Supplementary material for: Efficient moment calculations for variance components in large unbalanced crossed random effects models
|
|
|
- Ἰσμήνη Κωνσταντόπουλος
- 7 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Supplementay mateal fo: Effcent moment calculaton fo vaance component n lage unbalanced coed andom effect model Katelyn Gao Stanfod Unvety At B Owen Stanfod Unvety Augut 015 Abtact Th a upplementay document contanng poof fo ome eult n the man document The ecton numbe contnue whee that document left off Some contextual mateal epeated fo claty Alo a th a upplementay document, mateal that tadtonally left out a beng tedou algeba ncluded n full detal, makng the numeou tep eae to follow and check 10 Patally obeved andom effect model The andom effect model Y = µ + a + b + e,, N 100 d d d fo a Fa, b Fb and e Fe ndependent of each othe Thee andom vaable have mean 0, vaance σa, σ B, σ E and kutoe κ A, κ B, κ E, epectvely We wll not need the kewnee We ue lette,,, to ndex ow Lette,,, ae ued fo column In ntenet applcaton, the actual ndce may be people atng tem, tem beng ated, cooke, URL, IP addee, quey tng, mage dentfe and o on We mplfy the ndex et to N fo notatonal convenence One featue of thee vaable that we fully expect futue data to bng htheto uneen level That why a countable ndex et appopate We wll want to etmate σa, σ B, σ E and get a fomula fo the vaance of thoe etmate Many, pehap mot, of the Y value ae mng Hee we aume that the mngne not nfomatve Fo futhe dcuon ee Secton 71 of the man document The vaable Z {0, 1} take the value 1 f Y avalable and 0 othewe The total ample ze N = Z We aume that 1 N < We alo need N = Z and N = Z The numbe of unque obeved ow and column ae, epectvely, R 1 N>0, and C 1 N >0 In the um above, only fntely many ummand ae nonzeo When we um ove,,,, the um ove the et { N > 0} Smlaly um ove column ndce,,, ae ove the et { N > 0} Thee ange ae what one would natually get n a pa ove data log howng all ecod We fequently need the numbe of column ontly obeved n two ow uch a and Th Z Z = ZZ T Smlaly, column and ae ontly obeved n Z Z = Z T Z ow The matx Z encode eveal dffeent meauement egme a pecal cae Thee nclude coed degn, neted degn and IID amplng, a follow A coed degn wth an R C matx of completely obeved data can be epeented va Z = 1 1 R 1 1 C If max N = 1 and max N > 1 then the data have a neted tuctue, wth N dtnct ow n column and Z T Z = 0 fo Smlaly 1
2 max N = 1 wth max N > 1 yeld column neted n ow If max N = max N = 1 then we have N IID obevaton We note ome dentte: ZZ T = Z Z = N, and 101 ZZT = Z Z = Z N 10 We need ome notaton fo equalty among ndex et The notaton 1 = mean 1 = 1 = It dffeent fom 1 {,}={,} whch we alo ue Addtonally, 1 mean 1 1 = 11 Weghted U tattc We wll wok wth weghted U-tattc U a = 1 u Z Z Y Y U b = 1 v Z Z Y Y, and U e = 1 w Z Z Y Y, fo weght u, v and w choen below We can wte U a = u N N 1 whee an unbaed etmate of σ B + σ E fom wthn any ow wth N Unde ou model the value n ow ae IID wth mean µ + a and vaance σb + σ E, and o Va = σb + σe N 1 + κb + e N whee κb + e = κ B σ B + κ Eσ E /σ B + σ E the kuto of Y fo the gven and any Thu Va = σ B + σ E N 1 + κ Bσ B N + κ Eσ E N 103 Invee vaance weghtng then ugget that we weght popotonally to a value between N and N 1 Weghtng popotonal to N 1 ha the advantage of zeong out ow wth N = 1 Th condeaton motvate u to take u = 1/N, and mlaly v = 1/N If U e domnated by contbuton fom e then the obevaton ente ymmetcally and thee no eaon to not take w = 1 Even f the e do not domnate, the tattc U e compae moe data pa than the othe It unlkely to be the nfomaton lmtng tattc So w = 1 a eaonable default If the data ae IID then only U e above nonzeo Th appopate a only the um σa + σ B + σ E can be dentfed n that cae Fo data that ae neted but not IID, only two of the U-tattc above ae nonzeo and n that cae only one of σa and σ B can be dentfed epaately fom σ E The U-tattc we ue ae then U a = 1 U b = 1 U e = 1 Z Z Y Y Z Z Y Y, Z Z Y Y Becaue we only um ove wth N > 0 and wth N > 0, ou um neve nclude 0/0 and 10
3 111 Expected U-tattc Hee we fnd the expected value fo ou thee U-tattc Lemma 1 Unde the andom effect model 100, the U-tattc n 10 atfy EU a 0 N R N R σa EU b = N C 0 N C EU e N N N σ B 105 N N N Poof Ft we note that Ea a = σ A1 1 = Eb b = σ B1 1 =, Ee e = σ E1 1 = 1 = Now Y Y = b b + e e, and o EU a = 1 Z Z σ B 1 1 = + σe1 1 = 1 = = σ B + σ E Z Z 1 1 = = σ B + σ E Z 1 1 = and σ E = σ B + σ E N 1 = σ B + σ EN R The ame agument gve EU b = σa + σ E N C The matx n 105 Ou moment baed etmate ae 0 N R N R M N C 0 N C N N N 106 N N N ˆσ A ˆσ B ˆσ E = M 1 They ae only well defned when M nonngula The detemnant of M N R [ N CN N N CN N ] + N R [ N CN N ] U a U b U e 107 = N R [ N C N N ] + N R [ N CN N ] = N RN C[N N N + N] The ft facto potve o long a max N > 1, and the econd facto eque max N > 1 We aleady knew that we needed thee condton n ode to have all thee U-tattc depend on the Y It tll of nteet to know when the thd facto potve It uffcent that no ow o column ha ove half of the data 3
4 1 The vaance Fom equaton 107 we get Va ˆσ A ˆσ B ˆσ E = M 1 Va U a U b U e M 1 whee M gven at 106 So we need the vaance and covaance of the thee U tattc To fnd vaance, we wll wok out EU fo ou U-tattc Thoe nvolve EY Y Y Y = E a a + b b + e e a a + b b + e e [ a = E a + b b + e e + a a b b + a a e e + b b e e a a + b b + e e + a a b b + a a e e + b b e e ] Th expeon nvolve 8 ndce and t ha 36 tem Some of thoe tem mplfy due to ndependence and ome vanh due to zeo mean To hoten ome expeon we ue B A,, Ea a a a D A, Ea a, and, Q A,, Ea a a a wth mnemonc blnea, dagonal and quatc Thee ae mlaly defned tem fo component B Fo the eo tem we have B E,, Ee e e e D E,, Ee e, and, Q E,, Ee e e e The genec contbuton EY Y Y Y to the mean quae of a U-tattc equal Q A,, + Q B,, + Q E,, + D A, D B, + D A, D E,, + D B, D A, + D B, D E,, D E,, D A, + D E,, D B, + B A,, B B,, + B A,, B E,, + B B,, B E,, The othe tem ae zeo 11 Vaance pat Hee we collect expeon fo the quantte appeang n the genec tem of ou quaed U-tattc Lemma In the andom effect model 100, B A,, = A σ 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 =, B B,, = B σ 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 =, and B E,, = E σ 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 =
5 Poof The ft one follow by expandng and ung Ea a = σ A 1 =, et cetea The othe two ue the ame agument Lemma 3 In the andom effect model 100, Poof Take = and = n Lemma D A, = σ A1 1 = D B, = σ B1 1 = D E,, = σ E1 1 = Lemma In the andom effect model 100, Q A,, = 1 1 σ A + κ A + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } Q B,, = 1 1 σ B + κ B + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } Q E,, = 1 1 σ E + κ E + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } Poof We pove the ft one; the othe ae mla Th quantty 0 f = o = When and, thee ae 3 cae to conde: {, } {, } = 0, {, } {, } = 1 and {, } {, } = The kuto defned va κ A = Ea /σ A 3, o Ea = κ A + 3σ A Fo no ovelap, we fnd Fo a ngle ovelap, Fo a double ovelap, Ea 1 a a 3 a = Ea 1 a = σ A Ea 1 a a 1 a 3 = Ea 1 a 1 a + a a 1 a 1 a 3 + a 3 = Ea 1 + 3σ A = σ Aκ A + 6 Ea 1 a = Ea 1 a 1 a 3 + 6a 1a a 3 1a + a = Ea 1 + 6σ A = σ Aκ A + 1 A a eult, σa, {, } {, } = 0, Ea a a a = σa κ A + 6, {, } {, } = 1, σa κ A + 1, {, } {, } =, and o Ea a a a equal 1 1 σa + κ A + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } 1 Vaance of U a We wll wok out EU a and then ubtact EU a Ft we wte U a = 1 Fo EUa we ue the pecal cae = and = of 108, EUa = 1 [ Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Y Y Y Y 5
6 = 1 Q A,, + Q B,, + Q E,, + D A, D B, + D A, D E,, + D B, D A, + D B, D E,, + D E,, D A, + D E,, D B, + B A,, B B,, + B A,,B E,, + B B,, B E,, ] [ Z Z Z Z Q B,, } {{ } Tem 1 + Q E,, Tem + D B, D E,, + D E,, D B, + B B,, B E,, Tem 3 Tem Tem 5 afte elmnatng tem that ae alway 0 We handle thee fve um n the next ububecton 11 U a tem 1 1 = σ B Z Z Z Z Q B,, Z Z Z Z κ B + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } = σ B Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 1 = + κ B + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } 11 1 and 13 1 Tem 1 now a um of fou tem, 11 though 1 Tem 11 σ B tme 1 = + Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z Tem 1 σb κ B + / tme Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z = N N N N + 1 = N R = Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 {, } Z Z Z Z 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = ] 6
7 + = Z Z Z 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = ZZ T Z Z Z 1 = Z Z 1 = ZZ T ZZT + ZZ T ZZ T + ZZ T = ZZ T N The expeon ZZT mplfe to N, changng t fom a ow quantty to a column quantty But the othe pat of th expeon ae equvalent to um of tem uch a Z N makng the column veon le convenent to wok wth Tem 13 the ame a tem 1 by ymmety of ndce Tem 1 σb tme = = = = = Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 1 = 1 {, }={, } Z Z Z Z {, }={, } Z Z Z Z = 1 = Z Z Z Z 1 Z Z Z Z ZZ T ZZ T Z Z Summng tem 11 though 1 yeld σb N R + κ B + ZZ T N + ZZ T ZZ T 1 1 U a tem 1 = σ E = σ E Z Z Z Z Q E,, Z Z Z Z κ E + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } Z Z Z Z 1 1 7
8 1 + κ E + 1 = 1 {, } + 1 {, } and = 1 {, }={, } Tem 1 σ E tme Z Z Z Z 1 1 = N R by the ame poce that evaluated tem 11 Tem σ E κ E + / tme = Z Z Z Z = 1 {, } N Z Z Z Z 1 {, } + N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 {, } N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 {, } N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = 1 {, } whch educe to N Z Z Z Z 1 {, } + = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 {, } N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = + = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = 1 = N Z Z Z N Z Z N Z Z + N Z Z + N Z N Z = N R R + R + 8
9 = N R + = N 1 The lat expeon eemble the dagonal pat of tem 1 Tem 3 the ame the ame a tem Tem σ E tme Z Z Z Z 1 = {, }={, } Th the ame um a the coeffcent n tem 1 ha except that t ha the addtonal contant = Impong = on that quantty yeld N ZZT N ZZT = 1 Tem thu σ E N R + κ E + N U a tem 3 and Thee tem ae equal by ymmety We evaluate tem 3 = 1 1 Z Z Z Z D B, D E,, Z Z D B, Z Z D E,, Now and by the ame tep σb σ E N R Z Z D B, = σ B = σ B Z Z 1 1 = N 1 = σ BN R Z Z D E,, = σe Z Z 1 1 = = σen R Theefoe tem 3 of EU a equal σ B σ E N R and the um of tem 3 and 1 U a tem 5 The tem equal = Z Z Z Z B B,, B E,, Z Z B B,, Z Z B E,, 9
10 Now Z Z B E,, = σ E Z Z 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = = σ E Z Z 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = Tem 5 then σe = σ Eσ B = σ Eσ B σ Eσ B σ Eσ B + σ Eσ B N Z Z Z Z 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = BB,, N Z Z Z Z 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 =, whch we call tem 51, 5, 53 and 5 Next we fnd the coeffcent of σb σ E n thee fou tem Fo tem 51, we get N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = = = N 1 = N R N Z Z Z 1 1= 1 = + 1 = Fo tem 5, we get = = N R N Z Z Z Z 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = N Z Z Z 1= 1 1 = + 1 = a well Tem 53 and 5 ae alo N 1, by the tep ued fo tem 5 and 51 epectvely A a eult tem 5 equal σb σ E N R 13 Combnaton Combnng the eult of the pevou ecton, we have EUa = σb N R + κ B + ZZ T N + ZZ T ZZ T 1 + σ Bσ EN R + σ Bσ EN R 10
11 + σe N R + κ E + N Subtactng EU a = N R σb + σ E we fnd VaU a = σb κ B + ZZ T 1 + σ Bσ EN R + σ E κ E N + N 1 + ZZ T ZZ T Check We can check ome pecal cae of th fomula 11 Row neted n column If fo ntance ow ae neted wthn column, then N = R, and all N = N = 1 and n th cae U a = 0 The above fomula gve VaU a = 0 fo th cae 1 Column neted n ow If column ae neted n ow, then ZZ T = 1 = N and equaton 109 yeld VaU a = σb κ B + N 1 = N + = + σ Bσ EN R + σ E σ Bκ B + + σ Eκ E + = κ B σ B + κ E σ E κ E + N 1 + N 1 + σe N 1 + σe 1 = N N σ Bσ EN R N σ Bσ EN R = κ B σ B + κ E σ E = κ B σ B + κ E σ E N 1 + σe N 1 + σ Bσ EN R N 1 + N Rσ B + σ E 110 When column ae neted n ow, then U a = N 1 and becaue the ow ae then ndependent, U a ha vaance σb + σe N 1 N 1 + κb 1 + e 11 N The kuto of b + e σ B σ κ B+E = κ B + E σb + κe σ E σb + σ E Theefoe fo column neted n ow VaU a = σb + σe N 1 + N 1 σ B σ κ B + E N σb + κe σ E σb + σ E = σ B + σ E N 1 + κ B σ B + κ E σ E N 1 = N Rσ B + σ E + κ B σ B + κ E σ E N 1, matchng the expeon 110 that come fom equaton 109 fo VaU a 11
12 13 σ B = 0 If σb = 0 then VaU a hould be the ame a t fo column neted n ow In th cae equaton 109 educe to VaU a = σe κ E + N κ E = σ E = σ E κ E N 1 + N 1 + N R N If ntead we ft take the column neted n ow pecal cae fom equaton 110 and then ubttute σb = 0, we get the ame expeon 1 σ E = 0 and κ B = In th pecal cae we take σe = 0 and take b U±1 Then σb = 1 and κ B = Then VaU a = σb ZZ T ZZ T 1 = ZZ T ZZ T 1 In th cae U a = 1 = 1 Z Z b b Z Z b b b + b = Z Z 1 b b = N Z Z b b and o VaU a = VaŨa whee Ũa = Z Z b b We ealy fnd that EŨa = Z Z 1 = = 1 = R To get the vaance of Ũa we need Eb b b b = 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = Now EŨ a = = + + Z Z Z Z Eb b b b Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = 1 = 1
13 = = = R + Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z ZZ T ZZ T ZZ T 1 Z Z ZZ T In th cae we get VaŨa = R + ZZ T ZZ T 1 R matchng the eult fom Coed degn In a coed degn N = C fo all and ZZ T = C fo all and Hee the vaance VaU a = σb κ B + C1 C 1 + C 1 C 1 + σe κ E + C1 C C 1 σ EN R = σb κ B + C1 C C 1 R + σe κ E + C1 C C 1 R σ ER 1C Vaance of U b Th cae exactly ymmetc to the one above wth VaU a gven by 109 Theefoe VaU b = σb κ A + Z T Z N + N 1 Z T Z Z T Z 1 + σ E κ E + N Vaance of U e A befoe, we fnd EUe and then ubtact EU e Now U e = 1 Z Z Z Z Y Y Y Y Fom 108, EU e = 1 Z Z Z Z [ Q A,, Tem 1 + Q B,, Tem + Q E,, Tem 3 + D A, D B, + D A, D E,, + D B, D A, + D B, D E,, Tem Tem 5 Tem 6 Tem 7 + D E,, D A, + D E,, D B, Tem 8 Tem 9 13
14 ] + B A,, B B,, + B A,, B E,, + B B,, B E,, Tem 10 Tem 11 Tem 1 We handle the twelve um n the next ubecton 161 U e Tem 1 A befoe, we plt tem 1 nto fou pat 1 Z Z Z Z Q A,, = 1 Z Z Z Z 1 1 σ A + κ A + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } = σ A Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 1 = + κ A + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } 11 1 and 13 1 Fo tem 11, we have σa tme Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = = Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z = N N N N N + N N = N N Tem 1 σa κ A + / tme Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 {, } = Z Z Z Z 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z 1 = + Z Z Z Z 1 = = Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z = N N + N N N N 3 1
15 N N 3 N N 3 + N N N 3 + N = N N N N 3 + N By ymmety of ndce, tem 13 the ame a tem 1 Fo tem 1, we have σ A tme Z Z Z Z {, }={, } = Z Z Z Z =1 = = Z Z Z Z 1 = N N N N 1 1 = = Summng tem 11 to 1 gve σ A N N N N N + 3 N + σaκ A + N N N N 3 + N N 16 U e Tem We can ue the ymmety of the ole of A and B and the ndce Theefoe, tem equal to N N N + 3 N κ B + N N N N 3 + σ B N N 163 U e Tem 3 A befoe, we plt tem 3 nto fou pat 1 Z Z Z Z Q E,, = 1 Z Z Z Z 1 1 σ E = σ E Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 1 = + κ E + 1 {, } + 1 {, } 31 3 and 33 + κ E + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } + 1 {, }={, } 3 15
16 Fo tem 31, we have σe tme Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = = Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + = N N 3 N 3 + N = N N 1 Z Z Tem 3 σ E κ E + / tme Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 {, } = Z Z Z Z 1 = + 1 = 1 =1 = Z Z Z 1 = + 1 = 1 =1 = Z Z Z 1 = + Z Z 1 = = Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z + Z = N 3 + N 3 N N N + N N + N = N 3 N + N = NN 1 By ymmety of ndce, tem 33 the ame a tem 3 Fo tem 3, we have σ E tme Z Z Z Z {, }={, } = Z Z Z Z =1 = = Z Z 1 = NN 1 Summng tem 31 to 3, we get σ ENN 1[NN 1 + ] + σ Eκ E + NN 1 16
17 16 U e Tem 1 = 1 Z Z Z Z D A, D B, Z Z D A, Z Z D B, The ft facto Z Z D A, = σ A Z Z 1 1 = = σan Z Z = σ AN N By the ame agument, the econd facto Z Z D B, = σ BN N, and o tem σ Aσ BN N N N 165 U e Tem 5 1 = 1 Z Z Z Z D A, D E,, Z Z D A, Z Z D E,, The ft facto computed n the pevou ecton The econd facto Z Z D E,, = σ E Z Z 1 1 = Thu, tem 5 = σen Z = σenn 1 σ Aσ ENN 1N N 166 U e Tem 6 By ymmety of ndce, th the ame a Tem : σ Aσ BN N N N 17
18 167 U e Tem 7 Th lke tem 5 wth facto A and B ntechanged Thu, tem 7 equal to σ Bσ ENN 1N N 168 U e Tem 8 By ymmety of ndce, th the ame a tem 5: σ Aσ ENN 1N N 169 U e Tem 9 By ymmety of ndce, th the ame a tem 7: σ Bσ ENN 1N N 1610 U e Tem 10 Z Z Z Z B A,, B B,, = σaσ B Z Z Z Z 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = = σaσ B Z Z Z Z 1 =1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 =1 = + 1 =1 = + 1 =1 = 1 =1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = = σaσ B Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z = σaσ B N 3 N Z N N N N N Z + NN N Z N N + N 3 + N N N N N Z N N N Z + N N + N 3 N Z N N + N N N N N Z N Z N N + N 3 = σaσ B N 3 N Z N N + NN 18
19 1611 U e Tem 11 Z Z Z Z B A,, B E,, = σaσ E Z Z Z Z 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = = σaσ E 1= 1 = 1 = 1 =1 = + 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = + 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 =1 = + 1 =1 = + 1 = 1 =1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = + 1 = = σaσ E Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z = σaσ E Z Z Z Z Z Z = σaσ E N 3 N Z Z Z N Z Z Z Ue Tem 1 We can ue the ymmety wth tem 11, ntechangng ow column Thu, tem 1 σbσ E N 3 N N 17 Combnaton Summng up the eult of the pevou twelve ecton, we have EUe = σan σan N + 3σA N σ A N + σaκ A + N N N N 3 + N σbn N + 3σB N σ B N κ B + N N N N σe N N 3 + 3N N + σeκ E + NN 1 + σaσ BN NN N N N + σ Aσ ENN 1N N + σ Aσ BN N N N σ ENN 1N N + σaσ ENN 1N N σ ENN 1N N + σaσ B N 3 N Z N N + NN + σaσ E N 3 N N + σ B σ E N 3 N N Then, we have VaU e = EU e EU e 19
20 = EU e σ AN N σ BN N σ EN N σ Aσ BN N N N σ Aσ ENN 1N N σ Bσ ENN 1N N = σa N σ A N + σaκ A + N N N N 3 + N N σ B N κ B + N N N N σen N + σeκ E + NN 1 + σaσ B N 3 N Z N N + N N N + σaσ E N 3 N N + σ B σe N 3 N N Next, we mplfy the fom of th expeon The coeffcent of κ A + σ A N N N N 3 + N = N N N and mlaly fo that of κ B The coeffcent of κ E + σe NN 1 The emanng multple of σa N N and mlaly fo σb The emanng multple of σ E NN 1 The coeffcent of σ A σ B N 3 N Z N N + NN = NN NZ N N + N Z becaue N Z = N 3 Theefoe the coeffcent of σ A σ B N N NZ Applyng thee mplfcaton VaU e = σa N N N N + σ ENN 1 + κ A + σa NN N + κ B N N N + κ E + σenn 1 + σaσ B N N NZ + σaσ EN N N + σ B σ EN N The coeffcent of σa σ B a meaue of how cloe to a egula R C gd the data ae 18 Check 181 σ A = σ B = 0 If σ A = σ B = 0 then Y ae IID wth vaance σ E and kuto κ E Then U e = 1 Y Y = NN 1 e 0 N 113
21 whee e the uual ample tandad devaton appled to all N of the Y Thu VaU e = σen N 1 N 1 + κ E = σ N E N N 1 + κ E NN 1 Subttutng σ A = σ B = 0 n VaU e fom Secton 17 yeld σen N + σeκ E + NN 1 = N N 1σE + NN 1 κ E σe whch matche the fomula Equaton 113 become VaU e = σenn 1 + κ E + σenn 1 whch alo matche 18 IID amplng If max N = max N = 1, then the obevaton ae IID wth vaance σ Y = σ A + σ B + σ E and kuto κ Y = κ AσA + κ BσB + κ EσE σy Now U e NN 1 tme the ample tandad devaton of all N obevaton Thu VaU e = N N 1σ Y + NN 1 κ Y σ Y = N N 1σ A + σ B + σ E + σ Aσ B + σ Aσ E + σ Bσ E + NN 1 κ A σ A + κ B σ B + κ E σ E 11 In th cae, the fomula gve σ A + σ B N σ A N σ B N + σaκ A + N N κ B + N + σ EN N + σ Eκ E + NN 1 + σ Aσ B N N N 3 + N N N 3 N N N 3 + N Z N N + N N + σaσ E N 3 N N + σ B σe N 3 N N If we et all potve N = 1 and all potve N = 1 then N = N becaue thee ae now R = N ow n the data Smlaly N 3 and N um to N and thee powe of N alo um to N Next Z N N = Z = N The mot ubtle of thee um N N = 1 = N becaue the ndce un ove all wth N > 0 and all wth N > 0 Makng thee ubttuton we get VaU e = σ AN σ AN + σ Aκ A + N 3 N + N + σ BN σ BN + σ Bκ B + N 3 N + N + σ EN N + σ Eκ E + NN 1 + σ Aσ BN 3 N + N + σaσ EN 3 N σ EN 3 N = σa N N + NN 1 N N + NN 1 + σe NN 1 + NN 1 + σaσ BN N 1 1
22 whch matche equaton 11 Equaton 113 gve VaU e = σ A + σ Aσ EN N 1 + σ Bσ EN N 1 + NN 1 κ A σ A + κ B σ B + κ E σ E = N N 1σA + σe + N N 1 σaσ B + σaσ E + σaσ E + NN 1 κ A σa + κ B σb + κ E σe N N N N + σ ENN 1 + κ A + σa NN N + κ B N N N + κ E + σenn 1 + σaσ B N N NZ + σaσ EN N = σ AN N + σ BN N + σ ENN 1 N + σ B σ EN N + κ A + σ ANN 1 + κ B + σ BNN 1 + κ E + σ ENN 1 + σ Aσ BN N 1 + σ Aσ ENN N + σ Bσ ENN N 183 IID amplng agan If max N = 1 and σb = 0, then once agan the obevaton ae IID and The fomula gve VaU e = σ A VaU e = N N 1σ Y + NN 1 κ Y σ Y = N N 1σ A + σ B + σ E + σ Aσ B + σ Aσ E + σ Bσ E + σ B N + NN 1 κ A σ A + κ B σ B + κ E σ E N = N N 1σ A + σ E + σ Aσ E + NN 1 κ A σ A + κ E σ E 115 σ A N σ B N + σaκ A + N N κ B + N + σ EN N + σ Eκ E + NN 1 + σ Aσ B N N N N N 3 N N 3 + N N 3 + N Z N N + N N + σaσ E N 3 N N + σ B σe N 3 N N = σ A N σ A N + σaκ A + N N N + σ EN N + σ Eκ E + NN 1 + σ Aσ EN 3 N N 3 + N N = σan σan + σaκ A + N 3 N + N + σen N + σeκ E + NN 1 + σaσ EN 3 N = N N 1σA + σe + σaσ E + NN 1 κ A σa + κ E σe, matchng 115
23 13 Covaance of U a and U b We ue the fomula CovU a, U b = EU a U b EU a EU b, o we ut need to compute EU a U b Ung ou pefeed nomalzaton, Then, U a U b = 1 = 1 EU a U b = 1 We conde each tem epaately 131 U a U b Tem 1 Fo 11, we have 1 = σ E Z Z Y Y Z Z Y Y Z Z Z Z Y Y Y Y Z Z Z Z QE,, Tem 1 + D B, D A, + D B, D E,, + D E,, D A, Tem Tem 3 Tem Z Z Z Z Q E,, Z Z Z Z κ E + 1 {, } + 1 {, } + 1 {, }={, } = σ E N 1 Z Z Z Z κ E + 1 {, } + 1 {, } 11 1 and 13 σe = σe Z Z Z Z 1 1 = σe N = σ E N R N C Z Z 1 1 = Z Fo 1, we have σe κ E + / tme Z Z Z Z {, } = = Z Z Z Z = Z Z Z 1 1 N + 1 {, }={, } 1 Z Z 1 1 = Z 3
24 = Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = = Z Z = Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z + Z = Z N Tem 13 the ame a 1 by ymmety of ndce Fo 1, we have σe Z Z Z Z {, }={, } = 0, nce the lat ndcato mple = and = but the econd one 1 Summng up, tem 1 equal to σe N R N C + σ E κ E + Z N = σe N R N C + σ E κ E + N R C + Z 13 U a U b Tem U a U b Tem 3 = 1 = σaσ B Z Z Z Z D B, D A, Z Z Z Z σb1 1 = σa1 1 = = σaσ B N = σ Aσ B N R N C 1 ung the pevou ecton 13 U a U b Tem Z Z 1 1 = Z N Z Z Z Z D B, D E,, = 1 = σbσ E N R N C 1 Z Z 1 1 = Z Z Z Z Z σb1 1 = σe1 1 = Z Z Z Z D E,, D A,
25 ung the pevou ecton = 1 N 1 Z Z Z Z σe1 1 = σa1 1 = = σaσ E N R N C 135 Combnaton Addng up the fou tem, we have EU a U b = σe N R N C + σ E κ E + Z N + σ Aσ B N R N C + σ B σ E N R N C + σ A σ E N R N C, and o CovU a, U b = EU a U b EU a EU b = EU a U b σb + σeσ A + σen RN C = σ Eκ E + Z N Notce that CovU a, U b = 0 when σ E = 0 Th can be vefed by notng that when σ E = 0 then U a a functon only of a whle U b a functon only of b Theefoe U a and U b ae ndependent when σ E = 0 1 Covaance of U a and U e We ue the fomula CovU a, U e = EU a U e EU a EU e, o we ut need to compute EU a U e Ft, U a U e = 1 Z Z Y Y Z Z Y Y = 1 Z Z Z Z Y Y Y Y Then, EU a U e = 1 Z Z Z Z QB,, + Q E,, + D B, D A, + D B, D E,, Tem 1 Tem Tem 3 Tem + D E,, D A, + D E,, D B, + B B,, B E,, Tem 5 Tem 6 Tem 7 We conde each tem epaately 11 U a U e Tem 1 1 Z Z Z Z Q B,, = 1 Tem 11 equal to σb tme Z Z Z Z 1 1 σ B + κ B + 1 {, } + 1 {, } 11 1 and 13 Z Z Z Z {, }={, } 1
26 = Z Z 1 1 = Z Z 1 1 = = N Z N Z Z = N R N N Tem 1 equal to σb κ B + / tme Z Z Z Z {, } = Z Z Z Z = = = Z Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 1 = = N = N Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z N N Z Z Z + Z N N Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z N N Z Z Z N + Z N = = Z NN N Z N N N 1 N N + N Tem 13 equal to tem 1 by ymmety of ndce Tem 1 equal to σb tme Z Z Z Z {, }={, } = Z Z Z Z =1 = = Z Z Z Z 1 1 = = Z Z N N = Z N Z Z Z Z N Summng the fou tem, we fnd that tem 1 equal to σb N R N N + σ B Z N Z N + σ Bκ B + Z N N N 1 6
27 1 U a U e Tem Fo 1, we get σ E tme 1 Z Z Z Z Q E,, = 1 Z Z Z Z 1 1 σ E + κ E + 1 {, } + 1 {, } 1 and 3 Fo, we get σe κ E + / tme Z Z Z Z 1 1 = NN 1 Z Z 1 1 = = NN 1 N = NN 1N R Z Z Z Z Z {, } = Z Z Z Z = = = = N Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 1 = + 1 {, }={, } Z Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = N N = N NR N + R = N RN 1 Z Z Z + Z Tem 3 the ame a by ymmety of ndce Fo tem, we get σe tme Z Z Z Z {, }={, } = Z Z Z Z =1 = = Z Z 1 = N Z = N R Addng up the fou tem, we fnd that tem equal σ ENN 1N R + σ EN R + σ Eκ E + N RN 1 7
28 13 U a U e Tem 3 1 Z Z Z Z D B, D A, = 1 = σ Aσ B Z Z Z Z σ B1 1 = σa1 1 = Z Z 1 1 = = σaσ B N = σaσ B N R N Z Z Z 1 1 = N Z Z N 1 U a U e Tem 1 Z Z Z Z D B, D E,, = 1 = σ Bσ E 15 U a U e Tem 5 Z Z Z Z σ B1 1 = σe1 1 = 1 = Z Z 1 1 = = σbσ E N R N Z = σbσ E N R N N 1 Z Z Z Z D E,, D A, = 1 = σ Aσ E Z Z 1 1 = 1 = Z Z Z Z σ E1 1 = σa1 1 = Z Z 1 1 = = σaσ E N R N N Z Z 1 1 = ung the eult fo tem 3 16 U a U e Tem 6 1 Z Z Z Z D E,, D B, = 1 = σ Bσ E Z Z Z Z σ E1 1 = σb1 1 = Z Z 1 1 = 8 Z Z 1 1 =
29 = σbσ E N R N Z Z = σbσ E N R N N 17 U a U e Tem 7 Z Z Z Z B B,, B E,, = Z Z Z Z σ B 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = σe 1= 1 = 1 = + 1 = = σbσ E Z Z Z Z 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 =1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = + 1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = = σbσ E + = σbσ E N 1 =1 = + 1 =1 = + 1 = 1 =1 = + 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = 1 = + 1 = Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z + Z Z Z + = σbσ EN N = σbσ ENN R 18 Combnaton Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z N 1 Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z + Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z We add up the even tem, eplacng ome N and N expeon by equvalent ung N and N, gettng EU a U e = σb N R N + σ Bκ B + N + σ B Z N N N 1 Z N + σenn 1N R + σen R + σeκ E + N RN 1 + σaσ B N R N N + σ B σ E N R N N N + σaσ E N R N + σ Bσ ENN R N + σ B σe N R N Z N 9
30 Now EU a EU e = N RσB + σe σan N + σ BN N + σen N whch contan tem equallng eveal of thoe n EU a U e above Subtactng thoe tem fom EU a U e yeld CovU a, U e = σ B + σ Bκ B + Z N Z N Z N N N 1 + σ EN R + σ Eκ E + N RN 1 + σ Bσ ENN R 15 Covaance of U b and U e By ntechangng the ole of the ow and column n CovU a, U e, we fnd that CovU b, U e = σ A + σ Aκ A + Z N Z N Z N N N 1 + σ EN C + σ Eκ E + N CN 1 + σ Aσ ENN C 16 Aymptotc appoxmaton: poof of Theoem We uppoe that the followng nequalte all hold N ɛn, N ɛn, R ɛn, C ɛn, N ɛ N, N ɛ N, N ɛn, and N ɛn fo the ame mall ɛ > 0 The ft x nequalte ae aumed n the theoem tatement The lat two follow fom the ft two We alo aume that 0 < m κ A +, κ B +, κ E +, σ A, σ B, σ E m < Note that we can bound σa σ B, σ A σ E, and σ A σ B away fom 0 and unfomly wth thoe othe quantte afte eplacng m by mnm, m and m by maxm, m We alo uppoe that Z N ɛ N, and Z N ɛ N 116 The bound n 116 eem eaonable but t appea that they cannot be deved fom the ft eght bound above We begn wth the coeffcent of σ B κ B + n VaU a fom equaton 1 It ZZ T 1 + = N Z N + Z 30
31 = N 1 + Oɛ The thd, fouth and ffth tem n VaU a ae all Oɛ The econd tem contan ZZ T ZZ T 1 ZZT = Z Z = Z N = Oɛ It follow that VaU a = σb κ B + N 1 + Oɛ Smlaly VaU b = σa κ A + N 1 + Oɛ The expeon fo VaU e contan tem σa κ A +N N +σ B κ B +N N All othe tem ae Oɛ tme thee two, motly though N N, N N The coeffcent of σa σ B contan N Z N N ɛn Z N = ɛn N o t of malle ode than the lead tem, a well a N N ɛn A a eult VaU e = σ Aκ A + N N N + σ Bκ B + N N 1 + Oɛ Tunng to the covaance CovU a, U b = σ Eκ E + Z 1 + = σ Eκ E + N R C + OR = σ Eκ E + N1 + Oɛ Next CovU a, U e contan the tem σb κ B + N Z N = σb κ B + N N The tem appeang afte that one ae ON = OɛN N The laget tem pecedng t domnated by Z N ɛn Z N Z N = ɛn It follow that CovU a, U e = σb κ B + N N 1 + Oɛ and mlaly, CovU b, U e = σa κ A + N N 1 + Oɛ Next, ung 19 Vaˆσ A VaUe = N + VaU a N CovU a, U e N Oɛ = σaκ A + 1 N N1 + Oɛ, and mlaly Vaˆσ B = σbκ B + 1 N N 1 + Oɛ The lat vaance Vaˆσ E VaUa = N + VaU b N + VaU e N N 3 CovU a, U e N 3 CovU b, U e + N CovU a, U b 1 + Oɛ 31
32 = σeκ E Oɛ N Next we vefy that thee vaance etmate ae aymptotcally uncoelated facto we have Covˆσ A, ˆσ B = 1 N VaU e 1 N 3 CovU b, U e 1 N 3 CovU a, U e + 1 N CovU a, U b = 1 N σaκ A + N κ B + N 1 N σ Aκ A + = 1 N σ Eκ E + whch Oɛ tme Vaˆσ A and Vaˆσ B Lkewe N 1 N σ Bκ B + N + 1 N σ Eκ E + Ignong the 1 + Oɛ Covˆσ A, ˆσ E = 1 N 3 CovU a, U e + 1 N 3 CovU b, U e 1 N VaU e 1 N VaU a 1 N CovU a, U b + 1 N 3 CovU a, U e = σbκ B + N N + σaκ A + 1 N N σaκ A + N κ B + 1 N N σbκ B + 1 N N σeκ E + 1 N = σ Eκ E + 1 N whch much malle than Vaˆσ A Smlaly Covˆσ B, ˆσ E = σe κ E + /N, much malle than Vaˆσ B 17 Etmatng Kutoe To etmate the kutoe κ A, κ B and κ E n the above vaance expeon, t uffce to etmate fouth cental moment uch a µ A, = σa κ A + 3 and mlaly defned µ B, and µ E, Gven ˆσ A, ˆσ B, and ˆσ E, we can do th va GMM Conde the followng etmatng equaton and the expectaton, W a = 1 1 Z Z Y Y N W b = 1 1 Z Z Y Y N W e = 1 Z Z Y Y Ung pevou eult, EW a = 1 1 Z Z E[Y Y N = 1 1 Z Z E b b + e e N = 1 = 1 1 N Z Z E b b + 6b b e e + e e 1 N Z Z µb, + 6σB σ E + µ E, + 6σE 1 1= 3
33 = 1 Z Z µb, + 3σB + 1σ N Bσ E + µ E, + 3σ E 1 1= = κb + 3σB + 1σBσ E + κ E + σe + 3σE N 1 = N R µ B, + 3σB + 1σBσ E + µ E, + 3σE By ymmety, EW b = N C µ A, + 3σA + 1σAσ E + µ E, + 3σE Next EW e = 1 Z Z E Y Y = 1 Z Z E a a + b b + e e = 1 Z Z E a a + 6a a b b + 6a a e e + b b + 6b b e e + e e = 1 Z Z µa, + 6σA1 1 = + σaσ B1 1 = 1 1 = + σaσ E1 1 = + µ B, + 6σB1 1 = σ E1 1 = + µ E, + 6σE1 1 = 1 = = µ A, + 3σA + 1σAσ E Z Z 1 1 = + µ B, + 3σB + 1σBσ E Z Z 1 1 = + µ E, + 3σE Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1σ AσB Z Z 1 1 = 1 = + 1 = 1 = = µ A, + 3σA + 1σAσ EN Z Z + µ B, + 3σB + 1σBσ EN Z Z + µ E, + 3σ ENN 1 + 1σ Aσ BN Z Z Z Z + N = µ A, + 3σ A + 1σ Aσ EN N + µ B, + 3σ B + 1σ Bσ EN N + µ E, + 3σ ENN 1 + 1σ Aσ BN N N + N Thee expectaton ae all lnea n the fouth moment Theefoe, gven etmate of σa, σ B, and σ E, we can olve anothe thee-by-thee ytem of equaton to get etmate of the fouth moment Lettng M be the matx n equaton 106 we fnd that whee EW a EW b = M EW e µ A, µ B, µ E, 3N RσB + 1N Rσ B σ E + 3N Rσ E + 3N CσA + 1N Cσ A σ E + 3N Cσ E H H = 3σ A + 1σ Aσ EN N + 3σ B + 1σ Bσ EN N + 3σ ENN 1 + 1σ Aσ BN N N + N Fo plug-n method of moment etmato we eplace expected W -tattc by the ample quantte, eplace the vaance component by the etmate and olve the matx equaton gettng ˆµ A, et cetea Then ˆκ A = ˆµ A, /ˆσ A 3 and o on 33
34 18 Bet lnea pedcto Hee we pedct conde lnea pedcton of Y We begn wth pedcton of the fom Ŷ = Ŷλ = λ Z Y Then we conde pedcton of a educed fom that conde only the total n ow, n ow and n the whole data et 181 Poof of Lemma 51 Let Ŷ = Z λ Y and L = EY Ŷ Then L = µ 1 λ Z + VaY + VaŶ CovY, Ŷ Ft VaY = σa + σ B + σ E Next CovY, Ŷ = λ Z σ A 1 = 1 = + σ E1 = 1 = = σa λ Z λ Z + σeλ Z, and fnally VaŶ = λ λ Z Z σ A 1 = 1 = + σe1 = 1 = = σa λ λ Z Z λ λ Z Z + σe λ Z Thu L = µ 1 λ Z + σ A + σe + σa λ λ Z Z λ λ Z Z + σe σa λ Z λ Z + σeλ Z λ Z Now uppoe that we conde the lo L = Eµ + a + b Ŷ To do o we eplace VaŶ and CovY, Ŷ above by Vaa + b and Cova + b, Ŷ epectvely, yeldng 18 Statonay condton L = µ 1 λ Z + σ A + σa λ λ Z Z λ λ Z Z + σe σa λ Z λ Z λ Z The patal devatve of L wth epect to λ µ 1 λ Z Z + σ Eλ Z + σa Z Z λ 1 = + λ 1 = 3
35 Z Z λ 1 = + λ 1 = σa Z 1 = σ B Z 1 = Afte takng account of the ndcato functon we get Z µ 1 λ Z 1 + σeλ + σ A σaz 1 = σbz 1 = Z λ + σ B Z λ We can eplace Z 1 = by 1 = becaue of the leadng facto Z Th and a coepondng change to the coeffcent of σb yeld Z µ 1 λ Z 1 + σeλ + σ A Z λ + σ B Z λ σa1 = σb1 = The mplfed expeon no longe eque the double pme and o we fnd that the patal devatve of L wth epect to λ Z µ λ Z 1 + σeλ + σa Z λ Z λ σa1 = σb1 = 183 Poof of Lemma 5 Hee we conde Ŷ = λ 0 Y + λ a Y + λ b Y whee Y = Z Y, Y = Z Y, and Y = Z Y The mean quaed eo L = EY Ŷ Expandng t we get L = µ 1 λ 0 N + λ a N + λ b N + VaY + λ 0VaY + λ avay + λ bvay λ 0 CovY, Y λ a CovY, Y λ b CovY, Y + λ 0 λ a CovY, Y + λ 0 λ b CovY, Y + λ a λ b CovY, Y A befoe VaY = σa + σ B + σ E We et about fndng the othe tem Ft VaY = σa N N + σen, Second VaY = σ AN + σ BN + σ EN, VaY = σ AN + σ BN + σ EN and CovY, Y = σ AN + σ BN + σ EZ, CovY, Y = σ AN + σ BZ + σ EZ, CovY, Y = σ AZ + σ BN + σ EZ and The emanng tem ue omewhat longe agument CovY, Y = Z Z CovY, Y 35
36 = Z Z 1= σa + 1 = σb + 1 = 1 = σ E = σan Z N + σen, CovY, Y = σa Z N N + σen and then by ymmety Fnally CovY, Y = Combnng thee pece we fnd that Z Z CovY, Y = Z Z σ A 1 = 1 = + σ E1 = 1 = = σa Z Z Z Z + σez = Z σ A N + σ BN + σ E L = µ 1 λ 0 N λ a N λ b N + σ A + σ B + σ E + λ 0 σ A N N + σen + λ a σan N + σen + λ b σan N + σen λ 0 σan N + σez λ a σan Z + σez λ b σaz N + σez + λ 0 λ a σ AN + σ B + λ a λ b Z σ AN + σ BN + σ E Z N + σ EN + λ 0 λ b σ A Z N N + σen Now uppoe we conde ntead L = Eµ + a + b Ŷ Then we mut eplace VaŶ by Vaµ + a + b = σa + σ B and emove the σ E Z tem fom the covaance wth Y The eult L = µ 1 λ 0 N λ a N λ b N + σ A + λ0 σa N N + σen + λ a σan N + σen + λ b σan N + σen λ 0 σan N λ a σan Z λ b σaz N + λ 0 λ a σan Z N + σen + λ 0 λ b σa Z N N + σen + λ a λ b Z σ AN + σ BN + σ E 18 Poof of Theoem 51 Fom the eult of Lemma 5, we ee that L quadatc n λ Snce L bounded below by 0, t follow that L attan t mnmum on R 3, whch would be any oluton of the tatonaty condton λ L = 0 We fnd the component of th gadent 1 L = Nµ λ 0 N + λ a N + λ b N 1 + λ 0 σa N N + σ λ EN σan N 0 + λ a σan Z N + σen + λ b σa Z N N + σen 36
37 1 L = N µ λ 0 N + λ a N + λ b N 1 + λ a λ a + λ 0 σan σan N + σen σan Z Z N + σ EN + λ b Z σ AN + σ BN + σ E, and 1 L = N µ λ 0 N + λ a N + λ b N 1 + λ b σ λ AN N + σen σaz N b + λ 0 σa Z N N + σen + λ a Z σan N + σe whee We wte th a Hλ = c Nµ + σa N N N N N c = N µ + σa N Z = N N Z N µ + σa Z N N Z N and H a ymmetc matx wth uppe tangle H = H 11 H 1 H 13 H H 3 H 33 µ σa σb wth element H 11 = µ N + σa N N + σen H 1 = µ NN + σan Z N + σen H 13 = µ NN + σa Z N N + σen H = µ N + σ AN + σ BN + σ EN H 3 = µ N N + σ AZ N + σ BZ N + σ EZ, H 33 = µ N + σ AN + σ BN + σ EN and Ung T Z N and T Z N ome of thee mplfy: H 1 = µ NN + σ AN + σ BT + σ EN, H 13 = µ NN + σ AT + σ BN + σ EN and 185 Poof of Theoem 5 To begn wth, we note that N = Z N Z ɛn We wte λ 0 = 1 H33 H 13 c1 det H H 31 H 11 c 3 Then λ b det Hλ 0 = H 33 c 1 H 13 c 3 = N µ N + σa N + σenµ + N σb µ NN + σa Z N N + σen N µ = µ µ NN + σann NN + σenn µ NN σan Z N σbn 3 σen 37
38 µ N 3 + σan N 3 + σen µ NN σan Z N σbn 3 σen = µ σann NN + σenn σan Z N σbn 3 σen + σ B µ N 3 + σ AN µ NN σ AN Z N = µ σann + σenn σan Z N σen + σ B σ AN σ AN Z N = µ σ A + σ ENN 1 + Oɛ and det Hλ b = H 11 c 3 H 31 c 1 = µ N + σa N N + σenn µ µ NN + σa Z N N + σen Nµ + N σb = µ µ N N + σan N N N + σenn µ N N σan Z N σbnn σenn µ N N + σan N N N + σenn µ NN σan Z N σbn 3 σen = µ σan N N N σan Z N σbnn µ N N + σan N N N + σenn µ NN σan Z N σbn 3 σen = µ σ BN N 1 + Oɛ Thu Next λ 0 λ b = σ A + σ E σb N 1 + Oɛ det H = H 11 H 33 H13 = µ N + σa N N + σen µ N N + σan + σen µ NN + σa µ N N µ + σ B µ NN = µ N N σ B N Z N + σen A a eult the pedcton fo a new ow n a lage column eentally that column aveage plu O1/N tme the global aveage 38
39 186 Specal cae N = 0 and N = 1 Now uppoe that we have no data n the taget ow and exactly one olde obevaton n the taget column Let be the ngle ow wth Z = 1 Thee ae enough lage ow and column that the uual condton N N N hold but thee ae alo ome lghtly obeved ow and column Then c = N µ σa σb = Nµ + σ B µ + σ B, and H 11 = µ N + σa N N + σen H 13 = µ NN + σa Z N N + σen = µ N + σ AN + σ B + σ E, and H 33 = µ N + σ AN + σ BN + σ EN = µ + σ A + σ B + σ E Then λ 0 1 H33 H λ = 13 Nµ + σ b H 11 H 33 H13 B H 13 H 11 µ The detemnant µ N + σa N N + σen µ + σa + σe µ N + σan + σe µ N µ + σ A + σ B + σ E = µ N σ A + σ B + σ E The numeato fo λ 0 µ N H 33 Nµ + σ B H 13 µ + σ B µ + σ A + σ B + σ ENµ µ Nµ + σ B = σ A + σ ENµ, and o Smlaly, the numeato fo λ b λ 0 1 σa + σ E N σa + σ B + σ E H 13 Nµ + σ B + H 11 µ + σ B µ NNµ + µ N µ + σ B = µ σ BN and o In th cae, the pedcton fo Y σ B λ b σa + σ B + σ E σb Y + σa + σ E Y σa + σ B + σ E 39
40 19 Aymptotc weght: poof of Theoem 53 Hee we have 1 N ɛn, 1 N ɛn, N ɛn, N ɛn, N ɛn, N ɛn, N ɛn, N Z ɛnn, and N Z ɛnn The ft fve follow ealy fom 1 < 1/ɛ N, N ɛn The lat fou follow fom the othe Fo ntance N N ɛn = ɛn, and N Z Z ɛn = ɛn N We alo have 0 < m µ, σa, σ B, σ E M < Then µ N µ NN µ NN H = µ NN µ + σa N µ N N 1 + Oɛ µ NN µ N N µ N and ung ymbolc computaton va Wolfam Alpha, Septembe 6, 015 µ σa + σ B + σ A σ B 1 1 σa σ B µ N σa N N σb N N H 1 = 1 1 σa N N σa N Oɛ 1 1 σb N 0 N σb N The detemnant of H 1 σa σ B µ N N N Oɛ, o we need N 1 and N 1 to make matx nveon a contnuou opeaton Smlaly Nµ c = N µ + σa 1 + Oɛ N µ Thu gnong the Oɛ tem λ 0 = µ σa + σ B + σ A σ B σa σ B µ N Nµ 1 σ A N N N µ + σa 1 σ B N N N µ + σ B = µ σ A + σ B + σ A σ B σ A σ B N µ + σ A σ A N µ + σ B σ B N = µ σ A + σ B + σ A σ B σ A σ B N = 1 N µ σ B + σ A σ B σ A σ B N µ σ A + σ B σ B σ A σ B N The end eult 1/N of the ame ode of magntude a the ognal tem Theefoe λ 0 = 1/N1 + Oɛ Smlaly λ a 1 = σa N N Nµ + 1 σa N N µ + σa = µ σ A N + µ + σa σa N = 1 N and λ b = 1, N and both of thee appoxmaton nvolve multplcaton by 1 + Oɛ In th lmt then whch make ntutve ene a ˆµ + â + ˆµ + ˆb ˆµ Ŷ = Y 1 + Oɛ + Y 1 + Oɛ Y 1 + Oɛ 0
41 0 Smoothng pedcto In ome cae we may want a bette etmate of EY than Y telf Such a pedcto could take the fom Ŷ = Ŷλ = λ 0 Z Y + λ a Z Y + λ b Z Y + λ ab Z Y 117 It put ethe exta o educed weght on Y telf, dependng on the gn of λ ab Th pedcto only ueful when Z = 1, o t doe not apply n the new ow o new column cae ethe It only nontval when ou goal to etmate µ + a + b, not Y telf So we only conde L = EŶ µ a b hee Lemma 5 The MSE fo the lnea pedcto 117 L = µ 1 λ 0 N λ a N λ b N + σ A + λ0 σa N N + σen + λ a σan N + σen + λ b σan N + σen λ 0 σan N λ a σan Z λ b σaz N + λ 0 λ a σan Z N + σen + λ 0 λ b σa Z N N + σen + λ a λ b Z σ AN + σ BN + σ E Poof Th poblem only ae when Z = 1, whch we aume fo the et of th ecton Then EỸ µ + a + b = EŶ + λ ab Y µ + a + b = L + λ abey + λ ab EY Ŷ λ ab EY µ + a + b Now EY µ + a + b = µ + σ A + σ B and EY Ŷ = µ Nλ 0 + N λ a + N λ b + CovY, Ŷ fo CovY, Ŷ = CovY, λ 0 Y + λ a Y + λ b Y = λ 0 σ A N + σ BN + σ EZ + λa σ A N + σ BZ + σ EZ + λb σ A Z + σ BN + σ EZ = λ 0 σ A N + σ BN + σ E + λa σ A N + σ BZ + σ E + λb σ A Z + σ BN + σ E, nce we aume that Z = 1 Theefoe EỸ µ a b equal µ 1 λ 0 N λ a N λ b N + σ A + λ 0 σa N N + σen + λ a σan N + σen + λ b σan N + σen λ 0 σan N λ a σan λ b σa N + λ 0 λ a σan Z N + σen + λ 0 λ b σa Z N N + σen + λ a λ b σan N + σe + λ abµ + σa + σe + λ ab λ 0 σ A N N + σe + λa σ A N + σe + λb σ A N + σe λ ab µ + σ A + σ B + µ λ ab Nλ 0 + N λ a + N λ b Gatheng up the coeffcent of µ we get µ 1 λ 0 N λ a N λ b N λ ab + σ A + σ B + λ 0 1 σ A N N + σen
42 + λ a σan N + σen + λ b σan N + σen λ 0 σan N λ a σan λ b σa N + λ 0 λ a σan Z N + σen + λ 0 λ b σa Z N N + σen + λ a λ b σan N + σe + λ abσa + σe + λ ab λ 0 σ A N N + σe + λa σ A N + σe + λb σ A N + σe λ ab σ A + σ B Half of the devatve of th quaed eo wth epect to λ ab λ ab µ + σa + σe + λ 0 σ A N N + σe + λa σ A N + σe + λb σ A N + σe µ σ A σ B + µ Nλ 0 + N λ a + N λ b We ee that gven the othe λ choce, th devatve deceang at 0 hence we favo potve elf-weght f µ +σ A+σ B > λ 0 Nµ +σ AN +σ BN +σ E +λa N µ +σ AN +σ B +σ E +λb N µ +σ A+σ BN +σ E Futhemoe, the optmal elf-weght, gven the othe λ 1 µ + σ A + σ B + σ E µ + σa λ 0 Nµ + σan N + σe λ a N µ + σ AN + σ B + σ E λb N µ + σ A + σ BN + σ E The pont of th pedcto that we mght expect anothe obevaton to be made late n ow and column Then etmatng µ + a + b a bette way to pedct than epeatng the eale Y To ue Lemma 5 afte a econd pa, one can compute L a the gven quadatc functon n the fou vaable λ 0, λ a, λ b and λ ab The mnmze of that quadatc gve weght to apply n pedcton When σe vey mall then Y aleady cloe to µ + a + b and placng pecal weght on Y wll be advantageou
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών. ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος. ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης. εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων.
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 2015 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 1. 1. Consder the gven expresson for R 1/2 : R 1/2
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 2015 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 1. 1. Consder the gven expresson for R 1/2 : R 1/2
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
Multi-dimensional Central Limit Theorem
 Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t tme
Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t tme
Multi-dimensional Central Limit Theorem
 Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t ();
Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t ();
Approximate System Reliability Evaluation
 Appoximate Sytem Reliability Evaluation Up MTTF Down 0 MTBF MTTR () Time Fo many engineeing ytem component, MTTF MTBF i.e. failue ate, failue fequency, f Fequency, Duation and Pobability Indice: failue
Appoximate Sytem Reliability Evaluation Up MTTF Down 0 MTBF MTTR () Time Fo many engineeing ytem component, MTTF MTBF i.e. failue ate, failue fequency, f Fequency, Duation and Pobability Indice: failue
1 Complete Set of Grassmann States
 Physcs 610 Homework 8 Solutons 1 Complete Set of Grassmann States For Θ, Θ, Θ, Θ each ndependent n-member sets of Grassmann varables, and usng the summaton conventon ΘΘ Θ Θ Θ Θ, prove the dentty e ΘΘ dθ
Physcs 610 Homework 8 Solutons 1 Complete Set of Grassmann States For Θ, Θ, Θ, Θ each ndependent n-member sets of Grassmann varables, and usng the summaton conventon ΘΘ Θ Θ Θ Θ, prove the dentty e ΘΘ dθ
Analytical Expression for Hessian
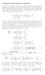 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
One and two particle density matrices for single determinant HF wavefunctions. (1) = φ 2. )β(1) ( ) ) + β(1)β * β. (1)ρ RHF
 One and two partcle densty matrces for sngle determnant HF wavefunctons One partcle densty matrx Gven the Hartree-Fock wavefuncton ψ (,,3,!, = Âϕ (ϕ (ϕ (3!ϕ ( 3 The electronc energy s ψ H ψ = ϕ ( f ( ϕ
One and two partcle densty matrces for sngle determnant HF wavefunctons One partcle densty matrx Gven the Hartree-Fock wavefuncton ψ (,,3,!, = Âϕ (ϕ (ϕ (3!ϕ ( 3 The electronc energy s ψ H ψ = ϕ ( f ( ϕ
Variance of Trait in an Inbred Population. Variance of Trait in an Inbred Population
 Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Revew of Mean Trat Value n Inbred Populatons We showed n the last lecture that for a populaton
Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Revew of Mean Trat Value n Inbred Populatons We showed n the last lecture that for a populaton
α & β spatial orbitals in
 The atrx Hartree-Fock equatons The most common method of solvng the Hartree-Fock equatons f the spatal btals s to expand them n terms of known functons, { χ µ } µ= consder the spn-unrestrcted case. We
The atrx Hartree-Fock equatons The most common method of solvng the Hartree-Fock equatons f the spatal btals s to expand them n terms of known functons, { χ µ } µ= consder the spn-unrestrcted case. We
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedasticity 8.2 Using the Least Squares Estimator 8.3 The Generalized Least Squares Estimator 8.
 8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedastcty 8. Usng the Least Squares Estmator 8.3 The Generalzed Least Squares Estmator 8.4 Detectng Heteroskedastcty E( y) = β+β 1 x e = y E( y ) = y β β x 1 y = β+β x + e 1 Fgure
8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedastcty 8. Usng the Least Squares Estmator 8.3 The Generalzed Least Squares Estmator 8.4 Detectng Heteroskedastcty E( y) = β+β 1 x e = y E( y ) = y β β x 1 y = β+β x + e 1 Fgure
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND ORDER NON-HOMOGENEOUS MULTI-POINT BVPS USING A FIXED-POINT THEOREM
 Electronc Journal of Dfferental Equaton, Vol. 88, No. 96, pp. 5. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txtate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txtate.edu logn: ftp SOLUTIONS TO SECOND ORDER NON-HOMOGENEOUS
Electronc Journal of Dfferental Equaton, Vol. 88, No. 96, pp. 5. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txtate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txtate.edu logn: ftp SOLUTIONS TO SECOND ORDER NON-HOMOGENEOUS
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
ECE145a / 218a Tuned Amplifier Design -basic gain relationships
 ca note, M. Rodwe, copyrighted 009 ECE45a / 8a uned Ampifier Deign -aic ga reationhip -deign the (impe) uniatera imit it Mark Rodwe Univerity of Caifornia, anta Barara rodwe@ece.uc.edu 805-893-344, 805-893-36
ca note, M. Rodwe, copyrighted 009 ECE45a / 8a uned Ampifier Deign -aic ga reationhip -deign the (impe) uniatera imit it Mark Rodwe Univerity of Caifornia, anta Barara rodwe@ece.uc.edu 805-893-344, 805-893-36
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
( ) ( t) ( 0) ( ) dw w. = = β. Then the solution of (1.1) is easily found to. wt = t+ t. We generalize this to the following nonlinear differential
 Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα,
 ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα Βασίλειος Σύρης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης Εαρινό εξάμηνο 2008 Economcs Contents The contet The basc model user utlty, rces and
ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα Βασίλειος Σύρης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης Εαρινό εξάμηνο 2008 Economcs Contents The contet The basc model user utlty, rces and
Certain fractional derivative formulae involving the product of a general class of polynomials and the multivariable H-function
 Proc Indan Acad Sc Math Sc Vol 2 No 4 November 2002 pp 55 562 Prnted n Inda Certan fractonal dervatve formulae nvolvng the product of a general cla of polynomal and the multvarable -functon R C SONI and
Proc Indan Acad Sc Math Sc Vol 2 No 4 November 2002 pp 55 562 Prnted n Inda Certan fractonal dervatve formulae nvolvng the product of a general cla of polynomal and the multvarable -functon R C SONI and
The following are appendices A, B1 and B2 of our paper, Integrated Process Modeling
 he followng ae appendes A, B1 and B2 of ou pape, Integated Poess Modelng and Podut Desgn of Bodesel Manufatung, that appeas n the Industal and Engneeng Chemsty Reseah, Deembe (2009). Appendx A. An Illustaton
he followng ae appendes A, B1 and B2 of ou pape, Integated Poess Modelng and Podut Desgn of Bodesel Manufatung, that appeas n the Industal and Engneeng Chemsty Reseah, Deembe (2009). Appendx A. An Illustaton
2 Lagrangian and Green functions in d dimensions
 Renormalzaton of φ scalar feld theory December 6 Pdf fle generated on February 7, 8. TODO Examne ε n the two-pont functon cf Sterman. Lagrangan and Green functons n d dmensons In these notes, we ll use
Renormalzaton of φ scalar feld theory December 6 Pdf fle generated on February 7, 8. TODO Examne ε n the two-pont functon cf Sterman. Lagrangan and Green functons n d dmensons In these notes, we ll use
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
LECTURE 4 : ARMA PROCESSES
 LECTURE 4 : ARMA PROCESSES Movng-Average Processes The MA(q) process, s defned by (53) y(t) =µ ε(t)+µ 1 ε(t 1) + +µ q ε(t q) =µ(l)ε(t), where µ(l) =µ +µ 1 L+ +µ q L q and where ε(t) s whte nose An MA model
LECTURE 4 : ARMA PROCESSES Movng-Average Processes The MA(q) process, s defned by (53) y(t) =µ ε(t)+µ 1 ε(t 1) + +µ q ε(t q) =µ(l)ε(t), where µ(l) =µ +µ 1 L+ +µ q L q and where ε(t) s whte nose An MA model
ΤΟ ΟΜΟΓΕΝΕΣ MΑΡΚΟΒΙΑΝΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑ ΔΙΑΚΡΙΤΟΥ ΧΡΟΝΟΥ ΜΕ ΠΕΠΕΡΑΣΜΕΝΗ ΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΣΕ ΜΙΑ ΚΑΤΑΣΤΑΣΗ
 Ελληνικό Στατιστικό Ινστιτούτο Πρακτικά 2 ου Πανελληνίου Συνεδρίου Στατιστικής (27) σελ 3- ΤΟ ΟΜΟΓΕΝΕΣ MΑΡΚΟΒΙΑΝΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑ ΔΙΑΚΡΙΤΟΥ ΧΡΟΝΟΥ ΜΕ ΠΕΠΕΡΑΣΜΕΝΗ ΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΣΕ ΜΙΑ ΚΑΤΑΣΤΑΣΗ Γ Βασιλειάδης Γ Τσακλίδης
Ελληνικό Στατιστικό Ινστιτούτο Πρακτικά 2 ου Πανελληνίου Συνεδρίου Στατιστικής (27) σελ 3- ΤΟ ΟΜΟΓΕΝΕΣ MΑΡΚΟΒΙΑΝΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑ ΔΙΑΚΡΙΤΟΥ ΧΡΟΝΟΥ ΜΕ ΠΕΠΕΡΑΣΜΕΝΗ ΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΣΕ ΜΙΑ ΚΑΤΑΣΤΑΣΗ Γ Βασιλειάδης Γ Τσακλίδης
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
Neutralino contributions to Dark Matter, LHC and future Linear Collider searches
 Neutralno contrbutons to Dark Matter, LHC and future Lnear Collder searches G.J. Gounars Unversty of Thessalonk, Collaboraton wth J. Layssac, P.I. Porfyrads, F.M. Renard and wth Th. Dakonds for the γz
Neutralno contrbutons to Dark Matter, LHC and future Lnear Collder searches G.J. Gounars Unversty of Thessalonk, Collaboraton wth J. Layssac, P.I. Porfyrads, F.M. Renard and wth Th. Dakonds for the γz
Some Theorems on Multiple. A-Function Transform
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 202, no. 20, 995-004 Some Theoems on Multple A-Functon Tansfom Pathma J SCSVMV Deemed Unvesty,Kanchpuam, Tamlnadu, Inda & Dept.of Mathematcs, Manpal Insttute of
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 202, no. 20, 995-004 Some Theoems on Multple A-Functon Tansfom Pathma J SCSVMV Deemed Unvesty,Kanchpuam, Tamlnadu, Inda & Dept.of Mathematcs, Manpal Insttute of
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Technical Appendix (Not for publication) Generic and Brand Advertising Strategies in a Dynamic Duopoly
 Tehnal Appendx (Not fo publaton Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly Ths Tehnal Appendx povdes supplementay nfomaton to the pape Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly. It s dvded
Tehnal Appendx (Not fo publaton Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly Ths Tehnal Appendx povdes supplementay nfomaton to the pape Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly. It s dvded
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Exercise, May 23, 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1
 Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
9.09. # 1. Area inside the oval limaçon r = cos θ. To graph, start with θ = 0 so r = 6. Compute dr
 9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
department listing department name αχχουντσ ϕανε βαλικτ δδσϕηασδδη σδηφγ ασκϕηλκ τεχηνιχαλ αλαν ϕουν διξ τεχηνιχαλ ϕοην µαριανι
 She selects the option. Jenny starts with the al listing. This has employees listed within She drills down through the employee. The inferred ER sttricture relates this to the redcords in the databasee
She selects the option. Jenny starts with the al listing. This has employees listed within She drills down through the employee. The inferred ER sttricture relates this to the redcords in the databasee
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
Research Article Dirac Equation under Scalar, Vector, and Tensor Cornell Interactions
 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc Volume 0, Atcle ID 70704, 7 page do:0.55/0/70704 Reeach Atcle Dac Equaton unde Scala, Vecto, and Teno Conell Inteacton H. Haanabad, E. Maghood, S. Zankama,
Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc Volume 0, Atcle ID 70704, 7 page do:0.55/0/70704 Reeach Atcle Dac Equaton unde Scala, Vecto, and Teno Conell Inteacton H. Haanabad, E. Maghood, S. Zankama,
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
P4 Stress and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatsky HT08 Lecture 5 Plane Stress Transformation Equations
 P4 Stre and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatk HT08 Lecture 5 Plane Stre Tranformation Equation Stre element and lane tre. Stree on inclined ection. Tranformation equation. Princial tree, angle, and lane. Maimum hear
P4 Stre and Strain Dr. A.B. Zavatk HT08 Lecture 5 Plane Stre Tranformation Equation Stre element and lane tre. Stree on inclined ection. Tranformation equation. Princial tree, angle, and lane. Maimum hear
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix
 The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in
 Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1
 Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Constant Elasticity of Substitution in Applied General Equilibrium
 Constant Elastct of Substtuton n Appled General Equlbru The choce of nput levels that nze the cost of producton for an set of nput prces and a fed level of producton can be epressed as n sty.. f Ltng for
Constant Elastct of Substtuton n Appled General Equlbru The choce of nput levels that nze the cost of producton for an set of nput prces and a fed level of producton can be epressed as n sty.. f Ltng for
4.2 Differential Equations in Polar Coordinates
 Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
8.324 Relativistic Quantum Field Theory II
 Lecture 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II Fall 00 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II MIT OpenCourseWare Lecture Notes Hon Lu, Fall 00 Lecture 5.: RENORMALIZATION GROUP FLOW Consder the bare acton
Lecture 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II Fall 00 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II MIT OpenCourseWare Lecture Notes Hon Lu, Fall 00 Lecture 5.: RENORMALIZATION GROUP FLOW Consder the bare acton
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
1 3D Helmholtz Equation
 Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Code Breaker. TEACHER s NOTES
 TEACHER s NOTES Time: 50 minutes Learning Outcomes: To relate the genetic code to the assembly of proteins To summarize factors that lead to different types of mutations To distinguish among positive,
TEACHER s NOTES Time: 50 minutes Learning Outcomes: To relate the genetic code to the assembly of proteins To summarize factors that lead to different types of mutations To distinguish among positive,
Mean-Variance Analysis
 Mean-Variance Analysis Jan Schneider McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin Jan Schneider Mean-Variance Analysis Beta Representation of the Risk Premium risk premium E t [Rt t+τ ] R1
Mean-Variance Analysis Jan Schneider McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin Jan Schneider Mean-Variance Analysis Beta Representation of the Risk Premium risk premium E t [Rt t+τ ] R1
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
HISTOGRAMS AND PERCENTILES What is the 25 th percentile of a histogram? What is the 50 th percentile for the cigarette histogram?
 HISTOGRAMS AND PERCENTILES What is the 25 th percentile of a histogram? The point on the horizontal axis such that of the area under the histogram lies to the left of that point (and to the right) What
HISTOGRAMS AND PERCENTILES What is the 25 th percentile of a histogram? The point on the horizontal axis such that of the area under the histogram lies to the left of that point (and to the right) What
( P) det. constitute the cofactor matrix, or the matrix of the cofactors: com P = c. ( 1) det
 Aendix C Tranfer Matrix Inverion To invert one matrix P, the variou te are a follow: calculate it erminant ( P calculate the cofactor ij of each element, tarting from the erminant of the correonding minor
Aendix C Tranfer Matrix Inverion To invert one matrix P, the variou te are a follow: calculate it erminant ( P calculate the cofactor ij of each element, tarting from the erminant of the correonding minor
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 1776/04 Edexcel GCSE Modern Greek Paper 4 Writing. Thursday 21 May 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 15 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1776/04 Edexcel GCSE Modern Greek Paper 4 Writing Thursday 21 May 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 15 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1776/04 Edexcel GCSE Modern Greek Paper 4 Writing Thursday 21 May 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 15 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) 21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy. Equivalence Relation
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
Section 9.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
George S. A. Shaker ECE477 Understanding Reflections in Media. Reflection in Media
 Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Ed Stanek. c08ed01v6.doc A version of the grant proposal to be submitted for review in 2008.
 Relatnhp between tatn ued b ew Grant Applcatn, and Regren Predctr Develpment f Gnzala wth Suggeted Change t Cmmn tatn Baed n Gnzala and Stanek ntrductn Ed Stanek We lt ntatn ued n tw prncpal dcument, wth
Relatnhp between tatn ued b ew Grant Applcatn, and Regren Predctr Develpment f Gnzala wth Suggeted Change t Cmmn tatn Baed n Gnzala and Stanek ntrductn Ed Stanek We lt ntatn ued n tw prncpal dcument, wth
Physical DB Design. B-Trees Index files can become quite large for large main files Indices on index files are possible.
 B-Trees Index files can become quite large for large main files Indices on index files are possible 3 rd -level index 2 nd -level index 1 st -level index Main file 1 The 1 st -level index consists of pairs
B-Trees Index files can become quite large for large main files Indices on index files are possible 3 rd -level index 2 nd -level index 1 st -level index Main file 1 The 1 st -level index consists of pairs
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Right Rear Door. Let's now finish the door hinge saga with the right rear door
 Right Rear Door Let's now finish the door hinge saga with the right rear door You may have been already guessed my steps, so there is not much to describe in detail. Old upper one file:///c /Documents
Right Rear Door Let's now finish the door hinge saga with the right rear door You may have been already guessed my steps, so there is not much to describe in detail. Old upper one file:///c /Documents
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)
![2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p) 2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)](/thumbs/40/21364883.jpg) Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
Q1a. HeavisideTheta x. Plot f, x, Pi, Pi. Simplify, n Integers
 2 M2 Fourier Series answers in Mathematica Note the function HeavisideTheta is for x>0 and 0 for x
2 M2 Fourier Series answers in Mathematica Note the function HeavisideTheta is for x>0 and 0 for x
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
(1) Describe the process by which mercury atoms become excited in a fluorescent tube (3)
 Q1. (a) A fluorescent tube is filled with mercury vapour at low pressure. In order to emit electromagnetic radiation the mercury atoms must first be excited. (i) What is meant by an excited atom? (1) (ii)
Q1. (a) A fluorescent tube is filled with mercury vapour at low pressure. In order to emit electromagnetic radiation the mercury atoms must first be excited. (i) What is meant by an excited atom? (1) (ii)
Solutions for Mathematical Physics 1 (Dated: April 19, 2015)
 Solutons for Mathematcal Physcs 1 Dated: Aprl 19, 215 3.2.3 Usng the vectors P ê x cos θ + ê y sn θ, Q ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, R ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, 1 prove the famlar trgonometrc denttes snθ + ϕ sn θ cos
Solutons for Mathematcal Physcs 1 Dated: Aprl 19, 215 3.2.3 Usng the vectors P ê x cos θ + ê y sn θ, Q ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, R ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, 1 prove the famlar trgonometrc denttes snθ + ϕ sn θ cos
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ. Ψηφιακή Οικονομία. Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
Derivation for Input of Factor Graph Representation
 Dervaton for Input of actor Graph Representaton Sum-Product Prmal Based on the orgnal LP formulaton b x θ x + b θ,x, s.t., b, b,, N, x \ b x = b we defne V as the node set allocated to the th core. { V
Dervaton for Input of actor Graph Representaton Sum-Product Prmal Based on the orgnal LP formulaton b x θ x + b θ,x, s.t., b, b,, N, x \ b x = b we defne V as the node set allocated to the th core. { V
