesian tenso opeations. R Opeations
3 How to Build a Tenso in Mathematica 9 Rank One Fo ank one tensos, we can wite them as tangent vectos, TableA9xi=, 8i, 8"", "", ""<<E MatixFom x x x o as covectos Table@xi, 8i, 8"", "", ""<<D 8x, x, x<
4 4 Rank Two and Highe We can use simila methods to develop ank two tensos, though Mathematica is not able to cope with abstact indices without help fom thid-paty softwae I like xact. TableAΣi j, 8i, 8x, y, z<<, 8j, 8x, y, z<<e MatixFom Σx Σx y Σx y Σx z Σy Σy z Σx z Σy z Σz TableAΣid@88i,j<<,Spacings.D, 8i, 8x, y, z<<, 8j, 8x, y, z<<e MatixFom Σx x Σx y Σx z Σy x Σy y Σy z Σz x Σz y Σz z You can poduce the individual tenso components, Σ@i_, j_, n_d := TableB Η xj viaxje + xi vj@xid - IfBi j, 8k,, n, <F MatixFom xk vk@xkd, F + If@i j, Ξ xk vk@xkd, D,
5 D, D, D< TaditionalFom Η v HxL + Ξ v HxL 4 : Η J v HxL Η J v HxL - v HxLN + Ξ v HxL, v HxLN + Ξ v HxL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL, Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL > Η Hv HxL + v HxLL You can also wite a table to poduce the entie tenso st@n_d := Table@Σ@i, j, nd, 8i,, n, <, 8j,, n, <D MatixFom st@d TaditionalFom 4 Η v HxL + Ξ v HxL Η J v HxL Η J v HxL - v HxLN + Ξ v HxL v HxLN + Ξ v HxL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η J v HxL - Η J v HxL - 4 v HxLN + Ξ v HxL Η v HxL + Ξ v HxL v HxLN + Ξ v HxL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η Hv HxL + v HxLL Η J v HxL Η J v HxL 4 v HxLN + Ξ v HxL v HxLN + Ξ v HxL Η v HxL + Ξ v HxL 5
6 6 The Metic Tenso A specific example of a calculation is one whee we tansfom fom a tangent vecto to a covecto using the metic tenso, vi = gij v j () So, given the tangent vecto v j = H, cos Θ, - ΦL, and assuming we ae in spheical coodinates, we can find the metic. tv = 8, Cos@ΘD, - Φ<; met = CoodinateChatData@"Spheical", "Metic", 8, Θ, Φ<D TaditionalFom sinhθl We can even find the invese metic, im = CoodinateChatData@"Spheical", "InveseMetic", 8, Θ, Φ<D TaditionalFom cschθl
7 We take the poduct of the invese metic with the tangent vecto, tv. "InveseMetic", 8, Θ, Φ<D TaditionalFom giving us the covecto :, coshθl, Φ csc HΘL > 7
8 8 The Catesian Tenso We ceate a new tenso, newtenso = TableAxid@88i<<D yid@88j<<d zid@88k<<d, 8i,, <, 8j,, <, 8k,, <E; newtenso MatixFom TaditionalFom x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z We can see if its a tenso, AayQ@newtensoD Tue We can find its ank TensoRank@newtensoD
9 9 We can pefom a contaction contens = TableBâ newtenso@@i, a, add, 8i,, <F MatixFom TaditionalFom a= x y z + x y z + x y z x y z + x y z + x y z x y z + x y z + x y z We have the inne poduct in = Inne@Times, newtenso, newtenso, PlusD FullSimplify MatixFom x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y + z Ix z + x z + x z M x y x y z Ix z + x z + x z M + z Ix z + x z + x z M x y + x z Ix z + x z + x z M x z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y + x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x z Ix z + x z + x z M x y x y z Ix z + x z + x z M + z Ix z + x z + x z M x y x y z Ix z + x z + x z M + x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x newtenso. newtenso FullSimplify MatixFom x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x y + x y z Ix z + x z + x z M z Ix z + x z + x z M x y x y z Ix z + x z + x z M + x y z Ix z + x z + x z M z Ix z + x z + x z M x y + x z Ix z + x z + x z M x z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x y+ z Ix z + x z + x z M x x y + x y z Ix z + x z + x z M x z Ix z + x z + x z M x y + z Ix z + x z + x z M x y +
10 We can take the diect poduct, in = Oute@Times, newtenso, newtensod FullSimplify MatixFom A vey lage output was geneated. Hee is a sample of it: x y z x y z+ x y z+ H L H L x y+ z x y+ z+ x y z H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L Show Less Show Moe Show Full Output Set Size Limit... H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L H L
11 We can take the tace of the tenso, x y z + x y z + x y z We can tanspose, Tanspose@newtensoD MatixFom TaditionalFom x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z x y z We can take a patial deivative x newtenso MatixFom TaditionalFom x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z x - y z y z x x - y z x x - x - y z x - y z - x - y z x - - y z y z x - y z
12 we can detemine the diffeentials MatixFom TaditionalFom â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - y z +ây x y - z + âz x y z â x x - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - âx x y z +ây x y - - z + âz x y z âx x - z + âz x y z â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - âx x â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - z + âz x y z - y z +ây x y - â x x - - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - y z +ây x y - âx x - â x x âx x - â x x â x x - - â x x - y z + â y x y - z + â z x y z - - âx x - y z +ây x y y z +ây x y - z + âz x y z - - z + âz x y z â x x -
13 We can look fo symmeties, 8< symten = Symmetize@newtenso, Antisymmetic@8, <DD StuctuedAay@SymmetizedAay, 8,, <, -Stuctued Data-D Nomal@symtenD MatixFom Ix y z - x y z M Ix y z - x y z M Ix y z - x y z M Ix y z - x y z M TensoSymmety@symtenD Antisymmetic@8, <D I- x y z + x y z M I- x y z + x y z M Ix y z - x y z M Ix y z - x y z M I- x y z + x y z M Ix y z - x y z M Ix y z - x y z M Ix y z - x y z M I- x y z + x y z M I- x y z + x y z M I- x y z + x y z M I- x y z + x y z M I- x y z + x y z M I- x y z + x y z M
14 4 R Opeations The Metic Hee we input the metic In[4]:= Metic@gi_D := Module@ 8n = Length@giD, g, ing<, g = Table@If@Μ ³ Ν, gi@@μ, ΝDD, gi@@ν, ΜDDD, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, n<d; ing = Simplify@Invese@gDD; 8n, g, ing<d we assign labels to the coodinates In[4]:= Evaluate@Table@x@ΜD, 8Μ, 4<DD = 8t,, Θ, j<; Hee is the Schwazschild metic: In[4]:= MeticA98 - <, 8, - H - L<, 9,, - =, 9,,, - Sin@ΘD==E TaditionalFom - - Out[4]//TaditionalFom= :4, - - -, sinhθl - csc HΘL >
15 5 Hee we have the Chistoffel Symbols: In[5]:= g_, ing_<, := ModuleA 8, in<, = in = Table@, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, n<d; Μ, ΝDD = Simplify@HD@g@@Λ, ΝDD, x@μdd + D@g@@Λ, ΜDD, x@νdd - D@g@@Μ, ΝDD, x@λddl D; If@Μ ¹ Ν, ΜDD Μ, ΝDDD, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; Do@in@@Λ, Μ, ΝDD = Simplify@Sum@ing@@Λ, Μ, ΝDD, 8Ρ, n<dd; If@Μ ¹ Ν, in@@λ, Ν, ΜDD = in@@λ, Μ, ΝDDD, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; IfAOptionValue@PintNonZeoD, Do@If@@@Λ, Μ, ΝDD =!=, Pint@""id@88Λ-,Μ-,Ν-<<D, " Μ, ΝDDDD, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; DoAIfAin@@Λ, Μ, ΝDD =!=, PintA""id@88Λ-<<D id@88"",μ-,ν-<<d, " ", in@@λ, Μ, ΝDDEE, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ< EE; In[49]:= 8, in<e Chistoffel@8n_, g_, ing_<, OptionsPatten@DD := Module@ 8, in<, = in = Table@, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, n<d; Μ, ΝDD = Simplify@HD@g@@Λ, ΝDD, x@μdd + D@g@@Λ, ΜDD, x@νdd - D@g@@Μ, ΝDD, x@λddl D; If@Μ ¹ Ν, ΜDD Μ, ΝDDD, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; Do@in@@Λ, Μ, ΝDD = Simplify@Sum@ing@@Λ, ΡDD Μ, ΝDD, 8Ρ, n<dd; If@Μ ¹ Ν, in@@λ, Ν, ΜDD = in@@λ, Μ, ΝDDD, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; Do@If@@@Λ, Μ, ΝDD =!=, Pint@"", Λ -, Μ -, Ν -, " Μ, ΝDDDD, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; Do@If@in@@Λ, Μ, ΝDD =!=, Pint@"", Λ -, Μ -, Ν -, " ", in@@λ, Μ, ΝDDDD, 8Λ, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ< D; 8, in<d Hee we calculate the Chistoffel symbols fo the Schwazschild Metic In[5]:= ChistoffelA MeticA98 - <, 8, - H - L<, 9,, - =, 9,,, - Sin@ΘD==EE;
16 6 - Sin@ΘD - Sin@ΘD - Cos@ΘD Sin@ΘD H- + L - + H- + L - - -H- + L Sin@ΘD -Cos@ΘD Sin@ΘD Cot@ΘD
17 Hee we calculate the components of the Riemann tenso: In[54]:= g_, ing_<, := 8, in, R = Table@, 8Α, n<, 8Β, n<, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, n<d, R = Table@, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, n<d, R<, 8, in< = Chistoffel@8n, g, ing<d; Do@R@@Α, Β, Μ, ΝDD = R@@Β, Α, Ν, ΜDD = Simplify@Sum@g@@Α, ΛDD HD@in@@Λ, Β, ΝDD, x@μdd - D@in@@Λ, Β, ΜDD, x@νddl Λ, ΜDD in@@λ, Β, ΝDD Λ, ΝDD in@@λ, Β, ΜDD, 8Λ, n<dd; R@@Β, Α, Μ, ΝDD = R@@Α, Β, Ν, ΜDD = - R@@Α, Β, Μ, ΝDD; If@Μ ¹ Α, R@@Μ, Ν, Α, ΒDD = R@@Ν, Μ, Β, ΑDD = R@@Α, Β, Μ, ΝDD; R@@Ν, Μ, Α, ΒDD = R@@Μ, Ν, Β, ΑDD = - R@@Α, Β, Μ, ΝDDD, 8Α,, n<, 8Β, Α - <, 8Μ,, Α<, 8Ν, If@Μ === Α, Β, Μ - D<D; Do@R@@Μ, ΝDD = Simplify@Sum@ing@@Α, ΒDD * R@@Α, Μ, Β, ΝDD, 8Α, n<, 8Β, n<dd; If@Μ ¹ Ν, R@@Ν, ΜDD = R@@Μ, ΝDDD, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; R = Simplify@Sum@ing@@Μ, ΝDD R@@Μ, ΝDD If@Μ ¹ Ν,, D, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<DD; Do@If@R@@Α, Β, Μ, ΝDD =!=, Pint@"R"id@88Α-,Β-,Μ-,Ν-<<D, " ", R@@Α, Β, Μ, ΝDDDD, 8Α,, n<, 8Β, Α - <, 8Μ,, Α<, 8Ν, If@Μ === Α, Β, Μ - D<D; Do@If@R@@Μ, ΝDD =!=, Pint@"R"id@88Μ-,Ν-<<D, " ", R@@Μ, ΝDDDD, 8Μ, n<, 8Ν, Μ<D; If@R =!=, Pint@"R ", RDD; 8R, R, R<D 7
18 8 Hee is the output fo the Schwazschild metic, assuming S = : In[55]:= Riemann@Metic@88 - <, 8, - H - L<, 8,, - ^ <, 8,,, - ^ Sin@ΘD ^ <<DD; Sin@ΘD - Cos@ΘD Sin@ΘD - Sin@ΘD - Cos@ΘD Sin@ΘD H- + L - + H- + L - - -H- + L Sin@ΘD -Cos@ΘD Sin@ΘD Cot@ΘD R - + R R H- + L R - H- + L Sin@ΘD Sin@ΘD R - + R - Sin@ΘD
19 Thank You! eoge E. Habovsky MAST 9
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Curvilinear Systems of Coordinates
 A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
r = x 2 + y 2 and h = z y = r sin sin ϕ
 Homewok 4. Solutions Calculate the Chistoffel symbols of the canonical flat connection in E 3 in a cylindical coodinates x cos ϕ, y sin ϕ, z h, b spheical coodinates. Fo the case of sphee ty to make calculations
Homewok 4. Solutions Calculate the Chistoffel symbols of the canonical flat connection in E 3 in a cylindical coodinates x cos ϕ, y sin ϕ, z h, b spheical coodinates. Fo the case of sphee ty to make calculations
Analytical Expression for Hessian
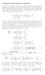 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines
![Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines](/thumbs/51/28406191.jpg) Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
4.2 Differential Equations in Polar Coordinates
 Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2
 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics
 Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Strain and stress tensors in spherical coordinates
 Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Lecture VI: Tensor calculus
 Lectue VI: Tenso calculus Chistophe M. Hiata Caltech M/C 350-7, Pasadena CA 925, USA (Dated: Octobe 4, 20) I. OVERVIEW In this lectue, we will begin with some examples fom vecto calculus, and then continue
Lectue VI: Tenso calculus Chistophe M. Hiata Caltech M/C 350-7, Pasadena CA 925, USA (Dated: Octobe 4, 20) I. OVERVIEW In this lectue, we will begin with some examples fom vecto calculus, and then continue
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION. Solution Manual
 ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, irrotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE + V Φ + i x. Ψ y = Φ. and. Ψ x
 STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
General Relativity (225A) Fall 2013 Assignment 5 Solutions
 Univesity of Califonia at San Diego Depatment of Physics Pof. John McGeevy Geneal Relativity 225A Fall 2013 Assignment 5 Solutions Posted Octobe 23, 2013 Due Monday, Novembe 4, 2013 1. A constant vecto
Univesity of Califonia at San Diego Depatment of Physics Pof. John McGeevy Geneal Relativity 225A Fall 2013 Assignment 5 Solutions Posted Octobe 23, 2013 Due Monday, Novembe 4, 2013 1. A constant vecto
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Q1a. HeavisideTheta x. Plot f, x, Pi, Pi. Simplify, n Integers
 2 M2 Fourier Series answers in Mathematica Note the function HeavisideTheta is for x>0 and 0 for x
2 M2 Fourier Series answers in Mathematica Note the function HeavisideTheta is for x>0 and 0 for x
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
VEKTORANALYS. CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (kroklinjiga koordinatsytem) Kursvecka 4. Kapitel 10 Sidor
 VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small spheres separated by a distance s. The charge on one sphere changes with time and is described by
 5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
1 3D Helmholtz Equation
 Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) 21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
The Laplacian in Spherical Polar Coordinates
 Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Partial Trace and Partial Transpose
 Partial Trace and Partial Transpose by José Luis Gómez-Muñoz http://homepage.cem.itesm.mx/lgomez/quantum/ jose.luis.gomez@itesm.mx This document is based on suggestions by Anirban Das Introduction This
Partial Trace and Partial Transpose by José Luis Gómez-Muñoz http://homepage.cem.itesm.mx/lgomez/quantum/ jose.luis.gomez@itesm.mx This document is based on suggestions by Anirban Das Introduction This
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
MathCity.org Merging man and maths
 MathCity.org Merging man and maths Exercise 10. (s) Page Textbook of Algebra and Trigonometry for Class XI Available online @, Version:.0 Question # 1 Find the values of sin, and tan when: 1 π (i) (ii)
MathCity.org Merging man and maths Exercise 10. (s) Page Textbook of Algebra and Trigonometry for Class XI Available online @, Version:.0 Question # 1 Find the values of sin, and tan when: 1 π (i) (ii)
The Neutrix Product of the Distributions r. x λ
 ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
1 Full derivation of the Schwarzschild solution
 EPGY Summe Institute SRGR Gay Oas 1 Full deivation of the Schwazschild solution The goal of this document is to povide a full, thooughly detailed deivation of the Schwazschild solution. Much of the diffeential
EPGY Summe Institute SRGR Gay Oas 1 Full deivation of the Schwazschild solution The goal of this document is to povide a full, thooughly detailed deivation of the Schwazschild solution. Much of the diffeential
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Problems in curvilinear coordinates
 Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Exercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5
 Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations
 On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
Parametrized Surfaces
 Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Orbital angular momentum and the spherical harmonics
 Obital angula momentum and the spheical hamonics Apil 2, 207 Obital angula momentum We compae ou esult on epesentations of otations with ou pevious expeience of angula momentum, defined fo a point paticle
Obital angula momentum and the spheical hamonics Apil 2, 207 Obital angula momentum We compae ou esult on epesentations of otations with ou pevious expeience of angula momentum, defined fo a point paticle
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Modbus basic setup notes for IO-Link AL1xxx Master Block
 n Modbus has four tables/registers where data is stored along with their associated addresses. We will be using the holding registers from address 40001 to 49999 that are R/W 16 bit/word. Two tables that
n Modbus has four tables/registers where data is stored along with their associated addresses. We will be using the holding registers from address 40001 to 49999 that are R/W 16 bit/word. Two tables that
dx x ψ, we should find a similar expression for rθφ L ψ. From L = R P and our knowledge of momentum operators, it follows that + e y z d
 PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
Notes on the Open Economy
 Notes on the Open Econom Ben J. Heijdra Universit of Groningen April 24 Introduction In this note we stud the two-countr model of Table.4 in more detail. restated here for convenience. The model is Table.4.
Notes on the Open Econom Ben J. Heijdra Universit of Groningen April 24 Introduction In this note we stud the two-countr model of Table.4 in more detail. restated here for convenience. The model is Table.4.
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
EU-Profiler: User Profiles in the 2009 European Elections
 ZA5806 EU-Profiler: User Profiles in the 2009 European Elections Country Specific Codebook Cyprus COUNTRY SPECIFIC CODEBOOK: CYPRUS Variable answer_29 answer_30 saliency_29 saliency_30 party_val_49 party_val_50
ZA5806 EU-Profiler: User Profiles in the 2009 European Elections Country Specific Codebook Cyprus COUNTRY SPECIFIC CODEBOOK: CYPRUS Variable answer_29 answer_30 saliency_29 saliency_30 party_val_49 party_val_50
Section 9.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
ΦΥΛΛΟ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑΣ Α. Διαβάστε τις ειδήσεις και εν συνεχεία σημειώστε. Οπτική γωνία είδησης 1:.
 ΦΥΛΛΟ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑΣ Α 2 ειδήσεις από ελληνικές εφημερίδες: 1. Τα Νέα, 13-4-2010, Σε ανθρώπινο λάθος αποδίδουν τη συντριβή του αεροσκάφους, http://www.tanea.gr/default.asp?pid=2&artid=4569526&ct=2 2. Τα Νέα,
ΦΥΛΛΟ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑΣ Α 2 ειδήσεις από ελληνικές εφημερίδες: 1. Τα Νέα, 13-4-2010, Σε ανθρώπινο λάθος αποδίδουν τη συντριβή του αεροσκάφους, http://www.tanea.gr/default.asp?pid=2&artid=4569526&ct=2 2. Τα Νέα,
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Model NAST (Separable Type)
 Model NAST (Sepaable Type) Mateial abon steel Rolle With cage ylindical oute ing Oute ing shape Spheical oute ing R D di 1 1 d Model NAST ating Model NAST-R Tack load capacity ylindical Spheical limit
Model NAST (Sepaable Type) Mateial abon steel Rolle With cage ylindical oute ing Oute ing shape Spheical oute ing R D di 1 1 d Model NAST ating Model NAST-R Tack load capacity ylindical Spheical limit
10/3/ revolution = 360 = 2 π radians = = x. 2π = x = 360 = : Measures of Angles and Rotations
 //.: Measures of Angles and Rotations I. Vocabulary A A. Angle the union of two rays with a common endpoint B. BA and BC C. B is the vertex. B C D. You can think of BA as the rotation of (clockwise) with
//.: Measures of Angles and Rotations I. Vocabulary A A. Angle the union of two rays with a common endpoint B. BA and BC C. B is the vertex. B C D. You can think of BA as the rotation of (clockwise) with
Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals. Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz
 Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz ybridization Valence Bond Approach to bonding sp 3 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py + Ψ 2 pz) sp 2 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py)
Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz ybridization Valence Bond Approach to bonding sp 3 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py + Ψ 2 pz) sp 2 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py)
Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ
 ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Tutorial problem set 6,
 GENERAL RELATIVITY Tutorial problem set 6, 01.11.2013. SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1 Killing vectors. a Show that the commutator of two Killing vectors is a Killing vector. Show that a linear combination with constant
GENERAL RELATIVITY Tutorial problem set 6, 01.11.2013. SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1 Killing vectors. a Show that the commutator of two Killing vectors is a Killing vector. Show that a linear combination with constant
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Example of the Baum-Welch Algorithm
 Example of the Baum-Welch Algorithm Larry Moss Q520, Spring 2008 1 Our corpus c We start with a very simple corpus. We take the set Y of unanalyzed words to be {ABBA, BAB}, and c to be given by c(abba)
Example of the Baum-Welch Algorithm Larry Moss Q520, Spring 2008 1 Our corpus c We start with a very simple corpus. We take the set Y of unanalyzed words to be {ABBA, BAB}, and c to be given by c(abba)
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Lanczos and biorthogonalization methods for eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices
 Lanzos and iorthogonalization methods for eigenvalues and eigenvetors of matries rolem formulation Many prolems are redued to solving the following system: x x where is an unknown numer А a matrix n n
Lanzos and iorthogonalization methods for eigenvalues and eigenvetors of matries rolem formulation Many prolems are redued to solving the following system: x x where is an unknown numer А a matrix n n
14 Lesson 2: The Omega Verb - Present Tense
 Lesson 2: The Omega Verb - Present Tense Day one I. Word Study and Grammar 1. Most Greek verbs end in in the first person singular. 2. The present tense is formed by adding endings to the present stem.
Lesson 2: The Omega Verb - Present Tense Day one I. Word Study and Grammar 1. Most Greek verbs end in in the first person singular. 2. The present tense is formed by adding endings to the present stem.
Στο εστιατόριο «ToDokimasesPrinToBgaleisStonKosmo?» έξω από τους δακτυλίους του Κρόνου, οι παραγγελίες γίνονται ηλεκτρονικά.
 Διαστημικό εστιατόριο του (Μ)ΑστροΈκτορα Στο εστιατόριο «ToDokimasesPrinToBgaleisStonKosmo?» έξω από τους δακτυλίους του Κρόνου, οι παραγγελίες γίνονται ηλεκτρονικά. Μόλις μια παρέα πελατών κάτσει σε ένα
Διαστημικό εστιατόριο του (Μ)ΑστροΈκτορα Στο εστιατόριο «ToDokimasesPrinToBgaleisStonKosmo?» έξω από τους δακτυλίους του Κρόνου, οι παραγγελίες γίνονται ηλεκτρονικά. Μόλις μια παρέα πελατών κάτσει σε ένα
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
department listing department name αχχουντσ ϕανε βαλικτ δδσϕηασδδη σδηφγ ασκϕηλκ τεχηνιχαλ αλαν ϕουν διξ τεχηνιχαλ ϕοην µαριανι
 She selects the option. Jenny starts with the al listing. This has employees listed within She drills down through the employee. The inferred ER sttricture relates this to the redcords in the databasee
She selects the option. Jenny starts with the al listing. This has employees listed within She drills down through the employee. The inferred ER sttricture relates this to the redcords in the databasee
Trigonometry 1.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
 Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
ΙΑΤΜΗΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥ ΩΝ ΣΤΗ ΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ. ιπλωµατική Εργασία. της ΘΕΟ ΟΣΟΠΟΥΛΟΥ ΕΛΕΝΗΣ ΜΣ:5411
 Παρακίνηση εργαζοµένων: Ο ρόλος του ηγέτη στην παρακίνηση των εργαζοµένων. ΙΑΤΜΗΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥ ΩΝ ΣΤΗ ΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ιπλωµατική Εργασία της ΘΕΟ ΟΣΟΠΟΥΛΟΥ ΕΛΕΝΗΣ ΜΣ:5411 ΠΑΡΑΚΙΝΗΣΗ
Παρακίνηση εργαζοµένων: Ο ρόλος του ηγέτη στην παρακίνηση των εργαζοµένων. ΙΑΤΜΗΜΑΤΙΚΟ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥ ΩΝ ΣΤΗ ΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ιπλωµατική Εργασία της ΘΕΟ ΟΣΟΠΟΥΛΟΥ ΕΛΕΝΗΣ ΜΣ:5411 ΠΑΡΑΚΙΝΗΣΗ
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
What happens when two or more waves overlap in a certain region of space at the same time?
 Wave Superposition What happens when two or more waves overlap in a certain region of space at the same time? To find the resulting wave according to the principle of superposition we should sum the fields
Wave Superposition What happens when two or more waves overlap in a certain region of space at the same time? To find the resulting wave according to the principle of superposition we should sum the fields
Homework for 1/27 Due 2/5
 Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2
![If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2 If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2](/thumbs/53/31933086.jpg) Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Mean bond enthalpy Standard enthalpy of formation Bond N H N N N N H O O O
 Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
Q1. (a) Explain the meaning of the terms mean bond enthalpy and standard enthalpy of formation. Mean bond enthalpy... Standard enthalpy of formation... (5) (b) Some mean bond enthalpies are given below.
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΠΕΛΟΠΟΝΝΗΣΟΥ
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΠΕΛΟΠΟΝΝΗΣΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΟΡΓΑΝΙΣΜΩΝ Κατ/νση Τοπικής Αυτοδιοίκησης ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ «Μοντέλα στρατηγικής διοίκησης και
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΠΕΛΟΠΟΝΝΗΣΟΥ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΟΡΓΑΝΙΣΜΩΝ Κατ/νση Τοπικής Αυτοδιοίκησης ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ «Μοντέλα στρατηγικής διοίκησης και
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π 2, π 2
 Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
2. Μηχανικό Μαύρο Κουτί: κύλινδρος με μια μπάλα μέσα σε αυτόν.
 Experiental Copetition: 14 July 011 Proble Page 1 of. Μηχανικό Μαύρο Κουτί: κύλινδρος με μια μπάλα μέσα σε αυτόν. Ένα μικρό σωματίδιο μάζας (μπάλα) βρίσκεται σε σταθερή απόσταση z από το πάνω μέρος ενός
Experiental Copetition: 14 July 011 Proble Page 1 of. Μηχανικό Μαύρο Κουτί: κύλινδρος με μια μπάλα μέσα σε αυτόν. Ένα μικρό σωματίδιο μάζας (μπάλα) βρίσκεται σε σταθερή απόσταση z από το πάνω μέρος ενός
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Potential Dividers. 46 minutes. 46 marks. Page 1 of 11
 Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories
 Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
Schwarzschild spacetime
 SageManifolds. Schwazschild spacetime This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of SageManifolds vesion., as included in SageMath 7.5) in computations egading Schwazschild spacetime. Click hee to download
SageManifolds. Schwazschild spacetime This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of SageManifolds vesion., as included in SageMath 7.5) in computations egading Schwazschild spacetime. Click hee to download
Εγκατάσταση λογισμικού και αναβάθμιση συσκευής Device software installation and software upgrade
 Για να ελέγξετε το λογισμικό που έχει τώρα η συσκευή κάντε κλικ Menu > Options > Device > About Device Versions. Στο πιο κάτω παράδειγμα η συσκευή έχει έκδοση λογισμικού 6.0.0.546 με πλατφόρμα 6.6.0.207.
Για να ελέγξετε το λογισμικό που έχει τώρα η συσκευή κάντε κλικ Menu > Options > Device > About Device Versions. Στο πιο κάτω παράδειγμα η συσκευή έχει έκδοση λογισμικού 6.0.0.546 με πλατφόρμα 6.6.0.207.
