Research Article Dirac Equation under Scalar, Vector, and Tensor Cornell Interactions
|
|
|
- Κασσιέπεια Ταμτάκος
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc Volume 0, Atcle ID 70704, 7 page do:0.55/0/70704 Reeach Atcle Dac Equaton unde Scala, Vecto, and Teno Conell Inteacton H. Haanabad, E. Maghood, S. Zankama, and H. Rahmov 3 Phyc Depatment, Shahood Unvety of Technology, Shahood , Ian Young Reeache Club, Gama Banch, Ilamc Azad Unvety, Gama, Ian 3 Compute Engneeng Depatment, Shahood Unvety of Technology, Shahood, Ian Coepondence hould be addeed to E. Maghood, e.maghood84@gmal.com Receved 4 July 0; Reved 7 Augut 0; Accepted 9 Augut 0 Academc Edto: S. H. Dong Copyght q 0 H. Haanabad et al. Th an open acce atcle dtbuted unde the Ceatve Common Attbuton Lcene, whch pemt unetcted ue, dtbuton, and epoducton n any medum, povded the ognal wok popely cted. Spn and peudopn ymmete of Dac equaton ae olved unde cala, vecto, and teno nteacton fo abtay quantum numbe va the analytcal anatz appoach. The pectum of the ytem numecally epoted fo typcal value of the potental paamete.. Intoducton No doubt, the Conell potental altenatvely called Funnel n the lteatue, f not the bet, among the mot appealng nteacton n patcle phyc. The Conell potental contan a confnng tem bede the Coulomb nteacton and ha uccefully accounted fo the patcle phyc data. Unfotunately, to ou bet knowledge, the potental doe not poe exact oluton unde all common equaton of quantum mechanc, that, the nonelatvtc Schödnge equaton, and elatvtc Dac, Klen-Godon, Poca, and Duffn-Kemme- Petau DKP equaton. Hee, we focu on the elatvtc ymmete of Dac equaton, that, pn and peudopn ymmete, whch povde a elable theoetcal ba fo hadonc and nuclea pectocopy. Th ha motvated many tude unde vaou nteacton wthn the pat two decade 3 8 and many efeence theen. Nevethele, none of thee pape ha nvetgated the ymmety lmt unde the Conell potental. Th defntely due to the complcated natue of the eultng dffeental equaton whch cannot be olved by common analytcal technque of quantum mechanc uch a the upeymmety quantum mechanc SUSYQ, Le goup, Nkfoov-Uvaov NU technque, and pont canoncal tanfomaton, In ou tudy, we make ue of the anatz appoach to deal wth th
2 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc complcated equaton. A uvey on the applcaton of th technque to othe wave equaton ncludng Schödnge, pnle-salpete, Dac, Klen-Godon, and DKP equaton can be found n 9 7. We oganze the tudy a follow. In the ft tep, we evew the mot eental equaton of the ymmety lmt. We next popoe a phycal anatz oluton to the equaton and, n a ytematc manne, calculate the pectum of the ytem fo any abtay tate. To povde a bette undetandng of the oluton, we povde ome numecal data fo the pectum a well.. Dac Equaton Includng Teno Couplng In phecal coodnate, Dac equaton wth both cala potental S and vecto potental V expeed a, 3 [ α p β M S β α U ] ψ E V ψ,. whee E the elatvtc enegy of the ytem; α and β ae the 4 4 Dac matce and p tand fo the momentum opeato. Fo a patcle n a phecal feld, the total angula momentum opeato J and pn-obt matx opeato K σ L, whee σ and L ae, epectvely, the Paul matx and obtal angula momentum, commute wth the Dac Hamltonan. The egenvalue of K ae κ j / fo the algned pn /,p 3/,etc. and κ j / fo the unalgned pn p /,d 3/,etc.. The complete et of the conevatve quantte can be choen a H, K, J,J z. A hown n 3, the Dac pno condeed a ψ nk fnk g nk G nk F nk Y l jm Y l jm θ, ϕ θ, ϕ,. whee F nk and G nk ae the adal wave functon of the uppe and lowe component, epectvely, and Y l l jm θ, ϕ and Yjm θ, ϕ, epectvely, tand fo pn and peudopn phecal hamonc coupled to the angula momentum j. m the pojecton of the angula momentum on the z-ax. The obtal angula momentum quantum numbe l and l efe to the uppe and lowe component, epectvely. The quadegeneate doublet tuctue can be expeed n tem of peudopn angula momentum / and peudoobtal angula momentum l, whch defned a l l fo algned pn j l / and l l fo unalgned pn j l /. A hown n, 3, ubttuton of. nto. yeld the followng two-coupled dffeental equaton: d d κ U F nk M E nk V S G nk, d d κ U G nk M E nk V S F nk,.3
3 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc 3 whch mply gve { d κ κ κ d U du d U dδ /d d M E nκ Δ d κ } U F nκ M E nκ Δ M E nκ Σ F nκ,.4 { d κ κ κ d U du d U dσ /d d M E nκ Σ d κ } U G nκ M E nκ Δ M E nκ Σ G nκ,.5 whee, a the notaton ndcate, Δ V S and Σ V S... Peudopn Symmety Lmt Unde the condton of the peudopn ymmety, dσ /d 0 o equvalently Σ C gp Cont., 3. We chooe Δ a the Conell potental: Δ b p..6 Fo the teno tem, we conde the Conell potental: U A B..7 Subttuton of thee two tem n nto.5 gve { d d κ κ κb B B A a p M E p nκ C p b p M b p E p nκ b p C p M MC p E p nκ } p E nκc p κa A AB.8 G p nκ 0, whee κ l and κ l foκ<0andκ>0, epectvely.
4 4 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc.. Spn Symmety Lmt In the pn ymmety lmt dδ /d 0oΔ C g ecton, we conde cont., 3. A the pevou Σ a b, U A B..9a.9b Subttuton of the latte n.4 gve { d d κ κ κb B B A a M a Enκ a C } b M b Enκ b C M MC Enκ p E nκ C κa A AB Fnκ 0,.0 whee κ l and κ l foκ<0andκ>0, epectvely. 3. The Anatz Soluton 3.. Soluton of the Peudopn Symmety Lmt In the pevou ecton, we obtaned a Schödnge-lke equaton of the fom d G p [ nκ ε p d nκ b p cp d p ] κ κ G p nκ 0, 3. whee ε p nκ M MC p E p nκ E p nκc p κa A AB, A, b p M E p nκ C p, c p b p M b p E p nκ b p C p, d p κb B B. 3.
5 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc 5 Equaton 3. fal to admt exact analytcal oluton. Theefoe, we follow the anatz appoach wth the tatng quae: G p nκ f p n exp g p κ, 3.3 whee f p n, f n 0, n α n 3.4, f n, g p κ αp β p δ p ln, α p > 0, β p > By ubttuton of f n and g κ nto 3.3, wefnd G p nκ [ g p κ p f p p p ] n g κ f n g κ f p n G p nκ. 3.6 Hee, we conde the cae n 0. Fom we fnd G p 0κ { α p α p β p α p δ p 0 β p β p δ p 0 δp δ p } G p 0κ. 3.7 By compang the coepondng powe of 3. and 3.7, we have α p, ap > 0, δ p ± c p bp β p β p δ p 0, κ 4d p, ± k p, 3.8 ε p 0κ αp δ p 0 β p, whee k p κ 4d p. Actually, to have well-behaved oluton of the adal wave functon at boundae, namely, the ogn and the nfnty, we need to take δ fom 3.8 a δ p k p. 3.9
6 6 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc Fom 3., 3.8, the gound-tate enegy atfe M MC p E p 0κ E p 0κ C p κa A AB α p δ p 0 β p 0 3.0a o E p 0κ p E 0κ C p M MC p κa A AB κ 4d p bp 4 0, 3.0b whch moe compactly wtten a E p 0κ { [ ± C p ± Cp 8κA 4A 8AB 4M 4MC p 8 4 4κ 4κ 4d p 4βp ] / }, 3.35, 3. whee the paamete of potental.6 fom 3.8 hould atfy the followng etcton: b p κ 4d p b p k p. 3. Fom 3.3, 3.4, and 3.8, the uppe and lowe component of the wave functon ae g κ bp G p 0κ N 0κ / κ 4d p exp κ 4d p ln, F p 0κ d M E p 0κ C p d κ bp U G p 0κ. 3.3a, 3.3b 3.3c
7 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc 7 Fo the ft node n, ungf α and g κ fom 3.5, we ave at b p cp κ κ d p ε p κ α p δp αp β p δ p α p β p δ p α p βp δ p αp β p δ p /. α 3.4 Hee, the conequent elaton between the potental paamete and the coeffcent α p, β p, δ p,andα ae α p, βp bp, δ p k p, ε p κ αp δ p β p, c p βp δ p α δ p, 3.5 c p βp δ p α p α. By olvng the above equaton one can fnd c p and α a c p bp κ 4d p bp 4 κ 4d p, 3.6a α p α β p α δ p 0, β α β p p 4α p δ p α p b p 4 bp 6 κ 4d p. 3.6b The enegy egenvalue theefoe ae E p κ { [ ± C p ± Cp 8κA 4A 8AB 4M 4MC p 6 4 4κ 4κ 4d p 4βp ] / }, 3.7
8 8 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc whee the paamete fom 3.8 c p cp kp 3M 4Mk p Mkp c p 3E p 6 4 κ 4Ep κ kp Ep kp κ kp 0 kp kp 3. 3Cp 4C p k p C pk p 3.8 Fo the uppe and lowe component of the wave functon we thu have G p κ N κ α / κ 4d p F p κ d M E p κ C p d κ exp bp U G p κ., 3.9a 3.9b Followng the analytc teaton pocedue fo the econd node n wth f α α and g κ a defned n 3.6, the elaton between the potental paamete and the coeffcent α p, β p, δ p, α,andα ae α p, βp bp, δ p k p, c p βp δ p α p ε p κ αp δ p β p, α, c p βp δ p α α j <j δ p α, 3.0 [ c p βp δ p ] α 4α p <j α α j δ p. The coeffcent α and α ae found fom the contant elaton 0, 7 9 : δ p α α α p α β p α β p j<k δ p 0, 3. α j α k α p j<k α j α k 0. 3.
9 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc 9 Theefoe, the enegy egenvalue n th cae E p κ { [ ± C p ± Cp 8κA 4A 8AB 4M 4MC p 4 4 4κ 4κ 4d p 4βp ] / }, 3.3 and the lowe component of the wave functon G p κ N κ α / κ 4d p exp bp Soluton of the Spn Symmety Lmt In th cae, ou odnay dffeental equaton d F nκ d [ εnκ a b c d κ κ ] F nκ 0, 3.5 wth ε nκ M MC E nκ E nκc κa A AB, a A, b a M a E nκ a C, 3.6 c b M b E nκ b C, d κb B B, whch cannot be olved by ou common exact analytcal technque. Let u popoe the anatz oluton: F nκ f n exp g κ, 3.7 whee, f n 0, fn n α n 3.8, f n, g κ α β δ ln, α > 0, β >
10 0 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc By ubttuton of f n and g κ nto 3.7, wefnd [ ] F nκ g κ gκ f n g κ f n fn Fnκ Fo the cae of n 0, fom , wefnd F nκ { α α β α δ 0 β β δ 0 δ δ } F nκ. 3.3 By compang the coepondng powe of 3.7 and 3.33, we have α a, β b a, a > 0, c β δ 0, δ ± κ 4d ± k, 3.3 ε 0κ α δ 0 β, whee k κ 4d. To have phycally acceptable oluton, we pck up the value δ k By condeng 3.6, 3.3, the ft node egenvalue atfe M MC E nκ E nκc κa A AB α δ 0 β 0, 3.34 o equvalently E ± 0κ { [ C ± C 4M 4MC 8κA 4A 8AB 8 a ] 4 a 4κ / 4κ 4d 4β, 3.35
11 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc whee the paamete a of potental.9a hould atfy the etcton b a a k Fom 3.7, 3.8, and 3.3, the uppe and lowe component of the wave functon ae g κ a b κ 4d a ln, κ F 0κ N 0κ / 4d exp a b G 0κ d M E 0κ C d κ U F 0κ. a 3.37, Secondly, fo the ft node n, ungf α and g κ fom , ou eultng equaton a b c d κ κ ε nκ α δ α β δ α β δ α β δ α β δ /. α 3.40 The elaton between the potental paamete and the coeffcent α,β,δ,andα ae α a, β b, a > 0, δ κ 4d k, ε κ α δ β, 3.4 c β δ α δ, c β δ α α,
12 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc whee c and α ae found fom 3.4 a 0, 7 9 c b a κ 4d b 4a a κ 4d, 3.4a α α β α δ 0, 3.4b o β α β 4α δ α b 4a b 6a κ 4d, 3.4c a whch detemne the coepondng enegy a E ± κ { C ± [ C 4M 4MC 8κA 4A 8AB 6 a ] / 4 a 4κ 4κ 4d }, 4β 3.43 wth a a c c k c 6 a a 4 k 0 a k a k 3 3M 4Mk Mk 3E κ 4E κ k E κ k 3C 4C k C k The uppe and lowe component of the wave functon ae then mply found to be F κ N κ α / κ 4d exp a b G κ d M E κ C d κ U F κ. a, 3.45a 3.45b
13 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc 3 Fo the econd node n, we chooe f α α and g κ a defned n 3.8 and 3.9. The elaton between the potental paamete and the coeffcent α,β,δ,α,andα ae α a, β b a, δ k, c β δ α ε κ α δ β, α, c β δ α <j α j δ α, 3.46 [ c β δ ] α 4α <j α α j δ, whee δ α α α α β α β j<k δ 0, 3.47 α j α k α j<k α j α k The enegy egenvalue theefoe E ± κ { C ± [ C 4M 4MC 8κA 4A 8AB 4 a ] / 4 a 4κ 4κ 4d }. 4β 3.49 Fo the uppe component of the wave functon, we have F κ N κ α / κ 4d exp a b a We have gven ome numecal value of the enegy egenvalue n Table,, 3, 4, 5, and 6 fo vaou tate. Fo the fnal pont, we wh to emphaze on the degeneacy-emovng ole of the Conell teno potental. A we aleady know, fo vanhng teno nteacton A B 0, the peudopn doublet, that, tate wth quantum numbe n, l, j l / and n,l,j l 3/ ae degeneate. The degeneate tate n the pn doublet ae thoe wth quantum numbe n, l, j l / and n, l, j l /, whee n, l,and j
14 4 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc Table : Bound tate fo the peudopn ymmety b, M fm, C p 0fm. l n, κ l, j fm A B 0 A 0.5,B 0. 0, 0S / , 0P 3/ , 3 0d 5/ , 4 0f 7/ , S / , p 3/ , 3 d 5/ , 4 f 7/ , 0d 3/ , 3 0f 5/ , 4 0g 7/ , 5 0h 9/ E p nκ Table : Bound tate fo the pn ymmety b, M fm, C 0fm. l n,κ l, j Enκ fm A B 0 A 0.5,B 0. 0, 0p 3/ , 3 0d 5/ , 4 0f 7/ , 5 0g 9/ , p 3/ , 3 d 5/ , 4 f 7/ , 5 g 9/ , 0p / , 0d 3/ ,3 0f 5/ ,4 0g 7/ , p / , d 3/ ,3 f 5/ ,4 g 7/ C p Table 3: Enege n the peudopn ymmety Lmt fo A 0.5, B 0., b, M fm. E p nκ fm P 3/ f 7/ 0d 3/ 0g 7/
15 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc 5 Table 4: Enege n the peudopn ymmety lmt fo A 0.5, B 0., b, C p 0fm. M fm E p nκ fm P 3/ f 7/ 0d 3/ 0g 7/ Table 5: Enege n the pn ymmety lmt fo A 0.5, B 0., b, M fm. C Enκ fm 0f 7/ d 5/ 0P / f 5/ Table 6: Enege n the pn ymmety lmt fo A 0.5, B 0., b, C 0fm. M fm Enκ fm 0f 7/ d 5/ 0P / f 5/ ae the adal, the obtal, and the total angula momentum quantum numbe, epectvely ee Table and. Ou numecal data eveal that, n the peudopn ymmety lmt, the degeneate tate fo A B 0 ae n /, n d 3/ fo l l 0, np 3/, n f 5/ fo l l, nd 5/, n g 7/ fo l 3 l, nf 7/, n h 9/ fo l 4 l 3, and o foth. Fo pn ymmety lmt and A B 0 one can clealy ee that the degeneacy occu n np /,np 3/ fo l, nd 3/,nd 5/ fo l, nf 5/,nf 7/ fo l 3, ng 7/,ng 9/ fo l 4, and o foth. 4. Concluon Becaue of the etablhed ole of the Conell potental and pn, and peudopn ymmete n nuclea and hadon pectocopy, we olved the Dac equaton unde thee ymmety lmt fo vecto, cala, and teno nteacton of Conell-type. In ou calculaton, on the one hand, due to the falue of othe common analytcal technque, and, on the othe hand, the bette nght whch analytcal technque povde u n compaon wth the numecal countepat, we ued the quaanalytcal anatz appoach. By popong novel phycal oluton and afte lengthy calculaton, we could fnd the abtay-tate oluton. Ou eult clealy how the degeneacy-emovng ole of the teno tem and povde the equte undetandng of the oluton fo poble futhe tude. Both the
16 6 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc enegy pectum and the egenfuncton can be ued n elated ytem afte the pope phenomenologcal ft done. Refeence D. H. Pekn, An Intoducton to Hgh Enegy Phyc, Cambdge Unvety Pe, 000. J. N. Gnoccho, Relatvtc ymmete n nucle and hadon, Phyc Repot, vol. 44, no. 4-5, pp. 65 6, J. N. Gnoccho and A. Levatan, On the elatvtc foundaton of peudopn ymmety n nucle, Phyc Lette B, vol. 45, no. -, pp. 5, G. Mao, Effect of teno couplng n a elatvtc Hatee appoach fo fnte nucle, Phycal Revew C, vol. 67, no. 4, Atcle ID 04438, page, P. Albeto, R. Lboa, M. Malheo, and A. S. de Cato, Teno couplng and peudopn ymmety n nucle, Phycal Revew C, vol. 7, no. 3, Atcle ID 03433, 7 page, R. J. Funtahl, J. J. Runak, and B. D. Seot, The nuclea pn-obt foce n chal effectve feld theoe, Nuclea Phyc A, vol. 63, no. 4, pp , G.-F. We and S.-H. Dong, Appoxmately analytcal oluton of the Mannng-Roen potental wth the pn-obt couplng tem and pn ymmety, Phyc Lette A, vol. 373, no., pp , G. F. We and S. H. Dong, Algebac appoach to peudopn ymmety fo the Dac equaton wth cala and vecto modfed Pöchl-Telle potental, Euophyc Lette, vol. 87, no. 4, atcle 40004, G. F. We and S. H. Dong, Spn ymmety n the elatvtc ymmetcal well potental ncludng a pope appoxmaton to the pn-obt couplng tem, Phyca Scpta, vol. 8, no. 3, Atcle ID , G. F. We and S. H. Dong, Peudopn ymmety fo modfed Roen-Moe potental ncludng a Peke-type appoxmaton to the peudo-centfugal tem, Euopean Phyc A, vol. 46, no., pp. 07, 00. G. F. We and S. H. Dong, Peudopn ymmety n the elatvtc Mannng-Roen potental ncludng a Peke-type appoxmaton to the peudo-centfugal tem, Phyc Lette B, vol. 686, no. 4-5, pp. 88 9, 00. W.-C. Qang and S.-H. Dong, SUSYQM and SWKB appoache to the elatvtc equaton wth hypebolc potental V 0 tanh /d, Phyca Scpta, vol. 7, no. -3, pp. 7 3, S. Zankama, A. A. Rajab, and H. Haanabad, Dac equaton fo the hamonc cala and vecto potental and lnea plu Coulomb-lke teno potental; the SUSY appoach, Annal of Phyc, vol. 35, no., pp. 5 58, O. Aydoğdu and R. Seve, Peudopn and pn ymmety n Dac-Moe poblem wth a teno potental, Phyc Lette. B, vol. 703, no. 3, pp , 0. 5 Y. Xu, S. He, and C.-S. Ja, Appoxmate analytcal oluton of the Dac equaton wth the Pöchl- Telle potental ncludng the pn-obt couplng tem, Phyc A, vol. 4, no. 5, atcle 5530, M. R. Setae and Z. Naza, Peudopn ymmety n defomed nucle wth axally-ymmetc hamonc ocllato potental, Moden Phyc Lette A, vol. 5, no. 549, K. J. Oyewum and C. O. Akohle, Bound-tate oluton of the Dac-Roen-Moe potental wth pn and peudopn ymmety, Euopean Phycal Jounal A, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 3 38, E. Maghood, H. Haanabad, and O. Aydogdu, Dac patcle n the peence of the Yukawa potental plu a teno nteacton n SUSYQMfamewok, Phyca Scpta, vol. 86, Atcle ID 05005, 0. 9 H. Haanabad and A. A. Rajab, Enegy level of a phecal quantum dot n a confnng potental, Phyc Lette A, vol. 373, no. 6, pp , H. Haanabad and A. A. Rajab, Relatvtc veu nonelatvtc oluton of the N-femon poblem n a hypeadu-confnng potental, Few-Body Sytem, vol. 4, no. 3-4, pp. 0 0, 007. S.-H. Dong, Z.-Q. Ma, and G. Epoto, Exact oluton of the Schödnge equaton wth nveepowe potental, Foundaton of Phyc Lette, vol., no. 5, pp , 999. S.-H. Dong, Exact oluton of the two-dmenonal Schödnge equaton wth cetan cental potental, Intenatonal Theoetcal Phyc, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 9 8, S. H. Dong, A new appoach to the elatvtc Schödnge equaton wth cental potental: Anatz method, Intenatonal Theoetcal Phyc, vol. 40, no., pp , 00.
17 Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc 7 4 H. Haanabad, H. Rahmov, and S. Zankama, Conell and Coulomb nteacton fo the D- dmenonal Klen-Godon equaton, Annalen de Phyk, vol. 53, no. 7, pp , 0. 5 D. Agboola and Y. Zhang, Unfed devaton of exact oluton fo a cla of qua-exactly olvable model, Mathematcal Phyc, vol. 53, Atcle ID 040, 3 page, 0. 6 H. Haanabad, B. H. Yazaloo, S. Zankama, and A. A. Rajab, Duffn-Kemme-Petau equaton unde a cala Coulomb nteacton, Phycal Revew C, vol. 84, Atcle ID , 4 page, 0. 7 S. M. Ikhda, Bound tate enege and wave functon of phecal quantum dot n peence of aconfnng potental model, 8 M. Znojl, Sngula anhamoncte and the analytc contnued facton, Mathematcal Phyc, vol. 30, no., pp. 3 7, M. Znojl, The genealzed contnued facton and potental of the Lennad-Jone type, Mathematcal Phyc, vol. 3, no. 955, 7 page, 990.
18 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton The Scentfc Wold Jounal Gavty Photonc Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Advance n Condened Matte Phyc Soft Matte Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Aeodynamc Flud Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Volume 04 Submt you manucpt at Intenatonal Intenatonal Optc Stattcal Mechanc Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Volume 04 Themodynamc Computatonal Method n Phyc Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Sold State Phyc Atophyc Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Phyc Reeach Intenatonal Advance n Hgh Enegy Phyc Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Intenatonal Supeconductvty Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04 Atomc and Molecula Phyc Bophyc Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Advance n Atonomy Volume 04 Hndaw Publhng Copoaton Volume 04
Supplementary material for: Efficient moment calculations for variance components in large unbalanced crossed random effects models
 Supplementay mateal fo: Effcent moment calculaton fo vaance component n lage unbalanced coed andom effect model Katelyn Gao Stanfod Unvety At B Owen Stanfod Unvety Augut 015 Abtact Th a upplementay document
Supplementay mateal fo: Effcent moment calculaton fo vaance component n lage unbalanced coed andom effect model Katelyn Gao Stanfod Unvety At B Owen Stanfod Unvety Augut 015 Abtact Th a upplementay document
Approximate System Reliability Evaluation
 Appoximate Sytem Reliability Evaluation Up MTTF Down 0 MTBF MTTR () Time Fo many engineeing ytem component, MTTF MTBF i.e. failue ate, failue fequency, f Fequency, Duation and Pobability Indice: failue
Appoximate Sytem Reliability Evaluation Up MTTF Down 0 MTBF MTTR () Time Fo many engineeing ytem component, MTTF MTBF i.e. failue ate, failue fequency, f Fequency, Duation and Pobability Indice: failue
The following are appendices A, B1 and B2 of our paper, Integrated Process Modeling
 he followng ae appendes A, B1 and B2 of ou pape, Integated Poess Modelng and Podut Desgn of Bodesel Manufatung, that appeas n the Industal and Engneeng Chemsty Reseah, Deembe (2009). Appendx A. An Illustaton
he followng ae appendes A, B1 and B2 of ou pape, Integated Poess Modelng and Podut Desgn of Bodesel Manufatung, that appeas n the Industal and Engneeng Chemsty Reseah, Deembe (2009). Appendx A. An Illustaton
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών. ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος. ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης. εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων.
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 2015 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 1. 1. Consder the gven expresson for R 1/2 : R 1/2
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 2015 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 1. 1. Consder the gven expresson for R 1/2 : R 1/2
α & β spatial orbitals in
 The atrx Hartree-Fock equatons The most common method of solvng the Hartree-Fock equatons f the spatal btals s to expand them n terms of known functons, { χ µ } µ= consder the spn-unrestrcted case. We
The atrx Hartree-Fock equatons The most common method of solvng the Hartree-Fock equatons f the spatal btals s to expand them n terms of known functons, { χ µ } µ= consder the spn-unrestrcted case. We
Analytical Expression for Hessian
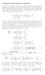 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
ΤΟ ΟΜΟΓΕΝΕΣ MΑΡΚΟΒΙΑΝΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑ ΔΙΑΚΡΙΤΟΥ ΧΡΟΝΟΥ ΜΕ ΠΕΠΕΡΑΣΜΕΝΗ ΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΣΕ ΜΙΑ ΚΑΤΑΣΤΑΣΗ
 Ελληνικό Στατιστικό Ινστιτούτο Πρακτικά 2 ου Πανελληνίου Συνεδρίου Στατιστικής (27) σελ 3- ΤΟ ΟΜΟΓΕΝΕΣ MΑΡΚΟΒΙΑΝΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑ ΔΙΑΚΡΙΤΟΥ ΧΡΟΝΟΥ ΜΕ ΠΕΠΕΡΑΣΜΕΝΗ ΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΣΕ ΜΙΑ ΚΑΤΑΣΤΑΣΗ Γ Βασιλειάδης Γ Τσακλίδης
Ελληνικό Στατιστικό Ινστιτούτο Πρακτικά 2 ου Πανελληνίου Συνεδρίου Στατιστικής (27) σελ 3- ΤΟ ΟΜΟΓΕΝΕΣ MΑΡΚΟΒΙΑΝΟ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑ ΔΙΑΚΡΙΤΟΥ ΧΡΟΝΟΥ ΜΕ ΠΕΠΕΡΑΣΜΕΝΗ ΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΣΕ ΜΙΑ ΚΑΤΑΣΤΑΣΗ Γ Βασιλειάδης Γ Τσακλίδης
One and two particle density matrices for single determinant HF wavefunctions. (1) = φ 2. )β(1) ( ) ) + β(1)β * β. (1)ρ RHF
 One and two partcle densty matrces for sngle determnant HF wavefunctons One partcle densty matrx Gven the Hartree-Fock wavefuncton ψ (,,3,!, = Âϕ (ϕ (ϕ (3!ϕ ( 3 The electronc energy s ψ H ψ = ϕ ( f ( ϕ
One and two partcle densty matrces for sngle determnant HF wavefunctons One partcle densty matrx Gven the Hartree-Fock wavefuncton ψ (,,3,!, = Âϕ (ϕ (ϕ (3!ϕ ( 3 The electronc energy s ψ H ψ = ϕ ( f ( ϕ
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
8.323 Relativistic Quantum Field Theory I
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocwmtedu 8323 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory I Sprng 2008 For nformaton about ctng these materals or our Terms of Use, vst: http://ocwmtedu/terms 1 The Lagrangan: 8323 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocwmtedu 8323 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory I Sprng 2008 For nformaton about ctng these materals or our Terms of Use, vst: http://ocwmtedu/terms 1 The Lagrangan: 8323 Lecture
21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) 21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
Multi-dimensional Central Limit Theorem
 Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t tme
Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t tme
Some Theorems on Multiple. A-Function Transform
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 202, no. 20, 995-004 Some Theoems on Multple A-Functon Tansfom Pathma J SCSVMV Deemed Unvesty,Kanchpuam, Tamlnadu, Inda & Dept.of Mathematcs, Manpal Insttute of
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 202, no. 20, 995-004 Some Theoems on Multple A-Functon Tansfom Pathma J SCSVMV Deemed Unvesty,Kanchpuam, Tamlnadu, Inda & Dept.of Mathematcs, Manpal Insttute of
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND ORDER NON-HOMOGENEOUS MULTI-POINT BVPS USING A FIXED-POINT THEOREM
 Electronc Journal of Dfferental Equaton, Vol. 88, No. 96, pp. 5. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txtate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txtate.edu logn: ftp SOLUTIONS TO SECOND ORDER NON-HOMOGENEOUS
Electronc Journal of Dfferental Equaton, Vol. 88, No. 96, pp. 5. ISSN: 7-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txtate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txtate.edu logn: ftp SOLUTIONS TO SECOND ORDER NON-HOMOGENEOUS
Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small spheres separated by a distance s. The charge on one sphere changes with time and is described by
 5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
2
 6 /9 / Downloaded fom enegy.kahanu.ac. at :7 + on Tueday Octobe th 8 * y.hok6@aut.ac. afzalan@bu.ac. : لا.. T-S. T-S «(PDC)». لا Lyapunov. (PID) لا.. : * 7... Downloaded fom enegy.kahanu.ac. at :7 + on
6 /9 / Downloaded fom enegy.kahanu.ac. at :7 + on Tueday Octobe th 8 * y.hok6@aut.ac. afzalan@bu.ac. : لا.. T-S. T-S «(PDC)». لا Lyapunov. (PID) لا.. : * 7... Downloaded fom enegy.kahanu.ac. at :7 + on
The Laplacian in Spherical Polar Coordinates
 Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedasticity 8.2 Using the Least Squares Estimator 8.3 The Generalized Least Squares Estimator 8.
 8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedastcty 8. Usng the Least Squares Estmator 8.3 The Generalzed Least Squares Estmator 8.4 Detectng Heteroskedastcty E( y) = β+β 1 x e = y E( y ) = y β β x 1 y = β+β x + e 1 Fgure
8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedastcty 8. Usng the Least Squares Estmator 8.3 The Generalzed Least Squares Estmator 8.4 Detectng Heteroskedastcty E( y) = β+β 1 x e = y E( y ) = y β β x 1 y = β+β x + e 1 Fgure
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Multi-dimensional Central Limit Theorem
 Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t ();
Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t ();
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Saigo-Maeda Fractional Differential Operators of the Multivariable H-Function
 Intenatonal Jounal of Computatonal Scence and athematcs. ISSN 0974-89 Volume 5, Numbe (0, pp. 4-54 Intenatonal Reseach ublcaton House http://www.phouse.com Sago-aeda Factonal Dffeental Opeatos of the ultvaable
Intenatonal Jounal of Computatonal Scence and athematcs. ISSN 0974-89 Volume 5, Numbe (0, pp. 4-54 Intenatonal Reseach ublcaton House http://www.phouse.com Sago-aeda Factonal Dffeental Opeatos of the ultvaable
George S. A. Shaker ECE477 Understanding Reflections in Media. Reflection in Media
 Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
CS348B Lecture 10 Pat Hanrahan, Spring 2002
 Page 1 Reflecton Models I Today Types of eflecton models The BRDF and eflectance The eflecton equaton Ideal eflecton and efacton Fesnel effect Ideal dffuse Next lectue Glossy and specula eflecton models
Page 1 Reflecton Models I Today Types of eflecton models The BRDF and eflectance The eflecton equaton Ideal eflecton and efacton Fesnel effect Ideal dffuse Next lectue Glossy and specula eflecton models
Probabilistic Image Processing by Extended Gauss-Markov Random Fields
 Pobablsc mage Pocessng b Eended Gauss-Makov Random Felds Kauuk anaka Munek asuda Ncolas Mon Gaduae School of nfomaon Scences ohoku Unves Japan and D. M. engon Depamen of Sascs Unves of Glasgow UK 3 Sepembe
Pobablsc mage Pocessng b Eended Gauss-Makov Random Felds Kauuk anaka Munek asuda Ncolas Mon Gaduae School of nfomaon Scences ohoku Unves Japan and D. M. engon Depamen of Sascs Unves of Glasgow UK 3 Sepembe
Variance of Trait in an Inbred Population. Variance of Trait in an Inbred Population
 Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Revew of Mean Trat Value n Inbred Populatons We showed n the last lecture that for a populaton
Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Revew of Mean Trat Value n Inbred Populatons We showed n the last lecture that for a populaton
Quantum ElectroDynamics II
 Quantum ElectroDynamcs II Dr.arda Tahr Physcs department CIIT, Islamabad Photon Coned by Glbert Lews n 1926. In Greek Language Phos meanng lght The Photons A What do you know about Photon? Photon Dscrete
Quantum ElectroDynamcs II Dr.arda Tahr Physcs department CIIT, Islamabad Photon Coned by Glbert Lews n 1926. In Greek Language Phos meanng lght The Photons A What do you know about Photon? Photon Dscrete
Technical Appendix (Not for publication) Generic and Brand Advertising Strategies in a Dynamic Duopoly
 Tehnal Appendx (Not fo publaton Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly Ths Tehnal Appendx povdes supplementay nfomaton to the pape Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly. It s dvded
Tehnal Appendx (Not fo publaton Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly Ths Tehnal Appendx povdes supplementay nfomaton to the pape Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly. It s dvded
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Neutralino contributions to Dark Matter, LHC and future Linear Collider searches
 Neutralno contrbutons to Dark Matter, LHC and future Lnear Collder searches G.J. Gounars Unversty of Thessalonk, Collaboraton wth J. Layssac, P.I. Porfyrads, F.M. Renard and wth Th. Dakonds for the γz
Neutralno contrbutons to Dark Matter, LHC and future Lnear Collder searches G.J. Gounars Unversty of Thessalonk, Collaboraton wth J. Layssac, P.I. Porfyrads, F.M. Renard and wth Th. Dakonds for the γz
EQUIVALENT MODEL OF HVDC-VSC AND ITS HYBRID SIMULATION TECHNIQUE
 7 Vol. 7 No. 003 Power Sytem Technology Fe. 003 000-36730030-0004-05 T7. A 3007 EQIVALENT ODEL OF HVDC-VSC AND ITS HYBRID SILATION TECHNIQE WANG Guan, CAI Ye, ZHANG Gu-n, X Zheng Department of Electrcal
7 Vol. 7 No. 003 Power Sytem Technology Fe. 003 000-36730030-0004-05 T7. A 3007 EQIVALENT ODEL OF HVDC-VSC AND ITS HYBRID SILATION TECHNIQE WANG Guan, CAI Ye, ZHANG Gu-n, X Zheng Department of Electrcal
RMTP Journal of Software. Vol.13, No /2002/13(08) , )
 000-985/00/3(08)70-08 00 Joun of oftwe Vo3, No8 T,,, (, 00876) E-m: {b0073056,wdwng,chd}@bupteducn http://wwwbupteducn : T(ebe mutct tnpot potoco) (ep eve) T,T ;,T,,T : ; ; ; : T393 : A Intenet,, T ],
000-985/00/3(08)70-08 00 Joun of oftwe Vo3, No8 T,,, (, 00876) E-m: {b0073056,wdwng,chd}@bupteducn http://wwwbupteducn : T(ebe mutct tnpot potoco) (ep eve) T,T ;,T,,T : ; ; ; : T393 : A Intenet,, T ],
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
8.324 Relativistic Quantum Field Theory II
 Lecture 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II Fall 00 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II MIT OpenCourseWare Lecture Notes Hon Lu, Fall 00 Lecture 5.: RENORMALIZATION GROUP FLOW Consder the bare acton
Lecture 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II Fall 00 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II MIT OpenCourseWare Lecture Notes Hon Lu, Fall 00 Lecture 5.: RENORMALIZATION GROUP FLOW Consder the bare acton
1 Complete Set of Grassmann States
 Physcs 610 Homework 8 Solutons 1 Complete Set of Grassmann States For Θ, Θ, Θ, Θ each ndependent n-member sets of Grassmann varables, and usng the summaton conventon ΘΘ Θ Θ Θ Θ, prove the dentty e ΘΘ dθ
Physcs 610 Homework 8 Solutons 1 Complete Set of Grassmann States For Θ, Θ, Θ, Θ each ndependent n-member sets of Grassmann varables, and usng the summaton conventon ΘΘ Θ Θ Θ Θ, prove the dentty e ΘΘ dθ
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines
![Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines](/thumbs/51/28406191.jpg) Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
dx x ψ, we should find a similar expression for rθφ L ψ. From L = R P and our knowledge of momentum operators, it follows that + e y z d
 PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
Generalized Fibonacci-Like Polynomial and its. Determinantal Identities
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 01, no. 9, 1415-140 Generalzed Fbonacc-Le Polynomal and ts Determnantal Identtes V. K. Gupta 1, Yashwant K. Panwar and Ompraash Shwal 3 1 Department of Mathematcs,
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 01, no. 9, 1415-140 Generalzed Fbonacc-Le Polynomal and ts Determnantal Identtes V. K. Gupta 1, Yashwant K. Panwar and Ompraash Shwal 3 1 Department of Mathematcs,
LECTURE 4 : ARMA PROCESSES
 LECTURE 4 : ARMA PROCESSES Movng-Average Processes The MA(q) process, s defned by (53) y(t) =µ ε(t)+µ 1 ε(t 1) + +µ q ε(t q) =µ(l)ε(t), where µ(l) =µ +µ 1 L+ +µ q L q and where ε(t) s whte nose An MA model
LECTURE 4 : ARMA PROCESSES Movng-Average Processes The MA(q) process, s defned by (53) y(t) =µ ε(t)+µ 1 ε(t 1) + +µ q ε(t q) =µ(l)ε(t), where µ(l) =µ +µ 1 L+ +µ q L q and where ε(t) s whte nose An MA model
Phasor Diagram of an RC Circuit V R
 ESE Lecture 3 Phasor Dagram of an rcut VtV m snt V t V o t urrent s a reference n seres crcut KVL: V m V + V V ϕ I m V V m ESE Lecture 3 Phasor Dagram of an L rcut VtV m snt V t V t L V o t KVL: V m V
ESE Lecture 3 Phasor Dagram of an rcut VtV m snt V t V o t urrent s a reference n seres crcut KVL: V m V + V V ϕ I m V V m ESE Lecture 3 Phasor Dagram of an L rcut VtV m snt V t V t L V o t KVL: V m V
A Class of Orthohomological Triangles
 A Class of Orthohomologcal Trangles Prof. Claudu Coandă Natonal College Carol I Craova Romana. Prof. Florentn Smarandache Unversty of New Mexco Gallup USA Prof. Ion Pătraşcu Natonal College Fraţ Buzeşt
A Class of Orthohomologcal Trangles Prof. Claudu Coandă Natonal College Carol I Craova Romana. Prof. Florentn Smarandache Unversty of New Mexco Gallup USA Prof. Ion Pătraşcu Natonal College Fraţ Buzeşt
Solutions for Mathematical Physics 1 (Dated: April 19, 2015)
 Solutons for Mathematcal Physcs 1 Dated: Aprl 19, 215 3.2.3 Usng the vectors P ê x cos θ + ê y sn θ, Q ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, R ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, 1 prove the famlar trgonometrc denttes snθ + ϕ sn θ cos
Solutons for Mathematcal Physcs 1 Dated: Aprl 19, 215 3.2.3 Usng the vectors P ê x cos θ + ê y sn θ, Q ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, R ê x cos ϕ ê y sn ϕ, 1 prove the famlar trgonometrc denttes snθ + ϕ sn θ cos
CHAPTER 10. Hence, the circuit in the frequency domain is as shown below. 4 Ω V 1 V 2. 3Vx 10 = + 2 Ω. j4 Ω. V x. At node 1, (1) At node 2, where V
 February 5, 006 CHAPTER 0 P.P.0. 0 in(t 0 0, ω H jωl j4 0. F -j.5 jωc Hence, e circuit in e frequency dmain i a hwn belw. -j.5 Ω 4 Ω 0 0 A Ω x j4 Ω x At nde, At nde, 0 - j.5 00 (5 j4 j ( 4 x where x j4
February 5, 006 CHAPTER 0 P.P.0. 0 in(t 0 0, ω H jωl j4 0. F -j.5 jωc Hence, e circuit in e frequency dmain i a hwn belw. -j.5 Ω 4 Ω 0 0 A Ω x j4 Ω x At nde, At nde, 0 - j.5 00 (5 j4 j ( 4 x where x j4
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Aerodynamics & Aeroelasticity: Eigenvalue analysis
 Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Natonal Techncal Unversty of Athens Aerodynamcs & Aeroelastcty: Egenvalue analyss Σπύρος Βουτσινάς / Spyros Voutsnas Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες
Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Natonal Techncal Unversty of Athens Aerodynamcs & Aeroelastcty: Egenvalue analyss Σπύρος Βουτσινάς / Spyros Voutsnas Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION. Solution Manual
 ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
CAPM. VaR Value at Risk. VaR. RAROC Risk-Adjusted Return on Capital
 C RAM 3002 C RAROC Rsk-Adjusted Return on Captal C C RAM Rsk-Adjusted erformance Measure C RAM RAM Bootstrap RAM C RAROC RAM Bootstrap F830.9 A CAM 2 CAM 3 Value at Rsk RAROC Rsk-Adjusted Return on Captal
C RAM 3002 C RAROC Rsk-Adjusted Return on Captal C C RAM Rsk-Adjusted erformance Measure C RAM RAM Bootstrap RAM C RAROC RAM Bootstrap F830.9 A CAM 2 CAM 3 Value at Rsk RAROC Rsk-Adjusted Return on Captal
ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα,
 ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα Βασίλειος Σύρης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης Εαρινό εξάμηνο 2008 Economcs Contents The contet The basc model user utlty, rces and
ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα Βασίλειος Σύρης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης Εαρινό εξάμηνο 2008 Economcs Contents The contet The basc model user utlty, rces and
Journal of Theoretics Vol.4-5
 Journal of Theoretcs Vol.4- A Unfed Feld Theory Peter Hckman peter.hckman@ntlworld.com Abstract: In ths paper, the extenson of Remann geometry to nclude an asymmetrc metrc tensor s presented. A new co-varant
Journal of Theoretcs Vol.4- A Unfed Feld Theory Peter Hckman peter.hckman@ntlworld.com Abstract: In ths paper, the extenson of Remann geometry to nclude an asymmetrc metrc tensor s presented. A new co-varant
Theoretical Competition: 12 July 2011 Question 1 Page 1 of 2
 Theoetical Competition: July Question Page of. Ένα πρόβλημα τριών σωμάτων και το LISA μ M O m EIKONA Ομοεπίπεδες τροχιές των τριών σωμάτων. Δύο μάζες Μ και m κινούνται σε κυκλικές τροχιές με ακτίνες και,
Theoetical Competition: July Question Page of. Ένα πρόβλημα τριών σωμάτων και το LISA μ M O m EIKONA Ομοεπίπεδες τροχιές των τριών σωμάτων. Δύο μάζες Μ και m κινούνται σε κυκλικές τροχιές με ακτίνες και,
( ) ( t) ( 0) ( ) dw w. = = β. Then the solution of (1.1) is easily found to. wt = t+ t. We generalize this to the following nonlinear differential
 Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
Exercise, May 23, 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1
 Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Parametrized Surfaces
 Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
Strain and stress tensors in spherical coordinates
 Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Certain fractional derivative formulae involving the product of a general class of polynomials and the multivariable H-function
 Proc Indan Acad Sc Math Sc Vol 2 No 4 November 2002 pp 55 562 Prnted n Inda Certan fractonal dervatve formulae nvolvng the product of a general cla of polynomal and the multvarable -functon R C SONI and
Proc Indan Acad Sc Math Sc Vol 2 No 4 November 2002 pp 55 562 Prnted n Inda Certan fractonal dervatve formulae nvolvng the product of a general cla of polynomal and the multvarable -functon R C SONI and
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων
 Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων Όρια Πιστότητας (Confidence Limits) 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 1 Τα όρια πιστότητας -Confidence Limits (CL) Tα όρια πιστότητας μιας μέτρησης Μπορεί να αναφέρονται
Υπολογιστική Φυσική Στοιχειωδών Σωματιδίων Όρια Πιστότητας (Confidence Limits) 2/4/2014 Υπολογ.Φυσική ΣΣ 1 Τα όρια πιστότητας -Confidence Limits (CL) Tα όρια πιστότητας μιας μέτρησης Μπορεί να αναφέρονται
The one-dimensional periodic Schrödinger equation
 The one-dmensonal perodc Schrödnger equaon Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmal.com Deparmen of Mahemacs, Unversy of Torono Aprl 23, 26 Translaons and convoluon For y, le τ y f(x f(x y. To say ha f : C s unformly
The one-dmensonal perodc Schrödnger equaon Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmal.com Deparmen of Mahemacs, Unversy of Torono Aprl 23, 26 Translaons and convoluon For y, le τ y f(x f(x y. To say ha f : C s unformly
8. ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΊΑ ΣΗΜΆΤΩΝ. ICA: συναρτήσεις κόστους & εφαρμογές
 8. ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΊΑ ΣΗΜΆΤΩΝ ICA: συναρτήσεις κόστους & εφαρμογές ΚΎΡΤΩΣΗ (KUROSIS) Αθροιστικό (cumulant) 4 ης τάξεως μίας τ.μ. x με μέσο όρο 0: kurt 4 [ x] = E[ x ] 3( E[ y ]) Υποθέτουμε διασπορά=: kurt[ x]
8. ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΊΑ ΣΗΜΆΤΩΝ ICA: συναρτήσεις κόστους & εφαρμογές ΚΎΡΤΩΣΗ (KUROSIS) Αθροιστικό (cumulant) 4 ης τάξεως μίας τ.μ. x με μέσο όρο 0: kurt 4 [ x] = E[ x ] 3( E[ y ]) Υποθέτουμε διασπορά=: kurt[ x]
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics
 Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2
 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Symplecticity of the Störmer-Verlet algorithm for coupling between the shallow water equations and horizontal vehicle motion
 Symplectcty of the Störmer-Verlet algorthm for couplng between the shallow water equatons and horzontal vehcle moton by H. Alem Ardakan & T. J. Brdges Department of Mathematcs, Unversty of Surrey, Guldford
Symplectcty of the Störmer-Verlet algorthm for couplng between the shallow water equatons and horzontal vehcle moton by H. Alem Ardakan & T. J. Brdges Department of Mathematcs, Unversty of Surrey, Guldford
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
1 3D Helmholtz Equation
 Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Vol. 34 ( 2014 ) No. 4. J. of Math. (PRC) : A : (2014) Frank-Wolfe [7],. Frank-Wolfe, ( ).
![Vol. 34 ( 2014 ) No. 4. J. of Math. (PRC) : A : (2014) Frank-Wolfe [7],. Frank-Wolfe, ( ). Vol. 34 ( 2014 ) No. 4. J. of Math. (PRC) : A : (2014) Frank-Wolfe [7],. Frank-Wolfe, ( ).](/thumbs/91/105872052.jpg) Vol. 4 ( 214 ) No. 4 J. of Math. (PRC) 1,2, 1 (1., 472) (2., 714) :.,.,,,..,. : ; ; ; MR(21) : 9B2 : : A : 255-7797(214)4-759-7 1,,,,, [1 ].,, [4 6],, Frank-Wolfe, Frank-Wolfe [7],.,,.,,,., UE,, UE. O-D,,,,,
Vol. 4 ( 214 ) No. 4 J. of Math. (PRC) 1,2, 1 (1., 472) (2., 714) :.,.,,,..,. : ; ; ; MR(21) : 9B2 : : A : 255-7797(214)4-759-7 1,,,,, [1 ].,, [4 6],, Frank-Wolfe, Frank-Wolfe [7],.,,.,,,., UE,, UE. O-D,,,,,
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΟΣ ΣΥΝΔΕΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY 21 ος ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ Δεύτερος Γύρος - 30 Μαρτίου 2011
 Διάρκεια Διαγωνισμού: 3 ώρες Απαντήστε όλες τις ερωτήσεις Μέγιστο Βάρος (20 Μονάδες) Δίνεται ένα σύνολο από N σφαιρίδια τα οποία δεν έχουν όλα το ίδιο βάρος μεταξύ τους και ένα κουτί που αντέχει μέχρι
Διάρκεια Διαγωνισμού: 3 ώρες Απαντήστε όλες τις ερωτήσεις Μέγιστο Βάρος (20 Μονάδες) Δίνεται ένα σύνολο από N σφαιρίδια τα οποία δεν έχουν όλα το ίδιο βάρος μεταξύ τους και ένα κουτί που αντέχει μέχρι
VBA Microsoft Excel. J. Comput. Chem. Jpn., Vol. 5, No. 1, pp (2006)
 J. Comput. Chem. Jpn., Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 29 38 (2006) Microsoft Excel, 184-8588 2-24-16 e-mail: yosimura@cc.tuat.ac.jp (Received: July 28, 2005; Accepted for publication: October 24, 2005; Published on
J. Comput. Chem. Jpn., Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 29 38 (2006) Microsoft Excel, 184-8588 2-24-16 e-mail: yosimura@cc.tuat.ac.jp (Received: July 28, 2005; Accepted for publication: October 24, 2005; Published on
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
Problems in curvilinear coordinates
 Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
10/3/ revolution = 360 = 2 π radians = = x. 2π = x = 360 = : Measures of Angles and Rotations
 //.: Measures of Angles and Rotations I. Vocabulary A A. Angle the union of two rays with a common endpoint B. BA and BC C. B is the vertex. B C D. You can think of BA as the rotation of (clockwise) with
//.: Measures of Angles and Rotations I. Vocabulary A A. Angle the union of two rays with a common endpoint B. BA and BC C. B is the vertex. B C D. You can think of BA as the rotation of (clockwise) with
physicsandmathstutor.com
 physicsadmathstuto.com physicsadmathstuto.com Jauay 009 blak 3. The ectagula hypebola, H, has paametic equatios x = 5t, y = 5 t, t 0. (a) Wite the catesia equatio of H i the fom xy = c. Poits A ad B o
physicsadmathstuto.com physicsadmathstuto.com Jauay 009 blak 3. The ectagula hypebola, H, has paametic equatios x = 5t, y = 5 t, t 0. (a) Wite the catesia equatio of H i the fom xy = c. Poits A ad B o
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
... 5 A.. RS-232C ( ) RS-232C ( ) RS-232C-LK & RS-232C-MK RS-232C-JK & RS-232C-KK
 RS-3C WIWM050 014.1.9 P1 :8... 1... 014.0.1 1 A... 014.0. 1... RS-3C()...01.08.03 A.. RS-3C()...01.08.03 3... RS-3C()... 003.11.5 4... RS-3C ()... 00.10.01 5... RS-3C().008.07.16 5 A.. RS-3C().0 1.08.
RS-3C WIWM050 014.1.9 P1 :8... 1... 014.0.1 1 A... 014.0. 1... RS-3C()...01.08.03 A.. RS-3C()...01.08.03 3... RS-3C()... 003.11.5 4... RS-3C ()... 00.10.01 5... RS-3C().008.07.16 5 A.. RS-3C().0 1.08.
Matrices and vectors. Matrix and vector. a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = b 1 b 2. b m. R m n, b = = ( a ij. a m1 a m2 a mn. def
 Matrices and vectors Matrix and vector a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = a m1 a m2 a mn def = ( a ij ) R m n, b = b 1 b 2 b m Rm Matrix and vectors in linear equations: example E 1 : x 1 + x 2 + 3x 4 =
Matrices and vectors Matrix and vector a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = a m1 a m2 a mn def = ( a ij ) R m n, b = b 1 b 2 b m Rm Matrix and vectors in linear equations: example E 1 : x 1 + x 2 + 3x 4 =
Sequent Calculi for the Modal µ-calculus over S5. Luca Alberucci, University of Berne. Logic Colloquium Berne, July 4th 2008
 Sequent Calculi for the Modal µ-calculus over S5 Luca Alberucci, University of Berne Logic Colloquium Berne, July 4th 2008 Introduction Koz: Axiomatisation for the modal µ-calculus over K Axioms: All classical
Sequent Calculi for the Modal µ-calculus over S5 Luca Alberucci, University of Berne Logic Colloquium Berne, July 4th 2008 Introduction Koz: Axiomatisation for the modal µ-calculus over K Axioms: All classical
An Inventory of Continuous Distributions
 Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Reflection Models. Reflection Models
 Reflecon Models Today Types of eflecon models The BRDF and eflecance The eflecon equaon Ideal eflecon and efacon Fesnel effec Ideal dffuse Thusday Glossy and specula eflecon models Rough sufaces and mcofaces
Reflecon Models Today Types of eflecon models The BRDF and eflecance The eflecon equaon Ideal eflecon and efacon Fesnel effec Ideal dffuse Thusday Glossy and specula eflecon models Rough sufaces and mcofaces
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
LAGRANGIAN EQUILIBRIUM EQUATIONS IN CYLINDRICAL AND SPHERICAL COORDINATES
 Compute, Mateial & Continua 3 (2006) 37-42 LAGANGIAN EQUILIBIUM EQUAIONS IN CYLINDICAL AND SHEICAL COODINAES.Y. Voloh Depatment of Mehanial Engineeing, John Hopin Univeity, Baltimoe, MD Abtat Lagangian
Compute, Mateial & Continua 3 (2006) 37-42 LAGANGIAN EQUILIBIUM EQUAIONS IN CYLINDICAL AND SHEICAL COODINAES.Y. Voloh Depatment of Mehanial Engineeing, John Hopin Univeity, Baltimoe, MD Abtat Lagangian
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Similarly, we may define hyperbolic functions cosh α and sinh α from the unit hyperbola
 Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
