Computable error bounds for asymptotic expansions formulas of distributions related to gamma functions
|
|
|
- ŌἈπολλύων Ζαχαρίου
- 7 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Computable error bounds for asymptotic expansions formulas of distributions related to gamma functions Hirofumi Wakaki (Math. of Department, Hiroshima Univ.) Hiroshima Statistical Group Meeting at RERF
2 . Introduction Examples of moment formulas which consist of gamma functions 2. General formulas of asymptotic expansions Two types of asymptotic expansion formulas of distributions 3. Uniform error bounds 3.. Previous results Expansion formulas under a high dimensional framework 3.2. Error bounds for large sample approximation Some lemmas and theorems for deriving error bounds 3.3. Wilks lambda distribution (MANOVA test) An error bound for large sample approximation 3.4. Comparison of error bounds between two types of expansions Numerical examples 2
3 . Introduction. Testing equality of r covariance matrices X ij, i =,..., n j H 0 : Σ = = Σ r i.i.d. N p (µ j, Σ j ), j =,..., r The modified likelihood ratio test rejects H 0 for small values of r V = (det A j) n j/2, (det A) n/2 A j : the matrix of sums of squares and products formed from the j nth sample A = A + + A r Moment formula (Under H 0 ) E[V h Γ p [n/2] ] = Γ p [n( + h)/2] p Γ p [a] = π p(p )/4 3 r Γ p [n j ( + h)/2], Γ p [n j /2] Γ[a (j )/2]
4 2. The sphericity test X i, i =,..., n i.i.d. N p (µ, Σ) H 0 : Σ = λi p, where λ is unspecified The likelihood ratio text rejects H 0 for small values of V = A : ( det A ) p, tra p the matrix of sums of squares and products Moment formula (Under H 0 ) E[V h ] = p ph Γ[pn/2]Γ p[(n + 2h)/2] Γ[p(n + 2h)/2]Γ p [n/2] 4
5 3. MANOVA test Y i = BX i + ε i, i =,..., N B : p r, X i : r, ε i i =,..., N i.i.d. N p (0, Σ) H 0 : BC = O, C is a known matrix of rank q The likelihood ratio text rejects H 0 for small values of V = A : B : det(b) det(a + B) the matrix of sums of squares and products due to the hypothesis the matrix of sums of squares and products due to the error Moment formula (Under H 0 ) E[V h ] = Γ p[(n + 2h)/2]Γ p [(n + q)/2] Γ p [n/2]γ p [(n + q + 2h)/2], n = N r 5
6 2. General formulas of asymptotic expansion Classical large sample approximation Box (949, Biometrika) E[V h ] = K [ p y j y j q i= x i x i ] h q i= Γ[x i( + h) + ξ i ] p Γ[y j( + h) + η j ] p y j = q x k, x k = a k M, y j = b j M, M (n ) T = 2ρ log V, ψ T (t) = log E[e itt ] = f 2 log( 2it)+ s [ q f = 2 β k = ( ρ)x k = O(), ϵ j = ( ρ)y j = O() ξ k [ q γ k = ( )k+ k(k + ) i= p η j ], 2 (q p) B k+ (β i + ξ i ) (ρx i ) k 6 γ k M k {( 2it) k } +O(M (s+) ) p ] B k+ (ϵ j + η j ), (ρy j ) k
7 Expansion of the characteristic function ϕ T (t) = exp{ψ T (t)} = ϕ s (t) + O(M (s+) ), ϕ s (t) = ( 2it) f/2 { s + M k k m= m! l + +l m =k l i Asymptotic expansion of the distribution function m i= } γ li [( 2it) l i ] P(T x) = G s (x) + O(M (s+) ) x { } G s (x) = e itx ψ s (t)dt dx (inverting formula) 2π 7
8 High dimensional Edgeworth expansion The moment generating function of log V ϕ log V (t) := E[exp(it log V )] = E[V it ] [ p = K y ] j y it j q i= Γ[x i( + it) + ξ i ] q i= x i x i p Γ[y j( + it) + η j ] cumulants κ = E[log V ] = log κ k = p y j y j q i= x i x i q x i ψ (k ) (x i + ξ i ) i= where ψ (k) (a) = dk+ log Γ[a] dak+ + q x i ψ (0) (x i + ξ i ) i= p y j ψ (0) (y j + η j ) p y j ψ (k ) (y j + η j ) (k 2) 8
9 Formal Edgeworth expansion { ϕ log V (t) φ s (t) := e t2 /2 + γ k,j = κ (j+3k)/2 2 s + +s k =j s k! s k j=0 } γ k,j (it) 3k+j, κ s +3 κ sk +3 (s + 3)! (s k + 3)!, ( log V κ P κ2 ) x Q s (x) := Φ(x) ϕ(x) h j : the j th order Hermite polynomial s k! s k γ k,j h 3k+j (x), j=0 9
10 3. Uniform error bounds If we find a function such that ϕ log V (t) φ s (t) G(t) and G(t) dt is computable t Then ( sup log V P κ x κ2 ) x Q s (x) 2π ϕ log V (t) φ s (t) dt t G(t) dt t 0
11 3.. Previous results We have found computable error bounds of the following statistics under a framework MANOVA test p, n i, with p n i c i (0, ) The modified likelihood ratio test testing Σ = I p The likelihood ratio test testing the sphericity The modified likelihood ratio test testing Σ = Σ 2 = = Σ r
12 Numerical examples Error bounds for testing H 0 : Σ = Σ 2 in the case of s = 2 n = n 2 = 8 n = 8, n 2 = 36 p BOUND p BOUND (0.55) (0.65) (0.55) (0.65) (0.60) (0.65) (0.70) (0.80) (0.95) (0.95) 2
13 Error bounds for testing H 0 : Σ = λi p in the case of s = 2 n = 30 n = 60 p BOUND p BOUND (0.75) (0.55) (0.60) (0.40) (0.60) (0.40) (0.65) (0.45) (0.90) (0.60) 3
14 Error bounds for testing H 0 : Σ = I p in the case of s = 2 n = 30 n = 60 p BOUND p BOUND (0.70) (0.50) (0.60) (0.40) (0.60) (0.40) (0.65) (0.40) (0.85) (0.55) 4
15 3.2. Error bounds for large sample approximation ψ T (t) = where q p {g k (t) g k (0)} {h j (t) h j (0)}, g k (t) = 2itρx k log x k + log Γ[ρx k ( 2it) + β k + ξ k ], h j (t) = 2itρy j log y j + log Γ[ρy j ( 2it) + ϵ j + η j ], and β k = ( ρ)x k = O(), ϵ j = ( ρ)y j = O() Generalized Stirling s theorem due to Barnes (899): log Γ[x + h] = log 2π + (x + h 2 ) log x x s ( ) k B k+ (h) k(k + )x k + R s+ (x), rigorous representation of R s (x) is required. 5
16 Lemma (from the infinite product definition due to Euler) log Γ[z + a] = lim n { + (z + a ) log n n } {log k log(z + a + k)} Lemma generalized Euler Maclaurin s formula f(x) : complex valued function of real argument n G n (x) = f(x + l) s k=0 G (k) l= n (0) a k = k! + n n f(x)dx + s k=0 B k+ (a) (k + )! {f (k) (n) f (k) ()} B s+ (a) + ( ) s B s+ (x [x] a) f (s+) (x)dx (s + )! 6
17 Lemma n log(z + a + l) = l= + + s m= n n ( ) m+ B m+ (a) { m(m + ) C s+ (x; a) s + log(z + x)dx + B (a) log z + n z + (z + n) } m (z + ) m (z + x) s+ dx + R s,n(z, a), where C k (x; a) = B k (x [x] a) B k ( a), n ( a ) k R s,n (z, a) = k z + l l= k=s+ 7
18 Lemma g k (t) g k (0) = B (β k + ξ k ) log( 2it) s ( ) m+ B m+ (β k + ξ k ) { } + m(m + )(ρx k ) m ( 2it) s + m= + l=0 C s+ (x; β k + ξ k ) 0 s + { } (ρx k + x) dx s+ (ρx k ( 2it) + x) s+ { ( βk ξ ) m ( k β k ξ ) } m k m ρx k + l ρx k ( 2il) + l m=s+ 8
19 Theorem ψ T (t) = f s 2 log( 2it)+ [ q f = 2 ξ k m= p η j ], 2 (q p) [ q γ m = ( )m+ m(m + ) B m+ (β k + ξ k ) (ρx k ) m γ m M m { ( 2it) m } +Rem s, p ] B m+ (ϵ j + η j ), (ρy j ) m 9
20 Rem s = q + p q p 0 0 l=0 l=0 { C s+ (x; β k + ξ k ) s + (ρx k + x) s+ (ρx k ( 2it) + x) s+ { C s+ (x; ϵ j + η j ) s + (ρy j + x) s+ (ρy j ( 2it) + x) s+ { ( βk ξ ) m ( k β k ξ ) } m k m ρx k + l ρx k ( 2it) + l m=s+ m=s+ m { ( ϵj η j ρy j + l ) m ( ϵ j η ) } m j ρy j ( 2it) + l } dx } dx 20
21 3.3. Wilks lambda distribution (MANOVA test) Moment formula Λ = det{b(w + B) } Λ p (q, n) B W p (q, Σ), W W p (n, Σ) (n > p) E[Λ h ] = q Γ[ n p+j + h]γ[ n+j ] 2 2 Γ[ n p+j ]Γ[ n+j + h]
22 High dimensional approximation (Tonda and Fujikoshi (2004), Wakaki (2007)) { } log Λ κ Pr x (κ 2 ) /2 { } κ3 = Φ(x) ϕ(x) 6 h 2(x) + + O(m (s+)/2 ), κ i : cumulants, κ i : standardized cumulant, m = n p 2 (κ 2 ) /2 2 n, (n p) 22
23 Error bound(wakaki(2007)) F s (x) : Edgeworth expansion with using (s + 2)-th cumulants Table : The error bounds for s = 2 and n = 50. p q error-bound p q error-bound
24 Error bound for the large sample approximation Theorem where ψ T (t) log E[exp{ Mit log Λ}] = pq s 2 log( 2it) + γ k M { ( k 2it) k } q + Rem c p+j,s+ (it), γ k = ( 2)k q {B k+( c+j ) B 2 k+( c p+j )} 2, k(k + ) c = (p q + ) 2 24
25 where C s+ (x; p+a Rem a,s (it) = ) C 2 s+(x; a) 2 s + { ( M( 2it) + x ) 2 s+ ( ) k+ + k l= k=s+ {( ) (p + a) k a k {M( 2it) + 2l} k ( M 2 + x )s+ ( (p + a) k a k (M + 2l) k } dx )}, 25
26 Note k : odd γ k = 0 (Box (949) : γ = γ 3 = γ 5 = 0) ψ T (t) = pq s 2 log( 2it) + γ 2k M { ( 2k 2it) 2k } + q Rem c p+j,2s+2 (it), 26
27 The residual of the expansion of the characteristic function ψ(t) = ψ 0 (t) + s u= g u (t) = γ 2u { ( 2it) 2u }, q R s (t) = M 2s Rem c p+j,2s, g u (t) M + R s+(t) (s = 0,, ), 2u M 2(s+) ϕ T (t) = E[exp{ Mit log Λ}] = ϕ s (t) + ( 2it) pq/2 R p,q,s(t) M 2(m+) 27
28 ϕ s (t) = ( 2it) pq/2 { + s M 2j [ ] R p,q,s (t) = {R (t)} s+ R (t) E,s+ + R s+ + s k=2 + R s k+2 R k { k 2 k! j=0 M 2 l i : k j i= l i s j j ( k j i= k! }, E,s (x) = x s { e x l + +l k =j l i k g li }, i= g li )R s+ j li R j s } x k k! 28
29 Lemma q Rem c p+j,m (it) M K p,q,m(t), m R s (t) K p,q,2s (t) { } 2t K p,q,m (t) = min A p,q,m, B p,q,m + 4t 2 { } 2t + C p,q,m min, 2 + 4t 2 m + 29
30 A p,q,m = q { ( c + j ) (c + j) m+ L,m 2 M ( c p + j ) } (c p + j) m+ L,m, M q { ( c + j ) B p,q,m = (c + j) m+ L 2,m M ( c p + j ) } (c p + j) m+ L 2,m, M C p,q,m = 2m m max q ( C m+ x; c + j ) ( C m+ x; c p + j ), 0 x 2 2 L,m (x) = { m log( x) x m L 2,m (x) = x m+ } x k, k { m ( x) log( x) + x 30 } x k+. k(k + )
31 Theorem sup Pr{ M log Λ x} F s (x) x F s (x) = x { } e itx ϕ s (t)dt dx 2π 2πM 2(s+) [ ] G p,q,s (t) = {K p,q,2 (t)} s+ Kp,q,2 (t) E,s+ + K p,q,2s+2 (t) + s k=2 { k 2 k! j=0 l i : k j i= l i s j k j i= + K p,q,2(s k+2) (t)k p,q,2 (t) k }, M 2 G p,q,s (t) dt, t g li K p,q,2(s+ j li )(t)k p,q,2 (t) j 3
32 case of s = case of s = 2 F (x) = G f (x) + γ 2 M 2 {G f(x) G f+4 (x)}, G p,q, (t) = ( + 4t 2 ) pq/4 { K p,q,4 (t) + {K p,q,2 (t)} 2 E,2 [ Kp,q,2 (t) M 2 ]} F 2 (x) = G f (x) + γ 2 M 2 {G f(x) G f+4 (x)} + M 4 {( c c 2 )G f (x) + c G f+4 (x) + c 2 G f+8 (x)}. c = γ 2 ( + γ 2 ), c 2 = γ2 2 2 γ 4, γ 4 = pq(59 50p2 + 3p 4 50q 2 + 0p 2 q 2 + 3q 4 ), 920 G p,q,2 (t) = ( + 4t 2 ) pq/4 {K p,q,6 (t)+ γ 2 2 ( 2it) 2 K p,q,4 (t) + {K p,q,2 (t)} 3 E,3 [ Kp,q,2 (t) M 2 ]}. 32
33 3.4. Comparison of error bounds between two types of expansions Table 2: n = 50.HD(High dimension)(s = 2), LS(Large sample)(s = ) p q HD LS > p q HD LS > 33
34 Table 3: n = 50, p = 20, q = 5 s HD s LS
35 End of this talk. Thank you. 35
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Laplace Expansion. Peter McCullagh. WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, Department of Statistics University of Chicago
 Laplace Expansion Peter McCullagh Department of Statistics University of Chicago WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, 2017 Outline Laplace approximation in 1D Laplace expansion in 1D Laplace expansion in R p Formal
Laplace Expansion Peter McCullagh Department of Statistics University of Chicago WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, 2017 Outline Laplace approximation in 1D Laplace expansion in 1D Laplace expansion in R p Formal
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review
 Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SCITECH Volume 13, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION Published online: March 29, 2018
 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
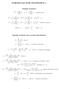 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model
 Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation. Mathematica StandardForm notation
 KelvinKei Notations Traditional name Kelvin function of the second kind Traditional notation kei Mathematica StandardForm notation KelvinKei Primary definition 03.5.0.000.0 kei kei 0 Specific values Values
KelvinKei Notations Traditional name Kelvin function of the second kind Traditional notation kei Mathematica StandardForm notation KelvinKei Primary definition 03.5.0.000.0 kei kei 0 Specific values Values
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain. Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics
 A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
Theorem 8 Let φ be the most powerful size α test of H
 Testing composite hypotheses Θ = Θ 0 Θ c 0 H 0 : θ Θ 0 H 1 : θ Θ c 0 Definition 16 A test φ is a uniformly most powerful (UMP) level α test for H 0 vs. H 1 if φ has level α and for any other level α test
Testing composite hypotheses Θ = Θ 0 Θ c 0 H 0 : θ Θ 0 H 1 : θ Θ c 0 Definition 16 A test φ is a uniformly most powerful (UMP) level α test for H 0 vs. H 1 if φ has level α and for any other level α test
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data
 Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Supplementary Material For Testing Homogeneity of. High-dimensional Covariance Matrices
 Supplementary Material For Testing Homogeneity of High-dimensional Covariance Matrices Shurong Zheng, Ruitao Lin, Jianhua Guo, and Guosheng Yin 3 School of Mathematics & Statistics and KLAS, Northeast
Supplementary Material For Testing Homogeneity of High-dimensional Covariance Matrices Shurong Zheng, Ruitao Lin, Jianhua Guo, and Guosheng Yin 3 School of Mathematics & Statistics and KLAS, Northeast
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
6. MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATION
 6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Solution Series 9. i=1 x i and i=1 x i.
 Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
g-selberg integrals MV Conjecture An A 2 Selberg integral Summary Long Live the King Ole Warnaar Department of Mathematics Long Live the King
 Ole Warnaar Department of Mathematics g-selberg integrals The Selberg integral corresponds to the following k-dimensional generalisation of the beta integral: D Here and k t α 1 i (1 t i ) β 1 1 i
Ole Warnaar Department of Mathematics g-selberg integrals The Selberg integral corresponds to the following k-dimensional generalisation of the beta integral: D Here and k t α 1 i (1 t i ) β 1 1 i
A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence
 International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 3, 143-149 A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence Santosh Kr. Saxena H. N. 419, Jawaharpuri, Badaun, U.P., India Presently working in
International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 3, 143-149 A General Note on δ-quasi Monotone and Increasing Sequence Santosh Kr. Saxena H. N. 419, Jawaharpuri, Badaun, U.P., India Presently working in
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
DiracDelta. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
Abstract Storage Devices
 Abstract Storage Devices Robert König Ueli Maurer Stefano Tessaro SOFSEM 2009 January 27, 2009 Outline 1. Motivation: Storage Devices 2. Abstract Storage Devices (ASD s) 3. Reducibility 4. Factoring ASD
Abstract Storage Devices Robert König Ueli Maurer Stefano Tessaro SOFSEM 2009 January 27, 2009 Outline 1. Motivation: Storage Devices 2. Abstract Storage Devices (ASD s) 3. Reducibility 4. Factoring ASD
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Tridiagonal matrices. Gérard MEURANT. October, 2008
 Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Reminders: linear functions
 Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
STAT200C: Hypothesis Testing
 STAT200C: Hypothesis Testing Zhaoxia Yu Spring 2017 Some Definitions A hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter. The two complementary hypotheses in a hypothesis testing are the null hypothesis
STAT200C: Hypothesis Testing Zhaoxia Yu Spring 2017 Some Definitions A hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter. The two complementary hypotheses in a hypothesis testing are the null hypothesis
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations
 On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Figure A.2: MPC and MPCP Age Profiles (estimating ρ, ρ = 2, φ = 0.03)..
 Supplemental Material (not for publication) Persistent vs. Permanent Income Shocks in the Buffer-Stock Model Jeppe Druedahl Thomas H. Jørgensen May, A Additional Figures and Tables Figure A.: Wealth and
Supplemental Material (not for publication) Persistent vs. Permanent Income Shocks in the Buffer-Stock Model Jeppe Druedahl Thomas H. Jørgensen May, A Additional Figures and Tables Figure A.: Wealth and
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
ExpIntegralE. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. Traditional name. Traditional notation. Mathematica StandardForm notation
 ExpIntegralE Notations Traditional name Exponential integral E Traditional notation E Mathematica StandardForm notation ExpIntegralE, Primary definition 06.34.0.000.0 E t t t ; Re 0 Specific values Specialied
ExpIntegralE Notations Traditional name Exponential integral E Traditional notation E Mathematica StandardForm notation ExpIntegralE, Primary definition 06.34.0.000.0 E t t t ; Re 0 Specific values Specialied
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
Divergence for log concave functions
 Divergence or log concave unctions Umut Caglar The Euler International Mathematical Institute June 22nd, 2013 Joint work with C. Schütt and E. Werner Outline 1 Introduction 2 Main Theorem 3 -divergence
Divergence or log concave unctions Umut Caglar The Euler International Mathematical Institute June 22nd, 2013 Joint work with C. Schütt and E. Werner Outline 1 Introduction 2 Main Theorem 3 -divergence
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE
 Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE BLUE: Robustness of LSE against normality We now study properties of l τ β and σ 2 under assumption A2, i.e., without the normality assumption on ε. From Theorem
Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE BLUE: Robustness of LSE against normality We now study properties of l τ β and σ 2 under assumption A2, i.e., without the normality assumption on ε. From Theorem
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Lanczos and biorthogonalization methods for eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices
 Lanzos and iorthogonalization methods for eigenvalues and eigenvetors of matries rolem formulation Many prolems are redued to solving the following system: x x where is an unknown numer А a matrix n n
Lanzos and iorthogonalization methods for eigenvalues and eigenvetors of matries rolem formulation Many prolems are redued to solving the following system: x x where is an unknown numer А a matrix n n
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Homework for 1/27 Due 2/5
 Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
HW 3 Solutions 1. a) I use the auto.arima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA(3,1)
 HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
The Jordan Form of Complex Tridiagonal Matrices
 The Jordan Form of Complex Tridiagonal Matrices Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University ILAS p.1 Goal Complex tridiagonal matrix α 1 β 1. γ T = 1 α 2........ β n 1 γ n 1 α n Jordan decomposition T =
The Jordan Form of Complex Tridiagonal Matrices Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University ILAS p.1 Goal Complex tridiagonal matrix α 1 β 1. γ T = 1 α 2........ β n 1 γ n 1 α n Jordan decomposition T =
Trigonometric Formula Sheet
 Trigonometric Formula Sheet Definition of the Trig Functions Right Triangle Definition Assume that: 0 < θ < or 0 < θ < 90 Unit Circle Definition Assume θ can be any angle. y x, y hypotenuse opposite θ
Trigonometric Formula Sheet Definition of the Trig Functions Right Triangle Definition Assume that: 0 < θ < or 0 < θ < 90 Unit Circle Definition Assume θ can be any angle. y x, y hypotenuse opposite θ
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix
 The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs
 Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs Philippe Jaming Bordeaux Fourier Workshop 2013, Renyi Institute Joint work with K. Kellay Heisenberg Uniqueness Pairs µ : finite measure on R 2 µ(x, y) = R 2 e i(sx+ty) dµ(s,
Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs Philippe Jaming Bordeaux Fourier Workshop 2013, Renyi Institute Joint work with K. Kellay Heisenberg Uniqueness Pairs µ : finite measure on R 2 µ(x, y) = R 2 e i(sx+ty) dµ(s,
A Hierarchy of Theta Bodies for Polynomial Systems
 A Hierarchy of Theta Bodies for Polynomial Systems Rekha Thomas, U Washington, Seattle Joint work with João Gouveia (U Washington) Monique Laurent (CWI) Pablo Parrilo (MIT) The Theta Body of a Graph G
A Hierarchy of Theta Bodies for Polynomial Systems Rekha Thomas, U Washington, Seattle Joint work with João Gouveia (U Washington) Monique Laurent (CWI) Pablo Parrilo (MIT) The Theta Body of a Graph G
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian
 The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Series representations. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 Pi Notations Traditional name Π Traditional notation Π Mathematica StandardForm notation Pi Primary definition.3... Π Specific values.3.3.. Π 3.5965358979338663383795889769399375589795937866868998683853
Pi Notations Traditional name Π Traditional notation Π Mathematica StandardForm notation Pi Primary definition.3... Π Specific values.3.3.. Π 3.5965358979338663383795889769399375589795937866868998683853
CHAPTER 101 FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD
 CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
An Inventory of Continuous Distributions
 Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet
 Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Wishart α-determinant, α-hafnian
 Wishart α-determinant, α-hafnian (, JST CREST) (, JST CREST), Wishart,. ( )Wishart,. determinant Hafnian analogue., ( )Wishart,. 1 Introduction, Wishart. p ν M = (µ 1,..., µ ν ) = (µ ij ) i=1,...,p p p
Wishart α-determinant, α-hafnian (, JST CREST) (, JST CREST), Wishart,. ( )Wishart,. determinant Hafnian analogue., ( )Wishart,. 1 Introduction, Wishart. p ν M = (µ 1,..., µ ν ) = (µ ij ) i=1,...,p p p
Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries
 1 Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries Ulf Kähler Chemnitz University of Technology Workshop on Fast Boundary Element Methods in Industrial Applications
1 Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries Ulf Kähler Chemnitz University of Technology Workshop on Fast Boundary Element Methods in Industrial Applications
557: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS II RESULTS FROM CLASSICAL HYPOTHESIS TESTING
 Most Powerful Tests 557: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS II RESULTS FROM CLASSICAL HYPOTHESIS TESTING To construct and assess the quality of a statistical test, we consider the power function β(θ). Consider a
Most Powerful Tests 557: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS II RESULTS FROM CLASSICAL HYPOTHESIS TESTING To construct and assess the quality of a statistical test, we consider the power function β(θ). Consider a
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix Measuring crisis risk using conditional copulas: An empirical analysis of the 2008 shipping crisis Sebastian Opitz, Henry Seidel and Alexander Szimayer Model specification Table
Supplementary Appendix Measuring crisis risk using conditional copulas: An empirical analysis of the 2008 shipping crisis Sebastian Opitz, Henry Seidel and Alexander Szimayer Model specification Table
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation. Tanguy Rivoal. Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble 1
 Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
5. Choice under Uncertainty
 5. Choice under Uncertainty Daisuke Oyama Microeconomics I May 23, 2018 Formulations von Neumann-Morgenstern (1944/1947) X: Set of prizes Π: Set of probability distributions on X : Preference relation
5. Choice under Uncertainty Daisuke Oyama Microeconomics I May 23, 2018 Formulations von Neumann-Morgenstern (1944/1947) X: Set of prizes Π: Set of probability distributions on X : Preference relation
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Local Approximation with Kernels
 Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines
 New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
Vol. 37 ( 2017 ) No. 3. J. of Math. (PRC) : A : (2017) k=1. ,, f. f + u = f φ, x 1. x n : ( ).
 Vol. 37 ( 2017 ) No. 3 J. of Math. (PRC) R N - R N - 1, 2 (1., 100029) (2., 430072) : R N., R N, R N -. : ; ; R N ; MR(2010) : 58K40 : O192 : A : 0255-7797(2017)03-0467-07 1. [6], Mather f : (R n, 0) R
Vol. 37 ( 2017 ) No. 3 J. of Math. (PRC) R N - R N - 1, 2 (1., 100029) (2., 430072) : R N., R N, R N -. : ; ; R N ; MR(2010) : 58K40 : O192 : A : 0255-7797(2017)03-0467-07 1. [6], Mather f : (R n, 0) R
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Exercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5
 Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Supplementary Materials: Proofs
 Supplementary Materials: Proofs The following lemmas prepare for the proof of concentration properties on prior density π α (β j /σ for j = 1,..., p n on m n -dimensional vector β j /σ. As introduced earlier,
Supplementary Materials: Proofs The following lemmas prepare for the proof of concentration properties on prior density π α (β j /σ for j = 1,..., p n on m n -dimensional vector β j /σ. As introduced earlier,
forms This gives Remark 1. How to remember the above formulas: Substituting these into the equation we obtain with
 Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Forced Pendulum Numerical approach
 Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 24/3/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Όλοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα μικρότεροι του 10000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Όλοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα μικρότεροι του 10000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise. Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University
 Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
Takeaki Yamazaki (Toyo Univ.) 山崎丈明 ( 東洋大学 ) Oct. 24, RIMS
 Takeaki Yamazaki (Toyo Univ.) 山崎丈明 ( 東洋大学 ) Oct. 24, 2017 @ RIMS Contents Introduction Generalized Karcher equation Ando-Hiai inequalities Problem Introduction PP: The set of all positive definite operators
Takeaki Yamazaki (Toyo Univ.) 山崎丈明 ( 東洋大学 ) Oct. 24, 2017 @ RIMS Contents Introduction Generalized Karcher equation Ando-Hiai inequalities Problem Introduction PP: The set of all positive definite operators
