Integral representations and asymptotic behaviour of a mittag-leffler type function of two variables
|
|
|
- Ἑκάβη Ζυγομαλάς
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Integral representations and asymptotic behaviour of a mittag-leffler type function of two variables Christian Lavault To cite this version: Christian Lavault. Integral representations and asymptotic behaviour of a mittag-leffler type function of two variables. Adv. Oper. Theory, Tusi Mathematical Research Group, A Paraître, 3 (2), pp < < /aot >. <hal > HAL Id: hal Submitted on 29 Oct 207 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access archive for the deposit and dissemination of scientific research documents, whether they are published or not. The documents may come from teaching and research institutions in France or abroad, or from public or private research centers. L archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des établissements d enseignement et de recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires publics ou privés.
2 INTEGRAL REPRESENTATIONS AND ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR OF A MITTAG-LEFFLER TYPE FUNCTION OF TWO VARIABLES CHRISTIAN LAVAULT Communicated by C. Lizama Abstract. Integral representations play a prominent role in the analysis of entire functions. The representations of generalized Mittag-Leffler type functions and their asymptotics have been (and still are) investigated by plenty of authors in various conditions and cases. The present paper explores the integral representations of a special function extending to two variables the two-parametric Mittag-Leffler type function. Integral representations of this functions within different variation ranges of its arguments for certain values of the parameters are thus obtained. Asymptotic expansion formulas and asymptotic properties of this function are also established for large values of the variables. This yields corresponding theorems providing integral representations as well as expansion formulas. Let the power series E, (z) :=. Definition and notation n=0 z n Γ(n + ) (, C; R() > 0) define the two-parametric Mittag-Leffler function (or M-L function for short) [2]. For the first parameter with positive real part and any non restricted complex value of the second parameter, the function E, (z) is an entire functions of z C of order ρ = /R() and type σ = (see, e.g, [5, Chap. 4], [8], [9,.]). From here on, since we are concerned with integral representations and asymptotic expansions of generalized two-parametric M-L type functions, we shall restrict our attention to positive real-valued parameters and. Besides, the function E, (z) of one variable z C will also be denoted for simplicity by E (z; ) in the proof of Lemma 2., according to the notation used by Džrbašjan in [, 2]. Thus, the two-parametric M-L function of one variable z C extends to the generalized M-L type function E, (x, y; µ) of two variables x, y C [, 2]. Provided that, > 0, it is also an entire function defined by the double power Copyright 206 by the Tusi Mathematical Research Group. Date: Received: May 26, 207; Accepted: Oct. 8, Mathematics Subject Classification. Primary 32A25; Secondary 45P05, 32D99. Key words and phrases. Generalized two-parametric Mittag-Leffler type functions of two variables; Integral representations; Special functions; Hankel s integral contour; Asymptotic expansion formulas. 40
3 series [4, 0] E, (x, y; µ) := INTEGRAL REPRESENTATIONS AND ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR 4 n,m=0 x n y m Γ(n + m + µ) (, R,, > 0, µ C), (.) in which the arbitrary parameter µ takes in general complex values. Following [, 2] (see also, e.g., [5, 6, 7, ], [9,.2 & App. A, C & D], and references therein), E, (x, y; µ) can be written in terms of Hankel s integral representations depending on the variation ranges of the arguments, thereby as special cases of the Fox H-function. The Hankel path considered further in Lemma 2. to 2.4 and in Theorem 3. is denoted by γ(ɛ; η) := { 0 < η π, ɛ > 0 }, defining a contour integral oriented by non-decreasing arg ζ. It consists of the following two parts depicted for instance in [6, Fig. to 4]): () the two rays S η = { arg ζ = η, ζ ɛ } and S η = { arg ζ = η, ζ ɛ } ; (2) the circular arc C η (0; ɛ) = { ζ = ɛ, η arg ζ η }. If 0 < η < π, then the contour γ(ɛ; η) divides the complex ζ-plane into two unbounded regions, namely Ω ( ) (ɛ; η) to the left of γ(ɛ; η) by orientation and Ω (+) (ɛ; η) to the right of the contour. If η = π, then the contour consists of the circle { ζ = ɛ } and of the ray < ζ ɛ (ɛ > 0), which is a twoway path (one in each direction) along the real line. More precisely, this keyhole or Hankel contour is a path from inbound along the real line to ɛ < 0, counterclockwise around a circle of radius ɛ at 0, back to ɛ on the real line, and outbound back to along the real line. 2. Integral representations This section provides a few lemmas, which show various integral representations of the generalized M-L type function (.) corresponding to different variation ranges of the two arguments. Lemma 2.. Let 0 <, < 2 and < 2. Let µ be any complex number and let η satisfy the condition π/2 < η min ( π, π ). (2.) If x Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) and y Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ), where ɛ := ɛ /, ɛ := ɛ / and η := η/, η := η/, then the Hankel integral representation holds E, (x, y; µ) = 2πi e ζ/() ζ ++ µ dζ. (2.2) (ζ / y)(ζ / x) Proof. First, let x < ɛ. Taking into account the fact that ɛ = ɛ / = ( ɛ) / = ɛ / yields next the inequality (2.3) sup ζ γ(ɛ ;η ) xζ / <. (2.3)
4 42 C. LAVAULT From definition (.), the expansion of E, (x, y; µ) may be rewritten as follows in terms of the corresponding two-parametric M-L function E (y; n + µ) of one variable, E, (x, y; µ) = = x n y m Γ(n + m + µ) n=0 m=0 x n y m Γ(m + (n + µ)) = n=0 m=0 n=0 x n E (y; n + µ). (2.4) Under the assumptions of Lemma 2., it is possible to use the known integral representation of E (y; n+µ) (see, e.g., [2, Eq. (2.2)]) by taking the above ɛ and η as the parameters defining the Hankel contour, which is admissible according to inequalities (2.). For y Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ), and provided that η = η/, the following representations holds from the integral representation of E (y; n + µ) E, (x, y; µ) = x n E (y; n + µ) = n=0 x n 2πi n=0 γ(ɛ ;η ) e ζ/ ζ n µ ζ y And by simplifying and using inequality (2.3) one gets E, (x, y; µ) = ( e ζ/ ζ µ ( ) ) xζ / n dζ 2πi ζ y = 2πi γ(ɛ ;η ) γ(ɛ ;η ) n=0 dζ. (2.5) e ζ/ ζ + µ dζ. (2.6) (ζ y)(ζ / x) Now, by rewriting the above integral representation (2.6) along the suitable integral contour γ(ɛ; η), we obtain E, (x, y; µ) = 2πi e (ξ/ ) / ( ) + µ ξ / (ξ / y)(ξ / x) ξ dξ and get the desired integral representation (2.2) set out in Lemma 2. E, (x, y; µ) = e ξ/() ξ ++ µ 2πi (ξ / y)(ξ / x) dξ. The above resulting integral is absolutely convergent and it is an analytic function of x Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) and y Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ). The open disk D = { x < ɛ } is contained into the complex region Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) for all values of η taken in the interval ] π/2, min(π, π) ]. Therefore, from the principle of analytic continuation Eq. (2.2) is valid everywhere within the complex region Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) and the lemma is established.
5 INTEGRAL REPRESENTATIONS AND ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR 43 Lemma 2.2. Let 0 <, < 2 and < 2 Let µ be any complex number and let η verify inequalities (2.), π/2 < η min ( π, π ). If x Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) and y Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ), where ɛ := ɛ /, ɛ := ɛ / and η := η/, η := η/, then the integral representation holds E, (x, y; µ) = e y/ y + µ y / x + e ζ/() ζ ++ µ dζ. (2.7) 2πi (ζ / y)(ζ / x) Proof. By assumption, the point y is located to the right of the Hankel contour γ(ɛ ; η ), that is y Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ). Then, for any ɛ > y, we have that y Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) and x Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) for ɛ = ɛ /. Therefore, by (2.6) we get the integral representation E, (x, y; µ) = e ζ/ ζ + µ dζ. (2.8) 2πi (ζ y)(ζ / x) γ(ɛ ;η ) On the other hand, if ɛ < y < ɛ, then arg y < η and, by Cauchy theorem, E, (x, y; µ) = e ζ/ ζ + µ 2πi (ζ / y)(ζ / x) dζ = γ(ɛ ;η ) γ(ɛ ;η ) e y/ y + µ y / x. (2.9) Hence, from Eqs. (2.8) and (2.9), we obtain the integral representation (2.7) and Lemma 2.2 follows. Remark 2.3. Symmetrically, for x Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ), y Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) and under the assumptions of Lemma 2.2, the integral representation of E, (x, y; µ) is shown in a same manner to be E, (x, y; µ) = e x/ x + µ x / y + 2πi by simply interchanging and in representation (2.7). e ζ/() ζ ++ µ dζ, (2.0) (ζ / y)(ζ / x) Lemma 2.4. Let 0 <, < 2 and < 2. Let µ be any complex number and let η verify inequalities (2.). If x Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ) and y Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ), where ɛ := ɛ /, ɛ := ɛ / and η := η/, η := η/, then the integral representation holds E, (x, y; µ) = e x/ x + µ x / y + e y/ y + µ y / x + 2πi e ζ/() ζ ++ µ dζ. (2.) (ζ / y)(ζ / x)
6 44 C. LAVAULT Proof. By assumption, each of the points x and y lies on the right-hand side of the Hankel contours γ(ɛ ; η ) and γ(ɛ ; η ), respectively; that is in the two regions of the complex plane defined by x Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ) and y Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ) (where the parameters ɛ and ɛ correspond to ɛ). Now, choose ɛ > ɛ such that one of the coordinates is to the right of the contour and the other coordinate to its left (which is always possible provided that x y ). Let x Ω ( ) (ɛ ; η ) and y Ω (+) (ɛ ; η ) (i.e., x < y) for ɛ = ɛ / and ɛ = ɛ /. Then, by Eq. (2.7) in Lemma 2.2, we have the integral representation E, (x, y; µ) = e y/ y + µ y / x + 2πi γ(ɛ ;η) e ζ/() ζ ++ µ dζ. (2.2) (ζ / y)(ζ / x) Upon changing the variable ζ / for t in (2.2), the above integral may be rewritten under the form 2πi e t/ t + µ dt. (t x)(t / y) (2.3) γ(ɛ ;η) Now, when ɛ < x < ɛ, then arg x < η and, by Cauchy theorem, E, (x, y; µ) = 2πi γ(ɛ ;η ) γ(ɛ ;η ) e ζ/ ζ + µ (ζ / y)(ζ x) dζ = e x/ x + µ x / y. (2.4) Finally, from Eqs. (2.2) and (2.4) the representation (2.) holds true, and the lemma is established. Lemma 2.5. If R(µ) > 0, then the integral representations (2.2), (2.7), (2.0) and (2.) remain valid for = 2 or = 2. Proof. The lemma follows immediately by passing to the limit with respect to the corresponding parameters in representations (2.2), (2.7), (2.0) and (2.). 3. Asymptotic behaviour The asymptotic properties of the function E, (x, y; µ) for large values of x and y are of particular interest. Theorem 3.. Let 0 <, < 2 and < 2. Let µ be any complex number and τ be any real number satisfying inequalities (2.) π/2 < τ min ( π, π ). Then, for all integer r, the function E, (x, y; µ) verifies the following asymptotic formulas drawn from its integral representations whenever x and y.
7 INTEGRAL REPRESENTATIONS AND ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR 45 ) If arg x τ/ and arg y τ/, then E, (x, y; µ) = + r r n= m= e x/ x + µ x / y + e y/ y + µ y / x x n y m Γ(µ n m) + o ( xy x r) + o ( ) xy y r (3.) 2) If arg x τ/ and τ/ < arg y π, then E, (x, y; µ) = + r r n= m= e x/ x + µ x / y x n y m Γ(µ n m) + o ( xy x r) + o ( ) xy y r (3.2) 3) If τ/ < arg x π and arg y τ/, then E, (x, y; µ) = + r r n= m= e y/ y + µ y / x x n y m Γ(µ n m) + o ( xy x r) + o ( ) xy y r (3.3) 4) If τ/ < arg x π and τ/ < arg y π, then E, (x, y; µ) = r r n= m= x n y m Γ(µ n m) + o ( xy x r) + o ( xy y r ). (3.4) Proof. The proof below focuses on the first case, since the proofs ot the three other cases are easily completed along the same lines as in case, that is as the proof of asymptotic formula (3.). So, under the conditions required in case, i.e. arg x τ/ and arg y τ/, pick a real number θ satisfying the condition (3.5): It is easy to expand the equality (ζ / x)(ζ / y) = π/2 < τ < θ min ( π, π ). (3.5) r r n= m= ζ n + m x n y m r + xr ζ + y r ζ r x r y r (ζ / x)(ζ / y). (3.6) ζ r + r Set ɛ = in the representation (2.) in Lemma 2.4. Then, to the right of the contour γ(; θ) (i.e. within the complex region Ω (+) (; θ)), in view of expansion (3.6) and by Eq. (2.), the integral representation of E, (x, y; µ) takes the form
8 46 C. LAVAULT E, (x, y; µ) = + r n= m= e x/ x + µ x / y + r + 2πi 2πi e y/ y + µ y / x e ζ/() ζ ++ µ + n + m e ζ/() ζ ++ µ x r r ζ + y r ζ r r ζ + r x r y r (ζ / x)(ζ / y) dζ) x n y m dζ. (3.7) Now, the Hankel representation of the reciprocal gamma function is obtained through the suited Hankel contour H detailed in [9, Eq. C3], [, Chap. 3, 3.2.6], etc., and written as the well-known contour integral formula Γ(s) = H e u u s du (s C, u > 0). In the present setting, the integral contour is defined by H θ = γ(; θ) (π/2 < τ < θ min ( π, π ) ), according to the definition of the Hankel path γ(ɛ; η) in Section and the assumptions of the theorem. As a consequence, the summand of the double sum, the second term in (3.7), satisfies the relation 2πi = 2πi e ζ/() ζ ++ µ + n + m dζ = 2πi ( ) e ζ/() ζ µ n m + dζ = e ζ/() ζ µ + n + m dζ Γ(µ n m). (3.8) Therefore, under the constraints resulting from inequalities (3.5), substituting the above summand (3.8) into representation (3.7) yields the transformation E, (x, y; µ) = + 2πi e x/ x + µ x / y + e y/ y + µ y / x + r r n= m= x n y m Γ(µ n m) e ζ/() ζ ++ µ x r ζ r / + y r ζ r/ ζ r/+r / x r y r (ζ dζ. (3.9) / x)(ζ / y)
9 INTEGRAL REPRESENTATIONS AND ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR 47 Next, expanding and simplifying the final term above makes the obvious sum of the three integrals I + I 2 + I 3 appear in Eq. (3.9); precisely, I = e ζ/() ζ ++ µ +r / dζ, (3.0) 2πi y r (ζ / x)(ζ / y) I 2 = 2πi I 3 = 2πi e ζ/() ζ ++ µ +r / dζ and (3.) x r (ζ / x)(ζ / y) e ζ/() ζ ++ µ +r /+r / x r y r (ζ dζ. (3.2) / x)(ζ / y) Assuming that arg x τ/ and arg y τ/, each of the three integrals in the sum (3.9), I in (3.0), I 2 in (3.) and I 3 in (3.2), can be evaluated for large values of x and y. Provided that arg x τ/ for x large enough, it can be checked that min ζ ζ / x ( = x sin(θ/ τ/) = x sin ) θ τ and analogously, when arg y τ/ for y large enough, min ζ / y ( = y sin(θ/ τ/) = y sin θ τ ). ζ Hence, when arg x τ/ and arg y τ/ for large x and y, the following estimate for the integral I can be obtained: x y r I 2π sin ( ) ( ) θ τ sin θ τ eζ ζ ++ µ + r dζ. (3.3) Of course, an analogous estimate holds also symmetrically for the integral I 2 by substituting r for r and r / for r / (resp.) into inequality (3.3). Besides, since the rays defined by S θ = { arg ζ = ±θ, ζ } belong to the contour γ(; θ), the integral in inequality (3.3) is convergent; whence the equality ( e ζ/() = exp ζ θ cos ). Now, according to inequalities (3.5), we have that cos θ < 0. Thus, I = o ( xy y r) and I 2 = o ( xy x r ). Furthermore, by referring to Eq. (3.2), the next estimate is also obtained for the integral I 3. x r y r I 3 2π sin ( ) ( ) ζ e ζ/() ++ µ +r /+r / dζ, (3.4) θ τ sin θ τ which yields the asymptotic formula I 3 = o ( xy x r y r ).
10 48 C. LAVAULT Hence, this leads finally to the overall asymptotic formula I + I 2 + I 3 = o ( ) ( xy x r + o xy y r) and the proof of Eq. (3.) (in case of Theorem 3.) is established. Similarly, the proofs of Eq. (3.2) (case 2), Eq. (3.3) (case 3) and Eq. (3.4) (case 4) run along the same lines as the above proof of Eq. (3.) (case ). This completes the proof of Theorem 3.. Acknowledgments. The author would like to thank an anonymous reviewer for his/her very careful reading and valuable suggestions. His/her remarks benefited to a great help in correcting several mistakes and improved the quality of the paper. References. M. M. Džrbašjan, On the integral transformations generated by generalized functions of the Mittag-Leffler type (in Russian), Izv. Akad. Nauk Armjan. SSR Ser. Fiz.-Mat. Nauk 3 (960), no. 3, M. M. Džrbašjan, Integral transforms and representations of functions in the complex domain (in Russian), Izdat. Nauka, Moscow 966, 67 pp. 3. A. Erdélyi, W. Magnus, F. Oberhettinger, and F. G. Tricomi, Higher Transcendental Functions, Based, in part, on notes left by Harry Bateman. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., New York-Toronto-London, M. Garg, P. Manohar, and S. L. Kalla, A Mittag-Leffler function of two variables, Integral Transforms Spec. Funct. 24 (203), no., R. Gorenflo, A. A. Kilbas, F. Mainardi, and S. V. Rogosin, Mittag-Leffler functions, related topics and applications,springer Monographs in Mathematics. Springer, Heidelberg, R. Gorenflo, J. Loutchko, and Yu. Luchko, Computation of the Mittag-Leffler function E, (z) and its derivatives, Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 5 (2002), no. 4, H. Haubold, A. M. Mathai, and R. K. Saxena, Mittag-Leffler functions and their applications, J. Appl. Math. 20, Art. ID , 5 pp. 8. P. Humbert and R. P. Agarwal, Sur la fonction de Mittag-Leffler et quelques-unes de ses généralisations, Bull. Sci. Math. 77 (953), no. 2, C. Lavault, Fractional calculus and generalized Mittag-Leffler type functions, preprint (207), arxiv: & HAL:hal E. N. Ogorodnikov and N. S. Yashagin, Setting and solving of the Cauchy type problems for the second order differential equations with Riemann Liouville fractional derivatives, Vestn. Samar. Gos. Tekhn. Univ. Ser. Fiz.-Mat. Nauki (200), no. 20, N. M. Temme, Special functions. An introduction to the classical functions of mathematical physics, A Wiley-Interscience Publication. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, A. Wiman, Über den fundamentalsatz in der theorie der funktionen E a(z), Acta Math. 29 (905), no., LIPN, CNRS UMR 7030, Université Paris 3, Sorbonne Paris Cité, F Villetaneuse, France. address: lavault@lipn.univ-paris3.fr
Enzymatic Synthesis of Dithiolopyrrolone Antibiotics Using Cell-Free Extract of Saccharothrix
 Enzymatic Synthesis of Dithiolopyrrolone Antibiotics Using Cell-Free Extract of Saccharothrix algeriensis NRRL B-24137 and Biochemical Characterization of Two Pyrrothine N-Acyltransferases in This Extract.
Enzymatic Synthesis of Dithiolopyrrolone Antibiotics Using Cell-Free Extract of Saccharothrix algeriensis NRRL B-24137 and Biochemical Characterization of Two Pyrrothine N-Acyltransferases in This Extract.
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
The k-α-exponential Function
 Int Journal of Math Analysis, Vol 7, 213, no 11, 535-542 The --Exponential Function Luciano L Luque and Rubén A Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National University of Nordeste Av Libertad 554 34 Corrientes,
Int Journal of Math Analysis, Vol 7, 213, no 11, 535-542 The --Exponential Function Luciano L Luque and Rubén A Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National University of Nordeste Av Libertad 554 34 Corrientes,
Chemical and biological evaluations of an (111)in-labeled RGD-peptide targeting integrin alpha(v) beta(3) in a preclinical tumor model.
 Chemical and biological evaluations of an (111)in-labeled RGD-peptide targeting integrin alpha(v) beta(3) in a preclinical tumor model. Mitra Ahmadi, Lucie Sancey, Arnaud Briat, Laurent Riou, Didier Boturyn,
Chemical and biological evaluations of an (111)in-labeled RGD-peptide targeting integrin alpha(v) beta(3) in a preclinical tumor model. Mitra Ahmadi, Lucie Sancey, Arnaud Briat, Laurent Riou, Didier Boturyn,
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
DYNAMICS OF CHANGE WITHIN LIVESTOCK SUB-SECTOR IN CHAD : a key-study of raw milk commodity chain in N Djamena
 DYNAMICS OF CHANGE WITHIN LIVESTOCK SUB-SECTOR IN CHAD : a key-study of raw milk commodity chain in N Djamena Koussou Mian Oudanang To cite this version: Koussou Mian Oudanang. DYNAMICS OF CHANGE WITHIN
DYNAMICS OF CHANGE WITHIN LIVESTOCK SUB-SECTOR IN CHAD : a key-study of raw milk commodity chain in N Djamena Koussou Mian Oudanang To cite this version: Koussou Mian Oudanang. DYNAMICS OF CHANGE WITHIN
Coefficient Inequalities for a New Subclass of K-uniformly Convex Functions
 International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 0974-89 Volume, Number (00), pp. 67--75 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Coefficient Inequalities for
International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 0974-89 Volume, Number (00), pp. 67--75 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Coefficient Inequalities for
SCITECH Volume 13, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION Published online: March 29, 2018
 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
A summation formula ramified with hypergeometric function and involving recurrence relation
 South Asian Journal of Mathematics 017, Vol. 7 ( 1): 1 4 www.sajm-online.com ISSN 51-151 RESEARCH ARTICLE A summation formula ramified with hypergeometric function and involving recurrence relation Salahuddin
South Asian Journal of Mathematics 017, Vol. 7 ( 1): 1 4 www.sajm-online.com ISSN 51-151 RESEARCH ARTICLE A summation formula ramified with hypergeometric function and involving recurrence relation Salahuddin
Statistical analysis of extreme events in a nonstationary context via a Bayesian framework. Case study with peak-over-threshold data
 Statistical analysis of extreme events in a nonstationary context via a Bayesian framework. Case study with peak-over-threshold data B. Renard, M. Lang, P. Bois To cite this version: B. Renard, M. Lang,
Statistical analysis of extreme events in a nonstationary context via a Bayesian framework. Case study with peak-over-threshold data B. Renard, M. Lang, P. Bois To cite this version: B. Renard, M. Lang,
Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation. Mathematica StandardForm notation
 KelvinKei Notations Traditional name Kelvin function of the second kind Traditional notation kei Mathematica StandardForm notation KelvinKei Primary definition 03.5.0.000.0 kei kei 0 Specific values Values
KelvinKei Notations Traditional name Kelvin function of the second kind Traditional notation kei Mathematica StandardForm notation KelvinKei Primary definition 03.5.0.000.0 kei kei 0 Specific values Values
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
DiracDelta. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
Multi-GPU numerical simulation of electromagnetic waves
 Multi-GPU numerical simulation of electromagnetic waves Philippe Helluy, Thomas Strub To cite this version: Philippe Helluy, Thomas Strub. Multi-GPU numerical simulation of electromagnetic waves. ESAIM:
Multi-GPU numerical simulation of electromagnetic waves Philippe Helluy, Thomas Strub To cite this version: Philippe Helluy, Thomas Strub. Multi-GPU numerical simulation of electromagnetic waves. ESAIM:
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
On the k-bessel Functions
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 7, 01, no. 38, 1851-1857 On the k-bessel Functions Ruben Alejandro Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National University of Nordeste. Avda. Libertad 5540 (3400) Corrientes,
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 7, 01, no. 38, 1851-1857 On the k-bessel Functions Ruben Alejandro Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National University of Nordeste. Avda. Libertad 5540 (3400) Corrientes,
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
forms This gives Remark 1. How to remember the above formulas: Substituting these into the equation we obtain with
 Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Couplage dans les applications interactives de grande taille
 Couplage dans les applications interactives de grande taille Jean-Denis Lesage To cite this version: Jean-Denis Lesage. Couplage dans les applications interactives de grande taille. Réseaux et télécommunications
Couplage dans les applications interactives de grande taille Jean-Denis Lesage To cite this version: Jean-Denis Lesage. Couplage dans les applications interactives de grande taille. Réseaux et télécommunications
SPFC: a tool to improve water management and hay production in the Crau region
 SPFC: a tool to improve water management and hay production in the Crau region J.C. Mailhol, A. Merot To cite this version: J.C. Mailhol, A. Merot. SPFC: a tool to improve water management and hay production
SPFC: a tool to improve water management and hay production in the Crau region J.C. Mailhol, A. Merot To cite this version: J.C. Mailhol, A. Merot. SPFC: a tool to improve water management and hay production
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation. Tanguy Rivoal. Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble 1
 Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Annulations de la dette extérieure et croissance. Une application au cas des pays pauvres très endettés (PPTE)
 Annulations de la dette extérieure et croissance. Une application au cas des pays pauvres très endettés (PPTE) Khadija Idlemouden To cite this version: Khadija Idlemouden. Annulations de la dette extérieure
Annulations de la dette extérieure et croissance. Une application au cas des pays pauvres très endettés (PPTE) Khadija Idlemouden To cite this version: Khadija Idlemouden. Annulations de la dette extérieure
Consommation marchande et contraintes non monétaires au Canada ( )
 Consommation marchande et contraintes non monétaires au Canada (1969-2008) Julien Boelaert, François Gardes To cite this version: Julien Boelaert, François Gardes. Consommation marchande et contraintes
Consommation marchande et contraintes non monétaires au Canada (1969-2008) Julien Boelaert, François Gardes To cite this version: Julien Boelaert, François Gardes. Consommation marchande et contraintes
Solving an Air Conditioning System Problem in an Embodiment Design Context Using Constraint Satisfaction Techniques
 Solving an Air Conditioning System Problem in an Embodiment Design Context Using Constraint Satisfaction Techniques Raphael Chenouard, Patrick Sébastian, Laurent Granvilliers To cite this version: Raphael
Solving an Air Conditioning System Problem in an Embodiment Design Context Using Constraint Satisfaction Techniques Raphael Chenouard, Patrick Sébastian, Laurent Granvilliers To cite this version: Raphael
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
A Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Objective Video Quality Assessment
 A Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Objective Video Quality Assessment Patrick Le Callet, Christian Viard-Gaudin, Dominique Barba To cite this version: Patrick Le Callet, Christian Viard-Gaudin,
A Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Objective Video Quality Assessment Patrick Le Callet, Christian Viard-Gaudin, Dominique Barba To cite this version: Patrick Le Callet, Christian Viard-Gaudin,
Transformations d Arbres XML avec des Modèles Probabilistes pour l Annotation
 Transformations d Arbres XML avec des Modèles Probabilistes pour l Annotation Florent Jousse To cite this version: Florent Jousse. Transformations d Arbres XML avec des Modèles Probabilistes pour l Annotation.
Transformations d Arbres XML avec des Modèles Probabilistes pour l Annotation Florent Jousse To cite this version: Florent Jousse. Transformations d Arbres XML avec des Modèles Probabilistes pour l Annotation.
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
ExpIntegralE. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. Traditional name. Traditional notation. Mathematica StandardForm notation
 ExpIntegralE Notations Traditional name Exponential integral E Traditional notation E Mathematica StandardForm notation ExpIntegralE, Primary definition 06.34.0.000.0 E t t t ; Re 0 Specific values Specialied
ExpIntegralE Notations Traditional name Exponential integral E Traditional notation E Mathematica StandardForm notation ExpIntegralE, Primary definition 06.34.0.000.0 E t t t ; Re 0 Specific values Specialied
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy. Equivalence Relation
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
PROPERTIES OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS. a n z n (1.1)
 GEORGIAN MATHEMATICAL JOURNAL: Vol. 2, No. 5, 995, 535-545 PROPERTIES OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS SHIGEYOSHI OWA Abstract. Two integral operators P α and Q α for analytic functions in the open unit disk
GEORGIAN MATHEMATICAL JOURNAL: Vol. 2, No. 5, 995, 535-545 PROPERTIES OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS SHIGEYOSHI OWA Abstract. Two integral operators P α and Q α for analytic functions in the open unit disk
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
SOME PROPERTIES OF FUZZY REAL NUMBERS
 Sahand Communications in Mathematical Analysis (SCMA) Vol. 3 No. 1 (2016), 21-27 http://scma.maragheh.ac.ir SOME PROPERTIES OF FUZZY REAL NUMBERS BAYAZ DARABY 1 AND JAVAD JAFARI 2 Abstract. In the mathematical
Sahand Communications in Mathematical Analysis (SCMA) Vol. 3 No. 1 (2016), 21-27 http://scma.maragheh.ac.ir SOME PROPERTIES OF FUZZY REAL NUMBERS BAYAZ DARABY 1 AND JAVAD JAFARI 2 Abstract. In the mathematical
n=2 In the present paper, we introduce and investigate the following two more generalized
 MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 59 (007), 65 73 UDK 517.54 originalni nauqni rad research paper SOME SUBCLASSES OF CLOSE-TO-CONVEX AND QUASI-CONVEX FUNCTIONS Zhi-Gang Wang Abstract. In the present paper, the author
MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 59 (007), 65 73 UDK 517.54 originalni nauqni rad research paper SOME SUBCLASSES OF CLOSE-TO-CONVEX AND QUASI-CONVEX FUNCTIONS Zhi-Gang Wang Abstract. In the present paper, the author
Émergence des représentations perceptives de la parole : Des transformations verbales sensorielles à des éléments de modélisation computationnelle
 Émergence des représentations perceptives de la parole : Des transformations verbales sensorielles à des éléments de modélisation computationnelle Anahita Basirat To cite this version: Anahita Basirat.
Émergence des représentations perceptives de la parole : Des transformations verbales sensorielles à des éléments de modélisation computationnelle Anahita Basirat To cite this version: Anahita Basirat.
Physique des réacteurs à eau lourde ou légère en cycle thorium : étude par simulation des performances de conversion et de sûreté
 Physique des réacteurs à eau lourde ou légère en cycle thorium : étude par simulation des performances de conversion et de sûreté Alexis Nuttin To cite this version: Alexis Nuttin. Physique des réacteurs
Physique des réacteurs à eau lourde ou légère en cycle thorium : étude par simulation des performances de conversion et de sûreté Alexis Nuttin To cite this version: Alexis Nuttin. Physique des réacteurs
Développement de virus HSV-1 (virus de l herpes simplex de type 1) oncolytiques ciblés pour traiter les carcinomes hépatocellulaires
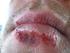 Développement de virus HSV-1 (virus de l herpes simplex de type 1) oncolytiques ciblés pour traiter les carcinomes hépatocellulaires Aldo Decio Pourchet To cite this version: Aldo Decio Pourchet. Développement
Développement de virus HSV-1 (virus de l herpes simplex de type 1) oncolytiques ciblés pour traiter les carcinomes hépatocellulaires Aldo Decio Pourchet To cite this version: Aldo Decio Pourchet. Développement
Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence MRI in Multiple Sclerosis
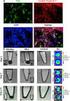
 Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence MRI in Multiple Sclerosis Daniel García-Lorenzo To cite this version: Daniel García-Lorenzo. Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence
Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence MRI in Multiple Sclerosis Daniel García-Lorenzo To cite this version: Daniel García-Lorenzo. Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence
Pax8 and Pax2 are specifically required at different steps of Xenopus pronephros development
 Pax8 and Pax2 are specifically required at different steps of Xenopus pronephros development Isabelle Buisson, Ronan Le Bouffant, Mélinée Futel, Jean-François Riou, Muriel Umbhauer To cite this version:
Pax8 and Pax2 are specifically required at different steps of Xenopus pronephros development Isabelle Buisson, Ronan Le Bouffant, Mélinée Futel, Jean-François Riou, Muriel Umbhauer To cite this version:
ACI sécurité informatique KAA (Key Authentification Ambient)
 ACI sécurité informatique KAA (Key Authentification Ambient) Samuel Galice, Veronique Legrand, Frédéric Le Mouël, Marine Minier, Stéphane Ubéda, Michel Morvan, Sylvain Sené, Laurent Guihéry, Agnès Rabagny,
ACI sécurité informatique KAA (Key Authentification Ambient) Samuel Galice, Veronique Legrand, Frédéric Le Mouël, Marine Minier, Stéphane Ubéda, Michel Morvan, Sylvain Sené, Laurent Guihéry, Agnès Rabagny,
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
The Negative Neumann Eigenvalues of Second Order Differential Equation with Two Turning Points
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 009, no., 6-66 The Negative Neumann Eigenvalues of Second Order Differential Equation with Two Turning Points A. Neamaty and E. A. Sazgar Department of Mathematics,
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 009, no., 6-66 The Negative Neumann Eigenvalues of Second Order Differential Equation with Two Turning Points A. Neamaty and E. A. Sazgar Department of Mathematics,
9.09. # 1. Area inside the oval limaçon r = cos θ. To graph, start with θ = 0 so r = 6. Compute dr
 9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
Pg The perimeter is P = 3x The area of a triangle is. where b is the base, h is the height. In our case b = x, then the area is
 Pg. 9. The perimeter is P = The area of a triangle is A = bh where b is the base, h is the height 0 h= btan 60 = b = b In our case b =, then the area is A = = 0. By Pythagorean theorem a + a = d a a =
Pg. 9. The perimeter is P = The area of a triangle is A = bh where b is the base, h is the height 0 h= btan 60 = b = b In our case b =, then the area is A = = 0. By Pythagorean theorem a + a = d a a =
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence
 International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 3, 143-149 A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence Santosh Kr. Saxena H. N. 419, Jawaharpuri, Badaun, U.P., India Presently working in
International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 3, 143-149 A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence Santosh Kr. Saxena H. N. 419, Jawaharpuri, Badaun, U.P., India Presently working in
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Forêts aléatoires : aspects théoriques, sélection de variables et applications
 Forêts aléatoires : aspects théoriques, sélection de variables et applications Robin Genuer To cite this version: Robin Genuer. Forêts aléatoires : aspects théoriques, sélection de variables et applications.
Forêts aléatoires : aspects théoriques, sélection de variables et applications Robin Genuer To cite this version: Robin Genuer. Forêts aléatoires : aspects théoriques, sélection de variables et applications.
Section 9.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
A Two-Sided Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bounds and Its Applications in Financial Engineering
 Electronic Companion A Two-Sie Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bouns an Its Applications in Financial Engineering Ning Cai, S. G. Kou, Zongjian Liu HKUST an Columbia University Appenix
Electronic Companion A Two-Sie Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bouns an Its Applications in Financial Engineering Ning Cai, S. G. Kou, Zongjian Liu HKUST an Columbia University Appenix
Parametrized Surfaces
 Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in
 Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Strain gauge and rosettes
 Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Radio détection des rayons cosmiques d ultra-haute énergie : mise en oeuvre et analyse des données d un réseau de stations autonomes.
 Radio détection des rayons cosmiques d ultra-haute énergie : mise en oeuvre et analyse des données d un réseau de stations autonomes. Diego Torres Machado To cite this version: Diego Torres Machado. Radio
Radio détection des rayons cosmiques d ultra-haute énergie : mise en oeuvre et analyse des données d un réseau de stations autonomes. Diego Torres Machado To cite this version: Diego Torres Machado. Radio
Inflation Bias after the Euro: Evidence from the UK and Italy
 Inflation Bias after the Euro: Evidence from the UK and Italy Pasquale Scaramozzino, Giancarlo Marini, Alessandro Piergallini To cite this version: Pasquale Scaramozzino, Giancarlo Marini, Alessandro Piergallini.
Inflation Bias after the Euro: Evidence from the UK and Italy Pasquale Scaramozzino, Giancarlo Marini, Alessandro Piergallini To cite this version: Pasquale Scaramozzino, Giancarlo Marini, Alessandro Piergallini.
Jie He. To cite this version: HAL Id: halshs https://halshs.archives-ouvertes.fr/halshs
 Pollution haven hypothesis and Environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: The Case of Industrial Emission of Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces Jie He To cite this version: Jie He. Pollution
Pollution haven hypothesis and Environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: The Case of Industrial Emission of Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces Jie He To cite this version: Jie He. Pollution
Jeux d inondation dans les graphes
 Jeux d inondation dans les graphes Aurélie Lagoutte To cite this version: Aurélie Lagoutte. Jeux d inondation dans les graphes. 2010. HAL Id: hal-00509488 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00509488
Jeux d inondation dans les graphes Aurélie Lagoutte To cite this version: Aurélie Lagoutte. Jeux d inondation dans les graphes. 2010. HAL Id: hal-00509488 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00509488
Network Neutrality Debate and ISP Inter-Relations: Traffi c Exchange, Revenue Sharing, and Disconnection Threat
 Network Neutrality Debate and ISP Inter-Relations: Traffi c Exchange, Revenue Sharing, and Disconnection Threat Pierre Coucheney, Patrick Maillé, runo Tuffin To cite this version: Pierre Coucheney, Patrick
Network Neutrality Debate and ISP Inter-Relations: Traffi c Exchange, Revenue Sharing, and Disconnection Threat Pierre Coucheney, Patrick Maillé, runo Tuffin To cite this version: Pierre Coucheney, Patrick
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
CHAPTER 101 FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD
 CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Homomorphism in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Automata
 International Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics Systems. ISSN 2248-9940 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 39-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijfms.htm Homomorphism in Intuitionistic
International Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics Systems. ISSN 2248-9940 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 39-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijfms.htm Homomorphism in Intuitionistic
Lecture 26: Circular domains
 Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without eplicit written permission from the copyright owner. 1 Lecture 6: Circular domains
Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without eplicit written permission from the copyright owner. 1 Lecture 6: Circular domains
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Les gouttes enrobées
 Les gouttes enrobées Pascale Aussillous To cite this version: Pascale Aussillous. Les gouttes enrobées. Fluid Dynamics. Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris VI,. French. HAL Id: tel-363 https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-363
Les gouttes enrobées Pascale Aussillous To cite this version: Pascale Aussillous. Les gouttes enrobées. Fluid Dynamics. Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris VI,. French. HAL Id: tel-363 https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-363
Reccurence Relation of Generalized Mittag Lefer Function
 Palestine Journal of Mathematics Vol. 6(2)(217), 562 568 Palestine Polytechnic University-PPU 217 Reccurence Relation of Generalized Mittag Lefer Function Vana Agarwal Monika Malhotra Communicated by Ayman
Palestine Journal of Mathematics Vol. 6(2)(217), 562 568 Palestine Polytechnic University-PPU 217 Reccurence Relation of Generalized Mittag Lefer Function Vana Agarwal Monika Malhotra Communicated by Ayman
Generating Set of the Complete Semigroups of Binary Relations
 Applied Mathematics 06 7 98-07 Published Online January 06 in SciRes http://wwwscirporg/journal/am http://dxdoiorg/036/am067009 Generating Set of the Complete Semigroups of Binary Relations Yasha iasamidze
Applied Mathematics 06 7 98-07 Published Online January 06 in SciRes http://wwwscirporg/journal/am http://dxdoiorg/036/am067009 Generating Set of the Complete Semigroups of Binary Relations Yasha iasamidze
