AdS black disk model for small-x DIS
|
|
|
- Σίβύλλα Παπανικολάου
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 AdS black disk model for small-x DIS Miguel S. Costa Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade do Porto [hep-th], [hep-ph] Work with. Cornalba and J. Penedones Rencontres de Moriond, March 2010
2 Motivation QCD is approximately conformal at high energies, for very small probes with r probe Λ QCD 1 Regge limit of high center of mass energy with other kinematic invariants fixed corresponds to low Bjorken - x in DIS.
3 Motivation QCD is approximately conformal at high energies, for very small probes with r probe Λ QCD 1 Regge limit of high center of mass energy with other kinematic invariants fixed corresponds to low Bjorken - x in DIS. Use conformal symmetry and AdS/CFT to make general predictions for conformal limit of DIS in QCD (weak coupling).
4 Deep Inelastic Scattering e γ e Q 2 = q 2 Q>1 Gev α s small X P
5 Deep Inelastic Scattering e γ e Q 2 = q 2 Q>1 Gev α s small X P Optical theorem γ 2 γ γ s = (q + P ) 2 Q2 x X P X = Im P P Regge limit of large s small x
6 Hadronic tensor structure functions F i ( x,q 2 ) = 1 2π Im Π i T ab = i d 4 ye iq y P T { j a (y 1 ) j b (y 3 ) } P (η ab qa q b ) (p a + qa )(p b + qb ) T ab = q 2 Π 1 (x,q 2 ) 2x Q 2 2x 2x Π 2 (x,q 2 )
7 Hadronic tensor structure functions F i ( x,q 2 ) = 1 2π Im Π i T ab = i d 4 ye iq y P T { j a (y 1 ) j b (y 3 ) } P (η ab qa q b ) (p a + qa )(p b + qb ) T ab = q 2 Π 1 (x,q 2 ) 2x Q 2 2x 2x Π 2 (x,q 2 ) Simulate proton with scalar operator O of dimension and off-shellness p 2 = M 2 Λ 2 QCD ( kj ) (2π) d δ T ab (k j )= j a (k 1 ) O(k 2 ) j b (k 3 ) O(k 4 ) j a with dimension ξ =3
8 Regge limit in CFTs F.T. T ab (k i ) A ab (y i ) C.T. B mn (p, p) A mn (x, x) F.T.
9 Regge limit in CFTs F.T. Amplitude depends on 2 cross ratios T ab (k i ) A ab (y i ) B mn = B mn (S, ) C.T. S =4 p p B mn (p, p) F.T. A mn (x, x) H 3 p p + cosh = p p p p Regge limit is S large, fixed
10 Regge limit in CFTs F.T. Amplitude depends on 2 cross ratios T ab (k i ) A ab (y i ) B mn = B mn (S, ) C.T. S =4 p p B mn (p, p) F.T. A mn (x, x) H 3 p p + cosh = p p p p Regge limit is S large, fixed Current conservation p m B mn =0 B i j matrix on H 3 polarization space
11 Regge limit in CFTs F.T. Amplitude depends on 2 cross ratios T ab (k i ) A ab (y i ) B mn = B mn (S, ) C.T. S =4 p p B mn (p, p) F.T. A mn (x, x) H 3 p p + cosh = p p p p Regge limit is S large, fixed Current conservation p m B mn =0 B i j matrix on H 3 polarization space ( )] Regge theory B i j 2πi dν S j(ν) 1 [β 1 (ν) δ i j + β 4 (ν) i j 1 3 δi j Ω iν ()
12 Regge limit in CFTs F.T. Amplitude depends on 2 cross ratios T ab (k i ) A ab (y i ) B mn = B mn (S, )? C.T. S =4 p p B mn (p, p) F.T. A mn (x, x) H 3 p p + cosh = p p p p Regge limit is S large, fixed Current conservation p m B mn =0 B i j matrix on H 3 polarization space ( )] Regge theory B i j 2πi dν S j(ν) 1 [β 1 (ν) δ i j + β 4 (ν) i j 1 3 δi j Ω iν ()
13 AdS/CFT in Regge limit T ab (k j ) 2is d 2 l e iq l dr r 3 d r r 3 (ψ in) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) φ( r) φ ( r) B i j(s, )
14 [1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab AdS/CFT in Regge limit T ab (k j ) 2is d 2 l e iq l dr r 3 d r r 3 (ψ in) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) φ( r) φ ( r) B i j(s, )
15 [1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab AdS/CFT in Regge limit T ab (k j ) 2is d 2 l e iq l dr r 3 d r r 3 (ψ in) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) φ( r) φ ( r) B i j(s, ) r l S = r rs, AdS energy squared r R 2 H 3 cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r, impact parameter
16 [1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab AdS/CFT in Regge limit T ab (k j ) 2is r d 2 l e iq l dr r 3 d r r 3 (ψ in) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) φ( r) φ ( r) B i j(s, ) AdS gauge field wave function l S = r rs, AdS energy squared r R 2 H 3 cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r, impact parameter
17 AdS/CFT in Regge limit T ab (k j ) 2is r d 2 l e iq l dr r 3 d r AdS gauge field wave function AdS scalar wave function r 3 (ψ in) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) φ( r) φ ( r) B i j(s, ) [1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab l S = r rs, AdS energy squared r R 2 H 3 cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r, impact parameter
18 AdS/CFT in Regge limit T ab (k j ) 2is r d 2 l e iq l dr r 3 d r AdS gauge field wave function AdS scalar wave function r 3 (ψ in) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) φ( r) φ ( r) B i j(s, ) [1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab l S = r rs, AdS energy squared r R 2 H 3 cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r, impact parameter CFT impact parameter representation (AdS phase shift)
19 AdS/CFT in Regge limit T ab (k j ) 2is r d 2 l e iq l dr r 3 d r AdS gauge field wave function AdS scalar wave function r 3 (ψ in) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) φ( r) φ ( r) B i j(s, ) [1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab l S = r rs, AdS energy squared r R 2 H 3 cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r, impact parameter CFT impact parameter representation (AdS phase shift) Graviton/Pomeron trajectory [Brower, Polchinski, Strassler, Tan 06] j = j(ν, ᾱ s ), β = β(ν, ᾱ s )
20 AdS black disk model for small-x DIS T ab (k j ) = 2is d 2 l e iq l [ 1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab
21 AdS black disk model for small-x DIS T ab (k j ) = 2is d 2 l e iq l [ 1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab r [ ] 1 e iδ(s,l ab ) dr d r = r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i [1 e iχ(s,)] i j l R 2 H 3 r S = r rs cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r
22 AdS black disk model for small-x DIS T ab (k j ) = 2is d 2 l e iq l [ 1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab r [ ] 1 e iδ(s,l ab ) dr d r = r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i [1 e iχ(s,)] i j l R 2 H 3 r Ψ ab j i (r) =(ψ in ) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) non-normalizable, localized around 0 < r < 1/Q S = r rs cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r
23 AdS black disk model for small-x DIS T ab (k j ) = 2is d 2 l e iq l [ 1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab r [ ] 1 e iδ(s,l ab ) dr d r = r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i [1 e iχ(s,)] i j l R 2 H 3 r Ψ ab j i (r) =(ψ in ) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) non-normalizable, localized around 0 < r < 1/Q S = r rs cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r Φ( r) = φ( r) 2 normalizable, localized around r 1/M
24 AdS black disk model for small-x DIS T ab (k j ) = 2is d 2 l e iq l [ 1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab r [ ] 1 e iδ(s,l ab ) dr d r = r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i [1 e iχ(s,)] i j l R 2 H 3 r Ψ ab j i (r) =(ψ in ) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) non-normalizable, localized around 0 < r < 1/Q S = r rs cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r Φ( r) = φ( r) 2 normalizable, localized around r 1/M S Q x ln Q M
25 AdS black disk model for small-x DIS T ab (k j ) = 2is d 2 l e iq l [ 1 e iδ(s,l ) ] ab r [ ] 1 e iδ(s,l ab ) dr d r = r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i [1 e iχ(s,)] i j l R 2 H 3 r Ψ ab j i (r) =(ψ in ) a i(r)(ψ out ) bj (r) non-normalizable, localized around 0 < r < 1/Q S = r rs cosh = r2 + r 2 + l 2 2r r Φ( r) = φ( r) 2 normalizable, localized around r 1/M S Q x ln Q M At zero momentum transfer d 2 l 2πr r ln r r d sinh
26 At weak coupling T ab =4πs dr d r r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i ln r r d sinh χ i j(s, )
27 At weak coupling T ab =4πs dr d r r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i ln r r d sinh χ i j(s, ) Can estimate growth with linear pomeron exchange. Saddle point gives χ i j 1 N 2 dνβ(ν) e (j(ν) 1) ln S (1+iν) j (ν) ln S = i
28 At weak coupling T ab =4πs dr d r r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i ln r r d sinh χ i j(s, ) Can estimate growth with linear pomeron exchange. Saddle point gives χ i j 1 N 2 dνβ(ν) e (j(ν) 1) ln S (1+iν) j (ν) ln S = i Non-linear effects become important for Im χ i j(s, ) 1 This happens when phase in saddle vanishes ln S S Q x s (S) ω ln S ln Q M s (S) ω ln S B B
29 At weak coupling T ab =4πs dr d r r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i ln r r d sinh χ i j(s, ) Can estimate growth with linear pomeron exchange. Saddle point gives χ i j 1 N 2 dνβ(ν) e (j(ν) 1) ln S (1+iν) j (ν) ln S = i Non-linear effects become important for Im χ i j(s, ) 1 This happens when phase in saddle vanishes ln S S Q x s (S) ω ln S ln Q M s (S) ω ln S inear pomeron gives ω = ij (ν s ) = 2.44ᾱ s B B
30 At weak coupling T ab =4πs dr d r r 3 r 3 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i ln r r d sinh χ i j(s, ) Can estimate growth with linear pomeron exchange. Saddle point gives χ i j 1 N 2 dνβ(ν) e (j(ν) 1) ln S (1+iν) j (ν) ln S = i Non-linear effects become important for Im χ i j(s, ) 1 This happens when phase in saddle vanishes ln S S Q x s (S) ω ln S ln Q M s (S) ω ln S inear pomeron gives ω = ij (ν s ) = 2.44ᾱ s From DIS geometric scaling ω 0.14 B B
31 AdS black disk Im χ i j(s, ) 1 Black disk in AdS (or in conformal QCD) [1 e iχ(s,)] i j = Θ ( s (S) ) δ i j
32 AdS black disk Im χ i j(s, ) 1 Black disk in AdS (or in conformal QCD) [1 e iχ(s,)] i j = Θ ( s (S) ) δ i j T ab 4πis dr d r r 2 r 2 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i s ln r r d sinh δ i j Black disk ln S S Q x 2πis dr r 2 d r r 2 Ψab i i (r) Φ( r) [ (sr r) ω +(sr r) ω r r r r ] B B
33 AdS black disk Im χ i j(s, ) 1 Black disk in AdS (or in conformal QCD) [1 e iχ(s,)] i j = Θ ( s (S) ) δ i j T ab 4πis dr d r r 2 r 2 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i s ln r r d sinh δ i j Black disk ln S S Q x 2πis dr r 2 d r r 2 Ψab i i (r) Φ( r) [ (sr r) ω +(sr r) ω r r r r ] dominant for low x B B
34 AdS black disk Im χ i j(s, ) 1 Black disk in AdS (or in conformal QCD) [1 e iχ(s,)] i j = Θ ( s (S) ) δ i j T ab 4πis dr d r r 2 r 2 Ψab j (r) Φ( r) i s ln r r d sinh δ i j Black disk ln S S Q x 2πis dr r 2 d r r 2 Ψab i i (r) Φ( r) [ (sr r) ω +(sr r) ω r r r r ] dominant for low x B B It is all AdS (or CFT) kinematics. Only dynamical information is: - on-set of black disk region - the target wave function ( integrals) r d r h(ω) Φ( r) = r 2 ω M 1+ω
35 Universal ratio from kinematics deep inside disk T ab 2πis 1+ω dr i Ψab r2 ω i (r) d r Φ( r) r 2 ω ln S S Q x T îĵ = δîĵ Π 1, T x 2 (Π 2 2xΠ 1 ) B B
36 Universal ratio from kinematics deep inside disk T ab 2πis 1+ω dr i Ψab r2 ω i (r) d r Φ( r) r 2 ω ln S S Q x T îĵ = δîĵ Π 1, T x 2 (Π 2 2xΠ 1 ) F 2 2xF 1 x ω (Q/M) 1+ω π 5 2 Γ 3 ( ) 3+ω Ch(ω) ( 2 ), 3Γ 4+ω 2xF 1 x ω (Q/M) 1+ω π 5 ( 2 Γ 5+ω 2 2 ) Γ ( 3+ω 2 12 Γ ( 4+ω 2 ) ( Γ 1+ω ) 2 ) Ch(ω) B B
37 Universal ratio from kinematics deep inside disk T ab 2πis 1+ω dr i Ψab r2 ω i (r) d r Φ( r) r 2 ω ln S S Q x T îĵ = δîĵ Π 1, T x 2 (Π 2 2xΠ 1 ) F 2 2xF 1 x ω (Q/M) 1+ω π 5 2 Γ 3 ( ) 3+ω Ch(ω) ( 2 ), 3Γ 4+ω 2xF 1 x ω (Q/M) 1+ω π 5 ( 2 Γ 5+ω 2 2 ) Γ ( 3+ω 2 12 Γ ( 4+ω 2 ) ( Γ 1+ω ) 2 ) Ch(ω) Q/x GeV B B GeV Q
38 Universal ratio from kinematics deep inside disk T ab 2πis 1+ω dr i Ψab r2 ω i (r) d r Φ( r) r 2 ω ln S S Q x T îĵ = δîĵ Π 1, T x 2 (Π 2 2xΠ 1 ) F 2 2xF 1 x ω (Q/M) 1+ω π 5 2 Γ 3 ( ) 3+ω Ch(ω) ( 2 ), 3Γ 4+ω 2xF 1 x ω (Q/M) 1+ω π 5 ( 2 Γ 5+ω 2 Ratio is fixed by power in 1/x 2 ) Γ ( 3+ω 2 12 Γ ( 4+ω 2 ) ( Γ 1+ω ) 2 ) Ch(ω) Q/x GeV B B 10 2 F F 2xF ω F T 2xF 1 3+ω GeV Q
39 Final Comments Is deeply saturated DIS showing us a black disk in AdS (or in conformal QCD)?
40 Final Comments Is deeply saturated DIS showing us a black disk in AdS (or in conformal QCD)? Non-conformal extension Understand AdS unitarization
41 Final Comments Is deeply saturated DIS showing us a black disk in AdS (or in conformal QCD)? Non-conformal extension Understand AdS unitarization THANK YOU
42 ADDITIONA SIDES
43 Use different Poincaré patches to cover each operator P 4 P 3 P 4 P 3 x 4 x 3 x 1 x 2 P 1 P 2 P 1 P 2
44 Cross ratios P 4 P 3 Translations in or Special Conformal in P 1,P 3 P 2,P 4 x 1,3 x 1,3 + a, x 2,4 x 2,4 + O(a 2 ) x 4 x 3 Translations in P 2,P 4 or Special Conformal in P 1,P 3 x 1 x 2 x 1,3 x 1,3 + O(b 2 ), x 2,4 x 2,4 + b P 1 P 2 x x 1 x 3, x x 2 x 4 Invariants orentz Transformations x Λx, x Λ x Dilatations x λx, x 1 λ x σ 2 = x 2 x 2, cosh ρ = x x x x Residual transverse conformal group SO(1, 1) SO(3, 1) Regge limit σ 0 fixed ρ
45 j n O Single t-channel conformal partial wave gives in Regge limit j m (J, d2 + iν ) O A mn σ 1 J [ E(ρ) η mn + F (ρ) xm x n x 2 + G(ρ) xm x n x 2 + H(ρ) xm x n + x m x n x x ] Sum over spins and dimensions gives for a Regge pole j(ν) [Cornalba 07] 4 A mn 2πi dνσ 1 j(ν) α k (ν) D mn k Ω iν (ρ) k=1 Ω iν (ρ) harmonic functions on H 3 ( H3 + ν 2 +1 ) Ω iν (ρ) =0 Ω iν (ρ) = ν sin νρ 4π 2 sinh ρ D mn 1 = η mn xm x n x 2 D mn 2 = xm x n x 2 D mn 3 = x m n + x n m D mn 4 = x 2 m n +(x m n + x n m ) 1 3 (η mn xm x n x 2 ) x 2 x
46 Graviton/Pomeron Regge trajectory [Brower, Polchinski, Strassler, Tan 06] Trajectory depends on t Hooft coupling j = j(ν, ᾱ s ) α k = α k (ν, ᾱ s ) Strong coupling (N=4 graviton trajectory) Weak coupling (BFK Pomeron trajectory) ) )) j 2 4+ν2 4π ᾱ s j 1 + ᾱ s (2Ψ(1) Ψ ( 1+iν 2 Ψ ( 1 iν 2 α k real j a j b α k imaginary j a j b From now on weak coupling O O O O
47 Geometric scaling F 2 /Q 2 10 [Stasto et al] ln S 0.01 B s ω ln S τ B B BFK pomeron gives ω =2.44 ᾱ s ω fixed experimentally by geometric scaling to be ω =0.138 ± [Gelis et al]
48 Real Data Compare with Data F 2 /Q Y = 5.0 Y = 4.8 Y = 4.6 With 4 parameters can reproduce available data Y = 4.4 Y = 4.2 Y = Y = 3.8 Y = 3.6 GeV Q/x Q [GeV] GeV Q
NLO BFKL and anomalous dimensions of light-ray operators
 NLO BFKL and anomalous dimensions of light-ray operators I. Balitsky JLAB & ODU (Non)Perturbative QFT 13 June 013 (Non)Perturbative QFT 13 June 013 1 / Outline Light-ray operators. Regge limit in the coordinate
NLO BFKL and anomalous dimensions of light-ray operators I. Balitsky JLAB & ODU (Non)Perturbative QFT 13 June 013 (Non)Perturbative QFT 13 June 013 1 / Outline Light-ray operators. Regge limit in the coordinate
Space-Time Symmetries
 Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories
 Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
Three coupled amplitudes for the πη, K K and πη channels without data
 Three coupled amplitudes for the πη, K K and πη channels without data Robert Kamiński IFJ PAN, Kraków and Łukasz Bibrzycki Pedagogical University, Kraków HaSpect meeting, Kraków, V/VI 216 Present status
Three coupled amplitudes for the πη, K K and πη channels without data Robert Kamiński IFJ PAN, Kraków and Łukasz Bibrzycki Pedagogical University, Kraków HaSpect meeting, Kraków, V/VI 216 Present status
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Graded Refractive-Index
 Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님
 상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
wave energy Superposition of linear plane progressive waves Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture Oblique Plane Waves:
 3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
L. F avart. CLAS12 Workshop Genova th of Feb CLAS12 workshop Feb L.Favart p.1/28
 L. F avart I.I.H.E. Université Libre de Bruxelles H Collaboration HERA at DESY CLAS Workshop Genova - 4-8 th of Feb. 9 CLAS workshop Feb. 9 - L.Favart p./8 e p Integrated luminosity 96- + 3-7 (high energy)
L. F avart I.I.H.E. Université Libre de Bruxelles H Collaboration HERA at DESY CLAS Workshop Genova - 4-8 th of Feb. 9 CLAS workshop Feb. 9 - L.Favart p./8 e p Integrated luminosity 96- + 3-7 (high energy)
Higher spin gauge theories and their CFT duals
 Higher spin gauge theories and their CFT duals E-mail: hikida@phys-h.keio.ac.jp 2 AdS Vasiliev AdS/CFT 4 Vasiliev 3 O(N) 3 Vasiliev 2 W N 1 AdS/CFT g µν Vasiliev AdS [1] AdS/CFT anti-de Sitter (AdS) (CFT)
Higher spin gauge theories and their CFT duals E-mail: hikida@phys-h.keio.ac.jp 2 AdS Vasiliev AdS/CFT 4 Vasiliev 3 O(N) 3 Vasiliev 2 W N 1 AdS/CFT g µν Vasiliev AdS [1] AdS/CFT anti-de Sitter (AdS) (CFT)
Hadronic Tau Decays at BaBar
 Hadronic Tau Decays at BaBar Swagato Banerjee Joint Meeting of Pacific Region Particle Physics Communities (DPF006+JPS006 Honolulu, Hawaii 9 October - 3 November 006 (Page: 1 Hadronic τ decays Only lepton
Hadronic Tau Decays at BaBar Swagato Banerjee Joint Meeting of Pacific Region Particle Physics Communities (DPF006+JPS006 Honolulu, Hawaii 9 October - 3 November 006 (Page: 1 Hadronic τ decays Only lepton
DiracDelta. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C
 DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves
 .0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
Coupling of a Jet-Slot Oscillator With the Flow-Supply Duct: Flow-Acoustic Interaction Modeling
 1th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, May 006 interactions Coupling of a Jet-Slot Oscillator With the Flow-Supply Duct: Interaction M. Glesser 1, A. Billon 1, V. Valeau, and A. Sakout 1 mglesser@univ-lr.fr
1th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, May 006 interactions Coupling of a Jet-Slot Oscillator With the Flow-Supply Duct: Interaction M. Glesser 1, A. Billon 1, V. Valeau, and A. Sakout 1 mglesser@univ-lr.fr
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
General 2 2 PT -Symmetric Matrices and Jordan Blocks 1
 General 2 2 PT -Symmetric Matrices and Jordan Blocks 1 Qing-hai Wang National University of Singapore Quantum Physics with Non-Hermitian Operators Max-Planck-Institut für Physik komplexer Systeme Dresden,
General 2 2 PT -Symmetric Matrices and Jordan Blocks 1 Qing-hai Wang National University of Singapore Quantum Physics with Non-Hermitian Operators Max-Planck-Institut für Physik komplexer Systeme Dresden,
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α
 Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Lecture 21: Scattering and FGR
 ECE-656: Fall 009 Lecture : Scattering and FGR Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA Review: characteristic times τ ( p), (, ) == S p p
ECE-656: Fall 009 Lecture : Scattering and FGR Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA Review: characteristic times τ ( p), (, ) == S p p
Dark matter from Dark Energy-Baryonic Matter Couplings
 Dark matter from Dark Energy-Baryonic Matter Coulings Alejandro Avilés 1,2 1 Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM, México 2 Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Nucleares (ININ) México January 10, 2010
Dark matter from Dark Energy-Baryonic Matter Coulings Alejandro Avilés 1,2 1 Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM, México 2 Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Nucleares (ININ) México January 10, 2010
Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev Model as Liouville Quantum Mechanics
 Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev Model as Liouville Quantum Mechanics Dmitry Bagrets Nucl. Phys. B 9, 9 (06) arxiv: 607.00694 Alexander Altland Univ. zu Köln Alex Kamenev Univ. of Minnesota PCS IBS Workshop, Daejeon,
Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev Model as Liouville Quantum Mechanics Dmitry Bagrets Nucl. Phys. B 9, 9 (06) arxiv: 607.00694 Alexander Altland Univ. zu Köln Alex Kamenev Univ. of Minnesota PCS IBS Workshop, Daejeon,
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Equations. BSU Math 275 sec 002,003 Fall 2018 (Ultman) Final Exam Notes 1. du dv. FTLI : f (B) f (A) = f dr. F dr = Green s Theorem : y da
 BSU Math 275 sec 002,003 Fall 2018 (Ultman) Final Exam Notes 1 Equations r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) k r = r (t) t s = r = r (t) t r(u, v) = x(u, v) î + y(u, v) ĵ + z(u, v) k S = ( ( ) r r u r v = u
BSU Math 275 sec 002,003 Fall 2018 (Ultman) Final Exam Notes 1 Equations r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) k r = r (t) t s = r = r (t) t r(u, v) = x(u, v) î + y(u, v) ĵ + z(u, v) k S = ( ( ) r r u r v = u
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Dong Liu State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics University of Science and Technology of China
 Dong Liu State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics University of Science and Technology of China ISSP, Erice, 7 Outline Introduction of BESIII experiment Motivation of the study Data sample
Dong Liu State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics University of Science and Technology of China ISSP, Erice, 7 Outline Introduction of BESIII experiment Motivation of the study Data sample
Large β 0 corrections to the energy levels and wave function at N 3 LO
 Large β corrections to the energy levels and wave function at N LO Matthias Steinhauser, University of Karlsruhe LCWS5, March 5 [In collaboration with A. Penin and V. Smirnov] M. Steinhauser, LCWS5, March
Large β corrections to the energy levels and wave function at N LO Matthias Steinhauser, University of Karlsruhe LCWS5, March 5 [In collaboration with A. Penin and V. Smirnov] M. Steinhauser, LCWS5, March
Constitutive Relations in Chiral Media
 Constitutive Relations in Chiral Media Covariance and Chirality Coefficients in Biisotropic Materials Roger Scott Montana State University, Department of Physics March 2 nd, 2010 Optical Activity Polarization
Constitutive Relations in Chiral Media Covariance and Chirality Coefficients in Biisotropic Materials Roger Scott Montana State University, Department of Physics March 2 nd, 2010 Optical Activity Polarization
HW 3 Solutions 1. a) I use the auto.arima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA(3,1)
 HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations
 On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
ECE 468: Digital Image Processing. Lecture 8
 ECE 468: Digital Image Processing Lecture 8 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Image Reconstruction from Projections X-ray computed tomography: X-raying an object from different directions
ECE 468: Digital Image Processing Lecture 8 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Image Reconstruction from Projections X-ray computed tomography: X-raying an object from different directions
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
F19MC2 Solutions 9 Complex Analysis
 F9MC Solutions 9 Complex Analysis. (i) Let f(z) = eaz +z. Then f is ifferentiable except at z = ±i an so by Cauchy s Resiue Theorem e az z = πi[res(f,i)+res(f, i)]. +z C(,) Since + has zeros of orer at
F9MC Solutions 9 Complex Analysis. (i) Let f(z) = eaz +z. Then f is ifferentiable except at z = ±i an so by Cauchy s Resiue Theorem e az z = πi[res(f,i)+res(f, i)]. +z C(,) Since + has zeros of orer at
Analytical Expression for Hessian
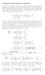 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
The mass and anisotropy profiles of nearby galaxy clusters from the projected phase-space density
 The mass and anisotropy profiles of nearby galaxy clusters from the projected phase-space density 5..29 Radek Wojtak Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center collaboration: Ewa Łokas, Gary Mamon, Stefan
The mass and anisotropy profiles of nearby galaxy clusters from the projected phase-space density 5..29 Radek Wojtak Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center collaboration: Ewa Łokas, Gary Mamon, Stefan
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
is like multiplying by the conversion factor of. Dividing by 2π gives you the
 Chapter Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Answer Ke. Radian Measure Answers. π. π. π. π. 7π. π 7. 70 8. 9. 0 0. 0. 00. 80. Multipling b π π is like multipling b the conversion factor of. Dividing b 0 gives
Chapter Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Answer Ke. Radian Measure Answers. π. π. π. π. 7π. π 7. 70 8. 9. 0 0. 0. 00. 80. Multipling b π π is like multipling b the conversion factor of. Dividing b 0 gives
ω ω ω ω ω ω+2 ω ω+2 + ω ω ω ω+2 + ω ω+1 ω ω+2 2 ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ω+1 ω ω2 ω ω2 + ω ω ω2 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω ω+1 ω ω2 + ω ω+1 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω
 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl
 Around Vortices: from Cont. to Quantum Mech. Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl Maicon José Benvenutti (UNICAMP)
Around Vortices: from Cont. to Quantum Mech. Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl Maicon José Benvenutti (UNICAMP)
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 2017 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations
 ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 07 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations Answers to problems on Midterm Examination #, Spring 009. x(t) = r(t + ) r(t ) u(t ) r(t ) + r(t 3) + u(t +
ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 07 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations Answers to problems on Midterm Examination #, Spring 009. x(t) = r(t + ) r(t ) u(t ) r(t ) + r(t 3) + u(t +
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
CONSULTING Engineering Calculation Sheet
 E N G I N E E R S Consulting Engineers jxxx 1 Structure Design - EQ Load Definition and EQ Effects v20 EQ Response Spectra in Direction X, Y, Z X-Dir Y-Dir Z-Dir Fundamental period of building, T 1 5.00
E N G I N E E R S Consulting Engineers jxxx 1 Structure Design - EQ Load Definition and EQ Effects v20 EQ Response Spectra in Direction X, Y, Z X-Dir Y-Dir Z-Dir Fundamental period of building, T 1 5.00
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
Duality Symmetry in High Energy Scattering
 Duality Symmetry in High Energy Scattering Alex Prygarin Hamburg University 10 March 010 Outline Introduction BFKL Hamiltonian Duality symmetry of forward BFKL Duality symmetry of BK and non-forward BFKL
Duality Symmetry in High Energy Scattering Alex Prygarin Hamburg University 10 March 010 Outline Introduction BFKL Hamiltonian Duality symmetry of forward BFKL Duality symmetry of BK and non-forward BFKL
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Eulerian Simulation of Large Deformations
 Eulerian Simulation of Large Deformations Shayan Hoshyari April, 2018 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 / 11 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 Muscle Animation 2 / 11 Some Applications
Eulerian Simulation of Large Deformations Shayan Hoshyari April, 2018 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 / 11 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 Muscle Animation 2 / 11 Some Applications
Oscillatory Gap Damping
 Oscillatory Gap Damping Find the damping due to the linear motion of a viscous gas in in a gap with an oscillating size: ) Find the motion in a gap due to an oscillating external force; ) Recast the solution
Oscillatory Gap Damping Find the damping due to the linear motion of a viscous gas in in a gap with an oscillating size: ) Find the motion in a gap due to an oscillating external force; ) Recast the solution
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
4.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves
 .0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 08 Lecture 6 Copyright c 08 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved..0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6 4.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive
.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 08 Lecture 6 Copyright c 08 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved..0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6 4.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals. Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz
 Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz ybridization Valence Bond Approach to bonding sp 3 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py + Ψ 2 pz) sp 2 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py)
Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz ybridization Valence Bond Approach to bonding sp 3 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py + Ψ 2 pz) sp 2 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py)
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations
 Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Appendix A. Curvilinear coordinates. A.1 Lamé coefficients. Consider set of equations. ξ i = ξ i (x 1,x 2,x 3 ), i = 1,2,3
 Appendix A Curvilinear coordinates A. Lamé coefficients Consider set of equations ξ i = ξ i x,x 2,x 3, i =,2,3 where ξ,ξ 2,ξ 3 independent, single-valued and continuous x,x 2,x 3 : coordinates of point
Appendix A Curvilinear coordinates A. Lamé coefficients Consider set of equations ξ i = ξ i x,x 2,x 3, i =,2,3 where ξ,ξ 2,ξ 3 independent, single-valued and continuous x,x 2,x 3 : coordinates of point
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
CE 530 Molecular Simulation
 C 53 olecular Siulation Lecture Histogra Reweighting ethods David. Kofke Departent of Cheical ngineering SUNY uffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu Histogra Reweighting ethod to cobine results taken at different
C 53 olecular Siulation Lecture Histogra Reweighting ethods David. Kofke Departent of Cheical ngineering SUNY uffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu Histogra Reweighting ethod to cobine results taken at different
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Bessel functions. ν + 1 ; 1 = 0 for k = 0, 1, 2,..., n 1. Γ( n + k + 1) = ( 1) n J n (z). Γ(n + k + 1) k!
 Bessel functions The Bessel function J ν (z of the first kind of order ν is defined by J ν (z ( (z/ν ν Γ(ν + F ν + ; z 4 ( k k ( Γ(ν + k + k! For ν this is a solution of the Bessel differential equation
Bessel functions The Bessel function J ν (z of the first kind of order ν is defined by J ν (z ( (z/ν ν Γ(ν + F ν + ; z 4 ( k k ( Γ(ν + k + k! For ν this is a solution of the Bessel differential equation
Computing the Macdonald function for complex orders
 Macdonald p. 1/1 Computing the Macdonald function for complex orders Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University Macdonald p. 2/1 Integral representation K ν (x) = complex order ν = α + iβ e x
Macdonald p. 1/1 Computing the Macdonald function for complex orders Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University Macdonald p. 2/1 Integral representation K ν (x) = complex order ν = α + iβ e x
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
Parametrized Surfaces
 Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Lifting Entry (continued)
 ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Solar Neutrinos: Fluxes
 Solar Neutrinos: Fluxes pp chain Sun shines by : 4 p 4 He + e + + ν e + γ Solar Standard Model Fluxes CNO cycle e + N 13 =0.707MeV He 4 C 1 C 13 p p p p N 15 N 14 He 4 O 15 O 16 e + =0.997MeV O17
Solar Neutrinos: Fluxes pp chain Sun shines by : 4 p 4 He + e + + ν e + γ Solar Standard Model Fluxes CNO cycle e + N 13 =0.707MeV He 4 C 1 C 13 p p p p N 15 N 14 He 4 O 15 O 16 e + =0.997MeV O17
Galatia SIL Keyboard Information
 Galatia SIL Keyboard Information Keyboard ssignments The main purpose of the keyboards is to provide a wide range of keying options, so many characters can be entered in multiple ways. If you are typing
Galatia SIL Keyboard Information Keyboard ssignments The main purpose of the keyboards is to provide a wide range of keying options, so many characters can be entered in multiple ways. If you are typing
9.09. # 1. Area inside the oval limaçon r = cos θ. To graph, start with θ = 0 so r = 6. Compute dr
 9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
9.9 #. Area inside the oval limaçon r = + cos. To graph, start with = so r =. Compute d = sin. Interesting points are where d vanishes, or at =,,, etc. For these values of we compute r:,,, and the values
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
ExpIntegralE. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. Traditional name. Traditional notation. Mathematica StandardForm notation
 ExpIntegralE Notations Traditional name Exponential integral E Traditional notation E Mathematica StandardForm notation ExpIntegralE, Primary definition 06.34.0.000.0 E t t t ; Re 0 Specific values Specialied
ExpIntegralE Notations Traditional name Exponential integral E Traditional notation E Mathematica StandardForm notation ExpIntegralE, Primary definition 06.34.0.000.0 E t t t ; Re 0 Specific values Specialied
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACEG
 Lecture 4 Material behavior: Constitutive equations Field of the game Print version Lecture on Theory of lasticity and Plasticity of Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACG 4.1 Contents
Lecture 4 Material behavior: Constitutive equations Field of the game Print version Lecture on Theory of lasticity and Plasticity of Dr. D. Dinev, Department of Structural Mechanics, UACG 4.1 Contents
Α Ρ Ι Θ Μ Ο Σ : 6.913
 Α Ρ Ι Θ Μ Ο Σ : 6.913 ΠΡΑΞΗ ΚΑΤΑΘΕΣΗΣ ΟΡΩΝ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΥ Σ τ η ν Π ά τ ρ α σ ή μ ε ρ α σ τ ι ς δ ε κ α τ έ σ σ ε ρ ι ς ( 1 4 ) τ ο υ μ ή ν α Ο κ τ ω β ρ ί ο υ, η μ έ ρ α Τ ε τ ά ρ τ η, τ ο υ έ τ ο υ ς δ
Α Ρ Ι Θ Μ Ο Σ : 6.913 ΠΡΑΞΗ ΚΑΤΑΘΕΣΗΣ ΟΡΩΝ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΥ Σ τ η ν Π ά τ ρ α σ ή μ ε ρ α σ τ ι ς δ ε κ α τ έ σ σ ε ρ ι ς ( 1 4 ) τ ο υ μ ή ν α Ο κ τ ω β ρ ί ο υ, η μ έ ρ α Τ ε τ ά ρ τ η, τ ο υ έ τ ο υ ς δ
Quantum Electrodynamics
 Quantum Electrodynamics Ling-Fong Li Institute Slide_06 QED / 35 Quantum Electrodynamics Lagrangian density for QED, Equations of motion are Quantization Write L= L 0 + L int L = ψ x γ µ i µ ea µ ψ x mψ
Quantum Electrodynamics Ling-Fong Li Institute Slide_06 QED / 35 Quantum Electrodynamics Lagrangian density for QED, Equations of motion are Quantization Write L= L 0 + L int L = ψ x γ µ i µ ea µ ψ x mψ
Non-Gaussianity from Lifshitz Scalar
 COSMO/CosPA 200 September 27, 200 Non-Gaussianity from Lifshitz Scalar Takeshi Kobayashi (Tokyo U.) based on: arxiv:008.406 with Keisuke Izumi, Shinji Mukohyama Lifshitz scalars with z=3 obtain super-horizon,
COSMO/CosPA 200 September 27, 200 Non-Gaussianity from Lifshitz Scalar Takeshi Kobayashi (Tokyo U.) based on: arxiv:008.406 with Keisuke Izumi, Shinji Mukohyama Lifshitz scalars with z=3 obtain super-horizon,
Tridiagonal matrices. Gérard MEURANT. October, 2008
 Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation. Mathematica StandardForm notation
 KelvinKei Notations Traditional name Kelvin function of the second kind Traditional notation kei Mathematica StandardForm notation KelvinKei Primary definition 03.5.0.000.0 kei kei 0 Specific values Values
KelvinKei Notations Traditional name Kelvin function of the second kind Traditional notation kei Mathematica StandardForm notation KelvinKei Primary definition 03.5.0.000.0 kei kei 0 Specific values Values
Local Approximation with Kernels
 Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
38 Te(OH) 6 2NH 4 H 2 PO 4 (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4
 Fig. A-1-1. Te(OH) NH H PO (NH ) HPO (TAAP). Projection of the crystal structure along the b direction [Ave]. 9 1. 7.5 ( a a )/ a [1 ] ( b b )/ b [1 ] 5..5 1.5 1 1.5 ( c c )/ c [1 ].5 1. 1.5. Angle β 1.
Fig. A-1-1. Te(OH) NH H PO (NH ) HPO (TAAP). Projection of the crystal structure along the b direction [Ave]. 9 1. 7.5 ( a a )/ a [1 ] ( b b )/ b [1 ] 5..5 1.5 1 1.5 ( c c )/ c [1 ].5 1. 1.5. Angle β 1.
Reminders: linear functions
 Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian
 The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
Matrices and vectors. Matrix and vector. a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = b 1 b 2. b m. R m n, b = = ( a ij. a m1 a m2 a mn. def
 Matrices and vectors Matrix and vector a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = a m1 a m2 a mn def = ( a ij ) R m n, b = b 1 b 2 b m Rm Matrix and vectors in linear equations: example E 1 : x 1 + x 2 + 3x 4 =
Matrices and vectors Matrix and vector a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = a m1 a m2 a mn def = ( a ij ) R m n, b = b 1 b 2 b m Rm Matrix and vectors in linear equations: example E 1 : x 1 + x 2 + 3x 4 =
