Gap Safe Screening Rules for Sparse-Group Lasso
|
|
|
- Σωστράτη Βιτάλη
- 5 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Gap Safe Screening Rules for Sparse-Group Lasso Eugene Ndiaye Olivier Fercoq, Alexandre Gramfort, Joseph Salmon LTCI, CNRS, Télécom ParisTech, Université Paris-Saclay, 75013, Paris, France Olivier Alexandre Joseph
2 Sparse regression y P R n : signal X rx 1,..., x p s P R nˆp : design matrix y Xβ ` ε where ε is a noise and p " n. Objective: approximate y «X with a sparse vector P R p The Lasso estimator Tibshirani (1996): Ωpβq }β} 1 P arg min βpr p ˆ 1 2 y Xβ 2 2 loooooomoooooon ` λ Ωpβq loomoon data fitting sparsity
3 Sparse regression y P R n : signal X rx 1,..., x p s P R nˆp : design matrix y Xβ ` ε where ε is a noise and p " n. Objective: approximate y «X with a sparse vector P R p The Lasso estimator Tibshirani (1996): Ωpβq }β} 1 P arg min βpr p ˆ 1 2 y Xβ 2 2 loooooomoooooon ` λ Ωpβq loomoon data fitting sparsity
4 Sparsity inducing norms l 1 : Ωpβq }β} 1 l 1 {l 2 : Ωpβq ÿ gpg w g β g 2 l 1 l 1 {l 2 : Ωpβq τ β 1 ` p1 τq ÿ gpg w g β g 2 where w g ě 0 is the weight of the group g and τ P p0, 1q.
5 Climate dataset Group of 7 features [Air Temperature, Precipitable water, Relative humidity, Pressure, Sea Level Pressure, Horizontal Wind Speed, Vertical Wind Speed]
6 Convex optimization problem P arg min βpr p ˆ 1 2 y Xβ 2 2 loooooomoooooon data fitting ` λ Ωpβq loomoon sparsity Algorithms ISTA/FISTA Beck & Teboulle (2009) Coordinate descent Friedman et al. (2007)
7 Convex optimization problem P arg min βpr p ˆ 1 2 y Xβ 2 2 loooooomoooooon data fitting ` λ Ωpβq loomoon sparsity Algorithms ISTA/FISTA Beck & Teboulle (2009) Coordinate descent Friedman et al. (2007)
8 How can we speed-up those algorithms by using sparsity information? Support: p S λ : tj P rps, Sparsity: p S λ ăă p. j 0u.
9 How can we speed-up those algorithms by using sparsity information? Support: p S λ : tj P rps, Sparsity: p S λ ăă p. j 0u. Idea: Solve the optimization problem by restricting to the support
10 How can we speed-up those algorithms by using sparsity information? Support: p S λ : tj P rps, Sparsity: p S λ ăă p. j 0u. Idea: Solve the optimization problem by restricting to the support The support p S λ is unknown!!!
11 How can we speed-up those algorithms by using sparsity information? Support: p S λ : tj P rps, Sparsity: p S λ ăă p. j 0u. Idea: Solve the optimization problem by restricting to the support The support p S λ is unknown!!!
12 Optimality condition Bf px q tz P R d P R d, f pyq ě f px q ` z J py x qu If f is differentiable at x : Bf px q t f px qu. Fermat s rule : For any convex function f : R d Ñ R: x P arg min xpr d f pxq ðñ 0 P Bf px q.
13 Optimality condition Bf px q tz P R d P R d, f pyq ě f px q ` z J py x qu If f is differentiable at x : Bf px q t f px qu. Fermat s rule : For any convex function f : R d Ñ R: x P arg min xpr d f pxq ðñ 0 P Bf px q.
14 Optimality condition Bf px q tz P R d P R d, f pyq ě f px q ` z J py x qu If f is differentiable at x : Bf px q t f px qu. Fermat s rule : For any convex function f : R d Ñ R: x P arg min xpr d f pxq ðñ 0 P Bf px q.
15 Optimality condition Bf px q tz P R d P R d, f pyq ě f px q ` z J py x qu If f is differentiable at x : Bf px q t f px qu. Fermat s rule : For any convex function f : R d Ñ R: x P arg min xpr d f pxq ðñ 0 P Bf px q.
16 Critical threshold: λ max Objective primal function: Fermat s rule: P λ pβq 1 2 y Xβ 2 2 ` λωpβq. x P arg min xpr d f pxq ðñ 0 P Bf px q. 0 P arg min P λ pβq ðñ 0 P BP λ p0q X J y ( ` λbωp0q βpr p ðñ Ω D px J yq ď λ Dual norm: Ω D pξq : max xβ, ξy Ωpβqď1
17 Critical threshold: λ max Objective primal function: Fermat s rule: P λ pβq 1 2 y Xβ 2 2 ` λωpβq. x P arg min xpr d f pxq ðñ 0 P Bf px q. 0 P arg min P λ pβq ðñ 0 P BP λ p0q X J y ( ` λbωp0q βpr p ðñ Ω D px J yq ď λ Dual norm: Ω D pξq : max xβ, ξy Ωpβqď1
18 First screening rule 0 P arg min P λ pβq ðñ Ω D px J yq ď λ βpr p Let λ max : Ω D px J yq. For all λ ě λ max, we have 0. From now on, we only consider the case λ ă λ max.
19 Duality Primal problem Dual problem Feasible set Strong duality P arg min 2 y Xβ 2 2 looooooooooooomooooooooooooon ` λωpβq βpr p 1 P λ pβq ˆθ 1 arg max θp X 2 y 2 2 λ2 2 θ y 2 λ looooooooooooomooooooooooooon2 D λ pθq X tθ P R n : Ω D px J θq ď 1u P λ p q D λ pˆθ q KKT s optimality conditions λˆθ y X plink equationq, X J ˆθ P BΩp q psub-differential inclusionq.
20 Screening rules for separable norms Ωpβq ÿ gpg Ω g pβ g q, Ω D pβq max gpg ΩD g pβ g ą P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0.
21 Screening rules for separable norms Ωpβq ÿ gpg Ω g pβ g q, Ω D pβq max gpg ΩD g pβ g ą P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Proof: sub-differential P G, X J g ˆθ P BΩ g p g q.
22 Screening rules for separable norms Ωpβq ÿ gpg Ω g pβ g q, Ω D pβq max gpg ΩD g pβ g ą P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Proof: sub-differential P G, Xg J ˆθ P BΩ g p g q. Sub-differential of a norm # tz P R d : Ω D pzq ď 1u B BΩpxq Ω D, if x 0, tz P R d : Ω D pzq 1 and z J x Ωpxqu, otherwise.
23 Screening rules for separable norms Ωpβq ÿ gpg Ω g pβ g q, Ω D pβq max gpg ΩD g pβ g ą P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Proof: sub-differential P G, Xg J ˆθ P BΩ g p g q. Sub-differential of a norm # tz P R d : Ω D pzq ď 1u B BΩpxq Ω D, if x 0, tz P R d : Ω D pzq 1 and z J x Ωpxqu, otherwise. g 0 ùñ Ω D g px J g ˆθ q 1.
24 Screening rules for separable norms Ωpβq ÿ gpg Ω g pβ g q, Ω D pβq max gpg ΩD g pβ g ą P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Proof: sub-differential P G, Xg J ˆθ P BΩ g p g q. Sub-differential of a norm # tz P R d : Ω D pzq ď 1u B BΩpxq Ω D, if x 0, tz P R d : Ω D pzq 1 and z J x Ωpxqu, otherwise. g 0 ùñ Ω D g px J g ˆθ q 1.
25 Screening rule for P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Ωpβq β 1, Ω D pξq max jprps ξ P rps, X J j ˆθ ă 1 ùñ j 0
26 Screening rule for Group P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Ωpβq ÿ gpg w g β g 2, Ω D pξq max P G, X J g ˆθ 2 w g ă 1 ùñ g 0 ξ g 2 w g
27 Screening rule for Sparse-Group P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Ωpβq ÿ gpg τ β g 1 ` p1 τqw g β g 2 Ω D pξq max gpg ξ g ɛg τ ` p1 τqw g ɛ-norm Burdakov (1988), Burdakov & Merkulov (2002) ɛ P r0, 1s, x ɛ is the solution in ν of dÿ p x i p1 ɛqνq 2` pɛνq 2. i 1
28 Screening rule for Sparse-Group P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Ωpβq ÿ gpg τ β g 1 ` p1 τqw g β g 2 Ω D pξq max gpg ξ g ɛg τ ` p1 τqw g ɛ-norm Burdakov (1988), Burdakov & Merkulov (2002) ɛ P r0, 1s, x ɛ is the solution in ν of dÿ p x i p1 ɛqνq 2` pɛνq 2. i 1
29 Screening for the Sparse-Group P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ ξ Ω D g ɛg g pξ g q τ ` p1 τqw g Group level screening: X J ˆθ g P G, ă 1 ùñ τ ` p1 τqw g g 0. g 0.
30 Screening for the Sparse-Group P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ ξ Ω D g ɛg g pξ g q τ ` p1 τqw g Group level screening: X J ˆθ g P G, ă 1 ùñ τ ` p1 τqw g Feature level screening: g 0. g P g, X J j ˆθ ă τ ùñ j 0.
31 Screening for the Sparse-Group P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ ξ Ω D g ɛg g pξ g q τ ` p1 τqw g Group level screening: X J ˆθ g P G, ă 1 ùñ τ ` p1 τqw g Feature level screening: g 0. g P g, X J j ˆθ ă τ ùñ j 0.
32 Screening rule for separable P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. ˆθ IS UNKNOWN!!!
33 Screening rule for separable P G, Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. ˆθ IS UNKNOWN!!!
34 Safe screening rules Find a Safe region R such that ˆθ P R Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă max θpr ΩD g `X J g θ ă 1 ùñ g 0.
35 Safe screening rules Find a Safe region R such that ˆθ P R Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă max θpr ΩD g `X J g θ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Desirable properties of a Safe region R as small as possible Computation of max θpr Ω D g `X J g θ is cheap
36 Safe screening rules Find a Safe region R such that ˆθ P R Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă max θpr ΩD g `X J g θ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Desirable properties of a Safe region R as small as possible Computation of max θpr Ω D g `X J g θ is cheap Ball as a safe region: Bpc, rq Ω D g `X J g c ` rω D g px g q ă 1 ùñ g 0.
37 Safe screening rules Find a Safe region R such that ˆθ P R Ω D g X J g ˆθ ă max θpr ΩD g `X J g θ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Desirable properties of a Safe region R as small as possible Computation of max θpr Ω D g `X J g θ is cheap Ball as a safe region: Bpc, rq Ω D g `X J g c ` rω D g px g q ă 1 ùñ g 0.
38 How to construct a safe region R such that ˆθ P R?
39 Geometrical interpretation of the dual ˆθ 1 arg max θp X 2 y 2 λ2 2 θ y 2 λ X tθ P R n : Ω D px J θq ď 1u. ˆθ arg min θp X θ y y λ : Π X λ.
40 Geometrical interpretation of the dual ˆθ 1 arg max θp X 2 y 2 λ2 2 θ y 2 λ X tθ P R n : Ω D px J θq ď 1u. ˆθ arg min θp X θ y y λ : Π X λ.
41 Visualization of the feasible set X tθ P R n : Ω D px J θq ď 1u. (a) Lasso (b) Group-Lasso (c) Sparse-Group Lasso
42 Seminal Safe Region ˆ El Ghaoui et al. (2012) : ˆθ y P B λ, y y λ max λ
43 Dynamic Safe Region Bonnefoy et al. (2014) : ˆθ P B ` y λ, θ k y λ
44 Dynamic Safe Region Bonnefoy et al. (2014) : ˆθ P B ` y λ, θ k y λ
45 Dynamic Safe Region Bonnefoy et al. (2014) : ˆθ P B ` y λ, θ k y λ
46 Critical limitations of those methods Can we do better?
47 Critical limitations of those methods Can we do better?
48 Yes we can! R Bpθ, rq Theoretical screening rule Ω D g Xg J ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Safe sphere test Ω D g `X J g c ` rω D g px g q ă 1 ùñ g 0. Objectives c as close as possible to r as small as possible ˆθ
49 Yes we can! R Bpθ, rq Theoretical screening rule Ω D g Xg J ˆθ ă 1 ùñ g 0. Safe sphere test Ω D g `X J g c ` rω D g px g q ă 1 ùñ g 0. Objectives c as close as possible to r as small as possible ˆθ
50 Mind the duality gap ;-) Fercoq, Gramfort & Salmon (ICML 2015) For all θ P X and all β P R p : ˆθ P B pθ, r λ pβ, θqq where r λ pβ, θq c 2pPλ pβq D λ pθqq λ 2 c 2Gλ pβ, θq λ 2.
51 How to compute a θ P X? X tθ P R n : Ω D px J θq ď 1u pfeasible setq ˆθ y X λ θ k y Xβ k α plink equationq with α st Ω D px J θ k q ď 1
52 How to compute a θ P X? X tθ P R n : Ω D px J θq ď 1u pfeasible setq ˆθ y X λ θ k y Xβ k α plink equationq with α st Ω D px J θ k q ď 1 α maxpλ, Ω D px J ρ k qq where ρ k y Xβ k.
53 How to compute a θ P X? X tθ P R n : Ω D px J θq ď 1u pfeasible setq ˆθ y X λ θ k y Xβ k α plink equationq with α st Ω D px J θ k q ď 1 α maxpλ, Ω D px J ρ k qq where ρ k y Xβ k.
54 Convergence of the Gap Safe region lim β k ùñ lim θ k ˆθ kpn kpn lim G λ pβ k, θ k q G λ p, ˆθ q 0 kpn c 2Gλ pβ k, θ k q lim r λ pβ k, θ k q lim kpn kpn λ 2 0 c 2Gλ pβ k, θ k q B θ k, ÝÑ tˆθ u λ 2
55 Convergence of the Gap Safe region lim β k ùñ lim θ k ˆθ kpn kpn lim G λ pβ k, θ k q G λ p, ˆθ q 0 kpn c 2Gλ pβ k, θ k q lim r λ pβ k, θ k q lim kpn kpn λ 2 0 c 2Gλ pβ k, θ k q B θ k, ÝÑ tˆθ u λ 2
56 Gap safe sphere c ˆθ 2Gλ pβ k, θ k q P B θ k, λ 2
57 Gap safe sphere c ˆθ 2Gλ pβ k, θ k q P B θ k, λ 2
58 Gap safe sphere c ˆθ 2Gλ pβ k, θ k q P B θ k, λ 2
59 Algorithm with Gap Safe rules Algorithm 1 Gap Safe screening algorithm Input : X, y, K, f ce, λ for k P rks do if k mod f ce 1 then Compute θ P X ˆ b and set R B θ, 2pP λ pβq D λ pθqq λ 2 // Compute the active set A R if Stopping criterion is met then break β SolverUpdatepX AR, y, β AR q // restricted to active set Output: β
60 Numerical experiments Figure: Proportion of screened variables on Leukemia dataset n 72 samples and p 7129 features.
61 Numerical experiments Figure: Computational time on Climate dataset n 814, p
62 GitHub : Page Web :
Nondifferentiable Convex Functions
 Nondifferentiable Convex Functions DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Applications Subgradients
Nondifferentiable Convex Functions DS-GA 1013 / MATH-GA 2824 Optimization-based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_fall17/index.html Carlos Fernandez-Granda Applications Subgradients
70. Let Y be a metrizable topological space and let A Ď Y. Show that Cl Y A scl Y A.
 Homework for MATH 4603 (Advanced Calculus I) Fall 2017 Homework 14: Due on Tuesday 12 December 66 Let s P pr 2 q N let a b P R Define p q : R 2 Ñ R by ppx yq x qpx yq y Show: r s Ñ pa bq in R 2 s ô r ppp
Homework for MATH 4603 (Advanced Calculus I) Fall 2017 Homework 14: Due on Tuesday 12 December 66 Let s P pr 2 q N let a b P R Define p q : R 2 Ñ R by ppx yq x qpx yq y Show: r s Ñ pa bq in R 2 s ô r ppp
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review
 Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Monetary Policy Design in the Basic New Keynesian Model
 Monetary Policy Design in the Basic New Keynesian Model Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE June 216 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy Design June 216 1 / 12 The Basic New Keynesian
Monetary Policy Design in the Basic New Keynesian Model Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE June 216 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy Design June 216 1 / 12 The Basic New Keynesian
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
6. MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATION
 6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix
 The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
Solution Series 9. i=1 x i and i=1 x i.
 Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
Overview. Transition Semantics. Configurations and the transition relation. Executions and computation
 Overview Transition Semantics Configurations and the transition relation Executions and computation Inference rules for small-step structural operational semantics for the simple imperative language Transition
Overview Transition Semantics Configurations and the transition relation Executions and computation Inference rules for small-step structural operational semantics for the simple imperative language Transition
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Parametrized Surfaces
 Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
Parametrized Surfaces Recall from our unit on vector-valued functions at the beginning of the semester that an R 3 -valued function c(t) in one parameter is a mapping of the form c : I R 3 where I is some
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Tridiagonal matrices. Gérard MEURANT. October, 2008
 Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Empirical best prediction under area-level Poisson mixed models
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor Empirical best prediction under area-level Poisson mixed models Miguel Boubeta María José Lombardía Domingo Morales eceived: date / Accepted: date
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor Empirical best prediction under area-level Poisson mixed models Miguel Boubeta María José Lombardía Domingo Morales eceived: date / Accepted: date
Tutorial on Multinomial Logistic Regression
 Tutorial on Multinomial Logistic Regression Javier R Movellan June 19, 2013 1 1 General Model The inputs are n-dimensional vectors the outputs are c-dimensional vectors The training sample consist of m
Tutorial on Multinomial Logistic Regression Javier R Movellan June 19, 2013 1 1 General Model The inputs are n-dimensional vectors the outputs are c-dimensional vectors The training sample consist of m
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Απόκριση σε Μοναδιαία Ωστική Δύναμη (Unit Impulse) Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο. Απόστολος Σ.
 Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Απόκριση σε Δυνάμεις Αυθαίρετα Μεταβαλλόμενες με το Χρόνο The time integral of a force is referred to as impulse, is determined by and is obtained from: Newton s 2 nd Law of motion states that the action
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Module 5. February 14, h 0min
 Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ. Μειέηε Υξόλνπ Απνζηείξσζεο Κνλζέξβαο κε Τπνινγηζηηθή Ρεπζηνδπλακηθή. Αζαλαζηάδνπ Βαξβάξα
 ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΔΚΠΑΙΓΔΤΣΙΚΟ ΙΓΡΤΜΑ ΘΔΑΛΟΝΙΚΗ ΥΟΛΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ & ΓΙΑΣΡΟΦΗ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ Μειέηε Υξόλνπ Απνζηείξσζεο Κνλζέξβαο κε Τπνινγηζηηθή Ρεπζηνδπλακηθή Αζαλαζηάδνπ Βαξβάξα
ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΔΚΠΑΙΓΔΤΣΙΚΟ ΙΓΡΤΜΑ ΘΔΑΛΟΝΙΚΗ ΥΟΛΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ & ΓΙΑΣΡΟΦΗ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΣΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ ΠΣΤΥΙΑΚΗ ΔΡΓΑΙΑ Μειέηε Υξόλνπ Απνζηείξσζεο Κνλζέξβαο κε Τπνινγηζηηθή Ρεπζηνδπλακηθή Αζαλαζηάδνπ Βαξβάξα
Lecture 2. Soundness and completeness of propositional logic
 Lecture 2 Soundness and completeness of propositional logic February 9, 2004 1 Overview Review of natural deduction. Soundness and completeness. Semantics of propositional formulas. Soundness proof. Completeness
Lecture 2 Soundness and completeness of propositional logic February 9, 2004 1 Overview Review of natural deduction. Soundness and completeness. Semantics of propositional formulas. Soundness proof. Completeness
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
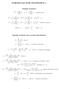 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Figure A.2: MPC and MPCP Age Profiles (estimating ρ, ρ = 2, φ = 0.03)..
 Supplemental Material (not for publication) Persistent vs. Permanent Income Shocks in the Buffer-Stock Model Jeppe Druedahl Thomas H. Jørgensen May, A Additional Figures and Tables Figure A.: Wealth and
Supplemental Material (not for publication) Persistent vs. Permanent Income Shocks in the Buffer-Stock Model Jeppe Druedahl Thomas H. Jørgensen May, A Additional Figures and Tables Figure A.: Wealth and
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data
 Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories
 Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
Higher Derivative Gravity Theories Black Holes in AdS space-times James Mashiyane Supervisor: Prof Kevin Goldstein University of the Witwatersrand Second Mandelstam, 20 January 2018 James Mashiyane WITS)
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Econ Spring 2004 Instructor: Prof. Kiefer Solution to Problem set # 5. γ (0)
 Cornell University Department of Economics Econ 60 - Spring 004 Instructor: Prof. Kiefer Solution to Problem set # 5. Autocorrelation function is defined as ρ h = γ h γ 0 where γ h =Cov X t,x t h =E[X
Cornell University Department of Economics Econ 60 - Spring 004 Instructor: Prof. Kiefer Solution to Problem set # 5. Autocorrelation function is defined as ρ h = γ h γ 0 where γ h =Cov X t,x t h =E[X
From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams
 From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams WIR 2014 Fanny He f.he@bath.ac.uk Alexis Saurin alexis.saurin@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr 12 July 2014 The Λµ-calculus Syntax of Λµ t ::= x λx.t (t)u
From the finite to the transfinite: Λµ-terms and streams WIR 2014 Fanny He f.he@bath.ac.uk Alexis Saurin alexis.saurin@pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr 12 July 2014 The Λµ-calculus Syntax of Λµ t ::= x λx.t (t)u
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
MATRIX INVERSE EIGENVALUE PROBLEM
 English NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS Vol.14, No.2 Series A Journal of Chinese Universities May 2005 A STABILITY ANALYSIS OF THE (k) JACOBI MATRIX INVERSE EIGENVALUE PROBLEM Hou Wenyuan ( ΛΠ) Jiang Erxiong( Ξ)
English NUMERICAL MATHEMATICS Vol.14, No.2 Series A Journal of Chinese Universities May 2005 A STABILITY ANALYSIS OF THE (k) JACOBI MATRIX INVERSE EIGENVALUE PROBLEM Hou Wenyuan ( ΛΠ) Jiang Erxiong( Ξ)
Notes on the Open Economy
 Notes on the Open Econom Ben J. Heijdra Universit of Groningen April 24 Introduction In this note we stud the two-countr model of Table.4 in more detail. restated here for convenience. The model is Table.4.
Notes on the Open Econom Ben J. Heijdra Universit of Groningen April 24 Introduction In this note we stud the two-countr model of Table.4 in more detail. restated here for convenience. The model is Table.4.
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
forms This gives Remark 1. How to remember the above formulas: Substituting these into the equation we obtain with
 Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
A Lambda Model Characterizing Computational Behaviours of Terms
 A Lambda Model Characterizing Computational Behaviours of Terms joint paper with Silvia Ghilezan RPC 01, Sendai, October 26, 2001 1 Plan of the talk normalization properties inverse limit model Stone dualities
A Lambda Model Characterizing Computational Behaviours of Terms joint paper with Silvia Ghilezan RPC 01, Sendai, October 26, 2001 1 Plan of the talk normalization properties inverse limit model Stone dualities
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
Elements of Information Theory
 Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
10.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response)
 Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation
 Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation Praveen. C praveen@math.tifrbng.res.in Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Center for Applicable Mathematics Bangalore 560065 http://math.tifrbng.res.in/~praveen
Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation Praveen. C praveen@math.tifrbng.res.in Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Center for Applicable Mathematics Bangalore 560065 http://math.tifrbng.res.in/~praveen
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Probability and Random Processes (Part II)
 Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Dynamic types, Lambda calculus machines Section and Practice Problems Apr 21 22, 2016
 Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Dynamic types, Lambda calculus machines Apr 21 22, 2016 1 Dynamic types and contracts (a) To make sure you understand the
Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Dynamic types, Lambda calculus machines Apr 21 22, 2016 1 Dynamic types and contracts (a) To make sure you understand the
Exercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5
 Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Bayesian statistics. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
Appendix to On the stability of a compressible axisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe. By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee
 Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in
 Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Exercise 2: The form of the generalized likelihood ratio
 Stats 2 Winter 28 Homework 9: Solutions Due Friday, March 6 Exercise 2: The form of the generalized likelihood ratio We want to test H : θ Θ against H : θ Θ, and compare the two following rules of rejection:
Stats 2 Winter 28 Homework 9: Solutions Due Friday, March 6 Exercise 2: The form of the generalized likelihood ratio We want to test H : θ Θ against H : θ Θ, and compare the two following rules of rejection:
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
CE 530 Molecular Simulation
 C 53 olecular Siulation Lecture Histogra Reweighting ethods David. Kofke Departent of Cheical ngineering SUNY uffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu Histogra Reweighting ethod to cobine results taken at different
C 53 olecular Siulation Lecture Histogra Reweighting ethods David. Kofke Departent of Cheical ngineering SUNY uffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu Histogra Reweighting ethod to cobine results taken at different
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations
 On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
A Carleman estimate and the balancing principle in the Quasi-Reversibility method for solving the Cauchy problem for the Laplace equation
 A Carleman estimate and the balancing principle in the Quasi-Reversibility method for solving the Cauchy problem for the Laplace equation Hui Cao joint work with Michael Klibanov and Sergei Pereverzev
A Carleman estimate and the balancing principle in the Quasi-Reversibility method for solving the Cauchy problem for the Laplace equation Hui Cao joint work with Michael Klibanov and Sergei Pereverzev
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Lecture 34: Ridge regression and LASSO
 Lecture 34: Ridge regression and LASSO Ridge regression Consider linear model X = Z β + ε, β R p and Var(ε) = σ 2 I n. The LSE is obtained from the minimization problem min X Z β R β 2 (1) p A type of
Lecture 34: Ridge regression and LASSO Ridge regression Consider linear model X = Z β + ε, β R p and Var(ε) = σ 2 I n. The LSE is obtained from the minimization problem min X Z β R β 2 (1) p A type of
Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries
 1 Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries Ulf Kähler Chemnitz University of Technology Workshop on Fast Boundary Element Methods in Industrial Applications
1 Wavelet based matrix compression for boundary integral equations on complex geometries Ulf Kähler Chemnitz University of Technology Workshop on Fast Boundary Element Methods in Industrial Applications
Iterated trilinear fourier integrals with arbitrary symbols
 Cornell University ICM 04, Satellite Conference in Harmonic Analysis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea August 6, 04 Motivation the Coifman-Meyer theorem with classical paraproduct(979) B(f, f )(x) :=
Cornell University ICM 04, Satellite Conference in Harmonic Analysis, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea August 6, 04 Motivation the Coifman-Meyer theorem with classical paraproduct(979) B(f, f )(x) :=
Γραµµικός Προγραµµατισµός (ΓΠ)
 Γραµµικός Προγραµµατισµός (ΓΠ) Περίληψη Επίλυση δυσδιάστατων προβληµάτων Η µέθοδος simplex Τυπική µορφή Ακέραιος Προγραµµατισµός Προγραµµατισµός Παραγωγής Προϊόν Προϊόν 2 Παραγωγική Δυνατότητα Μηχ. 4 Μηχ.
Γραµµικός Προγραµµατισµός (ΓΠ) Περίληψη Επίλυση δυσδιάστατων προβληµάτων Η µέθοδος simplex Τυπική µορφή Ακέραιος Προγραµµατισµός Προγραµµατισµός Παραγωγής Προϊόν Προϊόν 2 Παραγωγική Δυνατότητα Μηχ. 4 Μηχ.
Differential equations
 Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
( y) Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Local Approximation with Kernels
 Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
Local Approximation with Kernels Thomas Hangelbroek University of Hawaii at Manoa 5th International Conference Approximation Theory, 26 work supported by: NSF DMS-43726 A cubic spline example Consider
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Answers - Worksheet A ALGEBRA PMT. 1 a = 7 b = 11 c = 1 3. e = 0.1 f = 0.3 g = 2 h = 10 i = 3 j = d = k = 3 1. = 1 or 0.5 l =
 C ALGEBRA Answers - Worksheet A a 7 b c d e 0. f 0. g h 0 i j k 6 8 or 0. l or 8 a 7 b 0 c 7 d 6 e f g 6 h 8 8 i 6 j k 6 l a 9 b c d 9 7 e 00 0 f 8 9 a b 7 7 c 6 d 9 e 6 6 f 6 8 g 9 h 0 0 i j 6 7 7 k 9
C ALGEBRA Answers - Worksheet A a 7 b c d e 0. f 0. g h 0 i j k 6 8 or 0. l or 8 a 7 b 0 c 7 d 6 e f g 6 h 8 8 i 6 j k 6 l a 9 b c d 9 7 e 00 0 f 8 9 a b 7 7 c 6 d 9 e 6 6 f 6 8 g 9 h 0 0 i j 6 7 7 k 9
HW 3 Solutions 1. a) I use the auto.arima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA(3,1)
 HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Applying Markov Decision Processes to Role-playing Game
 1,a) 1 1 1 1 2011 8 25, 2012 3 2 MDPRPG RPG MDP RPG MDP RPG MDP RPG MDP RPG Applying Markov Decision Processes to Role-playing Game Yasunari Maeda 1,a) Fumitaro Goto 1 Hiroshi Masui 1 Fumito Masui 1 Masakiyo
1,a) 1 1 1 1 2011 8 25, 2012 3 2 MDPRPG RPG MDP RPG MDP RPG MDP RPG MDP RPG Applying Markov Decision Processes to Role-playing Game Yasunari Maeda 1,a) Fumitaro Goto 1 Hiroshi Masui 1 Fumito Masui 1 Masakiyo
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata
 Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.1 L = {wcw R w (0+1) * } P c 0P0 1P1 1. Start at state q 0, push input symbol onto stack, and stay in q 0. 2. If input symbol is
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.1 L = {wcw R w (0+1) * } P c 0P0 1P1 1. Start at state q 0, push input symbol onto stack, and stay in q 0. 2. If input symbol is
ECON 381 SC ASSIGNMENT 2
 ECON 8 SC ASSIGNMENT 2 JOHN HILLAS UNIVERSITY OF AUCKLAND Problem Consider a consmer with wealth w who consmes two goods which we shall call goods and 2 Let the amont of good l that the consmer consmes
ECON 8 SC ASSIGNMENT 2 JOHN HILLAS UNIVERSITY OF AUCKLAND Problem Consider a consmer with wealth w who consmes two goods which we shall call goods and 2 Let the amont of good l that the consmer consmes
