Approximation of dynamic boundary condition: The Allen Cahn equation
|
|
|
- ÊΝηρεύς Κολιάτσος
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 1 Approximation of dynamic boundary condition: The Allen Cahn equation Matthias Liero I.M.A.T.I. Pavia and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin 6 th Singular Days 2010 Berlin
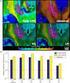
2 Introduction Interfacial dynamics in semiconductor models Schematic cross-section of thin film a-si:h photovoltaic cell Interaction with domain walls in spinodal decomposition Cahn Hilliard equation 2
3 3 AC Equation with Dynamic Boundary Condition Sprekels and Wu [2010]: Ω R d, d 2, with C 2 boundary t u u + F b (u) = 0, in Ω [0, T ] t φ φ + ν u + φ + F s(φ) = 0, on Ω [0, T ] u = φ, on Ω [0, T ] u(0, ) = u 0, φ(0, ) = φ 0 Laplace Beltrami operator on Ω Cahn Hilliard equation (R. Kenzler et al. [2001]) Caginalp system (R. Chill, E. Fasangova and J. Pruess [2006]) Nonisothermal Allen Cahn equation (C. Gal and M. Grasselli, A. Miranville [2008])
4 Layer Approximation Ω r b t u a b u + F b (u) = 0, in Ω [0, T ]
5 4 Layer Approximation Ω ε def = {x R d : (y, η) Ω (0, ε), x = y + ην(y)} Ω ε Ω ε r b t u a b u + F b (u) = 0, in Ω [0, T ]
6 4 Layer Approximation Ω ε def = {x R d : (y, η) Ω (0, ε), x = y + ην(y)} Ω ε Ω ε r b t u a b u + F b (u) = 0, in Ω [0, T ] r s ε δ t φ a s ε α φ + ε β F s(φ) = 0, in Ω ε [0, T ] u = φ on Ω [0, T ] a b ν u a s ε α ν φ = 0, on Ω [0, T ] a s ε α ν φ = 0, on Ω ε \ Ω [0, T ]
7 Layer Approximation Ω ε def = {x R d : (y, η) Ω (0, ε), x = y + ην(y)} Ω ε Ω ε r b t u a b u + F b (u) = 0, in Ω [0, T ] r s ε 1 t φ a s ε α φ + ε 1 F s(φ) = 0, in Ω ε [0, T ] u = φ on Ω [0, T ] a b ν u a s ε α ν φ = 0, on Ω [0, T ] a s ε α ν φ = 0, on Ω ε \ Ω [0, T ] Today: δ = 1, β = 1, α (, 1)
8 Setting r b t u a b u + F b r (u) = 0, s ε t φ a s ε α φ + 1 ε F s(φ) = 0 Spaces Ṽ ε = { (u, φ) H 1 (Ω) H 1 (Ω ε ) : u Ω = φ Ω } H ε = L 2 (Ω) L 2 (Ω ε ) Energy functionals a b a s ε Ẽ ε (u, φ) = 2 u 2 +F b (u)dx+ Ωε α 2 φ ε F s(φ)dx Ω Dissipation functionals R ε ( u, φ) = Ω r b 2 u 2 dx + 1 ε Ω ε r s 2 φ 2 dx 5
9 6 Setting In this setting r b t u a b u + F b r (u) = 0, s ε t φ a s ε α φ + 1 ε F s(φ) = 0 is formally equivalent to 0 = D R ε ( u, φ) + D Ẽ ε (u, φ) (Force balance) Basic existence theory yields solutions (u ε, φ ε ) L (0, T ; Ṽε) H 1 (0, T ; H ε )
10 Transformation Ω Ω Ω ε Change of coordinates x = y + ην(y) y ην(y) x x (y, η) Ω (0, ε) Scaling η = εη, η (0, 1) Mapping L 2 (Ω ε ) L 2 ( Ω (0, 1)) Spaces Ṽ ε V = {(u, φ) H 1 (Ω) H 1 ( Ω (0, 1)) : u Ω = φ η=0 } H ε H = L 2 (Ω) L 2 ( Ω (0, 1))
11 8 Transformation Energy functionals a b E ε (u, φ) = Ω 2 u 2 + F b (u)dx 1 [ ] + asε α+1 2 ( B ε φ ε 2 η φ 2 ) + F s (φ) J ε dηda Ω 0 Dissipation functionals R ε ( u, φ) = Ω r b2 u 2 dx + Ω 1 0 r s 2 φ 2 J ε dηda Transformed solutions solve DE ε (u ε, φ ε ) + DR ε ( u ε, φ ε ) = 0
12 8 Transformation Energy functionals E ε (u, φ) = + Ω 1 0 E b (u) [ ] asε α+1 2 ( B ε φ ε 2 η φ 2 ) + F s (φ) J ε dηda Dissipation functionals R ε ( u, φ) = Ω r b2 u 2 dx + Ω 1 0 r s 2 φ 2 J ε dηda Transformed solutions solve DE ε (u ε, φ ε ) + DR ε ( u ε, φ ε ) = 0
13 9 A priori estimates E ε (u ε (t), φ ε (t)) + t 0 R ε( u ε, φ ε )dτ E ε (u ε (0), φ ε (0)) Case α 1: Case α ( 1, 1): (u ε, φ ε ) L (0,T ;V ) C (u ε, φ ε ) L (0,T ;V ) C with V := {(u, φ) H 1 (Ω) L 2 ( Ω (0, 1)) : η φ L 2 ( Ω (0, 1)), u Ω = φ η=0 } Bounded dissipation functional ( u ε, φ ε ) L 2 (0,T ;H) C
14 10 Convergent subsequence We have (u ε, φ ε ) (u, φ) in L (0, T ; V ) (resp. in L (0, T ; V )) (u ε, φ ε ) (u, φ) in H 1 (0, T ; H) In particular = t [0, T ] : z ε (t) z(t) in H Moreover, z ε C w ([0, T ], V ) = t [0, T ] : z ε (t) z(t) in V with V = V for α 1 or Ṽ = V for α ( 1, 1)
15 with G ε = DR ε 11 λ-convexity F b and F s are λ-convex, i.e., λ R u F b (u) + λ u 2, φ F s (φ) + λ φ 2 are convex, e.g. C 1,1 -perturbation of a convex function, double well potential W(u) = 1 4 (1 u2 ) 2 F b (u v) F b (u) F b (u)v λ v 2, u, v R Consequence: For z ε = (u ε, φ ε ) E ε (z ε ẑ ε ) + λ ẑ ε 2 H E ε (z ε ) DE ε (z ε ), ẑ ε, ẑ ε V Hence force balance equivalent to E ε (z ε (t) ẑ ε ) + λ ẑ ε 2 H E ε (z ε (t)) + G ε ż ε (t), ẑ ε, ẑ ε V
16 12 Γ-convergence Definition: (Attouch [1984], Braides [2002], Dal Maso [1993]) I 0 : Y R Γ-limit of sequence (I ε ) ε>0 w.r.t. topology τ iff (i) liminf estimate: τ y ε y = I0 (y) lim inf I ε (y ε ) ε 0 (ii) limsup estimate (existence of recovery sequence): τ y Y (ŷ ε ) ε>0 : y ε y and I0 (y) lim sup I ε (ŷ ε ). ε 0 Theorem: (I ε ) ε>0 equi-coercive ( ε>0 {I ε E} precompact) and Γ I ε I 0 ; then min I 0 = lim min I Y ε 0 ε. Y (y ε ) ε>0 minimizers of I ε = cluster points y are minimizers of I 0
17 13 Γ-convergence Minimization problems: Homogenization, Two-scale convergence Singular limits (Cahn Hilliard Sharp interface) Young measure relaxation, penalization Rate independent systems (Mielke, Roubíček, Stefanelli [2008]) Two-scale Homogenization (Mielke & Timofte [2007], Hanke [2009]) Damage to Delamination (Mielke, Thomas, Roubíček in preparation) Dimension reduction in linearized elastoplasticity (Mielke & L. in preparation) Hamiltonian systems (Mielke [2008]) Gradient flows (Sandier & Serfaty [2004])
18 Γ-convergence of the Energies E ε (u, φ) = E b (u)+ Ω 1 0 [ ] asε α+1 2 ( B ε φ ε 2 η φ 2 ) + F s (φ) J ε dηda (i) Case α = 1 V { R, E 0 : E b (u) + a s (u, φ) Ω 2 φ 2 +F s (φ)da η φ = 0, otherwise (ii) Case α < 1 V R {, E 0 : E b (u) + H d 1 ( Ω)F s (φ)da (u, φ) φ constant, otherwise
19 Γ-convergence of the Energies E ε (u, φ) = E b (u)+ Ω 1 0 [ ] asε α+1 2 ( B ε φ ε 2 η φ 2 ) + F s (φ) J ε dηda (i) Case α = 1 V { R, E 0 : E b (u) + a s (u, φ) Ω 2 φ 2 +F s (φ)da (u, φ) V, otherwise (ii) Case α < 1 V R {, E 0 : E b (u) + H d 1 ( Ω)F s (φ)da (u, φ) φ constant, otherwise
20 Γ-convergence of the Energies E ε (u, φ) = E b (u)+ Ω 1 0 [ ] asε α+1 2 ( B ε φ ε 2 η φ 2 ) + F s (φ) J ε dηda (i) Case α = 1 V { R, E 0 : E b (u) + a s (u, φ) Ω 2 φ 2 +F s (φ)da (u, φ) V, otherwise (ii) Case α < 1 V R {, E 0 : E b (u) + H d 1 ( Ω)F s (φ)da (u, φ) V c, (u, φ) otherwise
21 15 Γ-convergence of the Energies (iii) Case α ( 1, 1) V := {(u, φ) H 1 (Ω) L 2 ( Ω (0, 1)) : η φ L 2 ( Ω (0, 1)), u Ω = φ η=0 } V R {, E 0 : E b (u) + (u, φ) Ω F s (φ)da η φ = 0, otherwise In the following: F s convex
22 15 Γ-convergence of the Energies (iii) Case α ( 1, 1) V := {(u, φ) H 1 (Ω) L 2 ( Ω (0, 1)) : η φ L 2 ( Ω (0, 1)), u Ω = φ η=0 } V R {, E 0 : E b (u) + (u, φ) Ω F s (φ)da (u, φ) V, otherwise In the following: F s convex
23 16 Main Result Theorem Let z ε = (u ε, φ ε ) be solutions w.r.t. (E ε, R ε ) with (u ε, φ ε ) (u, φ) in L (0, T ; V ) (resp. in L (0, T ; V )) (u ε, φ ε ) (u, φ) in H 1 (0, T ; H) then z = (u, φ) is a solution w.r.t. (E 0, R 0 ), i.e. E 0 (z(t) ẑ)+λ ẑ 2 H E 0 (z(t))+ G 0 ż(t), ẑ, ẑ ε V (resp. V ) with G 0 = DR 0. In particular, z solves G 0 (ż) + DE 0 (u, φ) = 0
24 17 The limit equations Formally equivalent to r b t u a b u + F b (u) = 0, in Ω [0, T ] Case α = 1 r s t φ a b φ + F s(φ) + a b ν u = 0, on Ω [0, T ] Case α < 1 r s t φ + a b [ ν u] + F s(φ) = 0, in [0, T ] u = φ = const, on Ω [0, T ] α ( 1, 1) r s t φ + a b ν u + F s(φ) = 0, on Ω [0, T ]
25 18 Sketch of proof Set ẑ ε = z ε z ε, with z ε (t) recovery sequence for z(t) z(t). T 0 E ε(z ε ) + λ z ε z ε 2 H dt T 0 E ε(z ε ) + G ε ż ε, z ε z ε dt 2. Integration by parts T 0 G εż ε, z ε z ε dt = T 0 G εz ε, z ε dt + R ε (z ε (T )) R ε (z ε (0)) 3. Passing to the limit + Integration by parts T 0 E 0(z) + λ z z 2 H dt T 0 E 0(z) G 0 ż, z z dt 4. Sequence z δ z ẑ in L 2 (0, T ; V 0 ). By arbitrariness of ẑ E 0 (z(t) ẑ) + λ ẑ 2 H E 0 (z(t)) + G 0 ż(t), ẑ, ẑ V/V
26 19 Outlook Different scalings in dissipation potential More complex dissipation potentials (Heat equation with entropy as driving potential) Interfaces
27 19 Outlook Different scalings in dissipation potential More complex dissipation potentials (Heat equation with entropy as driving potential) Interfaces Thank You
Phase-Field Force Convergence
 Phase-Field Force Convergence Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Quantitative Biology Graduate Program UC San Diego Collaborators: Shibin Dai and Jianfeng Lu Funding: NSF School of Mathematical Sciences
Phase-Field Force Convergence Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Quantitative Biology Graduate Program UC San Diego Collaborators: Shibin Dai and Jianfeng Lu Funding: NSF School of Mathematical Sciences
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Local Approximation with Kernels
 Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
ES440/ES911: CFD. Chapter 5. Solution of Linear Equation Systems
 ES440/ES911: CFD Chapter 5. Solution of Linear Equation Systems Dr Yongmann M. Chung http://www.eng.warwick.ac.uk/staff/ymc/es440.html Y.M.Chung@warwick.ac.uk School of Engineering & Centre for Scientific
ES440/ES911: CFD Chapter 5. Solution of Linear Equation Systems Dr Yongmann M. Chung http://www.eng.warwick.ac.uk/staff/ymc/es440.html Y.M.Chung@warwick.ac.uk School of Engineering & Centre for Scientific
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation. Tanguy Rivoal. Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble 1
 Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Arithmetical applications of lagrangian interpolation Tanguy Rivoal Institut Fourier CNRS and Université de Grenoble Conference Diophantine and Analytic Problems in Number Theory, The 00th anniversary
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
DiracDelta. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl
 Around Vortices: from Cont. to Quantum Mech. Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl Maicon José Benvenutti (UNICAMP)
Around Vortices: from Cont. to Quantum Mech. Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl Maicon José Benvenutti (UNICAMP)
Reminders: linear functions
 Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Nonlinear Fourier transform for the conductivity equation. Visibility and Invisibility in Impedance Tomography
 Nonlinear Fourier transform for the conductivity equation Visibility and Invisibility in Impedance Tomography Kari Astala University of Helsinki CoE in Analysis and Dynamics Research What is the non linear
Nonlinear Fourier transform for the conductivity equation Visibility and Invisibility in Impedance Tomography Kari Astala University of Helsinki CoE in Analysis and Dynamics Research What is the non linear
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian
 The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)
![2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p) 2. Let H 1 and H 2 be Hilbert spaces and let T : H 1 H 2 be a bounded linear operator. Prove that [T (H 1 )] = N (T ). (6p)](/thumbs/40/21364883.jpg) Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
Uppsala Universitet Matematiska Institutionen Andreas Strömbergsson Prov i matematik Funktionalanalys Kurs: F3B, F4Sy, NVP 2005-03-08 Skrivtid: 9 14 Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Manuella skrivdon, Kreyszigs bok
12. Radon-Nikodym Theorem
 Tutorial 12: Radon-Nikodym Theorem 1 12. Radon-Nikodym Theorem In the following, (Ω, F) is an arbitrary measurable space. Definition 96 Let μ and ν be two (possibly complex) measures on (Ω, F). We say
Tutorial 12: Radon-Nikodym Theorem 1 12. Radon-Nikodym Theorem In the following, (Ω, F) is an arbitrary measurable space. Definition 96 Let μ and ν be two (possibly complex) measures on (Ω, F). We say
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Modelli Matematici. Gianni Gilardi. Cortona, giugno Transizione di fase solido solido in un sistema meccanico
 Modelli Matematici e Problemi Analitici per Materiali Speciali Cortona, 25 29 giugno 2001 Transizione di fase solido solido in un sistema meccanico Gianni Gilardi Dipartimento di Matematica F. Casorati
Modelli Matematici e Problemi Analitici per Materiali Speciali Cortona, 25 29 giugno 2001 Transizione di fase solido solido in un sistema meccanico Gianni Gilardi Dipartimento di Matematica F. Casorati
Solvability of Brinkman-Forchheimer equations of flow in double-diffusive convection
 Solvability of Brinkman-Forchheimer equations of flow in double-diffusive convection Mitsuharu ÔTANI Waseda University, Tokyo, JAPAN One Forum, Two Cities: Aspect of Nonlinear PDEs 29 August, 211 Mitsuharu
Solvability of Brinkman-Forchheimer equations of flow in double-diffusive convection Mitsuharu ÔTANI Waseda University, Tokyo, JAPAN One Forum, Two Cities: Aspect of Nonlinear PDEs 29 August, 211 Mitsuharu
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Ηλεκτρονικοί Υπολογιστές IV
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ηλεκτρονικοί Υπολογιστές IV Εισαγωγή στα δυναμικά συστήματα Διδάσκων: Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Αθανάσιος Σταυρακούδης Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ηλεκτρονικοί Υπολογιστές IV Εισαγωγή στα δυναμικά συστήματα Διδάσκων: Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Αθανάσιος Σταυρακούδης Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό
Testing for Indeterminacy: An Application to U.S. Monetary Policy. Technical Appendix
 Testing for Indeterminacy: An Application to U.S. Monetary Policy Technical Appendix Thomas A. Lubik Department of Economics Johns Hopkins University Frank Schorfheide Department of Economics University
Testing for Indeterminacy: An Application to U.S. Monetary Policy Technical Appendix Thomas A. Lubik Department of Economics Johns Hopkins University Frank Schorfheide Department of Economics University
SCITECH Volume 13, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION Published online: March 29, 2018
 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequality for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x, y, z X.
 Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
Math 446 Homework 3 Solutions. (1). (i): Reverse triangle inequalit for metrics: Let (X, d) be a metric space and let x,, z X. Prove that d(x, z) d(, z) d(x, ). (ii): Reverse triangle inequalit for norms:
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Lecture 26: Circular domains
 Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without eplicit written permission from the copyright owner. 1 Lecture 6: Circular domains
Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. Not to be copied, used, or revised without eplicit written permission from the copyright owner. 1 Lecture 6: Circular domains
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom
 Technische Universität Graz Institut für Festkörperphysik Student project Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom Molecular and Solid State Physics 53. submitted on: 3. November 9 by: Markus Krammer
Technische Universität Graz Institut für Festkörperphysik Student project Variational Wavefunction for the Helium Atom Molecular and Solid State Physics 53. submitted on: 3. November 9 by: Markus Krammer
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Iterated trilinear fourier integrals with arbitrary symbols
 Cornell University ICM 04, Satellite Conference in Harmonic Analysis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea August 6, 04 Motivation the Coifman-Meyer theorem with classical paraproduct(979) B(f, f )(x) :=
Cornell University ICM 04, Satellite Conference in Harmonic Analysis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea August 6, 04 Motivation the Coifman-Meyer theorem with classical paraproduct(979) B(f, f )(x) :=
Nonlinear Fourier transform and the Beltrami equation. Visibility and Invisibility in Impedance Tomography
 Nonlinear Fourier transform and the Beltrami equation Visibility and Invisibility in Impedance Tomography Kari Astala University of Helsinki Beltrami equation: z f(z) = µ(z) z f(z) non linear Fourier transform
Nonlinear Fourier transform and the Beltrami equation Visibility and Invisibility in Impedance Tomography Kari Astala University of Helsinki Beltrami equation: z f(z) = µ(z) z f(z) non linear Fourier transform
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
Appendix to On the stability of a compressible axisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe. By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee
 Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations
 On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Forced Pendulum Numerical approach
 Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER
 ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER Abstract. We define ordinal arithmetic and show laws of Left- Monotonicity, Associativity, Distributivity, some minor related properties and the Cantor Normal Form.
ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER Abstract. We define ordinal arithmetic and show laws of Left- Monotonicity, Associativity, Distributivity, some minor related properties and the Cantor Normal Form.
ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2
 ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος 2007-08 -- Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2 Ημερομηνία Παραδόσεως: Παρασκευή
ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος 2007-08 -- Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2 Ημερομηνία Παραδόσεως: Παρασκευή
Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs
 Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs Philippe Jaming Bordeaux Fourier Workshop 2013, Renyi Institute Joint work with K. Kellay Heisenberg Uniqueness Pairs µ : finite measure on R 2 µ(x, y) = R 2 e i(sx+ty) dµ(s,
Heisenberg Uniqueness pairs Philippe Jaming Bordeaux Fourier Workshop 2013, Renyi Institute Joint work with K. Kellay Heisenberg Uniqueness Pairs µ : finite measure on R 2 µ(x, y) = R 2 e i(sx+ty) dµ(s,
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries
 1 Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries Ulf Kähler Chemnitz University of Technology Workshop on Fast Boundary Element Methods in Industrial Applications
1 Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries Ulf Kähler Chemnitz University of Technology Workshop on Fast Boundary Element Methods in Industrial Applications
The k-α-exponential Function
 Int Journal of Math Analysis, Vol 7, 213, no 11, 535-542 The --Exponential Function Luciano L Luque and Rubén A Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National University of Nordeste Av Libertad 554 34 Corrientes,
Int Journal of Math Analysis, Vol 7, 213, no 11, 535-542 The --Exponential Function Luciano L Luque and Rubén A Cerutti Faculty of Exact Sciences National University of Nordeste Av Libertad 554 34 Corrientes,
Limit theorems under sublinear expectations and probabilities
 Limit theorems under sublinear expectations and probabilities Xinpeng LI Shandong University & Université Paris 1 Young Researchers Meeting on BSDEs, Numerics and Finance 4 July, Oxford 1 / 25 Outline
Limit theorems under sublinear expectations and probabilities Xinpeng LI Shandong University & Université Paris 1 Young Researchers Meeting on BSDEs, Numerics and Finance 4 July, Oxford 1 / 25 Outline
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
STABILITY FOR RAYLEIGH-BENARD CONVECTIVE SOLUTIONS OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION
 STABILITY FOR RAYLEIGH-BENARD CONVECTIVE SOLUTIONS OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION L.Arkeryd, Chalmers, Goteborg, Sweden, R.Esposito, University of L Aquila, Italy, R.Marra, University of Rome, Italy, A.Nouri,
STABILITY FOR RAYLEIGH-BENARD CONVECTIVE SOLUTIONS OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION L.Arkeryd, Chalmers, Goteborg, Sweden, R.Esposito, University of L Aquila, Italy, R.Marra, University of Rome, Italy, A.Nouri,
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
forms This gives Remark 1. How to remember the above formulas: Substituting these into the equation we obtain with
 Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Mock Exam 7. 1 Hong Kong Educational Publishing Company. Section A 1. Reference: HKDSE Math M Q2 (a) (1 + kx) n 1M + 1A = (1) =
 Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
Online Appendix I. 1 1+r ]}, Bψ = {ψ : Y E A S S}, B W = +(1 s)[1 m (1,0) (b, e, a, ψ (0,a ) (e, a, s); q, ψ, W )]}, (29) exp( U(d,a ) (i, x; q)
![Online Appendix I. 1 1+r ]}, Bψ = {ψ : Y E A S S}, B W = +(1 s)[1 m (1,0) (b, e, a, ψ (0,a ) (e, a, s); q, ψ, W )]}, (29) exp( U(d,a ) (i, x; q) Online Appendix I. 1 1+r ]}, Bψ = {ψ : Y E A S S}, B W = +(1 s)[1 m (1,0) (b, e, a, ψ (0,a ) (e, a, s); q, ψ, W )]}, (29) exp( U(d,a ) (i, x; q)](/thumbs/85/92973547.jpg) Online Appendix I Appendix D Additional Existence Proofs Denote B q = {q : A E A S [0, +r ]}, Bψ = {ψ : Y E A S S}, B W = {W : I E A S R}. I slightly abuse the notation by defining B q (L q ) the subset
Online Appendix I Appendix D Additional Existence Proofs Denote B q = {q : A E A S [0, +r ]}, Bψ = {ψ : Y E A S S}, B W = {W : I E A S R}. I slightly abuse the notation by defining B q (L q ) the subset
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
Research Article Existence of Positive Solutions for m-point Boundary Value Problems on Time Scales
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 29, Article ID 189768, 12 pages doi:1.1155/29/189768 Research Article Existence of Positive Solutions for m-point Boundary
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 29, Article ID 189768, 12 pages doi:1.1155/29/189768 Research Article Existence of Positive Solutions for m-point Boundary
Lifting Entry (continued)
 ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
Sharp Interface Limit for the Navier Stokes Korteweg Equations
 Sharp Interface Limit for the Navier Stokes Korteweg Equations Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg Johannes Daube (Joint work with H. Abels, C. Kraus and D. Kröner) 11th DFG-CNRS Workshop Micro-Macro Modeling
Sharp Interface Limit for the Navier Stokes Korteweg Equations Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg Johannes Daube (Joint work with H. Abels, C. Kraus and D. Kröner) 11th DFG-CNRS Workshop Micro-Macro Modeling
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Section 8.2 Graphs of Polar Equations
 Section 8. Graphs of Polar Equations Graphing Polar Equations The graph of a polar equation r = f(θ), or more generally F(r,θ) = 0, consists of all points P that have at least one polar representation
Section 8. Graphs of Polar Equations Graphing Polar Equations The graph of a polar equation r = f(θ), or more generally F(r,θ) = 0, consists of all points P that have at least one polar representation
Asymptotic stability of boundary layers to the Euler-Poisson equation arising in plasma physics. Based on joint research with
 Asymptotic stability of boundary layers to the Euler-Poisson equation arising in plasma physics (, Based on joint research with ( ( Contents 1. Physical background of the problem 2. Mathematical formulation
Asymptotic stability of boundary layers to the Euler-Poisson equation arising in plasma physics (, Based on joint research with ( ( Contents 1. Physical background of the problem 2. Mathematical formulation
From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams
 From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams WIR 2014 Fanny He f.he@bath.ac.uk Alexis Saurin alexis.saurin@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr 12 July 2014 The Λµ-calculus Syntax of Λµ t ::= x λx.t (t)u
From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams WIR 2014 Fanny He f.he@bath.ac.uk Alexis Saurin alexis.saurin@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr 12 July 2014 The Λµ-calculus Syntax of Λµ t ::= x λx.t (t)u
Commutative Monoids in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets
 Commutative Monoids in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets S K Mala #1, Dr. MM Shanmugapriya *2 1 PhD Scholar in Mathematics, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu- 641021 Assistant Professor of Mathematics,
Commutative Monoids in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets S K Mala #1, Dr. MM Shanmugapriya *2 1 PhD Scholar in Mathematics, Karpagam University, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu- 641021 Assistant Professor of Mathematics,
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Homomorphism in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Automata
 International Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics Systems. ISSN 2248-9940 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 39-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijfms.htm Homomorphism in Intuitionistic
International Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics Systems. ISSN 2248-9940 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 39-45 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijfms.htm Homomorphism in Intuitionistic
The Spiral of Theodorus, Numerical Analysis, and Special Functions
 Theo p. / The Spiral of Theodorus, Numerical Analysis, and Special Functions Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University Theo p. 2/ Theodorus of ca. 46 399 B.C. Theo p. 3/ spiral of Theodorus 6
Theo p. / The Spiral of Theodorus, Numerical Analysis, and Special Functions Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University Theo p. 2/ Theodorus of ca. 46 399 B.C. Theo p. 3/ spiral of Theodorus 6
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Discontinuous Hermite Collocation and Diagonally Implicit RK3 for a Brain Tumour Invasion Model
 1 Discontinuous Hermite Collocation and Diagonally Implicit RK3 for a Brain Tumour Invasion Model John E. Athanasakis Applied Mathematics & Computers Laboratory Technical University of Crete Chania 73100,
1 Discontinuous Hermite Collocation and Diagonally Implicit RK3 for a Brain Tumour Invasion Model John E. Athanasakis Applied Mathematics & Computers Laboratory Technical University of Crete Chania 73100,
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
P AND P. P : actual probability. P : risk neutral probability. Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P. For example:
 (B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
(B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
GLOBAL WEAK SOLUTIONS TO COMPRESSIBLE QUANTUM NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS WITH DAMPING
 GLOBAL WEAK SOLUTIOS TO COMPRESSIBLE QUATUM AVIER-STOKES EQUATIOS WITH DAMPIG ALEXIS F. VASSEUR AD CHEG YU Abstract. The global-in-time existence of weak solutions to the barotropic compressible quantum
GLOBAL WEAK SOLUTIOS TO COMPRESSIBLE QUATUM AVIER-STOKES EQUATIOS WITH DAMPIG ALEXIS F. VASSEUR AD CHEG YU Abstract. The global-in-time existence of weak solutions to the barotropic compressible quantum
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님
 상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
상대론적고에너지중이온충돌에서 제트입자와관련된제동복사 박가영 인하대학교 윤진희교수님, 권민정교수님 Motivation Bremsstrahlung is a major rocess losing energies while jet articles get through the medium. BUT it should be quite different from low energy
The Negative Neumann Eigenvalues of Second Order Differential Equation with Two Turning Points
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 009, no., 6-66 The Negative Neumann Eigenvalues of Second Order Differential Equation with Two Turning Points A. Neamaty and E. A. Sazgar Department of Mathematics,
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 009, no., 6-66 The Negative Neumann Eigenvalues of Second Order Differential Equation with Two Turning Points A. Neamaty and E. A. Sazgar Department of Mathematics,
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Credit Risk. Finance and Insurance - Stochastic Analysis and Practical Methods Spring School Jena, March 2009
 Credit Risk. Finance and Insurance - Stochastic Analysis and Practical Methods Spring School Jena, March 2009 1 IV. Hedging of credit derivatives 1. Two default free assets, one defaultable asset 1.1 Two
Credit Risk. Finance and Insurance - Stochastic Analysis and Practical Methods Spring School Jena, March 2009 1 IV. Hedging of credit derivatives 1. Two default free assets, one defaultable asset 1.1 Two
Divergence for log concave functions
 Divergence or log concave unctions Umut Caglar The Euler International Mathematical Institute June 22nd, 2013 Joint work with C. Schütt and E. Werner Outline 1 Introduction 2 Main Theorem 3 -divergence
Divergence or log concave unctions Umut Caglar The Euler International Mathematical Institute June 22nd, 2013 Joint work with C. Schütt and E. Werner Outline 1 Introduction 2 Main Theorem 3 -divergence
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
NonEquilibrium Thermodynamics of Flowing Systems: 2
 *Following the development in Beris and Edwards, 1994, Section 9.2 NonEquilibrium Thermodynamics of Flowing Systems: 2 Antony N. Beris Schedule: Multiscale Modeling and Simulation of Complex Fluids Center
*Following the development in Beris and Edwards, 1994, Section 9.2 NonEquilibrium Thermodynamics of Flowing Systems: 2 Antony N. Beris Schedule: Multiscale Modeling and Simulation of Complex Fluids Center
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines
 New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
New bounds for spherical two-distance sets and equiangular lines Michigan State University Oct 8-31, 016 Anhui University Definition If X = {x 1, x,, x N } S n 1 (unit sphere in R n ) and x i, x j = a
D. BAINOV, YU. DOMSHLAK, AND S. MILUSHEVA
 GEORGIAN MATHEMATICAL JOURNAL: Vol. 3, No. 1, 1996, 11-26 PARTIAL AVERAGING FOR IMPULSIVE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH SUPREMUM D. BAINOV, YU. DOMSHLAK, AND S. MILUSHEVA Abstract. Partial averaging for
GEORGIAN MATHEMATICAL JOURNAL: Vol. 3, No. 1, 1996, 11-26 PARTIAL AVERAGING FOR IMPULSIVE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH SUPREMUM D. BAINOV, YU. DOMSHLAK, AND S. MILUSHEVA Abstract. Partial averaging for
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Space-Time Symmetries
 Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Elements of Information Theory
 Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C
 DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
Graded Refractive-Index
 Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
Graded Refractive-Index Common Devices Methodologies for Graded Refractive Index Methodologies: Ray Optics WKB Multilayer Modelling Solution requires: some knowledge of index profile n 2 x Ray Optics for
