HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES WITH REMAINDERS
|
|
|
- Φιλοκράτης Κουντουριώτης
- 7 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES WITH REMAINDERS W. D. EVANS AND ROGER T. LEWIS Astract. I this paper our primary cocer is with the estalishmet of weighted Hardy iequalities i L p () ad Rellich iequalities i L () depedig upo the distace to the oudary of domais R with a fiite diameter D(). Improved costats are preseted i most cases.. Itroductio Recetly, cosiderale attetio has ee give to extesios of the multi-dimesioal Hardy iequality of the form u(x) u(x) dx µ() dx + λ() u(x) dx, u H δ(x) (), (.) where is a ope coected suset of R ad δ(x) := dist(x, ). It is kow that for µ() = there are smooth domais for which 4 λ(), ad for λ() =, there are smooth domais for which µ() < - see M. Marcus, V.J. Mizel, ad Y. Pichover [8] ad 4 T. Matskewich ad P.E. Soolevskii [9]. I [], H. Brezis ad M. Marcus showed that for domais of class C iequality (.) holds for µ() = 4 ad some λ() (, ) ad whe is covex λ() 4D() (.) i which D() is the diameter of. M. Hoffma-Ostehof, T. Hoffma-Ostehof, ad A. Laptev [6] aswered a questio posed y H. Brezis ad M. Markus i [] y estalishig the improvemet to (.) that (.) holds for a covex domai Date: March 8, Mathematics Suject Classificatio. Primary 47A63; Secodary 46E35, 6D. Key words ad phrases. Rellich iequality, Hardy iequality, Remaider terms.
2 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS, with µ() = 4, K() λ(), ad K() := 4 [ s ] / (.3) i which s := S ad is the volume of. For a covex domai ad µ() = /4, a lower oud for λ() i (.) i terms of was also otaied y S. Filippas, V. Maz ya, ad A. Tertikas i [5] as a special case of results o L p Hardy iequalities. They prove that λ() 3D it (), where D it () = sup x δ(x), the iteral diameter of. Sice 3D it () 3 4 K()/ /, their result is a improvemet of (.3) for =, 3, ut the estimates do t compare for > 3. I this paper we show that (.) holds for (.3) replaced y µ() = 4 ad λ() 3K() as well as provig weighted versios of the Hardy iequality i L p () for p >. I the case p =, the followig are special cases of our results. If is covex ad σ (, ], the u(x) σ ( σ) dx 4D() σ B(, σ) δ(x) σ +3 ( s ) σ u(x) dx (.4) for p+ Γ( B(, p) := ) Γ( ) π Γ( +p ). (.5) If σ [, ] ad is covex, the δ(x) σ u(x) ( σ) dx B(, σ) δ(x) σ u(x) dx 4 + C H(, σ) δ(x) σ u(x) dx. ( σ) for C H (, σ) give i (3.4). Similar results for weighted forms of the Hardy iequality i L p () are give i sectio 4. Fially, we show that our oe-dimesioal iequalities i lead to improved costats for the Rellich iequality otaied y G. Baratis i [] for 4.. Oe-dimesioal iequalities As is the case i [6], our proofs are ased o oe-dimesioal Hardytype iequalities coupled with the use of the mea-distace fuctio itroduced y Davies to exted to higher dimesios; see [4]. The asic oe-dimesioal iequality is as follows:
3 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES 3 Lemma. Let u C (, ), (t) := mit, t ad let f C [, ] e mootoic o [, ]. The for p > f ((t)) u(t) p dt p p f((t)) f() p f ((t)) p u (t) p dt. (.) Proof. First let u := vχ (,], the restrictio to (, ] of some v C (, ). For ay costat c [f(t) c] u(t) p dt = [f(t) c] u(t) p By choosig c = f(), we have that + [f(t) c] p [ u(t) ] p [ u(t) ] dt. f (t) u(t) p dt = p [f(t) f()] u(t) p Re[u(t)u (t)]dt. (.) Similarly, for u = vχ [,), v C (, ), we have f ( s) u(s) p ds = p [f( s) f()] u(s) p Re[u(s)u (s)]ds. Therefore, sice f is mootoic, for ay u C(, ) f ((t)) u(t) p dt = p f((t)) f() u(t) p Re[u(t)u (t)]dt p f ((t)) p p u(t) p f((t)) f() u (t) dt [ p f ((t)) u(t) p dt ] p p f ((t)) p p [ f((t)) f() p f ((t)) p u (t) p dt o applyig Hölder s iequality. Iequality (.) ow follows. The ext lemma provides the oe-dimesioal result eeded to improve (.3), which was proved i [6]. Lemma. Let σ ad defie µ(t) := (t). For all u C(, ) ( σ ) ( (t) ) σ ] u(t) (t) σ u (t) dt (t) [+k(σ) σ dt, µ(t) (.3) for [ k(σ) := ] σ σ, σ <,, σ [, ]. Proof. O settig f(t) = t σ i (.) we get σ p (t) σ u(t) p dt p p ] p (t) p+σ [(t) ] σ p u (t) p dt. (.4)
4 4 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS With u C(, ), let p = ad sustitute v(t) = [ ( (t) ) σ]u(t) i (.4). We claim that this gives ( σ ) ( (t) ) σ ] v(t) σ (t) v (t) dt (t) [ σ dt (.5) for ay real umer σ. The sustitutio gives (t) σ/ v (t) = ( σ) σ (t) σ/ (t)u(t)+(t) σ/[ ( (t) ) σ ] u (t). Cosequetly, (t) σ v (t) = ( σ) σ (t) σ u(t) + (t) σ[ ( ) (t) σ ] u (t) ( σ) σ (t) [ ( (t) ) σ ] [ u ] which implies that (t)σ v (t) dt = (t)σ[ ( ) (t) σ ] u (t) dt + ( σ) σ (t) σ u(t) dt +( σ) [ σ d (t) [ ( (t) ) σ ] ] u dt dt = (t)σ[ ( (t) ) σ ] u (t) dt (.6) sice (t) = i (, ) ad i (, ). Therefore, (.5) follows from (.4). Sice = µ(t) + (t) for [ ( (t) k σ (x) := ) σ ] = [ + (t) σ = σ (t) σ ] [ + σ( (t) ) ] σkσ (.7) ( (t) ) µ(t) µ(t), x [, ), σ. ( + x) σ (x) σ For σ <, k σ (x) > i (, ), k σ () = ad k σ (x) as x. By examiig the derivative of k σ (x) we see that k σ(x) = ( σ)(( + x) σ σ x σ ) [( + x) σ (x) σ ] lim k σ(x) = x + For σ <, k σ (x) is miimized at Calculatios show that ( σ), σ <,,, σ =, < σ <. x σ := /( σ ) <. k σ (x σ ) = [ σ ] σ =: k(σ).
5 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES 5 For σ [, ), k σ(x) is ever zero i (, ) idicatig that k σ (x) is miimized at x = for σ [, ) ad x [, ). The iequality (.3) ow follows. I order to treat the case i which p, we make use of the methods of Tidlom [] ad prove a weighted versio of Theorem. i []. Lemma 3. Let u C (, ), p (, ), ad σ p. The [ ] p (t)σ u (t) p p σ dt p (t)σ p + (p ) σ p u(t) p dt. Proof. We may assume that σ p sice otherwise the coclusio is trivial. Accordig to (.) for a mootoic fuctio f ad a positive fuctio g, f (t) u(t) p dt p f(t) f() u(t) p u (t) dt [ ] [ /p ( ) ] p g(t) u (t) p dt f(t) f() p /(p ) /p g(t) u(t) p dt. Cosequetly, p p g(t) u (t) p dt ( ( ) p f (t) u(t) p dt ) /(p ) p. u(t) p dt) ( f(t) f() p g(t) Now, as i [], usig a corollary to Youg s iequality, amely A p /B p pa (p )B, ) /p u(t) p dt, it fol- with A = f (t) u(t) p dt, B = lows that p p g(t) u (t) p dt p f (t) (p ) ( f(t) f() p g(t) ( f(t) f() p g(t) ) /(p ) u(t) p dt. Choose f(t) = t σ p+ ad g(t) = (p σ ) (p ) t σ. The ( f(t) f() p g(t) ) /(p ) = (p σ ) [ t σ p+ σ p+ p t σ ] p = (p σ )t [( σ p ( ) ) t p σ p ] p.
6 6 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS Cosequetly, for t (, ) ( ) f(t) f() p /(p ) p f (t) (p ) g(t) [( = (p σ ) pt σ p (p )t σ p ( [ = (p σ )t σ p + (p ) (p σ )t σ p + (p ) ( ) t p σ ( t ( t ) ) p σ p ] p ) ] p ) p σ p (p σ ) t σ p + (p ) ( ). p σ ad the iequality follows. I the iequality aove we have used the fact that [ ( t p σ ] p ( p t ) p σ. ) The proof is completed y followig the last part of the proof of Lemma. For a certai rage of values take y σ, σ [ c σ, ) with c σ >, the iequality i L () give y Lemma gives a etter oud tha Lemma 3 with p =. I fact for σ < ( (t) ) σ ] (t) [ σ + k(σ) = (t) σ + σ k(σ) µ(t) (t)µ(t) + σ k(σ) σ (t) σ µ(t) σ with σ k(σ) + σ k(σ) (.8) (t)µ(t) σ (t) σ µ(t) σ 5 [ σ, σ [, ), σ σ + σ k(σ)(t) σ ] k(σ) σ, σ <. Sice k(σ) decreases to for σ < as σ ad k( 3)., the the left-had side of (.8) is greater tha σ for σ [ 3, ). 3. A Hardy iequality i L () We eed the followig otatio (c.f.[6]). For each x ad ν S, τ ν (x) := mis > : x + sν ; D ν (x) := τ ν (x) + τ ν (x); ν (x) := miτ ν (x), τ ν (x); µ ν (x) := maxτ ν (x), τ ν (x) = D ν (x) ν (x); D() := sup D ν (x); x, ν S x := y : x + t(y x), t [, ]. Note that D() is the diameter of ad x is the part of which ca e see from the poit x. The volume of x is deoted y x.
7 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES 7 Let dω(ν) deote the ormalized measure o S (so that = dω(ν)) ad defie S (x; s) := ν (x) s dω(ν). S (3.) Hece / (x; ) = (x) the mea-distace fuctio itroduced y Davies i [4]. For B(, p) := cos(e, ν) p dω(ν) = Γ( p+ ) Γ( ) S π Γ( +p ), e R, (3.) it is kow that B(, p) (x; p) := dω(ν) (3.3) S ν (x) p δ(x) p for covex domais see Exercise 5.7 i [4], [3], ad []. Note that B(, ) =. This fact ca e applied to most of the results elow whe is covex. For a Hardy iequality i L () with weights we will eed to defie ( s ) ( σ) C H (, σ) := k(σ)[ σ + σ k(σ)]( σ) (3.4) for σ [, ] ad where as give i Lemma [ k(σ) := ] σ σ, σ <,, σ [, ]. Note that C H (, ) = 3 K() for K() defied i (.3). Theorem. If σ, the for ay u C () δ(x) σ u(x) ( σ) dx (x; σ ) u(x) dx 4 δ(x) σ + C H (, σ) u(x) dx. (3.5) x ( σ) If < σ, the u(x) dx σ ( σ) 4D() σ (x; σ ) + 3 ( s x ) σ u(x) dx. (3.6) If is covex, the for ay u C() δ(x) σ u(x) ( σ) dx B(, σ) δ(x) σ u(x) dx 4 + C H(, σ) δ(x) σ u(x) dx. ( σ)
8 8 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS whe σ [, ] ad u(x) dx σ ( σ) 4D() σ whe σ (, ]. B(, σ)δ(x) σ + 3 ( s ) σ u(x) dx. Proof. Let ν u, ν S, deote the derivative of u i the directio of ν, i.e., ν u = ν ( u). It follows from Lemma that for σ (, ] σ ν(x) ν u dx ( σ ) ν(x) σ ( + k(σ) [ ν(x) µ ν(x) ] ( σ) ) u(x) dx. Expadig the itegrad i (3.7), we have ν (x) σ ( + k(σ) [ ν(x) ] ( σ) ) µ ν(x) = ν (x) σ + σ k(σ) ν(x) σ (τ ν(x)τ ν + ( σ) k(σ) ν(x) σ (x)) σ µ ν(x). ( σ) If σ ν (x) σ [ + k(σ) ( ν (x)) ( σ) ] µ ν (x) k(σ)δ(x) σ ν (x) σ + σ (τ ν(x)τ ν + ( σ) k(σ) δ(x) σ (x)) σ (3.7) (3.8) τ ν(x) ( σ) +τ ν (x) ( σ) sice ν (x) σ δ(x) σ i this case. As i [6], we ote that sice (τ S ν (x)τ ν (x)) σ dω(ν) (τ S ν (x)) ( σ) dω(ν) [ (τ S ν (x)) dω(ν) ] ( σ) = [ s x ] ( σ) for σ, the S (τ ν (x)τ ν dω(ν) [ (τ (x)) σ S ν (x)τ ν (x)) σ dω(ν) ] [ s x ] ( σ). For the third term i iequality (3.9) S (τ ν (x) ( σ) + τ ν (x) ( σ) )dω(ν) = implyig that for σ S (τ ν (x) ( σ) + τ ν (x) ( σ) ) dω(ν) S τ ν (x) ( σ) dω(ν) [ s x ] ( σ). (3.9) Cosequetly, for σ we have that S ν (x) σ [ + k(σ) ( ν (x)) ( σ) ] dω(ν) µ ν(x) (x; σ ) + C H (, σ)δ(x) σ / [ ] (3.) x ( σ).
9 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES 9 Upo comiig this fact with (3.7) we have ( ) σ (x; σ ) + C H (,σ)δ(x) σ x ( σ)/ u(x) dx S ν (x) σ ν u(x) dω(ν)dx = δ(x)σ cos(ν, u(x)) dω(ν) (3.) S u(x) dx for σ. Sice cos(ν, α) dω(ν) = (3.) S for ay fixed α S (see Tidlom [], p.7), iequality (3.5) follows. For < σ, we cosider first the third term o the right-had side of (3.8). We have S ν (x) σ µ ν (x) ( σ) dω(ν) σ (τ S ν (x) + τ ν (x)) σ (τ ν (x) + τ ν (x)) ( σ) dω(ν) = σ τ ν (x) + τ ν (x) σ L σ (S ) σ[ ] σ τ ν (x) L σ (S ) + τ ν (x) L σ (S ) = ( σ) τ S ν (x) σ dω(ν) ( σ)[ (τ S ν (x)) dω(ν) ] σ = ( σ)[ s x ] σ for y the Mikowski ad Hölder iequalities. Therefore, the term ν (x) S σ dω(ν) µ ν (σ )( s ) σ (x) ( σ) x. Similarly, i the secod term of (3.8) S ν (x)µ ν (x) σ dω(ν) (τ S ν (x) + τ ν (x))(τ ν (x) + τ ν (x)) σ dω(ν) σ[ s x ] σ as efore implyig that dω(ν) S ν (x)µ ν σ ( s ) σ (x) σ x. For < σ < we ow have that S ν (x) σ [ + k(σ) ( ν (x)) ( σ) ] dω(ν) (x; σ ) + 3 ( s x ) σ µ ν (x) sice k(σ) = i this case. Cosequetly, S ν (x) σ cos(ν, u(x)) dω(ν) u(x) dx ( ) [ ( σ (x; σ ) + 3 s ) σ ] x u(x) dx.
10 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS Accordig to (3.) it follows that S ν (x) σ cos(ν, u(x)) dω(ν) D()σ σ. Therefore, (3.6) holds. The iequalities i the statemet of the theorem for the case of a covex domai follow from (3.3) ad the fact that x = for all x. 4. A L p () iequality With the guidace of Tidlom s aalysis for the Hardy iequality i [], L p versios of the weighted Hardy theorem i the last sectio ca e proved y similar techiques. Whe σ =, the ext theorem reduces to Theorem. of []. Theorem. Let u C() ad p (, ). If σ, the for B(, p) defied i (3.) δ(x)σ u(x) p dx [ p σ /p] p B(,p) ad if σ [, p ], the u(x) p dx σ [ p σ /p] p B(,p) D() σ (x; σ p) + (p )[ s x (x; σ p) + (p )[ s x ] p σ u(x) p dx ] p σ u(x) p dx. (4.) (4.) If is covex, (x, σ p) ca e replaced i (4.) ad (4.) y the term B(, p σ)/δ(x) p σ (i view of (3.3)) ad x y. Proof. From Lemma 3 we have that for σ p, ay ν S, ad u C() ν(x) σ ν u(x) p dx [ p σ p ] p ν (x) σ p + (p )p σ D ν (x) u(x) p dx. p σ (4.3) If σ we oud ν (x) σ for ay ν S y δ(x) σ i the first itegral aove. If σ >, we oud it y D() σ / σ. As i [] we may use the fact that ν u(x) p dω(ν) = B(, p) u(x) p. (4.4) S After oudig ν (x) σ as descried aove, itegrate i (4.3) over S with respect to dω(ν). I order to evaluate the itegral of (/D ν (x)) p σ, we proceed as i []. Sice σ p, the f(t) = t σ p is covex for t > ad we have that ( ) p σdω(ν) ( D ν (x) ) σ p ( x ) p σ dω(ν) S D ν (x) S s (4.5)
11 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES y Jese s iequality ad Lemma. of []. The coclusio follows. 5. Rellich s iequality The methods descried aove with Propositio elow ca e used to prove a weighted Rellich iequality which, for 4 ad without weights, improves the costat give i a Rellich iequality proved recetly y Baratis ([], Theorem.). A compariso is made elow. The methods used y Baratis depeds upo the idetity (5.) first proved y M.P. Owe ([], see the proof of Theorem.3). I order to icorporate weights, our proof requires the poit-wise idetity (5.) which does ot follow from the proof of Owe. Propositio. Let e a domai i R. The, for all u C (R ) νu(x) [ dω(ν) = u(x) + u(x) ], (5.) S ( + ) x i x j ad for all u C() S νu(x) dω(ν)dx = Proof. For ν = (ν,..., ν ) we have νu = (ν ) u = l,m= ν lν m u lm = l= ν l u ll + i,j= 3 u(x) dx. (5.) ( + ) l<m ν l ν m u lm i which u pq (x) := u(x) x p x q. Cosequetly, S νu dω(ν) = l,m= u llu mm (ν S l ) (ν m ) dω(ν) +4 m= Re(u mm u pq ) (ν S m ) ν p ν q dω(ν) p<q +4 Re(u pq u jk ) ν S p ν q ν j ν k dω(ν). j<k p<q (5.3) Let θ j [, π] for j =,...,, ad θ [, π]. Usig the covetio that Π p j=q = for p < q ad θ =, we have ν j = Π j k= si θ k cos θ j, j =,...,, ( )!! dω(ν) := Π k= (si θ k) k dθ k dθ, (5.4) γ for!! := ( ) ( 4) ad (π) ( )/ for odd, γ = (π) / for eve. Calculatios show that S (ν m ) ν p ν q dω(ν) =, m =,...,, p < q
12 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS implyig that the secod term o the right-had side of (5.3) vaishes. A similar cosideratio for the third term o the right-had side of (5.3) shows that ν p ν q ν j ν k dω(ν), p < q, j < k, S oly if j = p ad k = q. Therefore, (5.3) reduces to S νu(x) dω(ν) = l,m= u llu mm (ν S l ) (ν m ) dω(ν) +4 u pq (ν S p ) (ν q ) dω(ν). (5.5) p<q However, further calculatios show that p < q, νpν q (+) dω(ν) = S p = q =,..., implyig that S νu dω(ν) = 3 (+) + (+) = (+) 3 (+) m= u mm [4 u pq + Re(u pp u qq )] p<q [ u(x) + i,j= u(x) ] x i x j which is (5.). Equality (5.) ow follows sice u(x) dx = u(x) dx. x i x j Defie ad i,j= δ(x) σ, σ <, d(x; σ) := ( D() ) σ, σ [, ]; β(, σ) := ( σ) (3 σ) ( + ) ; 6 C R (, σ) := 4 σ k(σ ) [ s for σ ad k(σ) defied i Lemma. Theorem 3. For σ ad u C (), d(x; σ) [ u(x) + holds whe 4 σ ad ] 4 σ ( ) + σ k(σ ) x i x j ]dx i,j= u(x) β(, σ) (x; σ 4) u(x) dx + 4 σ k(σ ) [ s ] 4 σ u(x) 4 σ x dx (5.6) (5.7) (5.8) (5.9)
13 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES 3 d(x; σ) [ u(x) + x i x j ]dx i,j= u(x) β(, σ) (x; σ 4) u(x) dx + 4 σ k(σ ) [ s ] 4 σ + (3 σ) k(σ ) [ s ] 4+t σ u(x) 4 σ x dx δ(x) t u(x) 4+t σ x dx (5.) holds whe 4 + t σ ad t σ. Proof. For σ, it follows that (t) σ u (t) dt (t) σ[ ( (t) ) σ ] u (t) dt µ(t) ( σ ) (t) σ u (t) dt y (.4). Therefore, for σ ad u C (, ), (t)σ u (t) dt ( ( σ)(3 σ) 4 ) (t)σ 4[ + k(σ ) ( (t) µ(t) y (.3). From (5.) we have for u C () ν(x) σ νu(x) dx ( ) ( σ)(3 σ) ν(x) σ 4 + k(σ ) 4 for σ. As i (3.8) we write ( ν(x) ) 3 σ ] u(t) dt (5.) µ ν (x) ) 3 σ u(x) dx (5.) ( ) 3 σ ν (x) σ 4 + k(σ ) ν (x) µ ν(x) = ν (x) σ σ k(σ ) ν (x) µ ν + (3 σ) k(σ ) σ+ ν (x) (x) 3 σ µ ν. (x) (3 σ) (5.3) Sice ν (x)µ ν (x) = τ ν (x)τ ν (x), i the secod term o the right-had side of (5.3) we may write ν (x) µ ν (x) = 3 σ =: I(ν; x). [τ ν (x)τ ν (x)]µ ν (x) σ
14 4 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS Thus S I(ν; x)dω(ν) = τ ν(x) τ ν (x) τ ν(x) σ 3 (x)τ ν (x) dω(ν) + τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τ ν(x) σ 3 (x)τ ν (x) dω(ν) τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τ ν(x) σ 4 (x)dω(ν) ad τ ν (x) dω(ν) σ 4 τ ν (x) τ ν (x) + τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τ ν(x) σ 4 (x)dω(ν) = τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τν (x)dω(ν) S ( ) (4 σ)/ x s τ ν (x) σ+4 dω(ν) (4 σ)/ for 4 σ. Therefore for the secod term o the right-had side of (5.3), for σ ad 4 σ, it follows that S ν (x)dω(ν) ( u(x) s ) 4 σ u(x) dx dx. (5.4) µ ν (x) 3 σ x 4 σ For ay t (, ), we may write the third term i (5.3) as σ+ ν (x) µ ν (x) = ν(x) t (τ (3 σ) ν (x)τ ν (x)) σ t µ(x) 8+3σ+t =: ν (x) t J(ν, x). If t σ S J(ν; x)dω(ν) As efore τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τ ν (x) 4+σ t dω(ν) τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τ ν(x) 4+σ t dω(ν) + τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τ ν(x) 4+σ t dω(ν). = τ ν (x) τ ν (x) τν (x)dω(ν) S ( x s τ ν (x) 4 σ+t dω(ν) ) (4 σ+t)/ (4 σ+t)/ if 4 σ + t. Associated with the third term o the right-had side of (5.3), we have for σ, t σ >, ad 4 σ + t S σ+ ν (x)dω(ν) ( u(x) s ) 4+t σ δ(x) t u(x) dx dx. µ ν (x) (3 σ ) x 4+t σ (5.5)
15 HARDY AND RELLICH INEQUALITIES 5 From (5.) (5.5) we otai S ν (x) σ νu(x) dω(ν)dx ( σ) (3 σ) (x; σ 4) u(x) dx + 4 σ k(σ ) [ s ] 4 σ + (3 σ) k(σ ) [ s ] 4+t σ u(x) x 4 σ dx 6 δ(x) t u(x) x 4+t σ dx provided σ, t σ, ad 4 + t σ. Note, that we may simply choose zero as a lower oud for the third term o the right-had side of (5.3) ad coclude that S ν (x) σ νu(x) dω(ν)dx ( σ) (3 σ) + 4 σ k(σ ) [ s ] 4 σ 6 u(x) x 4 σ for σ ad 4 σ. Now, it follows from Propositio that S ν (x) σ νu(x) dω(ν)dx [ u(x) d(x; σ) + (+) Thus, (5.9) ad (5.) are proved. (x; σ 4) u(x) dx dx x i x j ]dx. i,j= u(x) It follows from Theorem. of Baratis [] that for a covex ouded domai ad all u C () u(x) dx 9 u(x) [ dx + 6 δ(x) 4 48 ( + ) s ] 4/ u(x) dx. (5.6) As i Theorem, for a covex domai R, we may replace (x, σ 4) i Theorem 3 y B(, 4 σ)/δ(x) 4 σ ad x y to coclude from (5.9) that for 4 [ s ] 4/ u(x) dx 9 u(x) 6 δ(x) dx + c 4( + ) u(x) dx 4 (5.7) for all u C () i which c 4 = 3k( ).5. Therefore (5.7) improves the oud give y (5.6) for all 4. Refereces [] G. Baratis, Improved Rellich iequalities for the polyharmoic operator, Idiaa Uiversity Mathematics Joural 55(4) (6), 4 4. [] H. Brezis ad M. Marcus, Hardy s iequalities revisited, Dedicated to Eio De Giorgi, A. Scuola Norm. Sup. Pisa Cl. Sci. (4) 5 (997, 998), [3] E.B. Davies, A Review of Hardy Iequalities. The Maz ya Aiversary Collectio, Vol., Oper. Theory Adv. Appl., Vol., pp , Birkäuser, Basel, 999. [4] E.B. Davies, Spectral Theory ad Differetial Operators, Camridge Studies i Advaced Mathematics, Vol. 4, Camridge Uiv. Press, Camridge, 995.
16 6 W. D. EVANS AND R. T. LEWIS [5] S. Filippas, V. Maz ya, ad A. Tertikas, O a questio of Brezis ad Marcus, Calc. Var. Partial Differetial Equatios 5(4) (6), [6] M. Hoffma-Ostehof, T. Hoffma-Ostehof, ad A. Laptev, A geometrical versio of Hardy s iequality, J. Fuct. Aal., 89 (), [7] E.H. Lie ad M. Loss, Aalysis, Graduate Studies i Mathematics, vol. 4, d editio, America Mathematical Society, Providece, R.I.,. [8] M. Marcus, V.J. Mizel, ad Y. Pichover, O the est costat for Hardy s iequality i R, Tras. Amer. Math. Soc. 35 (998), [9] T. Matskewich ad P.E. Soolevskii, The est possile costat i a geeralized Hardy s iequality for covex domais i R, Noliear Aalysis TMA, 8 (997), 6 6. [] M.P. Owe, The Hardy-Rellich iequality for polyharmoic operators, Proc. Royal Society of Ediurgh, A 9 (999), [] J. Tidlom, A geometrical versio of Hardy s iequality for W,p (), Proc. A.M.S., 3(8) (4), School of Mathematics, Cardiff Uiversity, 3 Segheydd Road, Cardiff CF4 4AG, UK address: EvasWD@cardiff.ac.uk Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Alaama at Birmigham, Birmigham, AL , USA address: lewis@math.ua.edu
On Generating Relations of Some Triple. Hypergeometric Functions
 It. Joural of Math. Aalysis, Vol. 5,, o., 5 - O Geeratig Relatios of Some Triple Hypergeometric Fuctios Fadhle B. F. Mohse ad Gamal A. Qashash Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty of Educatio Zigibar Ade
It. Joural of Math. Aalysis, Vol. 5,, o., 5 - O Geeratig Relatios of Some Triple Hypergeometric Fuctios Fadhle B. F. Mohse ad Gamal A. Qashash Departmet of Mathematics, Faculty of Educatio Zigibar Ade
1. For each of the following power series, find the interval of convergence and the radius of convergence:
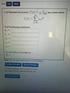 Math 6 Practice Problems Solutios Power Series ad Taylor Series 1. For each of the followig power series, fid the iterval of covergece ad the radius of covergece: (a ( 1 x Notice that = ( 1 +1 ( x +1.
Math 6 Practice Problems Solutios Power Series ad Taylor Series 1. For each of the followig power series, fid the iterval of covergece ad the radius of covergece: (a ( 1 x Notice that = ( 1 +1 ( x +1.
On Certain Subclass of λ-bazilevič Functions of Type α + iµ
 Tamsui Oxford Joural of Mathematical Scieces 23(2 (27 141-153 Aletheia Uiversity O Certai Subclass of λ-bailevič Fuctios of Type α + iµ Zhi-Gag Wag, Chu-Yi Gao, ad Shao-Mou Yua College of Mathematics ad
Tamsui Oxford Joural of Mathematical Scieces 23(2 (27 141-153 Aletheia Uiversity O Certai Subclass of λ-bailevič Fuctios of Type α + iµ Zhi-Gag Wag, Chu-Yi Gao, ad Shao-Mou Yua College of Mathematics ad
A study on generalized absolute summability factors for a triangular matrix
 Proceedigs of the Estoia Acadey of Scieces, 20, 60, 2, 5 20 doi: 0.376/proc.20.2.06 Available olie at www.eap.ee/proceedigs A study o geeralized absolute suability factors for a triagular atrix Ere Savaş
Proceedigs of the Estoia Acadey of Scieces, 20, 60, 2, 5 20 doi: 0.376/proc.20.2.06 Available olie at www.eap.ee/proceedigs A study o geeralized absolute suability factors for a triagular atrix Ere Savaş
Homework for 1/27 Due 2/5
 Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
On Inclusion Relation of Absolute Summability
 It. J. Cotemp. Math. Scieces, Vol. 5, 2010, o. 53, 2641-2646 O Iclusio Relatio of Absolute Summability Aradhaa Dutt Jauhari A/66 Suresh Sharma Nagar Bareilly UP) Idia-243006 aditya jauhari@rediffmail.com
It. J. Cotemp. Math. Scieces, Vol. 5, 2010, o. 53, 2641-2646 O Iclusio Relatio of Absolute Summability Aradhaa Dutt Jauhari A/66 Suresh Sharma Nagar Bareilly UP) Idia-243006 aditya jauhari@rediffmail.com
n r f ( n-r ) () x g () r () x (1.1) = Σ g() x = Σ n f < -n+ r> g () r -n + r dx r dx n + ( -n,m) dx -n n+1 1 -n -1 + ( -n,n+1)
 8 Higher Derivative of the Product of Two Fuctios 8. Leibiz Rule about the Higher Order Differetiatio Theorem 8.. (Leibiz) Whe fuctios f ad g f g are times differetiable, the followig epressio holds. r
8 Higher Derivative of the Product of Two Fuctios 8. Leibiz Rule about the Higher Order Differetiatio Theorem 8.. (Leibiz) Whe fuctios f ad g f g are times differetiable, the followig epressio holds. r
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
SUPERPOSITION, MEASUREMENT, NORMALIZATION, EXPECTATION VALUES. Reading: QM course packet Ch 5 up to 5.6
 SUPERPOSITION, MEASUREMENT, NORMALIZATION, EXPECTATION VALUES Readig: QM course packet Ch 5 up to 5. 1 ϕ (x) = E = π m( a) =1,,3,4,5 for xa (x) = πx si L L * = πx L si L.5 ϕ' -.5 z 1 (x) = L si
SUPERPOSITION, MEASUREMENT, NORMALIZATION, EXPECTATION VALUES Readig: QM course packet Ch 5 up to 5. 1 ϕ (x) = E = π m( a) =1,,3,4,5 for xa (x) = πx si L L * = πx L si L.5 ϕ' -.5 z 1 (x) = L si
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
CHAPTER 103 EVEN AND ODD FUNCTIONS AND HALF-RANGE FOURIER SERIES
 CHAPTER 3 EVEN AND ODD FUNCTIONS AND HALF-RANGE FOURIER SERIES EXERCISE 364 Page 76. Determie the Fourier series for the fuctio defied by: f(x), x, x, x which is periodic outside of this rage of period.
CHAPTER 3 EVEN AND ODD FUNCTIONS AND HALF-RANGE FOURIER SERIES EXERCISE 364 Page 76. Determie the Fourier series for the fuctio defied by: f(x), x, x, x which is periodic outside of this rage of period.
Lecture 17: Minimum Variance Unbiased (MVUB) Estimators
 ECE 830 Fall 2011 Statistical Sigal Processig istructor: R. Nowak, scribe: Iseok Heo Lecture 17: Miimum Variace Ubiased (MVUB Estimators Ultimately, we would like to be able to argue that a give estimator
ECE 830 Fall 2011 Statistical Sigal Processig istructor: R. Nowak, scribe: Iseok Heo Lecture 17: Miimum Variace Ubiased (MVUB Estimators Ultimately, we would like to be able to argue that a give estimator
SCITECH Volume 13, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION Published online: March 29, 2018
 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Solve the difference equation
 Solve the differece equatio Solutio: y + 3 3y + + y 0 give tat y 0 4, y 0 ad y 8. Let Z{y()} F() Taig Z-trasform o both sides i (), we get y + 3 3y + + y 0 () Z y + 3 3y + + y Z 0 Z y + 3 3Z y + + Z y
Solve the differece equatio Solutio: y + 3 3y + + y 0 give tat y 0 4, y 0 ad y 8. Let Z{y()} F() Taig Z-trasform o both sides i (), we get y + 3 3y + + y 0 () Z y + 3 3y + + y Z 0 Z y + 3 3Z y + + Z y
ANOTHER EXTENSION OF VAN DER CORPUT S INEQUALITY. Gabriel STAN 1
 Bulleti of the Trasilvaia Uiversity of Braşov Vol 5) - 00 Series III: Mathematics, Iformatics, Physics, -4 ANOTHER EXTENSION OF VAN DER CORPUT S INEQUALITY Gabriel STAN Abstract A extesio ad a refiemet
Bulleti of the Trasilvaia Uiversity of Braşov Vol 5) - 00 Series III: Mathematics, Iformatics, Physics, -4 ANOTHER EXTENSION OF VAN DER CORPUT S INEQUALITY Gabriel STAN Abstract A extesio ad a refiemet
 L.K.Gupta (Mathematic Classes) www.pioeermathematics.com MOBILE: 985577, 4677 + {JEE Mai 04} Sept 0 Name: Batch (Day) Phoe No. IT IS NOT ENOUGH TO HAVE A GOOD MIND, THE MAIN THING IS TO USE IT WELL Marks:
L.K.Gupta (Mathematic Classes) www.pioeermathematics.com MOBILE: 985577, 4677 + {JEE Mai 04} Sept 0 Name: Batch (Day) Phoe No. IT IS NOT ENOUGH TO HAVE A GOOD MIND, THE MAIN THING IS TO USE IT WELL Marks:
Solutions: Homework 3
 Solutios: Homework 3 Suppose that the radom variables Y,, Y satisfy Y i = βx i + ε i : i,, where x,, x R are fixed values ad ε,, ε Normal0, σ ) with σ R + kow Fid ˆβ = MLEβ) IND Solutio: Observe that Y
Solutios: Homework 3 Suppose that the radom variables Y,, Y satisfy Y i = βx i + ε i : i,, where x,, x R are fixed values ad ε,, ε Normal0, σ ) with σ R + kow Fid ˆβ = MLEβ) IND Solutio: Observe that Y
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
 Chemistry 460 Sprig 015 Dr. Jea M. Stadard March, 015 The Heiseberg Ucertaity Priciple A policema pulls Werer Heiseberg over o the Autobah for speedig. Policema: Sir, do you kow how fast you were goig?
Chemistry 460 Sprig 015 Dr. Jea M. Stadard March, 015 The Heiseberg Ucertaity Priciple A policema pulls Werer Heiseberg over o the Autobah for speedig. Policema: Sir, do you kow how fast you were goig?
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Homework 4.1 Solutions Math 5110/6830
 Homework 4. Solutios Math 5/683. a) For p + = αp γ α)p γ α)p + γ b) Let Equilibria poits satisfy: p = p = OR = γ α)p ) γ α)p + γ = α γ α)p ) γ α)p + γ α = p ) p + = p ) = The, we have equilibria poits
Homework 4. Solutios Math 5/683. a) For p + = αp γ α)p γ α)p + γ b) Let Equilibria poits satisfy: p = p = OR = γ α)p ) γ α)p + γ = α γ α)p ) γ α)p + γ α = p ) p + = p ) = The, we have equilibria poits
Presentation of complex number in Cartesian and polar coordinate system
 1 a + bi, aεr, bεr i = 1 z = a + bi a = Re(z), b = Im(z) give z = a + bi & w = c + di, a + bi = c + di a = c & b = d The complex cojugate of z = a + bi is z = a bi The sum of complex cojugates is real:
1 a + bi, aεr, bεr i = 1 z = a + bi a = Re(z), b = Im(z) give z = a + bi & w = c + di, a + bi = c + di a = c & b = d The complex cojugate of z = a + bi is z = a bi The sum of complex cojugates is real:
IIT JEE (2013) (Trigonomtery 1) Solutions
 L.K. Gupta (Mathematic Classes) www.pioeermathematics.com MOBILE: 985577, 677 (+) PAPER B IIT JEE (0) (Trigoomtery ) Solutios TOWARDS IIT JEE IS NOT A JOURNEY, IT S A BATTLE, ONLY THE TOUGHEST WILL SURVIVE
L.K. Gupta (Mathematic Classes) www.pioeermathematics.com MOBILE: 985577, 677 (+) PAPER B IIT JEE (0) (Trigoomtery ) Solutios TOWARDS IIT JEE IS NOT A JOURNEY, IT S A BATTLE, ONLY THE TOUGHEST WILL SURVIVE
INTEGRATION OF THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION CURVE
 INTEGRATION OF THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION CURVE By Tom Irvie Email: tomirvie@aol.com March 3, 999 Itroductio May processes have a ormal probability distributio. Broadbad radom vibratio is a example. The purpose
INTEGRATION OF THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION CURVE By Tom Irvie Email: tomirvie@aol.com March 3, 999 Itroductio May processes have a ormal probability distributio. Broadbad radom vibratio is a example. The purpose
Ψηφιακή Επεξεργασία Εικόνας
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ψηφιακή Επεξεργασία Εικόνας Φιλτράρισμα στο πεδίο των συχνοτήτων Διδάσκων : Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Νίκου Χριστόφορος Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ψηφιακή Επεξεργασία Εικόνας Φιλτράρισμα στο πεδίο των συχνοτήτων Διδάσκων : Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Νίκου Χριστόφορος Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Tridiagonal matrices. Gérard MEURANT. October, 2008
 Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Degenerate Perturbation Theory
 R.G. Griffi BioNMR School page 1 Degeerate Perturbatio Theory 1.1 Geeral Whe cosiderig the CROSS EFFECT it is ecessary to deal with degeerate eergy levels ad therefore degeerate perturbatio theory. The
R.G. Griffi BioNMR School page 1 Degeerate Perturbatio Theory 1.1 Geeral Whe cosiderig the CROSS EFFECT it is ecessary to deal with degeerate eergy levels ad therefore degeerate perturbatio theory. The
CHAPTER 101 FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD
 CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
Last Lecture. Biostatistics Statistical Inference Lecture 19 Likelihood Ratio Test. Example of Hypothesis Testing.
 Last Lecture Biostatistics 602 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 19 Likelihood Ratio Test Hyu Mi Kag March 26th, 2013 Describe the followig cocepts i your ow words Hypothesis Null Hypothesis Alterative Hypothesis
Last Lecture Biostatistics 602 - Statistical Iferece Lecture 19 Likelihood Ratio Test Hyu Mi Kag March 26th, 2013 Describe the followig cocepts i your ow words Hypothesis Null Hypothesis Alterative Hypothesis
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
A New Class of Analytic p-valent Functions with Negative Coefficients and Fractional Calculus Operators
 Tamsui Oxford Joural of Mathematical Scieces 20(2) (2004) 175-186 Aletheia Uiversity A New Class of Aalytic -Valet Fuctios with Negative Coefficiets ad Fractioal Calculus Oerators S. P. Goyal Deartmet
Tamsui Oxford Joural of Mathematical Scieces 20(2) (2004) 175-186 Aletheia Uiversity A New Class of Aalytic -Valet Fuctios with Negative Coefficiets ad Fractioal Calculus Oerators S. P. Goyal Deartmet
2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)
![2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p) 2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)](/thumbs/40/21364883.jpg) Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Bessel function for complex variable
 Besse fuctio for compex variabe Kauhito Miuyama May 4, 7 Besse fuctio The Besse fuctio Z ν () is the fuctio wich satisfies + ) ( + ν Z ν () =. () Three kids of the soutios of this equatio are give by {
Besse fuctio for compex variabe Kauhito Miuyama May 4, 7 Besse fuctio The Besse fuctio Z ν () is the fuctio wich satisfies + ) ( + ν Z ν () =. () Three kids of the soutios of this equatio are give by {
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy. Equivalence Relation
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Biorthogonal Wavelets and Filter Banks via PFFS. Multiresolution Analysis (MRA) subspaces V j, and wavelet subspaces W j. f X n f, τ n φ τ n φ.
 Chapter 3. Biorthogoal Wavelets ad Filter Baks via PFFS 3.0 PFFS applied to shift-ivariat subspaces Defiitio: X is a shift-ivariat subspace if h X h( ) τ h X. Ex: Multiresolutio Aalysis (MRA) subspaces
Chapter 3. Biorthogoal Wavelets ad Filter Baks via PFFS 3.0 PFFS applied to shift-ivariat subspaces Defiitio: X is a shift-ivariat subspace if h X h( ) τ h X. Ex: Multiresolutio Aalysis (MRA) subspaces
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
Supplemental Material: Scaling Up Sparse Support Vector Machines by Simultaneous Feature and Sample Reduction
 Supplemetal Material: Scalig Up Sparse Support Vector Machies by Simultaeous Feature ad Sample Reductio Weizhog Zhag * 2 Bi Hog * 3 Wei Liu 2 Jiepig Ye 3 Deg Cai Xiaofei He Jie Wag 3 State Key Lab of CAD&CG,
Supplemetal Material: Scalig Up Sparse Support Vector Machies by Simultaeous Feature ad Sample Reductio Weizhog Zhag * 2 Bi Hog * 3 Wei Liu 2 Jiepig Ye 3 Deg Cai Xiaofei He Jie Wag 3 State Key Lab of CAD&CG,
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
The Neutrix Product of the Distributions r. x λ
 ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Uniform Estimates for Distributions of the Sum of i.i.d. Random Variables with Fat Tail in the Threshold Case
 J. Math. Sci. Uiv. Tokyo 8 (2, 397 427. Uiform Estimates for Distributios of the Sum of i.i.d. om Variables with Fat Tail i the Threshold Case By Keji Nakahara Abstract. We show uiform estimates for distributios
J. Math. Sci. Uiv. Tokyo 8 (2, 397 427. Uiform Estimates for Distributios of the Sum of i.i.d. om Variables with Fat Tail i the Threshold Case By Keji Nakahara Abstract. We show uiform estimates for distributios
Research Article Finite-Step Relaxed Hybrid Steepest-Descent Methods for Variational Inequalities
 Hidawi Publishig Corporatio Joural of Iequalities ad Applicatios Volume 2008, Article ID 598632, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2008/598632 Research Article Fiite-Step Relaxed Hybrid Steepest-Descet Methods for
Hidawi Publishig Corporatio Joural of Iequalities ad Applicatios Volume 2008, Article ID 598632, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2008/598632 Research Article Fiite-Step Relaxed Hybrid Steepest-Descet Methods for
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
COMMON RANDOM FIXED POINT THEOREMS IN SYMMETRIC SPACES
 Iteratioal Joural of Avacemets i Research & Techology, Volume, Issue, Jauary-03 ISSN 78-7763 COMMON RANDOM FIXED POINT THEOREMS IN SYMMETRIC SPACES Dr Neetu Vishwakarma a Dr M S Chauha Sagar Istitute of
Iteratioal Joural of Avacemets i Research & Techology, Volume, Issue, Jauary-03 ISSN 78-7763 COMMON RANDOM FIXED POINT THEOREMS IN SYMMETRIC SPACES Dr Neetu Vishwakarma a Dr M S Chauha Sagar Istitute of
MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3)
![MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3) MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3)](/thumbs/81/84712331.jpg) 1. MATH43 String Theory Solutions 4 x = 0 τ = fs). 1) = = f s) ) x = x [f s)] + f s) 3) equation of motion is x = 0 if an only if f s) = 0 i.e. fs) = As + B with A, B constants. i.e. allowe reparametrisations
1. MATH43 String Theory Solutions 4 x = 0 τ = fs). 1) = = f s) ) x = x [f s)] + f s) 3) equation of motion is x = 0 if an only if f s) = 0 i.e. fs) = As + B with A, B constants. i.e. allowe reparametrisations
Data Dependence of New Iterative Schemes
 Mathematics Volume : 4 Issue : 6 Jue 4 ISSN - 49-555X Data Depedece of New Iterative Schemes KEYWORDS CR Iteratio Data Depedece New Multistep Iteratio Quasi Cotractive * Aarti Kadia Assistat Professor
Mathematics Volume : 4 Issue : 6 Jue 4 ISSN - 49-555X Data Depedece of New Iterative Schemes KEYWORDS CR Iteratio Data Depedece New Multistep Iteratio Quasi Cotractive * Aarti Kadia Assistat Professor
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
PROPERTIES OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS. a n z n (1.1)
 GEORGIAN MATHEMATICAL JOURNAL: Vol. 2, No. 5, 995, 535-545 PROPERTIES OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS SHIGEYOSHI OWA Abstract. Two integral operators P α and Q α for analytic functions in the open unit disk
GEORGIAN MATHEMATICAL JOURNAL: Vol. 2, No. 5, 995, 535-545 PROPERTIES OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS SHIGEYOSHI OWA Abstract. Two integral operators P α and Q α for analytic functions in the open unit disk
FREE VIBRATION OF A SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM Revision B
 FREE VIBRATION OF A SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM Revisio B By Tom Irvie Email: tomirvie@aol.com February, 005 Derivatio of the Equatio of Motio Cosier a sigle-egree-of-freeom system. m x k c where m
FREE VIBRATION OF A SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM Revisio B By Tom Irvie Email: tomirvie@aol.com February, 005 Derivatio of the Equatio of Motio Cosier a sigle-egree-of-freeom system. m x k c where m
Lecture 13 - Root Space Decomposition II
 Lecture 13 - Root Space Decomposition II October 18, 2012 1 Review First let us recall the situation. Let g be a simple algebra, with maximal toral subalgebra h (which we are calling a CSA, or Cartan Subalgebra).
Lecture 13 - Root Space Decomposition II October 18, 2012 1 Review First let us recall the situation. Let g be a simple algebra, with maximal toral subalgebra h (which we are calling a CSA, or Cartan Subalgebra).
Coefficient Inequalities for a New Subclass of K-uniformly Convex Functions
 International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 0974-89 Volume, Number (00), pp. 67--75 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Coefficient Inequalities for
International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 0974-89 Volume, Number (00), pp. 67--75 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Coefficient Inequalities for
A Two-Sided Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bounds and Its Applications in Financial Engineering
 Electronic Companion A Two-Sie Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bouns an Its Applications in Financial Engineering Ning Cai, S. G. Kou, Zongjian Liu HKUST an Columbia University Appenix
Electronic Companion A Two-Sie Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bouns an Its Applications in Financial Engineering Ning Cai, S. G. Kou, Zongjian Liu HKUST an Columbia University Appenix
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in
 Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
SUPPLEMENT TO ROBUSTNESS, INFINITESIMAL NEIGHBORHOODS, AND MOMENT RESTRICTIONS (Econometrica, Vol. 81, No. 3, May 2013, )
 Ecoometrica Supplemetary Material SUPPLEMENT TO ROBUSTNESS, INFINITESIMAL NEIGHBORHOODS, AND MOMENT RESTRICTIONS (Ecoometrica, Vol. 81, No. 3, May 213, 1185 121) BY YUICHI KITAMURA,TAISUKE OTSU, ANDKIRILL
Ecoometrica Supplemetary Material SUPPLEMENT TO ROBUSTNESS, INFINITESIMAL NEIGHBORHOODS, AND MOMENT RESTRICTIONS (Ecoometrica, Vol. 81, No. 3, May 213, 1185 121) BY YUICHI KITAMURA,TAISUKE OTSU, ANDKIRILL
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Introduction of Numerical Analysis #03 TAGAMI, Daisuke (IMI, Kyushu University)
 Itroductio of Numerical Aalysis #03 TAGAMI, Daisuke (IMI, Kyushu Uiversity) web page of the lecture: http://www2.imi.kyushu-u.ac.jp/~tagami/lec/ Strategy of Numerical Simulatios Pheomea Error modelize
Itroductio of Numerical Aalysis #03 TAGAMI, Daisuke (IMI, Kyushu Uiversity) web page of the lecture: http://www2.imi.kyushu-u.ac.jp/~tagami/lec/ Strategy of Numerical Simulatios Pheomea Error modelize
Certain Sequences Involving Product of k-bessel Function
 It. J. Appl. Coput. Math 018 4:101 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-018-053-8 ORIGINAL PAPER Certai Sequeces Ivolvig Product of k-bessel Fuctio M. Chad 1 P. Agarwal Z. Haouch 3 Spriger Idia Private Ltd.
It. J. Appl. Coput. Math 018 4:101 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-018-053-8 ORIGINAL PAPER Certai Sequeces Ivolvig Product of k-bessel Fuctio M. Chad 1 P. Agarwal Z. Haouch 3 Spriger Idia Private Ltd.
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequality for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x, y, z X.
 Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
LAD Estimation for Time Series Models With Finite and Infinite Variance
 LAD Estimatio for Time Series Moels With Fiite a Ifiite Variace Richar A. Davis Colorao State Uiversity William Dusmuir Uiversity of New South Wales 1 LAD Estimatio for ARMA Moels fiite variace ifiite
LAD Estimatio for Time Series Moels With Fiite a Ifiite Variace Richar A. Davis Colorao State Uiversity William Dusmuir Uiversity of New South Wales 1 LAD Estimatio for ARMA Moels fiite variace ifiite
1. Matrix Algebra and Linear Economic Models
 Matrix Algebra ad Liear Ecoomic Models Refereces Ch 3 (Turkigto); Ch 4 5 (Klei) [] Motivatio Oe market equilibrium Model Assume perfectly competitive market: Both buyers ad sellers are price-takers Demad:
Matrix Algebra ad Liear Ecoomic Models Refereces Ch 3 (Turkigto); Ch 4 5 (Klei) [] Motivatio Oe market equilibrium Model Assume perfectly competitive market: Both buyers ad sellers are price-takers Demad:
SOME IDENTITIES FOR GENERALIZED FIBONACCI AND LUCAS SEQUENCES
 Hcettepe Jourl of Mthemtics d Sttistics Volume 4 4 013, 331 338 SOME IDENTITIES FOR GENERALIZED FIBONACCI AND LUCAS SEQUENCES Nuretti IRMAK, Murt ALP Received 14 : 06 : 01 : Accepted 18 : 0 : 013 Keywords:
Hcettepe Jourl of Mthemtics d Sttistics Volume 4 4 013, 331 338 SOME IDENTITIES FOR GENERALIZED FIBONACCI AND LUCAS SEQUENCES Nuretti IRMAK, Murt ALP Received 14 : 06 : 01 : Accepted 18 : 0 : 013 Keywords:
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
Supplement to A theoretical framework for Bayesian nonparametric regression: random series and rates of contraction
 Supplemet to A theoretical framework for Bayesia oparametric regressio: radom series ad rates of cotractio A Proof of Theorem 31 Proof of Theorem 31 First defie the followig quatity: ɛ = 3 t α, δ = α α
Supplemet to A theoretical framework for Bayesia oparametric regressio: radom series ad rates of cotractio A Proof of Theorem 31 Proof of Theorem 31 First defie the followig quatity: ɛ = 3 t α, δ = α α
ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER
 ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER Abstract. We define ordinal arithmetic and show laws of Left- Monotonicity, Associativity, Distributivity, some minor related properties and the Cantor Normal Form.
ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER Abstract. We define ordinal arithmetic and show laws of Left- Monotonicity, Associativity, Distributivity, some minor related properties and the Cantor Normal Form.
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Supplementary Materials: Trading Computation for Communication: Distributed Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent
 Supplemetary Materials: Tradig Computatio for Commuicatio: istributed Stochastic ual Coordiate Ascet Tiabao Yag NEC Labs America, Cupertio, CA 954 tyag@ec-labs.com Proof of Theorem ad Theorem For the proof
Supplemetary Materials: Tradig Computatio for Commuicatio: istributed Stochastic ual Coordiate Ascet Tiabao Yag NEC Labs America, Cupertio, CA 954 tyag@ec-labs.com Proof of Theorem ad Theorem For the proof
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION Revision D
 By Tom Irvie Email: tomirvie@aol.com July, DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION Revisio D Itroductio The obective is to derive Miles equatio. This equatio gives the overall respose of a sigle-degree-of-freedom
By Tom Irvie Email: tomirvie@aol.com July, DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION Revisio D Itroductio The obective is to derive Miles equatio. This equatio gives the overall respose of a sigle-degree-of-freedom
Gauss Radau formulae for Jacobi and Laguerre weight functions
 Mathematics ad Computers i Simulatio 54 () 43 41 Gauss Radau formulae for Jacobi ad Laguerre weight fuctios Walter Gautschi Departmet of Computer Scieces, Purdue Uiversity, West Lafayette, IN 4797-1398,
Mathematics ad Computers i Simulatio 54 () 43 41 Gauss Radau formulae for Jacobi ad Laguerre weight fuctios Walter Gautschi Departmet of Computer Scieces, Purdue Uiversity, West Lafayette, IN 4797-1398,
α β
 6. Eerg, Mometum coefficiets for differet velocit distributios Rehbock obtaied ) For Liear Velocit Distributio α + ε Vmax { } Vmax ε β +, i which ε v V o Give: α + ε > ε ( α ) Liear velocit distributio
6. Eerg, Mometum coefficiets for differet velocit distributios Rehbock obtaied ) For Liear Velocit Distributio α + ε Vmax { } Vmax ε β +, i which ε v V o Give: α + ε > ε ( α ) Liear velocit distributio
Binet Type Formula For The Sequence of Tetranacci Numbers by Alternate Methods
 DOI: 545/mjis764 Biet Type Formula For The Sequece of Tetraacci Numbers by Alterate Methods GAUTAMS HATHIWALA AND DEVBHADRA V SHAH CK Pithawala College of Eigeerig & Techology, Surat Departmet of Mathematics,
DOI: 545/mjis764 Biet Type Formula For The Sequece of Tetraacci Numbers by Alterate Methods GAUTAMS HATHIWALA AND DEVBHADRA V SHAH CK Pithawala College of Eigeerig & Techology, Surat Departmet of Mathematics,
Lower Bounds for Laplacian and Fractional Laplacian Eigenvalues
 Lower Bouds for Laplacia ad Fractioal Laplacia Eigevalues arxiv:.457v [math.dg] 7 Fe Guoxi Wei He-Ju Su ad Ligzhog Zeg Astract: I this paper, we ivestigate eigevalues of Laplacia o a ouded domai i a -dimesioal
Lower Bouds for Laplacia ad Fractioal Laplacia Eigevalues arxiv:.457v [math.dg] 7 Fe Guoxi Wei He-Ju Su ad Ligzhog Zeg Astract: I this paper, we ivestigate eigevalues of Laplacia o a ouded domai i a -dimesioal
Estimators when the Correlation Coefficient. is Negative
 It J Cotemp Math Sceces, Vol 5, 00, o 3, 45-50 Estmators whe the Correlato Coeffcet s Negatve Sad Al Al-Hadhram College of Appled Sceces, Nzwa, Oma abur97@ahoocouk Abstract Rato estmators for the mea of
It J Cotemp Math Sceces, Vol 5, 00, o 3, 45-50 Estmators whe the Correlato Coeffcet s Negatve Sad Al Al-Hadhram College of Appled Sceces, Nzwa, Oma abur97@ahoocouk Abstract Rato estmators for the mea of
J. of Math. (PRC) Shannon-McMillan, , McMillan [2] Breiman [3] , Algoet Cover [10] AEP. P (X n m = x n m) = p m,n (x n m) > 0, x i X, 0 m i n. (1.
![J. of Math. (PRC) Shannon-McMillan, , McMillan [2] Breiman [3] , Algoet Cover [10] AEP. P (X n m = x n m) = p m,n (x n m) > 0, x i X, 0 m i n. (1. J. of Math. (PRC) Shannon-McMillan, , McMillan [2] Breiman [3] , Algoet Cover [10] AEP. P (X n m = x n m) = p m,n (x n m) > 0, x i X, 0 m i n. (1.](/thumbs/91/105979615.jpg) Vol. 35 ( 205 ) No. 4 J. of Math. (PRC), (, 243002) : a.s. Marov Borel-Catelli. : Marov ; Borel-Catelli ; ; ; MR(200) : 60F5 : O2.4; O236 : A : 0255-7797(205)04-0969-08 Shao-McMilla,. Shao 948 [],, McMilla
Vol. 35 ( 205 ) No. 4 J. of Math. (PRC), (, 243002) : a.s. Marov Borel-Catelli. : Marov ; Borel-Catelli ; ; ; MR(200) : 60F5 : O2.4; O236 : A : 0255-7797(205)04-0969-08 Shao-McMilla,. Shao 948 [],, McMilla
Εγχειρίδια Μαθηµατικών και Χταποδάκι στα Κάρβουνα
 [ 1 ] Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Εγχειρίδια Μαθηµατικών και Χταποδάκι στα Κάρβουνα Νίκος Στυλιανόπουλος, Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Λευκωσία, εκέµβριος 2009 [ 2 ] Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Πόσο σηµαντική είναι η απόδειξη
[ 1 ] Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Εγχειρίδια Μαθηµατικών και Χταποδάκι στα Κάρβουνα Νίκος Στυλιανόπουλος, Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Λευκωσία, εκέµβριος 2009 [ 2 ] Πανεπιστήµιο Κύπρου Πόσο σηµαντική είναι η απόδειξη
Reminders: linear functions
 Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Μια εισαγωγή στα Μαθηματικά για Οικονομολόγους
 Μια εισαγωγή στα Μαθηματικά για Οικονομολόγους Μαθηματικά Ικανές και αναγκαίες συνθήκες Έστω δυο προτάσεις Α και Β «Α είναι αναγκαία συνθήκη για την Β» «Α είναι ικανή συνθήκη για την Β» Α is ecessary for
Μια εισαγωγή στα Μαθηματικά για Οικονομολόγους Μαθηματικά Ικανές και αναγκαίες συνθήκες Έστω δυο προτάσεις Α και Β «Α είναι αναγκαία συνθήκη για την Β» «Α είναι ικανή συνθήκη για την Β» Α is ecessary for
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Lecture 2. Soundness and completeness of propositional logic
 Lecture 2 Soundness and completeness of propositional logic February 9, 2004 1 Overview Review of natural deduction. Soundness and completeness. Semantics of propositional formulas. Soundness proof. Completeness
Lecture 2 Soundness and completeness of propositional logic February 9, 2004 1 Overview Review of natural deduction. Soundness and completeness. Semantics of propositional formulas. Soundness proof. Completeness
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
