Electromagnetic. G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Jefferson Lab Professor of Physics Old Dominion University Physics 804 Electromagnetic Theory II
|
|
|
- Λυσιμάχη Μεσσηνέζης
- 7 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Physics 74/84 Elecomagneic Theoy II G. A. Kaff Jeffeson Lab Jeffeson Lab Pofesso of Physics Old Dominion Univesiy Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II -3-1
2 Pependicula Polaizaion = E + E E Tangenial E ( ) ε ( ) ε = E E cos i E cos Tangenial H µ µ E ncosi = E n cos i µ + n n sin µ i µ E ncosi n n sin i µ = E µ n cos i + n n sin i µ Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
3 Wave Guides: Suface Absobion Homogeneous Maxwell Equaions imply n B B c = n E E c = ( ) c ( ) Cul lhh Maxwell Equaion and lage bu finie i conduciviy i implies n H H c = ( ) 1 E = c H c σ i H c = E µω c c Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
4 ξ i ( + n H ) c = δ n H c = 1/ δ = µωσ c ξ / δ iξ / δ H = H e e H c pa pa ωµ E c i n H σ dp 1 Re * µωδ c = n E H = H da 4 c ( ξ = ) = ( 1 )( ) pa pa is he field a he suface Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
5 Alenaive Calculaion ˆ δ 1 * 1 powe/vol = J E = J σ K = Jd ξ = nˆ H 1 ( ) ( ) ( i) 1 / J = σ Ec = 1 i n H pa e ξ δ eff dp da pa 1 µωδ = Keff = σδ 4 c K eff suface cuen fo pefec conduco Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
6 Cylindical Sysems z z-axis along he cylinde diecion E = i ω B B = B = iµε E E = ( E + µεω ) = B ω B = B x, y e E = E x, y e ( ) ( ) ± ikz ± ikz ω Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
7 Tansvese Sepaaion E = E ˆ ( ˆ) zz + E E = E E z zˆ B = B ˆ ( ˆ ) zz + B B = B B z zˆ E + ( µεω ) k = B E + i ω zˆ B = ˆ ( ) Ez z E = i ω Bz z B iµεω zˆ E = B zˆ ( B ) = i µεω E z E z Bz E = B = z z z z Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
8 TEM Modes Soluions wih ansvese field only Eem = E, em Bem = B, em E = E =, em, em E em mus solve -D elecosaic poblem k = k = µεω B =± µε zˆ E em em Can hee be a soluion inside a single closed waveguide? No, need a leas wo conducos. No cuoff fffequency Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
9 Moe Geneal Case Tansvese field expessible in ems of z-field only! i E ˆ = k Ez ω z B z µεω k i B = k B + µεω zˆ E µεω k z z Tansvese Magneic (TM) B z = ; Bounday Condiion E = z S Tansvese Elecic (TE) E z B = ; Bounday Condiion z = n S Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
10 Waveguides ± 1 H = z ˆ E Z Wave Impedance Z k k µ = (TM) εω k ε = µω k µ = (TE) k k ε Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
11 Eigenvalue Poblem TM Waves TE Waves E H ik = ± ψ γ ik = ± ψ γ Tansvese Helmholz Equaion + = + + = x y γ ψ γ ψ ( ) Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
12 Bounday Condiions ψ S ψ = (TM) = (TE) nn S Specum of eigenvalues and eigenfuncions γ λ ψ λ ( x, y ) Wavelengh in mode λ k λ = µεω γ λ Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
13 Cuoff Fequency ω λ ω = γ λ µε No popagaion a fequencies below cuoff ( ) k λ = µε ω ω λ Fo single-mode popagaion choose fequency o be above cuoff fo lowes mode and below cuoff fo all ohe modes. Phase velociy infinie a cuoff! Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
14 Recangula Waveguide x y + + γ ψ = ψ mπ x nπ x = (TE) ψ mn ( x, y ) = Acos cos n a a S ω γ mn mn m = π + a n b π m = + µε a n b 1/ Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
15 Lowes Mode ω 1 = π µε m a π x H z = Acos e a ika π x H z = Asin e π a ω aµ π x Ey = i Asin e π a ikz iω ikz iω ikz iω Lowes TM mode has m and n one wih a sin soluion. Why? Is cuoff fo he lowes mode is a a fequency highe by ( 1/ 1 + a /b b ) Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
16 Enegy Flow 1 * S = E H γ * ε zˆ ψ + i ψ ψ ω k k S = 4 γ γ * µ zˆ ψ i ψ ψ k ω k ε * P = S zda ˆ = 4 ψ ψ da γ µ A A ωk ε ψ P = ψ dl ψ ψ da 4 + γ µ * * n C A Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
17 Enegy and Goup Velociy P U P U v v 1/ λ 1 1 ω ω λ ε = µε ωλ ω µ 1 ω ε = ω λ µ * ψ ψ ω λ = k v ω µε = µε ω = = 1 p g µε A da g A * ψψ da Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
18 Aenuaion Field aenuaion consan given by β λ ( ) = λ P z P e β λ β z 1 dp = P dz dp 1 = nˆ H dl dz σδ C 1 ψ 1 µ ω λ n = dl σδ C 1 ω λ ωλ 1 nˆ ψ ψ + µ ωλ ω ω Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
19 ψ n nˆ ψ µεω ψ λ C 1 ω λ ψ n C dl = ς λ µε A A ψ da ( / ) 1/ ε 1 C ω ω λ ω λ βλ = ς 1/ λ + ηλ µ σδ λ A 1 ω / ω ω λ ( 1 ω / ω ) λ Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
20 Resonan Caviies Pu end conducos on a cylindical waveguide. Example: Cylindical caviy of lengh d and adius R. In geneal, z dependence d is Asin kz + B cos kz ( ) ( ) π BCs k = p, p =,1,, K d TM pπ Ez = ψ ( x, y) cos, p =,1,, K d TE pπ H z = ψ ( x, y ) sin, p = 1,, K d Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
21 Field Paens TM sin p p E π π ψ = sin ˆ cos E d d i p H z ψ γ εω π ψ = TE d i ψ γ ˆ sin i p E z d ωµ π ψ γ = ( ) cos / p p H d d d π π ψ γ = Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II ( ) / p d γ µεω π =
22 1 ω = λ p γ pπ d µε + TM Eigenvalue Equaion ( ( / ) ) λ (, ) = AJ ( ) ψ ρ φ γ ρ m mn e ± imφ xmn γ mn = J m ( xmn ) = R ω mnp 1 x p π.45 mn = + ω = µε µε 1 R d R.45ρ ε.45ρ E z = AJ e H = i AJ e R µ R iω iω φ 1 Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
23 TE (, ) = AJ ( ) ψ ρ φ γ ρ γ ω ω m mn mn mn m mn mnp e ± imφ x = J ( x ) = R 1 x mn = + µε R p π d R = µε R d ρ π z H z = AJ1 cosφ sin e R d iω Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
24 Caviy Losses Q = du d Soed enegy ω boh popoional o ψ Powe loss ω = U Q U () = U e ω () Q / ( ω ω) ω / Q i + E = Ee e Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
25 ( ) Paallel Polaizaion = cos i E E cos E Tangenial E ε ( ) ε = E + E E Tangenial H µ µ E nn cosi = E µ n cos i + n n n sin µ i µ E n cos i n n n sin i µ = E µ n cos i + n n n sin i µ Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
26 Enegy Consevaion? Nomal Incidence E n = = E n n µε µε µε 1 E µε n n = = E n n µε + 1 µε + ε E ε E ε E = + µ µ µ Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
27 Misakes fom Las Time Enegy Consevaion a Nomal Incidence ε E ε E ε E = + µ µ µ E n = = E n n µε µε µε 1 E µε n n = = E n n µε + µ ε + 1 Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
28 Bewse s Angle Calculaion n cos i = n n n sin i B ( sin ) B n cos i = n n n i n 4 B B n ± n 4 n cos i sin i + n ± n ( 1 cos i ) B B B = = cos ib cos i B i Bewse = an 1 n n Zeo eflecion in pependicula polaizaion implies n' = n Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
29 µ = µ Bewse s Angle If efleced paallel polaizaion ampliude vanishes when inciden a he Bewse angle i Bewse = an 1 n n Refleced wave compleely plane-polaized (polaizaion pependicula o plane of incidence) if mixed-polaizaion beam inciden a Bewse angle. i Bewse o n = 56 fo = 1.5 n Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
30 Toal Inenal Reflecion Examine Snell s Law in case n > n' i = sin 1 n Fo angles of incidence geae, hee is no ansmied wave soluion o aach o, only an exponenially damped soluion. This implies oal eflecion, also called oal inenal eflecion. Opical communicaion sysems ae based on his phenomenon! n Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
31 Goup Velociy Unil now, we have assumed ha he elaive pemiiviy and pemeabiliy ae independen of fequency. This may be fa fom he case. Relaxing he equiemen of consan phase velociy as a funcion of fequency leads o moe geneal wave phenomena. Allow he fequency o depend on wavelengh in 1 dimension: 1 ikx ω k (, ) ( ) ( ) u x = A k e dk π The funcion ω(k) is known as he dispesion funcion. A sicly linea dispesion funcion, as we ve had up o now, does no lead o pulse speading, o dispesion. Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
32 ikx A k u x e dx ( ) (,) = dω ω ω ω ω ( k) = + ( k k ) + L = ( k ) (, ) dk e ( ω/ ) i k d dk ω i x ( dω / dk) k u x A k e dk π ( ω/ ) i k d dk ω = ( ) ( ( ω / ), ) e u x d dk The pulse shape avels a he goup velociy v g = dω dk Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
33 Dispesion 1 ikx ω ( k ) u( x, ) = A( k) e dk π Have exac calculaion fo modulaed Gaussian funcion ( ) ( ), = exp / u x x L e ikx A( k) = u( x, ) e dx ik x ( )( ) = π L exp L / k k a k ω = ν + ( k ) ν 1 Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
34 Pulse Speading, o Dispesion v g dω = = ν dk a k L ( L /)( k k ) ikx iv 1 + ( a k /) u( x, ) = e e dk π ( x ν a k ) exp ia ν L 1+ L ( = exp ik ) 1/ x iν 1 a k / + ia ν 1 + L Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
35 dω L L a L dk () ( = = + ν / ) d ω ν a v g = k = dk L ( ) ( ) ( ) x = x + v g Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
36 Causaliy D x E x (, ω ) = ε ( ω) (, ω) Convoluion Theoem (Fahlung Theoem) implies non-localiy in ime. 1 iω iω D( x, ) = D( x, ) e d = ( ) E( x, ) e d π 1 π ω ω ε ω ω ω ε ω e d e E x dω = iω + iω ( ) (, ) = ε E( x, ) + G( τ ) E( x, τ ) dτ Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
37 Geen funcion fo connecion 1 ( ) ( ) iωτ G τ = ε ω / ε 1 e dω π Damped oscillao connecion ( ) ( / 1= i ) 1 ε ω ε ω ω ω γω p / sin ν τ G τ = ω pe γ Θ τ ν ( ) ( ) ν ω γ = /4 Vanishes fo negaive τ,, cause canno pecede effec. Causal Geen s funcions mus be analyic in uppe ½ of complex plane. Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
38 Kames-Konig Relaions iωτ ε ( ω) / ε 1= G( τ ) e dτ Is auomaically causal fo a wide vaiey of choices fo G. Analyiciy in UH-ωP implies a elaionship beween eal and imaginay pa of he pemiiviy. Cauchy s heoem fo z inside a closed cuve C 1 ε ( ω ) / ε 1 ε ( z ) / ε = 1+ dω π i ω z 1 = 1 + πi C ( ) ε ω / ε 1 d ω ω z whee he inegal is now along he eal axis Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
39 1 1 = P + πδ i ( ω ω) ω ω iδ ω ω 1 Im ε ( ω ) / ε Re ε ( ω) / ε = 1+ P dω π ω z ( ) ε 1 Re ε ω / 1 Im ε ( ω) / ε = P dω π ω z ( ) ω Im ε ω / ε Re ε ( ω) / ε = 1+ P dω π ω ω ( ) ε ω Re ε ω / 1 Im ε ( ω) / ε = P dω * ( ) ( * = ) ε ω ε ω π ω ω Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
40 Sum Rules Sum Rules fo oscillao senghs Second Sum Rule ω p = 1+ P ω Im ε ( ω) / ε dω π 1 N N ( ) p d Re ε ω / ε ω = 1+ ω N Physics 84 Elecomagneic Theoy II
Physics 401 Final Exam Cheat Sheet, 17 April t = 0 = 1 c 2 ε 0. = 4π 10 7 c = SI (mks) units. = SI (mks) units H + M
 Maxwell' s Equations in vauum E ρ ε Physis 4 Final Exam Cheat Sheet, 7 Apil E B t B Loent Foe Law: F q E + v B B µ J + µ ε E t Consevation of hage: J + ρ t µ ε ε 8.85 µ 4π 7 3. 8 SI ms) units q eleton.6
Maxwell' s Equations in vauum E ρ ε Physis 4 Final Exam Cheat Sheet, 7 Apil E B t B Loent Foe Law: F q E + v B B µ J + µ ε E t Consevation of hage: J + ρ t µ ε ε 8.85 µ 4π 7 3. 8 SI ms) units q eleton.6
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Lecture 12 Modulation and Sampling
 EE 2 spring 2-22 Handou #25 Lecure 2 Modulaion and Sampling The Fourier ransform of he produc of wo signals Modulaion of a signal wih a sinusoid Sampling wih an impulse rain The sampling heorem 2 Convoluion
EE 2 spring 2-22 Handou #25 Lecure 2 Modulaion and Sampling The Fourier ransform of he produc of wo signals Modulaion of a signal wih a sinusoid Sampling wih an impulse rain The sampling heorem 2 Convoluion
Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small spheres separated by a distance s. The charge on one sphere changes with time and is described by
 5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
Lecture 6. Goals: Determine the optimal threshold, filter, signals for a binary communications problem VI-1
 Lecue 6 Goals: Deemine e opimal esold, file, signals fo a binay communicaions poblem VI- Minimum Aveage Eo Pobabiliy Poblem: Find e opimum file, esold and signals o minimize e aveage eo pobabiliy. s s
Lecue 6 Goals: Deemine e opimal esold, file, signals fo a binay communicaions poblem VI- Minimum Aveage Eo Pobabiliy Poblem: Find e opimum file, esold and signals o minimize e aveage eo pobabiliy. s s
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
Graded Refractive-Index
 Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines
![Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines](/thumbs/51/28406191.jpg) Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Electronic Companion to Supply Chain Dynamics and Channel Efficiency in Durable Product Pricing and Distribution
 i Eleconic Copanion o Supply Chain Dynaics and Channel Efficiency in Duable Poduc Picing and Disibuion Wei-yu Kevin Chiang College of Business Ciy Univesiy of Hong Kong wchiang@ciyueduh I Poof of Poposiion
i Eleconic Copanion o Supply Chain Dynaics and Channel Efficiency in Duable Poduc Picing and Disibuion Wei-yu Kevin Chiang College of Business Ciy Univesiy of Hong Kong wchiang@ciyueduh I Poof of Poposiion
Analytical Expression for Hessian
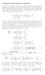 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Curvilinear Systems of Coordinates
 A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
( ) ( ) ( ) Fourier series. ; m is an integer. r(t) is periodic (T>0), r(t+t) = r(t), t Fundamental period T 0 = smallest T. Fundamental frequency ω
 Fourier series e jm when m d when m ; m is an ineger. jm jm jm jm e d e e e jm jm jm jm r( is periodi (>, r(+ r(, Fundamenal period smalles Fundamenal frequeny r ( + r ( is periodi hen M M e j M, e j,
Fourier series e jm when m d when m ; m is an ineger. jm jm jm jm e d e e e jm jm jm jm r( is periodi (>, r(+ r(, Fundamenal period smalles Fundamenal frequeny r ( + r ( is periodi hen M M e j M, e j,
3 Frequency Domain Representation of Continuous Signals and Systems
 3 Frequency Domain Represenaion of Coninuous Signals and Sysems 3. Fourier Series Represenaion of Periodic Signals............. 2 3.. Exponenial Fourier Series.................... 2 3..2 Discree Fourier
3 Frequency Domain Represenaion of Coninuous Signals and Sysems 3. Fourier Series Represenaion of Periodic Signals............. 2 3.. Exponenial Fourier Series.................... 2 3..2 Discree Fourier
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
Reflection Models. Reflection Models
 Reflecon Models Today Types of eflecon models The BRDF and eflecance The eflecon equaon Ideal eflecon and efacon Fesnel effec Ideal dffuse Thusday Glossy and specula eflecon models Rough sufaces and mcofaces
Reflecon Models Today Types of eflecon models The BRDF and eflecance The eflecon equaon Ideal eflecon and efacon Fesnel effec Ideal dffuse Thusday Glossy and specula eflecon models Rough sufaces and mcofaces
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
) 2. δ δ. β β. β β β β. r k k. tll. m n Λ + +
 Techical Appedix o Hamig eposis ad Helpig Bowes: The ispaae Impac of Ba Cosolidaio (o o be published bu o be made available upo eques. eails of Poofs of Poposiios 1 ad To deive Poposiio 1 s exac ad sufficie
Techical Appedix o Hamig eposis ad Helpig Bowes: The ispaae Impac of Ba Cosolidaio (o o be published bu o be made available upo eques. eails of Poofs of Poposiios 1 ad To deive Poposiio 1 s exac ad sufficie
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) 21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
George S. A. Shaker ECE477 Understanding Reflections in Media. Reflection in Media
 Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION. Solution Manual
 ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
1 3D Helmholtz Equation
 Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 553 Spring Quarter 2010 Homework Assignment 3 Due 04/26/10
 Universiy of Washingon Deparmen of Chemisry Chemisry 553 Spring Quarer 1 Homework Assignmen 3 Due 4/6/1 v e v e A s ds: a) Show ha for large 1 and, (i.e. 1 >> and >>) he velociy auocorrelaion funcion 1)
Universiy of Washingon Deparmen of Chemisry Chemisry 553 Spring Quarer 1 Homework Assignmen 3 Due 4/6/1 v e v e A s ds: a) Show ha for large 1 and, (i.e. 1 >> and >>) he velociy auocorrelaion funcion 1)
Κλασική Ηλεκτροδυναμική
 Κλασική Ηλεκτροδυναμική Ενότητα 22: Κυματοπακέτα-Κυματοδηγοί Ανδρέας Τερζής Σχολή Θετικών Επιστημών Τμήμα Φυσικής Σκοποί ενότητας Σκοπός της ενότητας είναι να παρουσιάσει την έννοια του κυματοπακέτου,
Κλασική Ηλεκτροδυναμική Ενότητα 22: Κυματοπακέτα-Κυματοδηγοί Ανδρέας Τερζής Σχολή Θετικών Επιστημών Τμήμα Φυσικής Σκοποί ενότητας Σκοπός της ενότητας είναι να παρουσιάσει την έννοια του κυματοπακέτου,
Broadband Spatiotemporal Differential-Operator Representations For Velocity-Dependent Scattering
 Broadband Spatiotemporal Differential-Operator Representations For Velocity-Dependent Scattering Dan Censor Ben Gurion University of the Negev Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Beer Sheva,
Broadband Spatiotemporal Differential-Operator Representations For Velocity-Dependent Scattering Dan Censor Ben Gurion University of the Negev Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Beer Sheva,
Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α
 Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
Accelerator Physics. G. A. Krafft, A. Bogacz, and H. Sayed Jefferson Lab Old Dominion University Lecture 9
 Acceleato Physics G. A. Kafft, A. Bogacz, and H. Sayed Jeffeson Lab Old Dominion Univesity Lectue 9 USPAS Acceleato Physics Jan. 11 Synchoton Radiation Acceleated paticles emit electomagnetic adiation.
Acceleato Physics G. A. Kafft, A. Bogacz, and H. Sayed Jeffeson Lab Old Dominion Univesity Lectue 9 USPAS Acceleato Physics Jan. 11 Synchoton Radiation Acceleated paticles emit electomagnetic adiation.
16. 17. r t te 2t i t 1. 18 19 Find the derivative of the vector function. 19. r t e t cos t i e t sin t j ln t k. 31 33 Evaluate the integral.
 SECTION.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES A Click here for answers. S Click here for soluions. Copyrigh Cengage Learning. All righs reserved.. Find he domain of he
SECTION.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES A Click here for answers. S Click here for soluions. Copyrigh Cengage Learning. All righs reserved.. Find he domain of he
Spherical Coordinates
 Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
VEKTORANALYS. CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (kroklinjiga koordinatsytem) Kursvecka 4. Kapitel 10 Sidor
 VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Appendix. The solution begins with Eq. (2.15) from the text, which we repeat here for 1, (A.1)
 Aenix Aenix A: The equaion o he sock rice. The soluion egins wih Eq..5 rom he ex, which we reea here or convenience as Eq.A.: [ [ E E X, A. c α where X u ε, α γ, an c α y AR. Take execaions o Eq. A. as
Aenix Aenix A: The equaion o he sock rice. The soluion egins wih Eq..5 rom he ex, which we reea here or convenience as Eq.A.: [ [ E E X, A. c α where X u ε, α γ, an c α y AR. Take execaions o Eq. A. as
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics
 Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 2017 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations
 ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 07 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations Answers to problems on Midterm Examination #, Spring 009. x(t) = r(t + ) r(t ) u(t ) r(t ) + r(t 3) + u(t +
ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 07 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations Answers to problems on Midterm Examination #, Spring 009. x(t) = r(t + ) r(t ) u(t ) r(t ) + r(t 3) + u(t +
6.003: Signals and Systems
 6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Communicaions Sysems Signals are no always well mached o he media hrough which we wish o ransmi hem. signal audio video inerne applicaions elephone, radio,
6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Communicaions Sysems Signals are no always well mached o he media hrough which we wish o ransmi hem. signal audio video inerne applicaions elephone, radio,
wave energy Superposition of linear plane progressive waves Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture Oblique Plane Waves:
 3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
( ) ( t) ( 0) ( ) dw w. = = β. Then the solution of (1.1) is easily found to. wt = t+ t. We generalize this to the following nonlinear differential
 Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
Analysis of optimal harvesting of a prey-predator fishery model with the limited sources of prey and presence of toxicity
 ES Web of Confeences 7, 68 (8) hps://doiog/5/esconf/8768 ICEIS 8 nalsis of opimal havesing of a pe-pedao fishe model wih he limied souces of pe and pesence of oici Suimin,, Sii Khabibah, and Dia nies Munawwaoh
ES Web of Confeences 7, 68 (8) hps://doiog/5/esconf/8768 ICEIS 8 nalsis of opimal havesing of a pe-pedao fishe model wih he limied souces of pe and pesence of oici Suimin,, Sii Khabibah, and Dia nies Munawwaoh
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation format: Markus Zahn, 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation format: Markus Zahn, 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall
Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st & 2 nd reprint)
 Wedesday, May 5, 3 Erraa (Icludes criical correcios oly for he s & d repri) Advaced Egieerig Mahemaics, 7e Peer V O eil ISB: 978474 Page # Descripio 38 ie 4: chage "w v a v " "w v a v " 46 ie : chage "y
Wedesday, May 5, 3 Erraa (Icludes criical correcios oly for he s & d repri) Advaced Egieerig Mahemaics, 7e Peer V O eil ISB: 978474 Page # Descripio 38 ie 4: chage "w v a v " "w v a v " 46 ie : chage "y
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
Reservoir modeling. Reservoir modelling Linear reservoirs. The linear reservoir, no input. Starting up reservoir modeling
 Reservoir modeling Reservoir modelling Linear reservoirs Paul Torfs Basic equaion for one reservoir:) change in sorage = sum of inflows minus ouflows = Q in,n Q ou,n n n jus an ordinary differenial equaion
Reservoir modeling Reservoir modelling Linear reservoirs Paul Torfs Basic equaion for one reservoir:) change in sorage = sum of inflows minus ouflows = Q in,n Q ou,n n n jus an ordinary differenial equaion
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Trigonometry 1.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
 Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
Trigonometry.TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. If a ray OP makes an angle with the positive direction of X-axis then y x i) Sin ii) cos r r iii) tan x y (x 0) iv) cot y x (y 0) y P v) sec x r (x 0) vi) cosec y r (y
ω = radians per sec, t = 3 sec
 Secion. Linear and Angular Speed 7. From exercise, =. A= r A = ( 00 ) (. ) = 7,00 in 7. Since 7 is in quadran IV, he reference 7 8 7 angle is = =. In quadran IV, he cosine is posiive. Thus, 7 cos = cos
Secion. Linear and Angular Speed 7. From exercise, =. A= r A = ( 00 ) (. ) = 7,00 in 7. Since 7 is in quadran IV, he reference 7 8 7 angle is = =. In quadran IV, he cosine is posiive. Thus, 7 cos = cos
Μικροκυματικές Επικοινωνίες & Τεχνολογίες Χιλιοστομετρικών Κυμάτων
 Μικροκυματικές Επικοινωνίες & Τεχνολογίες Χιλιοστομετρικών Κυμάτων ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ - Το μάθημα αυτό πραγματεύεται θεμελιώδεις έννοιες των γραμμών μεταφοράς στην επιστημονική περιοχή των ηλεκτρονικών συστημάτων
Μικροκυματικές Επικοινωνίες & Τεχνολογίες Χιλιοστομετρικών Κυμάτων ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ - Το μάθημα αυτό πραγματεύεται θεμελιώδεις έννοιες των γραμμών μεταφοράς στην επιστημονική περιοχή των ηλεκτρονικών συστημάτων
d dt S = (t)si d dt R = (t)i d dt I = (t)si (t)i
 d d S = ()SI d d I = ()SI ()I d d R = ()I d d S = ()SI μs + fi + hr d d I = + ()SI (μ + + f + ())I d d R = ()I (μ + h)r d d P(S,I,) = ()(S +1)(I 1)P(S +1, I 1, ) +()(I +1)P(S,I +1, ) (()SI + ()I)P(S,I,)
d d S = ()SI d d I = ()SI ()I d d R = ()I d d S = ()SI μs + fi + hr d d I = + ()SI (μ + + f + ())I d d R = ()I (μ + h)r d d P(S,I,) = ()(S +1)(I 1)P(S +1, I 1, ) +()(I +1)P(S,I +1, ) (()SI + ()I)P(S,I,)
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves
 .0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
6.003: Signals and Systems. Modulation
 6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Subjec Evaluaions Your feedback is imporan o us! Please give feedback o he saff and fuure 6.3 sudens: hp://web.mi.edu/subjecevaluaion Evaluaions are open
6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Subjec Evaluaions Your feedback is imporan o us! Please give feedback o he saff and fuure 6.3 sudens: hp://web.mi.edu/subjecevaluaion Evaluaions are open
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories
 Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
ECE 222b Applied Electromagnetics Notes Set 3a
 C b lid lcomagnics Nos S 3a Insuco: Pof. Viali Lomakin Damn of lcical and Comu ngining Univsi of Califonia San Digo Unifom Plan Wavs Consid Mawll s quaions: In a losslss mdium ε and µ a al and σ : Sinc
C b lid lcomagnics Nos S 3a Insuco: Pof. Viali Lomakin Damn of lcical and Comu ngining Univsi of Califonia San Digo Unifom Plan Wavs Consid Mawll s quaions: In a losslss mdium ε and µ a al and σ : Sinc
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
 φ(t) TE 0 φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) η(λ) G(z,λ) λ φ(z) η(λ) η(λ) = t CIGS 0 G(z,λ)φ(z)dz t CIGS η(λ) φ(z) 0 z
φ(t) TE 0 φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) η(λ) G(z,λ) λ φ(z) η(λ) η(λ) = t CIGS 0 G(z,λ)φ(z)dz t CIGS η(λ) φ(z) 0 z
Inflation and Reheating in Spontaneously Generated Gravity
 Univesità di Bologna Inflation and Reheating in Spontaneously Geneated Gavity (A. Ceioni, F. Finelli, A. Tonconi, G. Ventui) Phys.Rev.D81:123505,2010 Motivations Inflation (FTV Phys.Lett.B681:383-386,2009)
Univesità di Bologna Inflation and Reheating in Spontaneously Geneated Gavity (A. Ceioni, F. Finelli, A. Tonconi, G. Ventui) Phys.Rev.D81:123505,2010 Motivations Inflation (FTV Phys.Lett.B681:383-386,2009)
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations
 Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Oscillatory Gap Damping
 Oscillatory Gap Damping Find the damping due to the linear motion of a viscous gas in in a gap with an oscillating size: ) Find the motion in a gap due to an oscillating external force; ) Recast the solution
Oscillatory Gap Damping Find the damping due to the linear motion of a viscous gas in in a gap with an oscillating size: ) Find the motion in a gap due to an oscillating external force; ) Recast the solution
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
9.09. # 1. Area inside the oval limaçon r = cos θ. To graph, start with θ = 0 so r = 6. Compute dr
 9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
326. Dynamic synchronization of the unbalanced rotors for the excitation of longitudinal traveling waves
 . Dynamic synchonizaion of he unbalanced oos fo he exciaion of longiudinal aveling waves. Saseeyeva K. Ragulsis Z. Navicas Kazah Naional Pedagogical Univesiy named afe bay Tole bi s. 8 lmay Kazahsan E-mail:
. Dynamic synchonizaion of he unbalanced oos fo he exciaion of longiudinal aveling waves. Saseeyeva K. Ragulsis Z. Navicas Kazah Naional Pedagogical Univesiy named afe bay Tole bi s. 8 lmay Kazahsan E-mail:
Motion of an Incompressible Fluid. with Unit Viscosity
 Nonl. Analsis and Diffeenial Equaions Vol. 1 013 no. 3 143-148 HIKARI Ld www.m-hikai.com Moion of an Incompessible Fluid wih Uni Viscosi V. G. Gupa and Kapil Pal Depamen of Mahemaics Univesi of Rajashan
Nonl. Analsis and Diffeenial Equaions Vol. 1 013 no. 3 143-148 HIKARI Ld www.m-hikai.com Moion of an Incompessible Fluid wih Uni Viscosi V. G. Gupa and Kapil Pal Depamen of Mahemaics Univesi of Rajashan
Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom
 Technische Universität Graz Institut für Festkörperphysik Student project Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom Molecular and Solid State Physics 53. submitted on: 3. November 9 by: Markus Krammer
Technische Universität Graz Institut für Festkörperphysik Student project Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom Molecular and Solid State Physics 53. submitted on: 3. November 9 by: Markus Krammer
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
Review: Molecules = + + = + + Start with the full Hamiltonian. Use the Born-Oppenheimer approximation
 Review: Molecules Start with the full amiltonian Ze e = + + ZZe A A B i A i me A ma ia, 4πε 0riA i< j4πε 0rij A< B4πε 0rAB Use the Born-Oppenheimer approximation elec Ze e = + + A A B i i me ia, 4πε 0riA
Review: Molecules Start with the full amiltonian Ze e = + + ZZe A A B i A i me A ma ia, 4πε 0riA i< j4πε 0rij A< B4πε 0rAB Use the Born-Oppenheimer approximation elec Ze e = + + A A B i i me ia, 4πε 0riA
The Student s t and F Distributions Page 1
 The Suden s and F Disribuions Page The Fundamenal Transformaion formula for wo random variables: Consider wo random variables wih join probabiliy disribuion funcion f (, ) simulaneously ake on values in
The Suden s and F Disribuions Page The Fundamenal Transformaion formula for wo random variables: Consider wo random variables wih join probabiliy disribuion funcion f (, ) simulaneously ake on values in
Χρονοσειρές Μάθημα 3
 Χρονοσειρές Μάθημα 3 Ασυσχέτιστες (λευκός θόρυβος) και ανεξάρτητες (iid) παρατηρήσεις Chafield C., The Analysis of Time Series, An Inroducion, 6 h ediion,. 38 (Chaer 3): Some auhors refer o make he weaker
Χρονοσειρές Μάθημα 3 Ασυσχέτιστες (λευκός θόρυβος) και ανεξάρτητες (iid) παρατηρήσεις Chafield C., The Analysis of Time Series, An Inroducion, 6 h ediion,. 38 (Chaer 3): Some auhors refer o make he weaker
Calculus and Differential Equations page 1 of 17 CALCULUS and DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 alculus and Diffrnial Equaions pag of 7 ALULUS and DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Th following 55 qusions concrn calculus and diffrnial quaions. In his vrsion of h am, h firs choic is always h corrc on. In h acual
alculus and Diffrnial Equaions pag of 7 ALULUS and DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Th following 55 qusions concrn calculus and diffrnial quaions. In his vrsion of h am, h firs choic is always h corrc on. In h acual
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Chapter 7a. Elements of Elasticity, Thermal Stresses
 Chapte 7a lements of lasticit, Themal Stesses Mechanics of mateials method: 1. Defomation; guesswok, intuition, smmet, pio knowledge, epeiment, etc.. Stain; eact o appoimate solution fom defomation. Stess;
Chapte 7a lements of lasticit, Themal Stesses Mechanics of mateials method: 1. Defomation; guesswok, intuition, smmet, pio knowledge, epeiment, etc.. Stain; eact o appoimate solution fom defomation. Stess;
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Approximate System Reliability Evaluation
 Appoximate Sytem Reliability Evaluation Up MTTF Down 0 MTBF MTTR () Time Fo many engineeing ytem component, MTTF MTBF i.e. failue ate, failue fequency, f Fequency, Duation and Pobability Indice: failue
Appoximate Sytem Reliability Evaluation Up MTTF Down 0 MTBF MTTR () Time Fo many engineeing ytem component, MTTF MTBF i.e. failue ate, failue fequency, f Fequency, Duation and Pobability Indice: failue
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, irrotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE + V Φ + i x. Ψ y = Φ. and. Ψ x
 STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
STEADY, INVISCID ( potential flow, iotational) INCOMPRESSIBLE constant Benolli's eqation along a steamline, EQATION MOMENTM constant is a steamline the Steam Fnction is sbsititing into the continit eqation,
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
4.2 Differential Equations in Polar Coordinates
 Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
9.1 Introduction 9.2 Lags in the Error Term: Autocorrelation 9.3 Estimating an AR(1) Error Model 9.4 Testing for Autocorrelation 9.
 9.1 Inroducion 9.2 Lags in he Error Term: Auocorrelaion 9.3 Esimaing an AR(1) Error Model 9.4 Tesing for Auocorrelaion 9.5 An Inroducion o Forecasing: Auoregressive Models 9.6 Finie Disribued Lags 9.7
9.1 Inroducion 9.2 Lags in he Error Term: Auocorrelaion 9.3 Esimaing an AR(1) Error Model 9.4 Tesing for Auocorrelaion 9.5 An Inroducion o Forecasing: Auoregressive Models 9.6 Finie Disribued Lags 9.7
CHAPTER (2) Electric Charges, Electric Charge Densities and Electric Field Intensity
 CHAPTE () Electric Chrges, Electric Chrge Densities nd Electric Field Intensity Chrge Configurtion ) Point Chrge: The concept of the point chrge is used when the dimensions of n electric chrge distriution
CHAPTE () Electric Chrges, Electric Chrge Densities nd Electric Field Intensity Chrge Configurtion ) Point Chrge: The concept of the point chrge is used when the dimensions of n electric chrge distriution
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Problems in curvilinear coordinates
 Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
The Euler Equations! λ 1. λ 2. λ 3. ρ ρu. E = e + u 2 /2. E + p ρ. = de /dt. = dh / dt; h = h( T ); c p. / c v. ; γ = c p. p = ( γ 1)ρe. c v.
 hp://www.nd.ed/~gryggva/cfd-corse/ The Eler Eqaions The Eler Eqaions The Eler eqaions for D flow: + + p = x E E + p where Define E = e + / H = h + /; h = e + p/ Gréar Tryggvason Spring 3 Ideal Gas: p =
hp://www.nd.ed/~gryggva/cfd-corse/ The Eler Eqaions The Eler Eqaions The Eler eqaions for D flow: + + p = x E E + p where Define E = e + / H = h + /; h = e + p/ Gréar Tryggvason Spring 3 Ideal Gas: p =
F19MC2 Solutions 9 Complex Analysis
 F9MC Solutions 9 Complex Analysis. (i) Let f(z) = eaz +z. Then f is ifferentiable except at z = ±i an so by Cauchy s Resiue Theorem e az z = πi[res(f,i)+res(f, i)]. +z C(,) Since + has zeros of orer at
F9MC Solutions 9 Complex Analysis. (i) Let f(z) = eaz +z. Then f is ifferentiable except at z = ±i an so by Cauchy s Resiue Theorem e az z = πi[res(f,i)+res(f, i)]. +z C(,) Since + has zeros of orer at
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
J. of Math. (PRC) u(t k ) = I k (u(t k )), k = 1, 2,, (1.6) , [3, 4] (1.1), (1.2), (1.3), [6 8]
![J. of Math. (PRC) u(t k ) = I k (u(t k )), k = 1, 2,, (1.6) , [3, 4] (1.1), (1.2), (1.3), [6 8] J. of Math. (PRC) u(t k ) = I k (u(t k )), k = 1, 2,, (1.6) , [3, 4] (1.1), (1.2), (1.3), [6 8]](/thumbs/91/107007576.jpg) Vol 36 ( 216 ) No 3 J of Mah (PR) 1, 2, 3 (1, 4335) (2, 4365) (3, 431) :,,,, : ; ; ; MR(21) : 35A1; 35A2 : O17529 : A : 255-7797(216)3-591-7 1 d d [x() g(, x )] = f(, x ),, (11) x = ϕ(), [ r, ], (12) x(
Vol 36 ( 216 ) No 3 J of Mah (PR) 1, 2, 3 (1, 4335) (2, 4365) (3, 431) :,,,, : ; ; ; MR(21) : 35A1; 35A2 : O17529 : A : 255-7797(216)3-591-7 1 d d [x() g(, x )] = f(, x ),, (11) x = ϕ(), [ r, ], (12) x(
CS348B Lecture 10 Pat Hanrahan, Spring 2002
 Page 1 Reflecton Models I Today Types of eflecton models The BRDF and eflectance The eflecton equaton Ideal eflecton and efacton Fesnel effect Ideal dffuse Next lectue Glossy and specula eflecton models
Page 1 Reflecton Models I Today Types of eflecton models The BRDF and eflectance The eflecton equaton Ideal eflecton and efacton Fesnel effect Ideal dffuse Next lectue Glossy and specula eflecton models
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
九十七學年第一學期 PHYS2310 電磁學期中考試題 ( 共兩頁 )
 九十七學年第一學期 PHY 電磁學期中考試題 ( 共兩頁 ) [Giffiths Ch.-] 補考 8// :am :am, 教師 : 張存續記得寫上學號, 班別及姓名等 請依題號順序每頁答一題 Useful fomulas V ˆ ˆ V V = + θ+ V φ ˆ an θ sinθ φ v = ( v) (sin ) + θvθ + v sinθ θ sinθ φ φ. (8%,%) cos
九十七學年第一學期 PHY 電磁學期中考試題 ( 共兩頁 ) [Giffiths Ch.-] 補考 8// :am :am, 教師 : 張存續記得寫上學號, 班別及姓名等 請依題號順序每頁答一題 Useful fomulas V ˆ ˆ V V = + θ+ V φ ˆ an θ sinθ φ v = ( v) (sin ) + θvθ + v sinθ θ sinθ φ φ. (8%,%) cos
Solutions - Chapter 4
 Solutions - Chapter Kevin S. Huang Problem.1 Unitary: Ût = 1 ī hĥt Û tût = 1 Neglect t term: 1 + hĥ ī t 1 īhĥt = 1 + hĥ ī t ī hĥt = 1 Ĥ = Ĥ Problem. Ût = lim 1 ī ] n hĥ1t 1 ī ] hĥt... 1 ī ] hĥnt 1 ī ]
Solutions - Chapter Kevin S. Huang Problem.1 Unitary: Ût = 1 ī hĥt Û tût = 1 Neglect t term: 1 + hĥ ī t 1 īhĥt = 1 + hĥ ī t ī hĥt = 1 Ĥ = Ĥ Problem. Ût = lim 1 ī ] n hĥ1t 1 ī ] hĥt... 1 ī ] hĥnt 1 ī ]
Α Ρ Ι Θ Μ Ο Σ : 6.913
 Α Ρ Ι Θ Μ Ο Σ : 6.913 ΠΡΑΞΗ ΚΑΤΑΘΕΣΗΣ ΟΡΩΝ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΥ Σ τ η ν Π ά τ ρ α σ ή μ ε ρ α σ τ ι ς δ ε κ α τ έ σ σ ε ρ ι ς ( 1 4 ) τ ο υ μ ή ν α Ο κ τ ω β ρ ί ο υ, η μ έ ρ α Τ ε τ ά ρ τ η, τ ο υ έ τ ο υ ς δ
Α Ρ Ι Θ Μ Ο Σ : 6.913 ΠΡΑΞΗ ΚΑΤΑΘΕΣΗΣ ΟΡΩΝ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΥ Σ τ η ν Π ά τ ρ α σ ή μ ε ρ α σ τ ι ς δ ε κ α τ έ σ σ ε ρ ι ς ( 1 4 ) τ ο υ μ ή ν α Ο κ τ ω β ρ ί ο υ, η μ έ ρ α Τ ε τ ά ρ τ η, τ ο υ έ τ ο υ ς δ
