Chapter 4 : Linear Wire Antenna
|
|
|
- Ιολανθη Γιάγκος
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Chapt 4 : Lina Wi Antnna nfinitsima Dipo Sma Dipo Finit Lngth Dipo Haf-Wavngth Dipo Lina mnts na o on nfinit Pfct Conductos
2 nfinitsima Dipo Lngth << Usd to psnt capacito-pat top-hatoadd antnnas Capacitiv oading to maintain th unifom cunt
3 Radiatd Fid Th cunt on th infinitsima dipo is assumd to b constant, i.., ' ˆ Rca that jkr µ A x, y, J x', y', ' d' 4 C R Sinc th dipo is infinitsima, th foowing appoximations hod: d ' d' x' y' ' R ' constant
4 4 Radiatd Fid jk jk d y x µ µ 4 ˆ ' 4 ˆ,, / / A ; ; A A A A A, ˆ ˆ ˆ A A A A A A A Thus Sinc A has ony componnt, and µ A A ˆ H Th magntic fid bcoms:
5 5 Radiatd Fid jk jk k j H H H 4 4 k jk k j jk jk jk Thfo, Likwis, th ctic fid can b found to b
6 6 Pow Dnsity and Radiation Rsistanc Poynting vcto ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ * * * * H H H H W 6 8 k k j W k j W ˆ ˆ ˆ k j d d W d d W W d P S s W Outgoing Pow Componnts of Poynting Vcto
7 7 Pow Dnsity and Radiation Rsistanc ~ ~ k W W m ω ~ ~ m ad W W j P P ω diction A in adia activ pow; tim - avag imaginay ~ ~ tim - avag ctic ngy ~ tim - avag magntic ngy ~ tim - avag adiatd pow pow m m ad W W W W P P ω 8 R Radiation Rsistanc Compx Pow ad R P Ractiv Pow
8 Fa Fid k >> Fo k >>, th fids can b appoximatd as H k j 4 k j 4 H H jk k jk >> TM Wav 8 Z w Ratio of and H: wav impdanc Z w H intinsic impdanc Ω fo f -spac
9 Tim-avag pow dnsity: Wav R H Radiation intnsity: Dictivity k U Wav * k ˆ ˆ 4 Maximum adiation intnsity: Maximum dictivity: 4,, k U max 4 D U max 4 P ad Maximum ffctiv aa: A m D 4 8 9
10 Sma Dipo Lngth /5 < < /
11 Radiatd Fid Th cunt on th sma dipo is assumd to b a tiangua function, i.., ' / ', ˆ / ' ', ˆ ' / / ' ' ' ' 4 ˆ,, jkr jkr d R d R y x µ A wh is a constant. Vcto potntia bcoms: Appoximating R ~ yids th maximum phas o k/ / fo /.
12 Radiatd Fid 8 8 >> k H H k j H k j jk jk jk A y x µ 4 ˆ ˆ,, A Ug R~: Th fa-fid can b givn by which is on-haf of that fo th infinitsima dipo. P R ad Radiation sistanc:
13 Fid Spaation Fo a vy thin dipo, x y, thus ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' y x y x y y x x R ; wh y x
14 4
15 Fid Spaation 5 Rca aso th Tayo xpansion: f f '' x f f ' x x! which yids th sam sut: Rca that ' Lt x ' / x x x 8, thn L x R ' ' ' ' R ' L L 6
16 Fa Fid 6 By taining ony th fist two tms, i.., R ' Th most significant ngctd tm has th maximum vau ' ' whn max A maximum tota phas o of /8 is accptab, thus ' k 8 Fa-fid appoximation whn D / ' / R fo ampitud tm R ' ˆ ' fo phas tm
17 Radiating Na Fid By taining ony th fist th tms, i.., ' R ' Th most significant ngctd tm is th fouth tm. n od to find its maximum vau, on can diffntiat th fouth tm with spct to, and th sut is st to, i.., yids ' ' [ ] [ ] tan ± 7
18 8 Radiating Na Fid 8 8 ' tan / ' k.6 which ducs to o f th maximum tota phas o is aowd to b /8, Na-fid gion.6 D D
19 Lngth > / Finit Lngth Dipo Cunt on th finit ngth dipo assuming th wi is vy thin ˆ ' ˆ k k ', ', ' / / ' wh is a constant. This distibution assums that th antnna is cnt-fd and th cunt vanishs at th nd points. 9
20 d dh d Radiatd Fid Th ctic and magntic fid componnts in th fa fid fo th infinitsima dipo d a givn by k ' j 4R k ' j 4R d dh dh jkr jkr d' d' Ug th fa-fid appoximation yids d k j ' 4 jk jk' d'
21 Radiatd Fid Th tota ctic fid can b obtaind by summing up contibutions fom a infinitsima dipos, i.., / / jk k / jk' j ' ' d / d mnt facto spac facto tota fid mnt facto spac facto Thus, th ctic fid of th finit ngth dipo can b givn by jk k jk' j k ' / / 4 k ' jk' d' d'
22 Radiatd Fid k k j jk ] [ γ β β γ β α β α γ β α α x x dx x x x Ug Likwis, th magntic fid can b givn by yids k k j H jk
23 Cunt Distibutions and Radiation Pattn
24 4 Radiation Pattn fo.5
25 5 Pow Dnsity and Radiation ntnsity * * 8 ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ R R k k H av H W Tim-avag pow dnsity: Radiation intnsity: 8 k k W U av
26 6 P ad Ω 4 Radiatd Pow Radiatd pow can b obtaind by UdΩ which can b givn by Pad C n k C 4 wh k[ C i k n k / C U dd k k i k[ S k C i k S i k] C u's constant i d k]
27 Radiatd Pow C i S x i x x x y y dy y dy y x y 5 y dy Co intga Sin intga C i x is atd to C in x by 4 C in x wh C C n x C in x x i x y y dy C i x S i x 4 C in x
28 R Radiation Rsistanc and Radiation sistanc bcoms P ad nput Rsistanc C n k C k k[ S k[ C n k / Ci k C Sinc in Rin R assuming oss-ss nput sistanc can b givn by Rin R k in Fo a dipo of ngth, nput Rsistanc R in in R k i i i k S k] i k] 8
29 9 Dictivity Q F P U D ad max max 4 ] / n [ ] [ n k C k C k C k k S k S k k C k C Q i i i i i Dictivity is givn by and wh k k F
30 Radiation sistanc, input sistanc and dictivity
31 Haf-wavngth Dipo j jk j H jk 8 8 W av Lt /, thn 8 8 W U av Pow dnsity Radiation ntnsity
32 Radiatd Pow P wh Haf-wavngth Dipo ad C Dictivity 4 4 in Radiation Rsistanc nput mpdanc d y y dy C 8 C n C D R U Z in 7 j4.5 i 4.45 max 4 P ad Pad C in 4 in
33 Wi antnnas na o on infinit pfct conducto
34 mag Thoy tan nˆ on PC H tan nˆ H on PMC 4 NOT: Th fids obtaind a vaid ony in th top haf-pan.
35 5 Vtica ctic Dipo 4 k j jk d 4 4 k j k jr jk jk v Dict Componnt Rfctd Componnt
36 Vtica ctic Dipo n fa fid: Paa ay appoximation [ h h ] h [ h h ] h Phas tm Ampitud tm 6
37 Vtica ctic Dipo Tota ctic Fid k j 4 jk [ ] < h numb of obs 7
38 Pow Dnsity Radiation ntnsity Vtica ctic Dipo 4 * W R ˆ av H Maximum Radiation ntnsity Radiatd Pow U P ad / ˆ U max U dd / U d 8
39 9 Vtica ctic Dipo 5 max 4 P U D ad P R ad Dictivity Radiation Rsistanc
40 /4 Monopo Z in Zindipo 7 j j.5 4
41 4 Fids du to y-dictd dipo Vcto Potntia A A A A y µ 4 ˆ jk jk µ Ay 4 jk µ Ay 4 j jωa A ωµε Rca that Fa-fid ctic Fid jωa jωa µ jω 4 µ jω 4 jk jk
42 Fids du to y-dictd dipo ntoduc a nw sphica coodinat systm,ψ,ζ such that ˆ ˆ ψ ζ ψˆ ˆ ψ ζ ˆ ζ ˆ ψ xˆ ψ xˆ ψ ζ yˆ ψ xˆ ψ ζ yˆ ψ This can b obtaind by tting x,y,->,x,y and ψ,ζ->, thn Fa-fid ctic Fid Fa-fid Magntic Fid H ψ ζ µ jω 4 ωµ j 4 jk jk ψ ψ 4
43 4 Hoionta ctic Dipo ψ ψ 4 k j jk d ψ ψ ψ 4 4 k j k jr jk jk h Dict Componnt Rfctd Componnt
44 Hoionta ctic Dipo n fa fid: [ h h ] h [ h h ] h Ampitud tm ψ yˆ ˆ Phas tm 44
45 Hoionta ctic Dipo Tota ctic Fid ψ jk k j [ j ] 4 numb of obs h 45
46 46 Hoionta ctic Dipo 4 ˆ av W U / / d U d d U P ad Pow Dnsity Radiation ntnsity Radiatd Pow P R ad Radiation Rsistanc
47 47 Hoionta ctic Dipo 5 > / 4 / 4 R R D h h R Dictivity Fo sma Maximum Radiation ntnsity > and, /, / max max U
48 Hoionta ctic Dipo 6 wh R Fo sma 8 D
Faculdade de Engenharia. Transmission Lines ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINEERING MAP TELE 2008/2009
 Facudad d Ennharia Transmission ins EECTROMAGNETC ENGNEERNG MAP TEE 8/9 Transmission ins Facudad d Ennharia transmission ins wavuids supportin TEM wavs most common typs para-pat wavuids coaxia wavuids
Facudad d Ennharia Transmission ins EECTROMAGNETC ENGNEERNG MAP TEE 8/9 Transmission ins Facudad d Ennharia transmission ins wavuids supportin TEM wavs most common typs para-pat wavuids coaxia wavuids
Lecture 31. Wire Antennas. Generation of radiation by real wire antennas
 Lctu 31 Wi Antnnas n this lctu yu will lan: Gnatin f aiatin by al wi antnnas Sht ipl antnnas Half-wav ipl antnnas Th-half-wav ipl antnnas Small wi lp antnnas magntic ipl antnnas ECE 303 Fall 006 Fahan
Lctu 31 Wi Antnnas n this lctu yu will lan: Gnatin f aiatin by al wi antnnas Sht ipl antnnas Half-wav ipl antnnas Th-half-wav ipl antnnas Small wi lp antnnas magntic ipl antnnas ECE 303 Fall 006 Fahan
Transmission Line Theory
 Tansmiss Thy Micwav Engg EE 7 D. Ray Kwk Tansmiss - D. Ray Kwk RF Spctum km mm µm Å Advancd ight Suc Bky ab Tansmiss - D. Ray Kwk RF / Micwav icuit wis GND pt ntwk put suc pt ntwk utput ad Tansmiss - D.
Tansmiss Thy Micwav Engg EE 7 D. Ray Kwk Tansmiss - D. Ray Kwk RF Spctum km mm µm Å Advancd ight Suc Bky ab Tansmiss - D. Ray Kwk RF / Micwav icuit wis GND pt ntwk put suc pt ntwk utput ad Tansmiss - D.
Accelerator Physics Synchrotron Radiation. A. Bogacz, G. A. Krafft, and T. Zolkin Jefferson Lab Colorado State University Lecture 8
 Acclato Physics Synchoton Radiation A. Bogacz, G. A. Kafft, and T. Zolkin Jffson Lab Coloado Stat Univsity Lctu 8 USPAS Acclato Physics Jun 13 Synchoton Radiation Acclatd paticls mit lctomagntic adiation.
Acclato Physics Synchoton Radiation A. Bogacz, G. A. Kafft, and T. Zolkin Jffson Lab Coloado Stat Univsity Lctu 8 USPAS Acclato Physics Jun 13 Synchoton Radiation Acclatd paticls mit lctomagntic adiation.
19. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND NUCLEI HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS
 . ATOMS, MOLECULES AND NUCLEI HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS. Givn :.53 Å 3?? n n ε πm n n Radius of n t Bo obit, n n ε πm n n 3 n 3 n 3 (3) () (.53).77Å n n ( ) () (.53) 53 Å. Givn : 3 7.7 x m? n n ε πm Radius of
. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND NUCLEI HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS. Givn :.53 Å 3?? n n ε πm n n Radius of n t Bo obit, n n ε πm n n 3 n 3 n 3 (3) () (.53).77Å n n ( ) () (.53) 53 Å. Givn : 3 7.7 x m? n n ε πm Radius of
2/2/2018. PHY 712 Electrodynamics 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 105
 //8 H 7 Ectodynics 9-9: AM MW Oin n fo Lctu 8: Stt ding Chpt Mutipo ont pnsion of ctosttic potnti A. Sphic coodints B. Ctsin coodints //8 H 7 Sping 8 -- Lctu 8 //8 H 7 Sping 8 -- Lctu 8 oisson nd Lpc ution
//8 H 7 Ectodynics 9-9: AM MW Oin n fo Lctu 8: Stt ding Chpt Mutipo ont pnsion of ctosttic potnti A. Sphic coodints B. Ctsin coodints //8 H 7 Sping 8 -- Lctu 8 //8 H 7 Sping 8 -- Lctu 8 oisson nd Lpc ution
ECE 222b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 3a
 C b lid lcomagnics Nos S 3a Insuco: Pof. Viali Lomakin Damn of lcical and Comu ngining Univsi of Califonia San Digo Unifom Plan Wavs Consid Mawll s quaions: In a losslss mdium ε and µ a al and σ : Sinc
C b lid lcomagnics Nos S 3a Insuco: Pof. Viali Lomakin Damn of lcical and Comu ngining Univsi of Califonia San Digo Unifom Plan Wavs Consid Mawll s quaions: In a losslss mdium ε and µ a al and σ : Sinc
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
Lossy Medium EE142. Dr. Ray Kwok
 Lssy Mdium EE4 D. Ray Kwk fn: Fundamntals f Engining Eltmagntis, David K. Chng (Addisn-Wsly) Eltmagntis f Engins, Fawwaz T. Ulaby (Pnti Hall) Lssy Mdium - D. Ray Kwk Ohm s Law A E V V El IR ( JA) E Jρ
Lssy Mdium EE4 D. Ray Kwk fn: Fundamntals f Engining Eltmagntis, David K. Chng (Addisn-Wsly) Eltmagntis f Engins, Fawwaz T. Ulaby (Pnti Hall) Lssy Mdium - D. Ray Kwk Ohm s Law A E V V El IR ( JA) E Jρ
Written Examination. Antennas and Propagation (AA ) April 26, 2017.
 Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ELE 3310 Tutorial 11. Reflection of plane waves Wave impedance of the total field
 L 0 Tuto Rfcton of pn wvs Wv mpdnc of th tot fd Rfcton of M wvs Rfcton tks pc whn n M wv hts on bound. Pt of th wv gts fctd, nd pt of t gts tnsmttd. Popgton dctons nd mptuds of th fctd nd tnsmttd wvs dpnd
L 0 Tuto Rfcton of pn wvs Wv mpdnc of th tot fd Rfcton of M wvs Rfcton tks pc whn n M wv hts on bound. Pt of th wv gts fctd, nd pt of t gts tnsmttd. Popgton dctons nd mptuds of th fctd nd tnsmttd wvs dpnd
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, irrotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE + V Φ + i x. Ψ y = Φ. and. Ψ x
 STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines
![Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines](/thumbs/51/28406191.jpg) Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Homework #6. A circular cylinder of radius R rotates about the long axis with angular velocity
 Homwork #6 1. (Kittl 5.1) Cntrifug. A circular cylindr of radius R rotats about th long axis with angular vlocity ω. Th cylindr contains an idal gas of atoms of mass m at tmpratur. Find an xprssion for
Homwork #6 1. (Kittl 5.1) Cntrifug. A circular cylindr of radius R rotats about th long axis with angular vlocity ω. Th cylindr contains an idal gas of atoms of mass m at tmpratur. Find an xprssion for
Spherical Coordinates
 Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
Strain gauge and rosettes
 Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
LAPLACE TRANSFORM TABLE
 LAPLACE TRANSFORM TABLE Th Laplac afom of am mpl fuco a gv h Tabl. Fuco U mpul U Sp U Ramp Expoal Rpad Roo S Co Polyomal Dampd Dampd co f δ u -a -a co,,... -a -a co F / / /a /a / /!/ /a a/a Thom : Shf
LAPLACE TRANSFORM TABLE Th Laplac afom of am mpl fuco a gv h Tabl. Fuco U mpul U Sp U Ramp Expoal Rpad Roo S Co Polyomal Dampd Dampd co f δ u -a -a co,,... -a -a co F / / /a /a / /!/ /a a/a Thom : Shf
Pairs of Random Variables
 Pairs of Random Variabls Rading: Chaptr 4. 4. Homwork: (do at last 5 out of th following problms 4..4, 4..6, 4.., 4.3.4, 4.3.5, 4.4., 4.4.4, 4.5.3, 4.6.3, 4.6.7, 4.6., 4.7.9, 4.7., 4.8.3, 4.8.7, 4.9.,
Pairs of Random Variabls Rading: Chaptr 4. 4. Homwork: (do at last 5 out of th following problms 4..4, 4..6, 4.., 4.3.4, 4.3.5, 4.4., 4.4.4, 4.5.3, 4.6.3, 4.6.7, 4.6., 4.7.9, 4.7., 4.8.3, 4.8.7, 4.9.,
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
EE101: Resonance in RLC circuits
 EE11: Resonance in RLC circuits M. B. Patil mbatil@ee.iitb.ac.in www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~sequel Deartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay I V R V L V C I = I m = R + jωl + 1/jωC
EE11: Resonance in RLC circuits M. B. Patil mbatil@ee.iitb.ac.in www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~sequel Deartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay I V R V L V C I = I m = R + jωl + 1/jωC
ENGR 691/692 Section 66 (Fall 06): Machine Learning Assigned: August 30 Homework 1: Bayesian Decision Theory (solutions) Due: September 13
 ENGR 69/69 Section 66 (Fall 06): Machine Learning Assigned: August 30 Homework : Bayesian Decision Theory (solutions) Due: Septemer 3 Prolem : ( pts) Let the conditional densities for a two-category one-dimensional
ENGR 69/69 Section 66 (Fall 06): Machine Learning Assigned: August 30 Homework : Bayesian Decision Theory (solutions) Due: Septemer 3 Prolem : ( pts) Let the conditional densities for a two-category one-dimensional
Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small spheres separated by a distance s. The charge on one sphere changes with time and is described by
 5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
Analytical Expression for Hessian
 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Trigonometry 1.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
 Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Potential Dividers. 46 minutes. 46 marks. Page 1 of 11
 Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Bit Error Rate in Digital Photoreceivers
 Bit Eo Rat in Digital hotocivs In th pvious slids, w saw that th photociv aks a dcision as to whth th covd wavfo is abov ( o blow ( th thshold lvl. Whn nois is psnt, a wong dcision can b ad, i.. w hav
Bit Eo Rat in Digital hotocivs In th pvious slids, w saw that th photociv aks a dcision as to whth th covd wavfo is abov ( o blow ( th thshold lvl. Whn nois is psnt, a wong dcision can b ad, i.. w hav
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
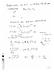 Prblma dl smipian Cas i cs ω µ Cas sin cs i cs Cas fas [ ] [ ] ] [ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ttal S S J L J J L A d I I A d I d I V d d V V d d V n J n J ˆ 0 ˆ ˆ ˆ 0 ˆ 0 ˆ ˆ ˆ 0 S S S S i i
Prblma dl smipian Cas i cs ω µ Cas sin cs i cs Cas fas [ ] [ ] ] [ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ttal S S J L J J L A d I I A d I d I V d d V V d d V n J n J ˆ 0 ˆ ˆ ˆ 0 ˆ 0 ˆ ˆ ˆ 0 S S S S i i
10.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response)
 Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix
 The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
The Neutrix Product of the Distributions r. x λ
 ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
ULLETIN u. Maaysia Math. Soc. Secod Seies 22 999 - of the MALAYSIAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY The Neuti Poduct of the Distibutios ad RIAN FISHER AND 2 FATMA AL-SIREHY Depatet of Matheatics ad Copute Sciece
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ
 ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ & ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΜΕΛΕΤΗ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΗ ΙΑΤΑΞΗΣ ΜΕΤΡΗΣΗΣ ΘΕΡΜΟΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΣΕ ΜΑΓΝΗΤΙΚΟ ΠΕ ΙΟ ΓΙΑ ΧΑΡΑΚΤΗΡΙΣΜΟ
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ & ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΜΕΛΕΤΗ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΗ ΙΑΤΑΞΗΣ ΜΕΤΡΗΣΗΣ ΘΕΡΜΟΧΩΡΗΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΣΕ ΜΑΓΝΗΤΙΚΟ ΠΕ ΙΟ ΓΙΑ ΧΑΡΑΚΤΗΡΙΣΜΟ
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
Differential equations
 Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
1. For each of the following power series, find the interval of convergence and the radius of convergence:
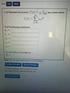 Math 6 Practice Problems Solutios Power Series ad Taylor Series 1. For each of the followig power series, fid the iterval of covergece ad the radius of covergece: (a ( 1 x Notice that = ( 1 +1 ( x +1.
Math 6 Practice Problems Solutios Power Series ad Taylor Series 1. For each of the followig power series, fid the iterval of covergece ad the radius of covergece: (a ( 1 x Notice that = ( 1 +1 ( x +1.
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
ΕΝΙΣΧΥΣΗ ΠΛΑΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΟΚΩΝ ΣΕ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΜΕ ΜΑΝΔΥΕΣ Η ΕΛΑΣΜΑΤΑ ΣΥΝΘΕΤΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ.
 ΕΝΙΣΧΥΣΗ ΠΛΑΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΟΚΩΝ ΣΕ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΜΕ ΜΑΝΔΥΕΣ Η ΕΛΑΣΜΑΤΑ ΣΥΝΘΕΤΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ. Σύμφωνα με τον Κανονιμό Επεμβάεων, ο νέος οπλιμός υπολοίζεται έτι ώτε ε υνεραία με τον υφιτάμενο παλαιό οπλιμό να αναλαμβάνονται
ΕΝΙΣΧΥΣΗ ΠΛΑΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΟΚΩΝ ΣΕ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΜΕ ΜΑΝΔΥΕΣ Η ΕΛΑΣΜΑΤΑ ΣΥΝΘΕΤΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ. Σύμφωνα με τον Κανονιμό Επεμβάεων, ο νέος οπλιμός υπολοίζεται έτι ώτε ε υνεραία με τον υφιτάμενο παλαιό οπλιμό να αναλαμβάνονται
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
ECE 222b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 3b
 C b Appl lcomancs Nos S 3b Insuco: Pof. Val Loman Dpamn of lccal an Compu nnn Unvs of Calfona San Do Rflcon an Tansmsson. Nomal ncnc T R T R Fs fn h manc fls: 3 Rflcon an Tansmsson T R T R T R T R R T
C b Appl lcomancs Nos S 3b Insuco: Pof. Val Loman Dpamn of lccal an Compu nnn Unvs of Calfona San Do Rflcon an Tansmsson. Nomal ncnc T R T R Fs fn h manc fls: 3 Rflcon an Tansmsson T R T R T R T R R T
Solution Series 9. i=1 x i and i=1 x i.
 Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
1. If log x 2 y 2 = a, then dy / dx = x 2 + y 2 1] xy 2] y / x. 3] x / y 4] none of these
![1. If log x 2 y 2 = a, then dy / dx = x 2 + y 2 1] xy 2] y / x. 3] x / y 4] none of these 1. If log x 2 y 2 = a, then dy / dx = x 2 + y 2 1] xy 2] y / x. 3] x / y 4] none of these](/thumbs/52/30390275.jpg) 1. If log x 2 y 2 = a, then dy / dx = x 2 + y 2 1] xy 2] y / x 3] x / y 4] none of these 1. If log x 2 y 2 = a, then x 2 + y 2 Solution : Take y /x = k y = k x dy/dx = k dy/dx = y / x Answer : 2] y / x
1. If log x 2 y 2 = a, then dy / dx = x 2 + y 2 1] xy 2] y / x 3] x / y 4] none of these 1. If log x 2 y 2 = a, then x 2 + y 2 Solution : Take y /x = k y = k x dy/dx = k dy/dx = y / x Answer : 2] y / x
ΚΕΦΑΛΑΙΟ 2. Περιγραφή της Κίνησης. 2.1 Κίνηση στο Επίπεδο
 ΚΕΦΑΛΑΙΟ 2 Περιγραφή της Κίνησης Στο κεφάλαιο αυτό θα δείξουμε πώς να προγραμματίσουμε απλές εξισώσεις τροχιάς ενός σωματιδίου και πώς να κάνουμε βασική ανάλυση των αριθμητικών αποτελεσμάτων. Χρησιμοποιούμε
ΚΕΦΑΛΑΙΟ 2 Περιγραφή της Κίνησης Στο κεφάλαιο αυτό θα δείξουμε πώς να προγραμματίσουμε απλές εξισώσεις τροχιάς ενός σωματιδίου και πώς να κάνουμε βασική ανάλυση των αριθμητικών αποτελεσμάτων. Χρησιμοποιούμε
α A G C T 國立交通大學生物資訊及系統生物研究所林勇欣老師
 A G C T Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A T C G A G 0 0 0-3 C T A() A( t ) ( 3 ) ( ) A() A() ( 3 ) ( ) A( A( A( A( t ) A( 3 A( t ) ( ) A( A( Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A( A( t ) A( d
A G C T Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A T C G A G 0 0 0-3 C T A() A( t ) ( 3 ) ( ) A() A() ( 3 ) ( ) A( A( A( A( t ) A( 3 A( t ) ( ) A( A( Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A( A( t ) A( d
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems Arithmetic Circuits
 EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems Arithmetic Circuits Spring 25 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu Arithmetic Circuits What we will learn Adders Basic High-speed 2 Adder -bit adder SSSSSS = AA BB CCCC CCCC =
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems Arithmetic Circuits Spring 25 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu Arithmetic Circuits What we will learn Adders Basic High-speed 2 Adder -bit adder SSSSSS = AA BB CCCC CCCC =
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C
 DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
5. Γραμμές μεταφοράς, κυματοδηγοί και κεραίες (Transmission lines, waveguides and antennas)
 5. Γραμμές μεταφοράς, κυματοδηγοί και κεραίες (Tanmiin lin, wavguid and antnna) Γραμμές μεταφοράς(tanmiin lin) Στο προηγούμενο μέρος μελετήσαμε τη διάδοση των κυμάτων σε απεριόριστο χώρο. Αυτή η διάδοση
5. Γραμμές μεταφοράς, κυματοδηγοί και κεραίες (Tanmiin lin, wavguid and antnna) Γραμμές μεταφοράς(tanmiin lin) Στο προηγούμενο μέρος μελετήσαμε τη διάδοση των κυμάτων σε απεριόριστο χώρο. Αυτή η διάδοση
21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) 21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
 y(t) S x(t) S dy dx E, E E T1 T2 T1 T2 1 T 1 T 2 2 T 2 1 T 2 2 3 T 3 1 T 3 2... V o R R R T V CC P F A P g h V ext V sin 2 S f S t V 1 V 2 V out sin 2 f S t x 1 F k q K x q K k F d F x d V
y(t) S x(t) S dy dx E, E E T1 T2 T1 T2 1 T 1 T 2 2 T 2 1 T 2 2 3 T 3 1 T 3 2... V o R R R T V CC P F A P g h V ext V sin 2 S f S t V 1 V 2 V out sin 2 f S t x 1 F k q K x q K k F d F x d V
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Reflection & Transmission
 Rflc & Tasmss 4 D. Ray Kw Rflc & Tasmss - D. Ray Kw Gmc Opcs (M wavs flc fac - asmss cdc.. Sll s Law: s s 3. Ccal agl: s c / 4. Tal flc wh > c ly f > Rflc & Tasmss - D. Ray Kw Pla Wav λ wavfs λ λ. < ;
Rflc & Tasmss 4 D. Ray Kw Rflc & Tasmss - D. Ray Kw Gmc Opcs (M wavs flc fac - asmss cdc.. Sll s Law: s s 3. Ccal agl: s c / 4. Tal flc wh > c ly f > Rflc & Tasmss - D. Ray Kw Pla Wav λ wavfs λ λ. < ;
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
Lifting Entry (continued)
 ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
physicsandmathstutor.com
 physicsadmathstuto.com physicsadmathstuto.com Jauay 009 blak 3. The ectagula hypebola, H, has paametic equatios x = 5t, y = 5 t, t 0. (a) Wite the catesia equatio of H i the fom xy = c. Poits A ad B o
physicsadmathstuto.com physicsadmathstuto.com Jauay 009 blak 3. The ectagula hypebola, H, has paametic equatios x = 5t, y = 5 t, t 0. (a) Wite the catesia equatio of H i the fom xy = c. Poits A ad B o
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
SOLUTIONS & ANSWERS FOR KERALA ENGINEERING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION-2018 PAPER II VERSION B1
 SOLUTIONS & ANSWERS FOR KERALA ENGINEERING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION-8 PAPER II VERSION B [MATHEMATICS]. Ans: ( i) It is (cs5 isin5 ) ( i). Ans: i z. Ans: i i i The epressin ( i) ( ). Ans: cs i sin cs i sin
SOLUTIONS & ANSWERS FOR KERALA ENGINEERING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION-8 PAPER II VERSION B [MATHEMATICS]. Ans: ( i) It is (cs5 isin5 ) ( i). Ans: i z. Ans: i i i The epressin ( i) ( ). Ans: cs i sin cs i sin
Κλασσική Θεωρία Ελέγχου
 ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΑΝΟΙΧΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΙΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ενότητα 8: Συστήματα πρώτης και δεύτερης τάξης Νίκος Καραμπετάκης Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΑΝΟΙΧΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΙΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ενότητα 8: Συστήματα πρώτης και δεύτερης τάξης Νίκος Καραμπετάκης Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό υπόκειται σε άδειες χρήσης
Pg The perimeter is P = 3x The area of a triangle is. where b is the base, h is the height. In our case b = x, then the area is
 Pg. 9. The perimeter is P = The area of a triangle is A = bh where b is the base, h is the height 0 h= btan 60 = b = b In our case b =, then the area is A = = 0. By Pythagorean theorem a + a = d a a =
Pg. 9. The perimeter is P = The area of a triangle is A = bh where b is the base, h is the height 0 h= btan 60 = b = b In our case b =, then the area is A = = 0. By Pythagorean theorem a + a = d a a =
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
Graded Refractive-Index
 Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model
 Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Electromagnetic Engineering MAPTele
 lcomagc gg MAPTl 8-9 Faculdad d ghaa Pogam lcomagc wavs Popagao Icdc Wavguds Tasmsso ls Radao Iês Cavalho Asssa Pofsso Faculdad d ghaa, Uvsdad do Poo www.f.up.p/~ms/ ms@f.up.p Popagao Faculdad d ghaa Sudg
lcomagc gg MAPTl 8-9 Faculdad d ghaa Pogam lcomagc wavs Popagao Icdc Wavguds Tasmsso ls Radao Iês Cavalho Asssa Pofsso Faculdad d ghaa, Uvsdad do Poo www.f.up.p/~ms/ ms@f.up.p Popagao Faculdad d ghaa Sudg
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION. Solution Manual
 ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
Homework for 1/27 Due 2/5
 Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΩΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΤΗΛΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ
 3/5/016 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΩΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΤΗΛΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΑΣΥΡΜΑΤΕΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ Παραδείγματα Κεραιών Αθανάσιος Κανάτας Καθηγητής Παν/μίου Πειραιώς Δίπολο Hetz L d
3/5/016 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΩΣ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΤΗΛΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΩΝ ΑΣΥΡΜΑΤΕΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ Παραδείγματα Κεραιών Αθανάσιος Κανάτας Καθηγητής Παν/μίου Πειραιώς Δίπολο Hetz L d
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
ECE 468: Digital Image Processing. Lecture 8
 ECE 468: Digital Image Processing Lecture 8 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Image Reconstruction from Projections X-ray computed tomography: X-raying an object from different directions
ECE 468: Digital Image Processing Lecture 8 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Image Reconstruction from Projections X-ray computed tomography: X-raying an object from different directions
CHAPTER 101 FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD
 CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
Τίτλος Μαθήματος: Εισαγωγή στους Ηλεκτρονικούς Υπολογιστές. Ενότητα: Μαθηματικές εκφράσεις στον κειμενογράφο
 Τίτλος Μαθήματος: Εισαγωγή στους Ηλεκτρονικούς Υπολογιστές Ενότητα: Μαθηματικές εκφράσεις στον κειμενογράφο Διδάσκων: Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Αλέξιος Δούβαλης Τμήμα: Φυσικής ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ
Τίτλος Μαθήματος: Εισαγωγή στους Ηλεκτρονικούς Υπολογιστές Ενότητα: Μαθηματικές εκφράσεις στον κειμενογράφο Διδάσκων: Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Αλέξιος Δούβαλης Τμήμα: Φυσικής ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΤΜΗΜΑ
ME 365: SYSTEMS, MEASUREMENTS, AND CONTROL (SMAC) I
 ME 365: SYSTEMS, MEASUREMENTS, AND CONTROL SMAC) I Dynamicresponseof 2 nd ordersystem Prof.SongZhangMEG088) Solutions to ODEs Forann@thorderLTIsystem a n yn) + a n 1 y n 1) ++ a 1 "y + a 0 y = b m u m)
ME 365: SYSTEMS, MEASUREMENTS, AND CONTROL SMAC) I Dynamicresponseof 2 nd ordersystem Prof.SongZhangMEG088) Solutions to ODEs Forann@thorderLTIsystem a n yn) + a n 1 y n 1) ++ a 1 "y + a 0 y = b m u m)
d dx x 2 = 2x d dx x 3 = 3x 2 d dx x n = nx n 1
 d dx x 2 = 2x d dx x 3 = 3x 2 d dx x n = nx n1 x dx = 1 2 b2 1 2 a2 a b b x 2 dx = 1 a 3 b3 1 3 a3 b x n dx = 1 a n +1 bn +1 1 n +1 an +1 d dx d dx f (x) = 0 f (ax) = a f (ax) lim d dx f (ax) = lim 0 =
d dx x 2 = 2x d dx x 3 = 3x 2 d dx x n = nx n1 x dx = 1 2 b2 1 2 a2 a b b x 2 dx = 1 a 3 b3 1 3 a3 b x n dx = 1 a n +1 bn +1 1 n +1 an +1 d dx d dx f (x) = 0 f (ax) = a f (ax) lim d dx f (ax) = lim 0 =
