Universalité pour des polymères aléatoires. Paris, 17 Novembre 2015
|
|
|
- Ίσις Λαγός
- 5 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Universalité pour des polymères aléatoires Niccolò Torri Paris, 17 Novembre 2015
2 1 Polymers 2 Pinning Model and DPRE 3 Universality of the Pinning Model New Results 4 Proofs Continuum model Proof of our results N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
3 Polymers Interactions with Itself External environment Depend on some parameters Aim Spatial configuration Phase transition? Critical Points? N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
4 Intermezzo: Some Basic Probabilistic Processes Random Walk on Z d S n = n i=1 X i, X i = increments. x i { Self Avoiding Random Walk (SAW) on Z d Conditioned to visit at most ones each state. N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
5 Abstract Monomers and Abstract Polymers Increment X i a monomer Use SAW: Abstract Polymer (N monomers): N-increments of a SAW N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
6 Abstract Monomers and Abstract Polymers Increment X i a monomer Use SAW: SAW: challenging object! Subclass: Directed Random Walks (Directed Polymers) Abstract Polymer (N monomers): N-increments of a SAW s n n N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
7 1 Polymers 2 Pinning Model and DPRE 3 Universality of the Pinning Model New Results 4 Proofs Continuum model Proof of our results
8 Interaction with the environment Pinning Model interaction with a membrane Directed Polymer in Random Environment (DPRE) interaction with the whole environment s n n region of interaction : straight line N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
9 Pinning Model s n n region of interaction : straight line Region of interaction Lattice Ω = {1,, N} Contact process Renewal Process τ = {n : S n = 0} N 0 Interaction P(τ i τ i 1 = n) P ω N, β, h (τ) = 1 Z ω N,β,h c n 1+α, α > 0 exp (βω i + h)1 {i τ} P(τ) i Ω N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
10 Directed Polymer in Random Environment (DPRE) Region of interaction Lattice Ω = {1,, N} Z sn =X Xn Polymer Directed Walk (n, S n ) n N Ω Interaction P ω N, β, h (S) = 1 Z ω exp (βω (i,x) + h)1 {Si =x} N,β,h P(S) (i,x) Ω x p(x,x+1) = 1 2 p(x,x - 1) = 1 2 n N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
11 1 Polymers 2 Pinning Model and DPRE 3 Universality of the Pinning Model New Results 4 Proofs Continuum model Proof of our results
12 Behavior of the model Pinning Model: interaction polymer and membrane. Renewal Process τ N 0 (τ i τ i 1 ) i N i.i.d. & P(τ i τ i 1 = n) c n 1+α, α > 0 Pinning Model τ [0, N] perturbed P ω N, β, h (τ) = 1 N Z ω exp (βω i + h)1 {i τ} P(τ) N,β,h disorder (quenched realisation of) (ω = (ω x ) x Ω, P) i.i.d. E(ω 1 ) = 0, Var(ω 1 ) = 1, Λ(z) = log E(e zω 1 ) <, z small. i=1 N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
13 Behavior of the model Pinning Model: interaction polymer and membrane. Renewal Process τ N 0 (τ i τ i 1 ) i N i.i.d. & P(τ i τ i 1 = n) c n 1+α, α > 0 Pinning Model τ [0, N] perturbed P ω N, β, h (τ) = 1 N Z ω exp (βω i + h)1 {i τ} P(τ) N,β,h disorder (quenched realisation of) (ω = (ω x ) x Ω, P) i.i.d. E(ω 1 ) = 0, Var(ω 1 ) = 1, Λ(z) = log E(e zω 1 ) <, z small. i=1 Goal: Study τ when N gets large. τ [0, N] c h,β N or τ [0, N] = o(n)? Phase Transition? Critical point? N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
14 Localization/Delocalization Free Energy F (α) 1 (β, h) = lim N N E [ ] log Z ω β,h,n ( ) {points of τ N} h F (α) (β, h) = lim EE ω N β,h,n N ( ) β 0 there exists a critical point h c (β) s n Delocalized Localized n h > h c (β) localization, ( ) > 0, h < h c (β) de-localization, ( ) = 0. N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
15 Analysis of the model Goal: understand h c (β). Homogeneous model h c (0) explicit. It provides Lower/Upper bounds h c (0) Λ(β) h c (β) < h c (0), h c (0) Λ(β) annealed critical point. N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
16 Analysis of the model Goal: understand h c (β). Homogeneous model h c (0) explicit. It provides Lower/Upper bounds h c (0) Λ(β) h c (β) < h c (0), h c (0) Λ(β) annealed critical point. P ω N, β, h (τ) = 1 Z ω N,β,h N exp (βω i + h)1 {i τ} P(τ) i=1 N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
17 Relevance/Irrelevance of the disorder α > 1/2 relevant disorder 0 < α < 1/2 irrelevant disorder h c(β) > h c(0)-λ(β) β>0 h c(β) = h c(0)-λ(β) if β small h (β) c h (0) c h (0)-Λ(β) c N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
18 Relevance/Irrelevance of the disorder α > 1/2 relevant disorder h c(β) > h c(0)-λ(β) β>0 h (β) c h (0) c h (0)-Λ(β) c Aim: When α > 1/2, asymptotics of h c (β) as β 0 (Weak Disorder). N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
19 An overview of the literature case α > 1 Theorem (Q. Berger, F. Caravenna, J. Poisat, R. Sun, N. Zygouras, 2014) Let α > 1, then h c (β) β 0 cβ 2, where c is explicit depending on the law of τ i τ i 1. case α (1/2, 1) several authors K. S. Alexander, B. Derrida, G. Giacomin, H. Lacoin, F. L. Toninelli and N. Zygouras ( ): Theorem Let α (1/2, 1), then there exist 0 < c < C < such that for β small. c β 2α 2α 1 hc (β) C β 2α 2α 1, N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
20 3 Universality of the Pinning Model New Results
21 Results Theorem (Caravenna, Toninelli, T., 2015) Universal feature of the Free Energy: α (1/2, 1) F (α) F ( ˆβ, (α)( ˆβ ε α 1 2, ĥ ε α) ĥ) = lim ε 0 ε Rescale relation F (α) ( ˆβ, ĥ) = β ( ) 2 2α 1 F (α) 1, ĥβ 2α 2α 1 ĉ universal constant depending on α and c. H (α) ( ˆβ) = ĉ ˆβ 2α 2α 1 Theorem (Caravenna, Toninelli, T., 2015) Universal Critical Behavior h c (β) β 0 ĉ β 2α 2α 1, N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
22 Conjectures for DPRE Universal feature of the Free Energy F DPRE F (α)( ε (1) = lim ε 0 ε 1 ) 4 F (α)( ε ) ε 4 F DPRE (1). Conjecture supported by Lacoin (2009) (no sharp result) N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
23 4 Proofs Continuum model Proof of our results
24 General Framework Discrete Lattice Ω = Ω Z d, Reference System (σ = (σ x ) x Ω, P Ω ), σ x {0, 1}, Disorder (quenched realisation of) (ω = (ω x ) x Ω, P) i.i.d. E(ω 1 ) = 0, Var(ω 1 ) = 1, Λ(z) = log E(e zω 1 ) <, z small. Interaction (disordered measure) P ω Ω,β,h (dσ) = 1 Z ω exp (βω i + h)σ x P Ω(dσ) N,β,h x Ω N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
25 General Framework Discrete Lattice Ω = Ω Z d, Reference System (σ = (σ x ) x Ω, P Ω ), σ x {0, 1}, Interaction (disordered measure) P ω Ω,β,h (dσ) = 1 Z ω exp (βω i + h)σ x P Ω(dσ) N,β,h x Ω Pinning Model DPRE Lattice Ω = (0, N) Ω = (0, N) R Reference System σ x = 1 {x τ} σ (n,x) = 1 {Sn =x} N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
26 General Framework: Goal Pinning Model DPRE Lattice Ω = (0, N) Ω = (0, N) R Reference System σ x = 1 {x τ} σ (n,x) = 1 {Sn =x} Assumption: Continuum Limit rescaling δ = δ N of Ω s.t. (σ = (σ x ) x Ωδ, P Ωδ ) δ 0 ( ˆσ = ( ˆσ x ) x Ω, ˆP Ω ) Pinning Model DPRE Rescaling δ = 1 N δ = ( 1 N, 1 ) N 1/2 Continuum limit Regenerative set ˆτ Brownian Motion (B t ) t Continuum system ˆσ x = 1 {x ˆτ} ˆσ x = 1 {Bt =y}, N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
27 General Framework: Goal Convergence of reference model: (σ = (σ x ) x Ωδ, P Ωδ ) δ 0 ( ˆσ = ( ˆσ x ) x Ω, ˆP Ω ) Convergence of the disordered model: rescaling of β, h = β, h(δ) δ 0 0: (σ = (σ x ) x Ωδ, P ω Ω δ,β δ,h δ ) δ 0? Idea look at the partition function Z ω Ω,β,h...Because it defines completely P ω Ω,β,h N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
28 Chaos Expansion Partition function Z ω Ω,β,h = E [ ] Ω e n Ω(βω n +h)σ n Polynomial Chaos Expansion where Z ω Ω,β,h = E Ω (1 + ε n σ n ) = n Ω Ω ϕ (k) k! Ω (n 1,, n k ) k=1 (n 1,,n k ) Ω k ε n = e (βω n+h) 1 ϕ (k) Ω (n 1,, n k ) = E Ω [ σn1 σ nk ] k k=1 ε ni N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
29 Continuum Model Theorem (Caravenna, Sun, Zygouras (2014)) Assumption γ : (δ γ ) k ϕ (k) Ω δ (x 1,, x k ) δ 0 ˆϕ (k) Ω (x 1,, x k ). Choosing β δ = ˆβδ d/2 γ, h δ = ĥδ d γ Z ω Ω δ,β δ,h δ (d) δ 0 ẐW Ω, ˆβ,ĥ Continuum Partition function: Wiener Chaos Expansion Ẑ W Ω, ˆβ,ĥ = k! k=1 (k) ˆϕ (x 1,,x k ) Ω k Ω (x 1,, x k ) k [ ] ˆβW(dx i ) + ĥdx i k=1 N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
30 Proof Ω δ Z ω Ω δ,β,h = 1 + k=1 1 k! (x 1,,x k ) Ω k δ Idea Lindeberg Principle: ε x is quite Gaussian : ϕ (k) Ω δ (x 1,, x k ) k k=1 ε xi ε x = e βω x+h 1 : Var(ε x ) β 2, E(ε x ) h + β2 2 = h : ε x βw 1 + h = β x d/2 W x + h (x 1,,x k ) Ω k δ ϕ (k) Ω δ (x 1,, x k ) (k) ϕ (x 1,,x k ) Ω k k k=1 ε xi Ω δ (x 1,, x k ) k [ ] βδ d/2 W(dx i ) + h δ d dx i k=1 N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
31 Example: Pinning Model Polynomial Chaos expansion: ϕ (k) Ω (n [ ] [ ] 1,, n k ) = E Ω σn1 σ nk = EΩ 1n1 τ 1 nk τ Theorem (Doney (1997)) P(τ 1 = n) c, α (0, 1) P(n τ) c n 1+α n 1 α N Z ω Ω,β,h 1 + k=1 0<n 1 < <n k <N C k n 1 α 1 (n k n k 1 ) 1 α k k=1 ε xi N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
32 Example: Pinning Model N Z ω Ω,β,h 1 + k=1 0<n 1 < <n k <N C k n 1 α 1 (n k n k 1 ) 1 α k k=1 ε xi k=1, contribution of one point + k=2, contribution of two points k=m, contribution of m-points N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
33 Example: Pinning Model N Z ω Ω,β,h 1 + k=1 0<n 1 < <n k <N C k n 1 α 1 (n k n k 1 ) 1 α k k=1 ε xi Rescaling δ = 1 N and Gaussian Approximation Z ω Ω δ,β,h δ k=1 0<x 1 < <x k <1 δ (1 α)k C k x 1 α 1 (x k x k 1 ) 1 α k [ ] βδ 1 2 W(dxi ) + h δ 1 dx i k=1 N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
34 Pinning Model and DPRE rescaling Pinning Model: γ = 1 α β δ = ˆβ δ α 1/2, h δ = ĥ δα must be α > 1/2 (Disorder relevance) ˆϕ (k) Ω (x 1,, x k ) = β δ = ˆβ δ 1/4, h δ = ĥ δ C k x 1 α (x 1 k x k 1 ) 1 α DPRE: γ = 2 ˆϕ (k) Ω ((x 1, t 1 ),, (x k, t k ))) = k e (x i x i 1 )2 /2(t i t i 1 ) i=1 2π(ti t i 1 ) N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
35 Universality of the free energy The continuum model captures the critical behavior of the system in the weak disorder regime (β, h 0): Naive approach ] 1 F ( ˆβ, ĥ) := lim [log Ω R d Ω E Ẑ W Ω =limδ 0 δ d Ω δ = Ω, ˆβ,ĥ 1 lim lim Ω R d δ 0 δ d Ω δ E [ ] log Z ω!!! Ω δ,β δ,h δ = lim lim 1 δ 0 Ω R d δ d Ω δ E [ ] log Z ω F(β δ, h δ ) Ω δ,β δ,h δ = lim. δ 0 δ d N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
36 Universality of the free energy The continuum model captures the critical behavior of the system in the weak disorder regime (β, h 0): Naive approach ] 1 F ( ˆβ, ĥ) := lim [log Ω R d Ω E Ẑ W Ω =limδ 0 δ d Ω δ = Ω, ˆβ,ĥ 1 lim lim Ω R d δ 0 δ d Ω δ E [ ] log Z ω!!! Ω δ,β δ,h δ = lim lim 1 δ 0 Ω R d δ d Ω δ E [ ] log Z ω F(β δ, h δ ) Ω δ,β δ,h δ = lim. δ 0 δ d Universal asymptotics F(β δ, h δ ) δ d ˆF(1, 1) as δ 0 N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
37 4 Proofs Continuum model Proof of our results
38 Recall the Results: Universal Critical Behavior Theorem (Caravenna, Toninelli, T., 2015) Universality of the Free Energy: F (α) F ( ˆβ, (α)( ˆβ ε α 1 2, ĥ ε α) ĥ) = lim ε 0 ε Theorem (Caravenna, Toninelli, T., 2015) h c (β) β 0 ĉ β 2α 2α 1, where ĉ universal constant depending on α and c. N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
39 Proof - Continuum Model τ := {n : S n = 0} ετ ε 0 Thm (C.S.Z.,15) (cond.) Pinning Model converges α (1/2, 1), β = ˆβε α 1 2, h = ĥε α : t 1 t 2 ετ β,h (d) ε 0 ˆτ ˆτ ˆβ,ĥ Continuum ingredients: - regenerative set (ˆτ) - White Noise (Cont. disorder) Problem: No Gibbs representation Wiener Chaos Expansion N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
40 Proof - Strategy: Coarse-Graining N = t ε. Consider 1 N E log Z N Convergence on each block Compare lim t lim ε & lim ε lim t Coarse-Graining of ετ and ˆτ 0 J 1= 1 J 2= 2 3 J 3= 4 J m= t 5 6 s t 1 s2 t 2 s3 t 3 sm t m t 1 t Partition function decomposition t s i t i (Ԑ) (Ԑ) Ԑ 0 s i t i Technical difficulty & c, disc Ԑ 0 Z (τ) Couple together convergence of ( si (ε), t i (ε) ) with Z c t/ε( a, b ) i c, cont Z i (τ) Z c 1(τ) Z c 2(τ) Z c 3(τ) Z c 4(τ) Z c,disc. i Z c,cont. i ( (τ/ε) = Z c t/ε si (ε), ) t i (ε) ( ) (ˆτ) = Z c si, t i t t Get: η > 0 ε 0 : ε < ε 0 F (α) ( ˆβ, ĥ η) ε 1 F (α)( ˆβ ε α 1 2, ĥ ε α) F (α) ( ˆβ, ĥ + η) N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
41 Proof - Strategy: Coarse-Graining N = t ε. Consider 1 N E log Z N Convergence on each block Compare lim t lim ε & lim ε lim t Coarse-Graining of ετ and ˆτ 0 J 1= 1 J 2= 2 3 J 3= 4 J m= t 5 6 s t 1 s2 t 2 s3 t 3 sm t m t 1 t Partition function decomposition t s i t i (Ԑ) (Ԑ) Ԑ 0 s i t i Technical difficulty & c, disc Ԑ 0 Z (τ) Couple together convergence of ( si (ε), t i (ε) ) with Z c t/ε( a, b ) i c, cont Z i (τ) Z c 1(τ) Z c 2(τ) Z c 3(τ) Z c 4(τ) Z c,disc. i Z c,cont. i ( (τ/ε) = Z c t/ε si (ε), ) t i (ε) ( ) (ˆτ) = Z c si, t i t t Get: η > 0 ε 0 : ε < ε 0 F (α) ( ˆβ, ĥ η) ε 1 F (α)( ˆβ ε α 1 2, ĥ ε α) F (α) ( ˆβ, ĥ + η) Similar to Copolymer Model (den Hollander & Bolthausen, 1997 and Caravenna & Giacomin, 2010) N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Random Polymers Paris, 17 Novembre / 26
42 Merci!
43 Merci!
Comportement critique du modèle d accrochage de. Toulouse, 29 Mars 2016
 Comportement critique du modèle d accrochage de polymère Niccolò Torri Toulouse, 29 Mars 2016 1 Pinning Model 2 New Results 3 Proof 4 Perspectives N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Polymères aléatoires Toulouse,
Comportement critique du modèle d accrochage de polymère Niccolò Torri Toulouse, 29 Mars 2016 1 Pinning Model 2 New Results 3 Proof 4 Perspectives N. Torri (Université de Nantes) Polymères aléatoires Toulouse,
HOW DOES A CHARGED POLYMER COLLAPSE?
 HOW DOES A CHARGED POLYMER COLLAPSE? Frank den Hollander Leiden University, The Netherlands P.C. Mahalanobis Lectures 2015 2016, Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi & Bangalore & Kolkata. Joint work with:
HOW DOES A CHARGED POLYMER COLLAPSE? Frank den Hollander Leiden University, The Netherlands P.C. Mahalanobis Lectures 2015 2016, Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi & Bangalore & Kolkata. Joint work with:
P AND P. P : actual probability. P : risk neutral probability. Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P. For example:
 (B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
(B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
The Probabilistic Method - Probabilistic Techniques. Lecture 7: The Janson Inequality
 The Probabilistic Method - Probabilistic Techniques Lecture 7: The Janson Inequality Sotiris Nikoletseas Associate Professor Computer Engineering and Informatics Department 2014-2015 Sotiris Nikoletseas,
The Probabilistic Method - Probabilistic Techniques Lecture 7: The Janson Inequality Sotiris Nikoletseas Associate Professor Computer Engineering and Informatics Department 2014-2015 Sotiris Nikoletseas,
Survival Analysis: One-Sample Problem /Two-Sample Problem/Regression. Lu Tian and Richard Olshen Stanford University
 Survival Analysis: One-Sample Problem /Two-Sample Problem/Regression Lu Tian and Richard Olshen Stanford University 1 One sample problem T 1,, T n 1 S( ), C 1,, C n G( ) and T i C i Observations: (U i,
Survival Analysis: One-Sample Problem /Two-Sample Problem/Regression Lu Tian and Richard Olshen Stanford University 1 One sample problem T 1,, T n 1 S( ), C 1,, C n G( ) and T i C i Observations: (U i,
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Overview. Transition Semantics. Configurations and the transition relation. Executions and computation
 Overview Transition Semantics Configurations and the transition relation Executions and computation Inference rules for small-step structural operational semantics for the simple imperative language Transition
Overview Transition Semantics Configurations and the transition relation Executions and computation Inference rules for small-step structural operational semantics for the simple imperative language Transition
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams
 From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams WIR 2014 Fanny He f.he@bath.ac.uk Alexis Saurin alexis.saurin@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr 12 July 2014 The Λµ-calculus Syntax of Λµ t ::= x λx.t (t)u
From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams WIR 2014 Fanny He f.he@bath.ac.uk Alexis Saurin alexis.saurin@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr 12 July 2014 The Λµ-calculus Syntax of Λµ t ::= x λx.t (t)u
Lecture 2. Soundness and completeness of propositional logic
 Lecture 2 Soundness and completeness of propositional logic February 9, 2004 1 Overview Review of natural deduction. Soundness and completeness. Semantics of propositional formulas. Soundness proof. Completeness
Lecture 2 Soundness and completeness of propositional logic February 9, 2004 1 Overview Review of natural deduction. Soundness and completeness. Semantics of propositional formulas. Soundness proof. Completeness
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in
 Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Elements of Information Theory
 Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
Abstract Storage Devices
 Abstract Storage Devices Robert König Ueli Maurer Stefano Tessaro SOFSEM 2009 January 27, 2009 Outline 1. Motivation: Storage Devices 2. Abstract Storage Devices (ASD s) 3. Reducibility 4. Factoring ASD
Abstract Storage Devices Robert König Ueli Maurer Stefano Tessaro SOFSEM 2009 January 27, 2009 Outline 1. Motivation: Storage Devices 2. Abstract Storage Devices (ASD s) 3. Reducibility 4. Factoring ASD
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
g-selberg integrals MV Conjecture An A 2 Selberg integral Summary Long Live the King Ole Warnaar Department of Mathematics Long Live the King
 Ole Warnaar Department of Mathematics g-selberg integrals The Selberg integral corresponds to the following k-dimensional generalisation of the beta integral: D Here and k t α 1 i (1 t i ) β 1 1 i
Ole Warnaar Department of Mathematics g-selberg integrals The Selberg integral corresponds to the following k-dimensional generalisation of the beta integral: D Here and k t α 1 i (1 t i ) β 1 1 i
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata
 Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.1 L = {wcw R w (0+1) * } P c 0P0 1P1 1. Start at state q 0, push input symbol onto stack, and stay in q 0. 2. If input symbol is
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.1 L = {wcw R w (0+1) * } P c 0P0 1P1 1. Start at state q 0, push input symbol onto stack, and stay in q 0. 2. If input symbol is
Theorem 8 Let φ be the most powerful size α test of H
 Testing composite hypotheses Θ = Θ 0 Θ c 0 H 0 : θ Θ 0 H 1 : θ Θ c 0 Definition 16 A test φ is a uniformly most powerful (UMP) level α test for H 0 vs. H 1 if φ has level α and for any other level α test
Testing composite hypotheses Θ = Θ 0 Θ c 0 H 0 : θ Θ 0 H 1 : θ Θ c 0 Definition 16 A test φ is a uniformly most powerful (UMP) level α test for H 0 vs. H 1 if φ has level α and for any other level α test
SCITECH Volume 13, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION Published online: March 29, 2018
 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain. Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics
 A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Local Approximation with Kernels
 Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
EE 570: Location and Navigation
 EE 570: Location and Navigation INS Initialization Aly El-Osery Kevin Wedeward Electrical Engineering Department, New Mexico Tech Socorro, New Mexico, USA In Collaboration with Stephen Bruder Electrical
EE 570: Location and Navigation INS Initialization Aly El-Osery Kevin Wedeward Electrical Engineering Department, New Mexico Tech Socorro, New Mexico, USA In Collaboration with Stephen Bruder Electrical
Mean-Variance Analysis
 Mean-Variance Analysis Jan Schneider McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin Jan Schneider Mean-Variance Analysis Beta Representation of the Risk Premium risk premium E t [Rt t+τ ] R1
Mean-Variance Analysis Jan Schneider McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin Jan Schneider Mean-Variance Analysis Beta Representation of the Risk Premium risk premium E t [Rt t+τ ] R1
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation. Tanguy Rivoal. Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble 1
 Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Markov chains model reduction
 Markov chains model reduction C. Landim Seminar on Stochastic Processes 216 Department of Mathematics University of Maryland, College Park, MD C. Landim Markov chains model reduction March 17, 216 1 /
Markov chains model reduction C. Landim Seminar on Stochastic Processes 216 Department of Mathematics University of Maryland, College Park, MD C. Landim Markov chains model reduction March 17, 216 1 /
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Major Concepts. Multiphase Equilibrium Stability Applications to Phase Equilibrium. Two-Phase Coexistence
 Major Concepts Multiphase Equilibrium Stability Applications to Phase Equilibrium Phase Rule Clausius-Clapeyron Equation Special case of Gibbs-Duhem wo-phase Coexistence Criticality Metastability Spinodal
Major Concepts Multiphase Equilibrium Stability Applications to Phase Equilibrium Phase Rule Clausius-Clapeyron Equation Special case of Gibbs-Duhem wo-phase Coexistence Criticality Metastability Spinodal
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs
 Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs Philippe Jaming Bordeaux Fourier Workshop 2013, Renyi Institute Joint work with K. Kellay Heisenberg Uniqueness Pairs µ : finite measure on R 2 µ(x, y) = R 2 e i(sx+ty) dµ(s,
Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs Philippe Jaming Bordeaux Fourier Workshop 2013, Renyi Institute Joint work with K. Kellay Heisenberg Uniqueness Pairs µ : finite measure on R 2 µ(x, y) = R 2 e i(sx+ty) dµ(s,
ANNEALED SCALING FOR A CHARGED POLYMER
 ANNEALED SCALING FOR A CHARGED POLYMER Frank den Hollander Leiden University The Netherlands Joint work with Francesco Caravenna (Milan), Nicolas Pétrélis (Nantes), Julien Poisat (Leiden) Workshop on Recent
ANNEALED SCALING FOR A CHARGED POLYMER Frank den Hollander Leiden University The Netherlands Joint work with Francesco Caravenna (Milan), Nicolas Pétrélis (Nantes), Julien Poisat (Leiden) Workshop on Recent
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise. Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University
 Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Iterated trilinear fourier integrals with arbitrary symbols
 Cornell University ICM 04, Satellite Conference in Harmonic Analysis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea August 6, 04 Motivation the Coifman-Meyer theorem with classical paraproduct(979) B(f, f )(x) :=
Cornell University ICM 04, Satellite Conference in Harmonic Analysis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea August 6, 04 Motivation the Coifman-Meyer theorem with classical paraproduct(979) B(f, f )(x) :=
A Lambda Model Characterizing Computational Behaviours of Terms
 A Lambda Model Characterizing Computational Behaviours of Terms joint paper with Silvia Ghilezan RPC 01, Sendai, October 26, 2001 1 Plan of the talk normalization properties inverse limit model Stone dualities
A Lambda Model Characterizing Computational Behaviours of Terms joint paper with Silvia Ghilezan RPC 01, Sendai, October 26, 2001 1 Plan of the talk normalization properties inverse limit model Stone dualities
Reflecting Brownian motion in two dimensions: Exact asymptotics for the stationary distribution
 Reflecting Brownian motion in two dimensions: Exact asymptotics for the stationary distribution Jim Dai Joint work with Masakiyo Miyazawa July 8, 211 211 INFORMS APS conference at Stockholm Jim Dai (Georgia
Reflecting Brownian motion in two dimensions: Exact asymptotics for the stationary distribution Jim Dai Joint work with Masakiyo Miyazawa July 8, 211 211 INFORMS APS conference at Stockholm Jim Dai (Georgia
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
The circle theorem and related theorems for Gauss-type quadrature rules
 OP.circle p. / The circle theorem and related theorems for Gauss-type quadrature rules Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University OP.circle p. 2/ Web Site http : //www.cs.purdue.edu/ archives/22/wxg/codes
OP.circle p. / The circle theorem and related theorems for Gauss-type quadrature rules Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University OP.circle p. 2/ Web Site http : //www.cs.purdue.edu/ archives/22/wxg/codes
12. Radon-Nikodym Theorem
 Tutorial 12: Radon-Nikodym Theorem 1 12. Radon-Nikodym Theorem In the following, (Ω, F) is an arbitrary measurable space. Definition 96 Let μ and ν be two (possibly complex) measures on (Ω, F). We say
Tutorial 12: Radon-Nikodym Theorem 1 12. Radon-Nikodym Theorem In the following, (Ω, F) is an arbitrary measurable space. Definition 96 Let μ and ν be two (possibly complex) measures on (Ω, F). We say
ω ω ω ω ω ω+2 ω ω+2 + ω ω ω ω+2 + ω ω+1 ω ω+2 2 ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ω+1 ω ω2 ω ω2 + ω ω ω2 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω ω+1 ω ω2 + ω ω+1 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω
 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequality for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x, y, z X.
 Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
5. Choice under Uncertainty
 5. Choice under Uncertainty Daisuke Oyama Microeconomics I May 23, 2018 Formulations von Neumann-Morgenstern (1944/1947) X: Set of prizes Π: Set of probability distributions on X : Preference relation
5. Choice under Uncertainty Daisuke Oyama Microeconomics I May 23, 2018 Formulations von Neumann-Morgenstern (1944/1947) X: Set of prizes Π: Set of probability distributions on X : Preference relation
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
Optimal Impartial Selection
 Optimal Impartial Selection Max Klimm Technische Universität Berlin Head of Junior Research Group Optimization under Uncertainty Einstein-Zentrum für Mathematik Introduction select member of a set of agents
Optimal Impartial Selection Max Klimm Technische Universität Berlin Head of Junior Research Group Optimization under Uncertainty Einstein-Zentrum für Mathematik Introduction select member of a set of agents
Probability and Random Processes (Part II)
 Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Affine Weyl Groups. Gabriele Nebe. Summerschool GRK 1632, September Lehrstuhl D für Mathematik
 Affine Weyl Groups Gabriele Nebe Lehrstuhl D für Mathematik Summerschool GRK 1632, September 2015 Crystallographic root systems. Definition A crystallographic root system Φ is a finite set of non zero
Affine Weyl Groups Gabriele Nebe Lehrstuhl D für Mathematik Summerschool GRK 1632, September 2015 Crystallographic root systems. Definition A crystallographic root system Φ is a finite set of non zero
Monte Carlo Methods. for Econometric Inference I. Institute on Computational Economics. July 19, John Geweke, University of Iowa
 Monte Carlo Methods for Econometric Inference I Institute on Computational Economics July 19, 2006 John Geweke, University of Iowa Monte Carlo Methods for Econometric Inference I 1 Institute on Computational
Monte Carlo Methods for Econometric Inference I Institute on Computational Economics July 19, 2006 John Geweke, University of Iowa Monte Carlo Methods for Econometric Inference I 1 Institute on Computational
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
MINIMAL CLOSED SETS AND MAXIMAL CLOSED SETS
 MINIMAL CLOSED SETS AND MAXIMAL CLOSED SETS FUMIE NAKAOKA AND NOBUYUKI ODA Received 20 December 2005; Revised 28 May 2006; Accepted 6 August 2006 Some properties of minimal closed sets and maximal closed
MINIMAL CLOSED SETS AND MAXIMAL CLOSED SETS FUMIE NAKAOKA AND NOBUYUKI ODA Received 20 December 2005; Revised 28 May 2006; Accepted 6 August 2006 Some properties of minimal closed sets and maximal closed
Depth versus Rigidity in the Design of International Trade Agreements. Leslie Johns
 Depth versus Rigidity in the Design of International Trade Agreements Leslie Johns Supplemental Appendix September 3, 202 Alternative Punishment Mechanisms The one-period utility functions of the home
Depth versus Rigidity in the Design of International Trade Agreements Leslie Johns Supplemental Appendix September 3, 202 Alternative Punishment Mechanisms The one-period utility functions of the home
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ
 ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
Bayesian modeling of inseparable space-time variation in disease risk
 Bayesian modeling of inseparable space-time variation in disease risk Leonhard Knorr-Held Laina Mercer Department of Statistics UW May, 013 Motivation Ohio Lung Cancer Example Lung Cancer Mortality Rates
Bayesian modeling of inseparable space-time variation in disease risk Leonhard Knorr-Held Laina Mercer Department of Statistics UW May, 013 Motivation Ohio Lung Cancer Example Lung Cancer Mortality Rates
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Homework for 1/27 Due 2/5
 Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
Reminders: linear functions
 Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
LAD Estimation for Time Series Models With Finite and Infinite Variance
 LAD Estimatio for Time Series Moels With Fiite a Ifiite Variace Richar A. Davis Colorao State Uiversity William Dusmuir Uiversity of New South Wales 1 LAD Estimatio for ARMA Moels fiite variace ifiite
LAD Estimatio for Time Series Moels With Fiite a Ifiite Variace Richar A. Davis Colorao State Uiversity William Dusmuir Uiversity of New South Wales 1 LAD Estimatio for ARMA Moels fiite variace ifiite
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines
 New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE
 Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE BLUE: Robustness of LSE against normality We now study properties of l τ β and σ 2 under assumption A2, i.e., without the normality assumption on ε. From Theorem
Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE BLUE: Robustness of LSE against normality We now study properties of l τ β and σ 2 under assumption A2, i.e., without the normality assumption on ε. From Theorem
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ. Ψηφιακή Οικονομία. Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
Sequent Calculi for the Modal µ-calculus over S5. Luca Alberucci, University of Berne. Logic Colloquium Berne, July 4th 2008
 Sequent Calculi for the Modal µ-calculus over S5 Luca Alberucci, University of Berne Logic Colloquium Berne, July 4th 2008 Introduction Koz: Axiomatisation for the modal µ-calculus over K Axioms: All classical
Sequent Calculi for the Modal µ-calculus over S5 Luca Alberucci, University of Berne Logic Colloquium Berne, July 4th 2008 Introduction Koz: Axiomatisation for the modal µ-calculus over K Axioms: All classical
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3)
![MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3) MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3)](/thumbs/81/84712331.jpg) 1. MATH43 String Theory Solutions 4 x = 0 τ = fs). 1) = = f s) ) x = x [f s)] + f s) 3) equation of motion is x = 0 if an only if f s) = 0 i.e. fs) = As + B with A, B constants. i.e. allowe reparametrisations
1. MATH43 String Theory Solutions 4 x = 0 τ = fs). 1) = = f s) ) x = x [f s)] + f s) 3) equation of motion is x = 0 if an only if f s) = 0 i.e. fs) = As + B with A, B constants. i.e. allowe reparametrisations
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
Credit Risk. Finance and Insurance - Stochastic Analysis and Practical Methods Spring School Jena, March 2009
 Credit Risk. Finance and Insurance - Stochastic Analysis and Practical Methods Spring School Jena, March 2009 1 IV. Hedging of credit derivatives 1. Two default free assets, one defaultable asset 1.1 Two
Credit Risk. Finance and Insurance - Stochastic Analysis and Practical Methods Spring School Jena, March 2009 1 IV. Hedging of credit derivatives 1. Two default free assets, one defaultable asset 1.1 Two
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
( y) Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ "ΠΟΛΥΚΡΙΤΗΡΙΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΛΗΨΗΣ ΑΠΟΦΑΣΕΩΝ. Η ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΕΠΙΛΟΓΗΣ ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΥ ΥΓΕΙΑΣ "
 ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΚΑΛΑΜΑΤΑΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΟΝΑΔΩΝ ΥΓΕΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΡΟΝΟΙΑΣ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ "ΠΟΛΥΚΡΙΤΗΡΙΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΛΗΨΗΣ ΑΠΟΦΑΣΕΩΝ. Η ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΕΠΙΛΟΓΗΣ ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΥ
ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΕΚΠΑΙΔΕΥΤΙΚΟ ΙΔΡΥΜΑ ΚΑΛΑΜΑΤΑΣ ΣΧΟΛΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗΣ ΟΙΚΟΝΟΜΙΑΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΜΟΝΑΔΩΝ ΥΓΕΙΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΠΡΟΝΟΙΑΣ ΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ "ΠΟΛΥΚΡΙΤΗΡΙΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ ΛΗΨΗΣ ΑΠΟΦΑΣΕΩΝ. Η ΠΕΡΙΠΤΩΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΕΠΙΛΟΓΗΣ ΑΣΦΑΛΙΣΤΗΡΙΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΑΙΟΥ
Graded Refractive-Index
 Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
Phase-Field Force Convergence
 Phase-Field Force Convergence Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Quantitative Biology Graduate Program UC San Diego Collaborators: Shibin Dai and Jianfeng Lu Funding: NSF School of Mathematical Sciences
Phase-Field Force Convergence Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Quantitative Biology Graduate Program UC San Diego Collaborators: Shibin Dai and Jianfeng Lu Funding: NSF School of Mathematical Sciences
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
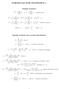 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
Models for Probabilistic Programs with an Adversary
 Models for Probabilistic Programs with an Adversary Robert Rand, Steve Zdancewic University of Pennsylvania Probabilistic Programming Semantics 2016 Interactive Proofs 2/47 Interactive Proofs 2/47 Interactive
Models for Probabilistic Programs with an Adversary Robert Rand, Steve Zdancewic University of Pennsylvania Probabilistic Programming Semantics 2016 Interactive Proofs 2/47 Interactive Proofs 2/47 Interactive
