CHAPTER 5. p(x,y) x
|
|
|
- Ζώνα Οικονόμου
- 8 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 CHAPTER 5 Sction 5.. a. P(X, Y p(,. b. P(X and Y p(, + p(, + p(, + p(,.4 c. At last on hos is in us at both islands. P(X and Y p(, + p(, + p(, + p(,.7 d. B summing row probabilitis, p (.6,.4,.5 for,,, and b summing column probabilitis, p (.4,.8,.8 for,,. P(X p ( + p (.5. P(,., but p ( p ( (.6(.4.84., so X and Y ar not indpndnt.. a. p(, b. P(X and Y p(, + p(, + p(, + p(,.56 (.8(.7 P(X P(Y c. P( X + Y P(X and Y p(,. d. P(X + Y p(, + p(, + p(,.5. a. p(,.5, th ntr in th st row and st column of th joint probabilit tabl. b. P( X X p(, + p(, + p(, + p(, c. A { (, : + } { (, : + } P(A p(, + p(, + p(4, + p(, + p(4, + p(4, + p(, + p(, + p(,. d. P( actl 4 p(, + p(, + p(, + p(4,.7 P(at last 4 P(actl 4 + p(4, + p(4, + p(4, + p(, + p(, + p(,.46 75
2 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 4. a. P ( P(X p(, + p(, + p(, + p(,.9 P ( P(X p(, + p(, + p(, + p(,., tc. 4 p ( b. P ( P(X p(, + p(, + p(, + p(, + p(4,.9, tc p ( c. p(4,, t p (4. > and p (.9 >, so p(, p ( p ( for vr (,, and th two variabls ar not indpndnt. 5. a. P(X, Y P( customrs, ach with packag P( ach has packag customrs P( customrs (.6 (.5.54 b. P(X 4, Y P(total of packags 4 customrs P(4 customrs Givn that thr ar 4 customrs, thr ar 4 diffrnt was to hav a total of packags:,,, or,,, or,,, or,,,. Each wa has probabilit (. (., so p(4, 4(. (.( a. p(4, P( Y X 4 P(X 4 (.6 (.4 ( b. P(X Y p(, + p(, + p(, + p(, + p(4,4.+(.(.6 + (.(.6 + (.5(.6 + (.5(
3 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls c. p(, unlss,,, ;,,,, 4. For an such pair, p(, P(Y X P(X (. 6 (.4 p ( p (4 p( 4 p( 4, 4 p(4,4 (.6 4 ( p ( p(, + p(4, (.6 (.5 + (.6 (.4( p ( p(, + p(, + p(4, (.6 (. + (.6 (.4( (.6 (.4 ( p ( p(, + p(, + p(, + p(4, (. 6(. + (.6(.4(. 4 (.6(.4 (.5 + (.6(.4 (.5.59 p ( [ ] a. p(,. b. P(X and Y p(, + p(, + p(, + p(,. c. P(X p(, + p(, + p(,.; P(Y p(, + + p(5,. d. P(ovrflow P(X + Y > 5 P(X + Y 5 P[(X,Y(, or or (5, or (, or (, or (,] Th marginal probabilitis for X (row sums from th joint probabilit tabl ar p (.5, p (., p (.5, p (., p (4., p (5.; thos for Y (column sums ar p (.5, p (., p (.. It is now asil vrifid that for vr (,, p(, p ( p (, so X and Y ar indpndnt. 77
4 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls , 6 a. numrator ( 56( 45(, 4,4 59,775 dnominator 775 ; p(,. 59 b. p(, ( +, _ ar _ non ngativ int grs _ such _ that + 6 othrwis 9. dd a. f (, dd K( + K K d dd + K dd K d + 9, K K 8, 6 6 ( d b. P(X < 6 and Y < 6 K + dd K c. 6 4K 6 8,4K.4 I + III II P( X Y rgion III f (, dd (, dd f f (, dd I 8 + II f (, dd (aftr much algbra.59 f (, dd 78
5 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls d. f ( f (, d K ( + d K + K +.5, K. f ( is obtaind b substituting for in (d; clarl f(, f ( f (, so X and Y ar not indpndnt.. a. f(, 5 6,5 6 othrwis sinc f (, f ( for 5 6, 5 6 b. P(5.5 X 5.75, 5.5 Y 5.75 P(5.5 X 5.75 P(5.5 Y 5.75 (b indpndnc (.5(.5.5 c. 6 I +/6 / 6 5 II P((X,Y A A dd ara of A (ara of I + ara of II a. p(, µ µ!! for,,, ;,,, µ b. p(, + p(, + p(, [ + + µ ] c. P( X+Ym P( X k, Y m k m! ( + µ m m k m k µ k k k! ( m k m ( + µ m m k mk ( + µ k! µ k m! +. Poisson distribution with paramtr µ µ, so th total # of rrors X+Y also has a 79
6 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls. (+ a. P(X> dd d. 5 b. Th marginal pdf of X is ( + d ( + (+ d th marginal pdf s, so th two r.v s ar not indpndnt. c. P( at last on cds P(X and Y d (+ dd for ; that of Y is for. It is now clar that f(, is not th product of ( d a. f(, f ( f (, othrwis b. P(X and Y P(X P(Y ( - ( -.4 ( c. P(X + Y dd [ ] d ( d. 594 ( d. P(X + Y [ ] d. 64 so P( X + Y P(X + Y P(X + Y , 4. a. P(X < t, X < t,, X < t P(X < t P( X < t ( t b. If succss {fail bfor t}, thn p P(succss t, and P(k succsss among trials ( k k t t k c. P(actl 5 fail P( 5 of l s fail and othr 5 don t + P(4 of l s fail, m fails, and othr t 5 ( + 4 t t 4 µ t t µ t 5 don t ( ( ( ( ( 8
7 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 8 5. a. F( P( Y P [(X ((X (X ] P (X + P[(X (X ] - P[(X (X (X ] ( ( ( + for b. f( F ( ( ( + ( ( 4 for E(Y ( 4 d 6. a. f(, (,, ( d k d f ( ( 7,, + b. P(X + X ( ( 7 d d (aftr much algbra.55 c. ( ( 7, ( ( d d f f a. (, ( Y X P within a circl of radius A R dd f A P, ( ( R A of ara dd πr A π b. π π, R R R Y R R X R P
8 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls c. P R X R, R Y R R πr π f f (, d πr d d. ( R R R πr for R R and similarl for f Y (. X and Y ar not indpndnt sinc.g. f (.9R f Y (.9R >, t f(.9r,.9r sinc (.9R,.9R is outsid th circl of radius R. 8. a. P X ( rsults from dividing ach ntr in row of th joint probabilit tabl b p (.4: P P P.8 (.4. (.4.6 ( b. P X ( is rqustd; to obtain this divid ach ntr in th row b p (.5: P X (..8.6 c. P( Y P X ( + P X ( d. P X Y ( rsults from dividing ach ntr in th column b p (.8: P (
9 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 9. a. f f (, k( + ( f ( k +.5 Y X X k( + X ( k k +.5 8, f Y b. P( Y 5 X f Y 5 fy X 5 ( d k(( + d.78 5 k( +.5 P( Y 5 ( d (k +.5 d k(( + k( +.5 Y X ( c. E( Y X f d d 5.79 E( Y k(( + X d k( +.5 V(Y X E( Y X [E( Y X ] f (,,, f (, whr f, (, a. f (,, th marginal joint pdf f ( d,, of (X, X b. f (, f (,,, whr f ( f f (,, d ( d. For vr and, f Y X ( f (, sinc thn f(, f Y X ( f X ( f Y ( f X (, as rquird. 8
10 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls Sction 5.. a. E( X + Y ( + p(, ( + (. + ( + 5( ( + 5(. 4. b. E[ma (X,Y] ma( + p(, ( (. + (5( (5( E(X X ( 4 p(, ( (.8 + ( ( (4 (.6.5 (which also quals E(X E(X Lt h(x,y # of individuals who handl th mssag. h(, Sinc p(, for ach possibl (,, E[h(X,Y] 84 h,. 8 ( 5. E(XY E(X E(Y L L L 6. Rvnu X + Y, so E (rvnu E (X + Y 5 ( + p(, p(, p(5,
11 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 7. E[h(X,Y] 6 dd ( 6 dd ( dd 5 6 d 8. E(XY p(, p( p ( p( p ( E(X E(Y. (rplac Σ with in th continuous cas µ µ. E(X 75 5 f ( d 4 ( d, so Var (X Similarl, Var(Y, so ρ X, Y Cov(X,Y and 5 5. a. E(X 5.55, E(Y 8.55, E(XY ((. + (( (5(. 44.5, so Cov(X,Y 44.5 (5.55( X Y, so ρ X, Y. 7 (.45(9.5 b..45, a. E(X f ( d [ K +.5] d 5.9 E( Y E(XY K( + dd Cov ( X, Y (5.9., so Var (X Var(Y ( b. E(X [ K +.5] d E( Y ρ..4 (8.664(
12 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls. Thr is a difficult hr. Eistnc of r rquirs that both X and Y hav finit mans and variancs. Yt sinc th marginal pdf of Y is ( ( + for, E( d d ( + d ( d ( + + ( + first intgral is not finit. Thus r itslf is undfind., and th. Sinc E(XY E(X E(Y, Cov(X,Y E(XY E(X E(Y E(X E(Y - E(X E(Y, and sinc Corr(X,Y Cov( X, Y, thn Corr(X,Y 4. a. In th discrt cas, Var[h(X,Y] E{[h(X,Y E(h(X,Y] } [ h(, E( h( X, Y ] p(, with rplacing in th continuous cas. [ h(, p(, ] [ E( h( X, Y ] b. E[h(X,Y] E[ma(X,Y] 9.6, and E[h (X,Y] E[(ma(X,Y ] ( (. +(5 ( (5 (. 5.5, so Var[ma(X,Y] 5.5 ( a. Cov(aX + b, cy + d E[(aX + b(cy + d] E(aX + b E(cY + d E[acXY + adx + bcy + bd] (ae(x + b(ce(y + d ace(xy ace(xe(y accov(x,y b. Corr(aX + b, cy + d Cov( ax + b, cy + d accov( X, Y Var( ax + b Var( cy + d a c Var( X Var( Y Corr(X,Y whn a and c hav th sam signs. c. Whn a and c diffr in sign, Corr(aX + b, cy + d -Corr(X,Y. 6. Cov(X,Y Cov(X, ax+b E[X (ax+b] E(X E(aX+b a Var(X, so Corr(X,Y avar( X Var( X Var( Y avar( X Var( X a Var( X if a >, and if a < 86
13 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls Sction P(..5. P( a p ( E ( (5(.4 +.5( ( µ b. s P(s.8... E(s.5 8. a. T 4 P(T b. µ E. µ T ( T c. T E( T E( T 5.8 (
14 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls /n p(/n X is a binomial random variabl with p a. Possibl valus of M ar:, 5,. M whn all nvlops contain mon, hnc p(m (.5.5. M whn thr is a singl nvlop with $, hnc p(m p(no nvlops with $ ( p(m 5 [ ].87. M 5 p(m An altrnativ solution would b to list all 7 possibl combinations using a tr diagram and computing probabilitis dirctl from th tr. b. Th statistic of intrst is M, th maimum of,, or, so that M, 5, or. Th population distribution is a s follows: 5 p( / / /5 Writ a computr program to gnrat th digits 9 from a uniform distribution. Assign a valu of to th digits 4, a valu of 5 to digits 5 7, and a valu of to digits 8 and 9. Gnrat sampls of incrasing sizs, kping th numbr of rplications constant and comput M from ach sampl. As n, th sampl siz, incrass, p(m gos to zro, p(m gos to on. Furthrmor, p(m 5 gos to zro, but at a slowr rat than p(m. 88
15 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 4. Outcom,,,,4,,,,4 Probabilit r Outcom,,,,4 4, 4, 4, 4,4 Probabilit a r b. P( p ( c. r p(r d. P ( X.5 P(,,, + P(,,, + + P(,,, + P(,,, + + P(,,, + P(,,, + + P(,,, ( (.4 (. + 6(.4 (. + 4(.4 ( a p ( b p ( c. all thr valus ar th sam:.4 89
16 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 4. Th statistic of intrst is th fourth sprad, or th diffrnc btwn th mdians of th uppr and lowr halvs of th data. Th population distribution is uniform with A 8 and B. Us a computr to gnrat sampls of sizs n 5,,, and from a uniform distribution with A 8 and B. Kp th numbr of rplications th sam (sa 5, for ampl. For ach sampl, comput th uppr and lowr fourth, thn comput th diffrnc. Plot th sampling distributions on sparat histograms for n 5,,, and. 44. Us a computr to gnrat sampls of sizs n 5,,, and from a Wibull distribution with paramtrs as givn, kping th numbr of rplications th sam, as in problm 4 abov. For ach sampl, calculat th man. Blow is a histogram, and a normal probabilit plot for th sampling distribution of for n 5, both gnratd b Minitab. This sampling distribution appars to b normal, so sinc largr sampl sizs will produc distributions that ar closr to normal, th othrs will also appar normal. 45. Using Minitab to gnrat th ncssar sampling distribution, w can s that as n incrass, th distribution slowl movs toward normalit. Howvr, vn th sampling distribution for n 5 is not t approimatl normal. n Normal Probabilit Plot 9 Frqunc Probabilit n Andrson-D arling N ormalit Tst A-Squard: 7.46 P-Valu:. n 5 Normal Probabilit Plot Frqunc Probabilit Andrson- Darl ing Normali t Ts t A- Squa r d : P-Valu :. 9
17 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls Sction µ cm.4 cm a. n 6 E( X cm.4 µ. cm n 4 b. n 64 E( X cm.4 µ. 5cm n 8 c. X is mor likl to b within. cm of th man ( cm with th scond, largr, sampl. This is du to th dcrasd variabilit of X with a largr sampl siz. 47. µ cm.4 cm.99. a. n 6 P(.99 X. P Z.. P(- Z Φ( - Φ( b. n 5 P( X >. Z >.4 / 5 P P( Z >.5 - Φ( µ X,. n P( X 5.5 P Z.. a. µ 5 P(-.5 Z b. P( X 5.5 P Z.. P(-.5 Z
18 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 49. a. P.M. 6:5 P.M. 5 minuts. With T X + + X 4 total grading tim, µ T nµ (4(6 4 and n, so P( T 5 P Z 5 4 P 7.95 ( Z T b. P ( T > 6 P Z > P( Z > µ, psi 5 psi a. n 4 9,9,,, P( 9,9 X, P Z 5/ 4 5/ 4 P(-.6 Z.5 Φ(.5 - Φ( b. According to th Rul of Thumb givn in Sction 5.4, n should b gratr than in ordr to appl th C.L.T., thus using th sam procdur for n 5 as was usd for n 4 would not b appropriat. 5. X ~ N(,4. For da, n 5 P( X P Z P( Z / 5 For da, n 6 P( X P Z P( Z / 6 For both das, P( X (.8686( X ~ N(, n 4 µ T nµ (4( 4 and n ((, T W dsir th 95 th prcntil: 4 + (.645( 4.9 9
19 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 5. µ 5,. a. n P( X 5 P Z P( Z / 9 b. n P( X 5 P Z P( Z 5.7. / µ X,. 7 n 5 a. µ P( X. P Z P( Z P(.65 X. P ( X. P( X b. P( X. P Z. 99 implis that.,.85/ n 85/ n which n.. Thus n will suffic. from µ npq np a. 4.5 P( 5 X P Z P(. Z b P( 5 X 5 P Z P (.59 Z a. With Y # of tickts, Y has approimatl a normal distribution with µ 5, , so P( 5 Y 7 Z Z P P( -.9 b. Hr µ 5, 5, Z , so P( 5 Y 75 P P( -.6 Z
20 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 57. E(X, Var(X, 4. 4 P( Z , so P( X 5 P Z 4.4 Sction a. E( 7X + 5X + 5X 7 E(X + 5 E(X + 5 E(X 7( + 5(5 + 5( 87,85 V(7X + 5X + 5X 7 V(X + 5 V(X + 5 V(X 7 ( + 5 ( + 5 (8 9,,6 b. Th pctd valu is still corrct, but th varianc is not bcaus th covariancs now also contribut to th varianc. 59. a. E( X + X + X 8, V(X + X + X 45, P(X + X + X P Z P( Z P(5 X + X + X P ( 4.47 Z µ X,. 6 n 55 6 P ( X 55 P Z P( Z P ( 58 X 6 P.89 Z.89. b. µ 6 ( 666 c. E( X -.5X -.5X ; V( X -.5X -.5X , sd P(- X -.5X -.5X 5 (..5 Z 5 P Z P
21 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls d. E( X + X + X 5, V(X + X + X 6, P(X + X + X P Z P( Z W want P( X + X X, or writtn anothr wa, P( X + X - X E( X + X - X (6 -, V(X + X - X , 6, sd 8.8, so 4 ( P( X + X - X P Z P( Z Y is normall distributd with ( µ + µ ( µ + µ + µ µ Y, and 4 5 Y , Y ( Thus, P ( Y P Z P(.56 Z. 877 and.7795 P ( Y P Z P( Z a. Th marginal pmf s of X and Y ar givn in th solution to Ercis 7, from which E(X.8, E(Y.7, V(X.66, V(Y.6. Thus E(X+Y E(X + E(Y.5, V(X+Y V(X + V(Y.7, and th standard dviation of X + Y is.5 b. E(X+Y E(X + E(Y 5.4, V(X+Y 9V(X + V(Y 75.94, and th standard dviation of rvnu is E( X + X + X E( X + E(X + E(X min., V(X + X + X , Thus, P(X + X + X 6 P Z P( Z a. E(X.7, E(X.55, E(X X p(,. E(X X - E(X E(X , so Cov(X,X b. V(X + X V(X + V(X + Cov(X,X (
22 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 64. Lt X,, X 5 dnot morning tims and X 6,, X dnot vning tims. a. E(X + + X E(X + + E(X 5 E(X + 5 E(X 6 5(4 + 5(5 45 b. Var(X + + X Var(X + + Var(X 5 Var(X + 5Var(X c. E(X X 6 E(X - E(X Var(X X 6 Var(X + Var(X d. E[(X + + X 5 (X X ] 5(4 5(5-5 Var[(X + + X 5 (X X ] Var(X + + X 5 + Var(X X ] µ 5.,. E V ( X Y +.,. 566 X Y 5 5 a. ( X Y ; (. X Y. P(.77 Z P (b th CLT b. V ( X Y +.,. 47 X Y 6 6 P. X Y. P. Z.. ( ( a. With M 5X + X, E(M 5( + (4 5, Var(M 5 (.5 + ( 6.5, M b. P( 75 < M P < Z P(.4 < Z. 75 c. M A X + A X with th A I s and X I s all indpndnt, so E(M E(A X + E(A X E(A E(X + E(A E(X 5 d. Var(M E(M [E(M]. Rcall that for an r.v. Y, E(Y Var(Y + [E(Y]. Thus, E(M E ( A X + AX A X + A X E ( A E( X + E( A E( X E( A E( X + E( A E( X (b indpndnc (.5 + 5( (5(((4 + (.5 + ( , so Var(M (
23 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls. E(M 5 still, but now Var ( M avar( X + a acov( X, X + avar( X (5(( Ltting X, X, and X dnot th lngths of th thr pics, th total lngth is X + X - X. This has a normal distribution with man valu + 5 4, varianc , and standard dviation.648. Standardizing givs P(4.5 X + X - X 5 P(.77 Z Lt X and X dnot th (constant spds of th two plans. a. Aftr two hours, th plans hav travld X km. and X km., rspctivl, so th scond will not hav caught th first if X + > X, i.. if X X < 5. X X has a man 5 5 -, varianc +, and standard dviation 4.4. Thus, 5 ( P ( X X < 5 P Z < P( Z < b. Aftr two hours, # will b + X km from whr # startd, whras # will b X from whr it startd. Thus th sparation distanc will b al most if X X, i.. X X, i.. X X. Th corrsponding probabilit is P( X X P(.4 Z a. E(X + X + X b. Assuming indpndnc of X, X, X, Var(X + X + X (6 + (5 + (8.5 c. E(X + X + X 4 as bfor, but now Var(X + X + X Var(X + Var(X + Var(X + Cov(X,X + Cov(X, X + Cov(X, X 745, with sd a. E (.5, so Y i n n n( n + E( W i E( Yi.5 i 4 i i n n n( n + (n + Var Y i so Var( W i Var( Yi.5 i 4 b. (.5, i i 97
24 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 7. W a. M a X + a X + W d a X + a X + 7, so E(M (5( + ((4 + (7(.5 58m M ( 5 (.5 + ( ( + ( 7 ( ,. 74 M 58 b. P ( M P Z P( Z Th total lapsd tim btwn laving and rturning is T o X + X + X + X 4, with E ( 4, 4, T o T o T o. T o is normall distributd, and th dsird valu t is th 99 th prcntil of th lapsd tim distribution addd to A.M.: : + [4+(5.477(.] : a. Both approimatl normal b th C.L.T. b. Th diffrnc of two r.v. s is just a spcial linar combination, and a linar combination X Y has approimatl a normal 8 6 µ and +.69,. 6 X Y X Y XY 4 5 of normal r.v s has a normal distribution, so distribution with P X Y & P Z.6.6 P (.7 Z c. ( 5 P & This probabilit is.6 µ d. ( X Y P Z P( Z.8.. quit small, so such an occurrnc is unlikl if µ 5, and w would thus doubt this claim. 74. X is approimatl normal with (5(.7 5 µ and (5(.7(.. 5 is Y with µ and. Thus 5 X Y p X Y 5 P Z X Y., so µ and 5 ( 5 P(. Z. 486, as 98
25 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls Supplmntar Erciss 75. a. p X ( is obtaind b adding joint probabilitis across th row labld, rsulting in p X (.,.5,. for, 5, rspctivl. Similarl, from column sums p (.,.5,.55 for, 5, rspctivl. b. P(X 5 and Y 5 p(, + p(,5 + p(5, + p(5,5.5 c. p ( p ( (.(..5 p(,, so X and Y ar not indpndnt. (Almost an othr (, pair ilds th sam conclusion. d. E ( X + Y ( + p(,. 5 (or E(X + E(Y.5. E ( X Y + p(, Th roll-up procdur is not valid for th 75 th prcntil unlss 77. and or or both, as dscribd blow. Sum of prcntils: µ + Z + µ + ( Z µ + µ + ( Z( + Prcntil of sums: ( µ + + µ + ( Z Ths ar qual whn Z (i.. for th mdian or in th unusual cas whn + +, which happns whn. + or or both and + a. f (, dd kdd+ 8,5 k k 8,5 kdd b. f X ( kd k(5 kd k(45 + and b smmtr f Y ( is obtaind b substituting for in f X (. Sinc f X (5 >, and f Y (5 >, but f(5, 5, f X ( f Y ( f(, for all, so X and Y ar not indpndnt. 99
26 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 5 c. P ( X + Y 5 kdd+ 5 5 kdd, ,5 4 d. E X + Y E( X + E( Y { k( 5 + ( } k 45 d k ( d + (5, E ( XY f (, dd + k k dd k dd,5, 6.4 Cov(X,Y 6.4 ( , and E(X E(Y 4.654, so ( and ρ f. Var (X + Y Var(X + Var(Y + Cov(X,Y 7.66, so 78. F Y ( P( ma(x,, X n P( X,, X n [P(X ] n. n for. n n n E n n n n u du n n + n + n Thus f Y ( ( n ( d ( u + n ( Y u du n n n for 79. E ( X + Y + Z Var ( X + Y + Z + +.4, and th std dv P ( X + Y + Z 5 P( Z 9.
27 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 8. a. Lt X,, X dnot th wights for th businss-class passngrs and Y,, Y 5 dnot th tourist-class wights. Thn T total wight X + + X + Y + + Y 5 X + Y E(X E(X ( 6; V(X V(X (6 4. E(Y 5E(Y 5(4 ; V(Y 5V(Y 5( 5. Thus E(T E(X + E(Y And V(T V(X + V(Y , std dv b. P ( T 5 P Z P( Z a. E(N µ ((4 4 minuts b. W pct componnts to com in for rpair during a 4 hour priod, so E(N µ (( X ~ Bin (,.45 and Y ~ Bin (,.6. Bcaus both n s ar larg, both X and Y ar approimatl normal, so X + Y is approimatl normal with man ((.45 + ((.6 7, varianc (.45(.55 + (.6(.4.4, and standard dviation.. Thus, P(X Y 5 P Z P( Z P( µ. X µ +. & P Z./ n./ n P(. n Z. n, but (.96 Z n 97. n Th C.L.T. P so 84. I hav 9 oz. Th amount which I would consum if thr wr no limit is T o X + + X 4 whr ach X I is normall distributd with µ and. Thus T o is normal with µ 8 and 7. 48, so P(T o < 9 P(Z < T o T o 85. Th pctd valu and standard dviation of volum ar 87,85 and 47.7, rspctivl, so, 87,85 P ( volum, P Z P( Z Th studnt will not b lat if X + X X, i.. if X X + X. This linar combination has man, varianc 4.5, and standard dviation.6, so ( P ( X X + X P Z P( Z
28 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 87. a. Var( ax + Y a + acov( X, Y + a + a ρ + Substituting a Y ilds + Y ρ + Y Y ( ρ X Y, so ρ X Y. b. Sam argumnt as in a c. Suppos ρ. Thn Var ( ax Y Y ( ρ, which implis that ax Y k (a constant, so ax Y ax k, which is of th form ax + b. 88. X + Y t ( + t E ( f (, dd. To find th minimizing valu of t, tak th drivativ with rspct to t and quat it to : ( + t( f (, tf (, dd t ( + f (, dd E( X + Y, so th bst prdiction is th individual s pctd scor ( a. With Y X + X, F Y ( ν / ( ν / Γ( ν / ν / Γ But th innr intgral can b shown to b qual to [ ( ν / + ν Γ ( ν + ν / ν ν + ( ν+ ν / ] /, from which th rsult follows. d d. b. B a, ν Z + is chi-squard with Z, tc, until ν, so ( Z Z + Z + 9s chi-squard withν n Z... + Z n + is chi-squard with c. X i µ is standard normal, so is chi-squard with ν n. X i µ is chi-squard with ν, so th sum
29 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 9. a. Cov(X, Y + Z E[X(Y + Z] E(X E(Y + Z E(XY + E(XZ E(X E(Y E(X E(Z E(XY E(X E(Y + E(XZ E(X E(Z Cov(X,Y + Cov(X,Z. b. Cov(X + X, Y + Y Cov(X, Y + Cov(X,Y + Cov(X, Y + Cov(X,Y (appl a twic a. V X V ( W + E + V ( W + E V ( and ( W E X ( X, X Cov( W + E, W + E Cov( W, W + Cov( W, E ( E, W + Cov( E, E Cov( W, W V ( W w. Cov Cov ρ + Thus, W + E W W + E W + W E b. ρ a. Cov(X,Y Cov(A+D, B+E Cov(A,B + Cov(D,B + Cov(A,E + Cov(D,E Cov(A,B. Thus Corr( X, Y A Cov( A, B + + A D Cov( A, B A B A B + + D B B E E Th first factor in this prssion is Corr(A,B, and (b th rsult of rcis 7a th scond and third factors ar th squar roots of Corr(X, X and Corr(Y, Y, rspctivl. Clarl, masurmnt rror rducs th corrlation, sinc both squar-root factors ar btwn and. b rducs th corrlation.. This is disturbing, bcaus masurmnt rror substantiall
30 Chaptr 5: Joint Probabilit Distributions and Random Sampls 9. E Y & h( µ, µ, µ, µ [ + + ] 6 ( 4 5 Th partial drivativs of µ, µ, µ, 4 4,, and 4 h ( µ 4 with rspct to,,, and 4 ar, + +, rspctivl. Substituting, 5,, and 4 givs., -.5, -., and.67, rspctivl, so V(Y ((-. + ((-.5 + (.5(-. + (4.( , and th approimat sd of is Th four scond ordr partials ar, E(Y , 4, and rspctivl. Substitution givs 4
Pairs of Random Variables
 Pairs of Random Variabls Rading: Chaptr 4. 4. Homwork: (do at last 5 out of th following problms 4..4, 4..6, 4.., 4.3.4, 4.3.5, 4.4., 4.4.4, 4.5.3, 4.6.3, 4.6.7, 4.6., 4.7.9, 4.7., 4.8.3, 4.8.7, 4.9.,
Pairs of Random Variabls Rading: Chaptr 4. 4. Homwork: (do at last 5 out of th following problms 4..4, 4..6, 4.., 4.3.4, 4.3.5, 4.4., 4.4.4, 4.5.3, 4.6.3, 4.6.7, 4.6., 4.7.9, 4.7., 4.8.3, 4.8.7, 4.9.,
Homework #6. A circular cylinder of radius R rotates about the long axis with angular velocity
 Homwork #6 1. (Kittl 5.1) Cntrifug. A circular cylindr of radius R rotats about th long axis with angular vlocity ω. Th cylindr contains an idal gas of atoms of mass m at tmpratur. Find an xprssion for
Homwork #6 1. (Kittl 5.1) Cntrifug. A circular cylindr of radius R rotats about th long axis with angular vlocity ω. Th cylindr contains an idal gas of atoms of mass m at tmpratur. Find an xprssion for
Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review
 Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
α A G C T 國立交通大學生物資訊及系統生物研究所林勇欣老師
 A G C T Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A T C G A G 0 0 0-3 C T A() A( t ) ( 3 ) ( ) A() A() ( 3 ) ( ) A( A( A( A( t ) A( 3 A( t ) ( ) A( A( Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A( A( t ) A( d
A G C T Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A T C G A G 0 0 0-3 C T A() A( t ) ( 3 ) ( ) A() A() ( 3 ) ( ) A( A( A( A( t ) A( 3 A( t ) ( ) A( A( Juks and Cantor s (969) on-aramtr modl A( A( t ) A( d
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Solution Series 9. i=1 x i and i=1 x i.
 Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
16 Electromagnetic induction
 Chatr : Elctromagntic Induction Elctromagntic induction Hint to Problm for Practic., 0 d φ or dφ 0 0.0 Wb. A cm cm 7 0 m, A 0 cm 0 cm 00 0 m B 0.8 Wb/m, B. Wb/m,, dφ d BA (B.A) BA 0.8 7 0. 00 0 80 0 8
Chatr : Elctromagntic Induction Elctromagntic induction Hint to Problm for Practic., 0 d φ or dφ 0 0.0 Wb. A cm cm 7 0 m, A 0 cm 0 cm 00 0 m B 0.8 Wb/m, B. Wb/m,, dφ d BA (B.A) BA 0.8 7 0. 00 0 80 0 8
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
HOMEWORK#1. t E(x) = 1 λ = (b) Find the median lifetime of a randomly selected light bulb. Answer:
 HOMEWORK# 52258 李亞晟 Eercise 2. The lifetime of light bulbs follows an eponential distribution with a hazard rate of. failures per hour of use (a) Find the mean lifetime of a randomly selected light bulb.
HOMEWORK# 52258 李亞晟 Eercise 2. The lifetime of light bulbs follows an eponential distribution with a hazard rate of. failures per hour of use (a) Find the mean lifetime of a randomly selected light bulb.
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
19. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND NUCLEI HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS
 . ATOMS, MOLECULES AND NUCLEI HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS. Givn :.53 Å 3?? n n ε πm n n Radius of n t Bo obit, n n ε πm n n 3 n 3 n 3 (3) () (.53).77Å n n ( ) () (.53) 53 Å. Givn : 3 7.7 x m? n n ε πm Radius of
. ATOMS, MOLECULES AND NUCLEI HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS. Givn :.53 Å 3?? n n ε πm n n Radius of n t Bo obit, n n ε πm n n 3 n 3 n 3 (3) () (.53).77Å n n ( ) () (.53) 53 Å. Givn : 3 7.7 x m? n n ε πm Radius of
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Calculus and Differential Equations page 1 of 17 CALCULUS and DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 alculus and Diffrnial Equaions pag of 7 ALULUS and DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Th following 55 qusions concrn calculus and diffrnial quaions. In his vrsion of h am, h firs choic is always h corrc on. In h acual
alculus and Diffrnial Equaions pag of 7 ALULUS and DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Th following 55 qusions concrn calculus and diffrnial quaions. In his vrsion of h am, h firs choic is always h corrc on. In h acual
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
PULLEYS 1. GROOVE SPECIFICATIONS FOR V-BELT PULLEYS. Groove dimensions and tolerances for Hi-Power PowerBand according to RMA engineering standards
 1. GROOVE SPECIFICATIONS FOR V-BELT PULLEYS Figur 3 - Groov dimnsion nomnclatur or V-blts α go lp b Ectiv diamtr Datum diamtr d Tabl No. 1 - Groov dimnsions and tolrancs or Hi-Powr PowrBand according to
1. GROOVE SPECIFICATIONS FOR V-BELT PULLEYS Figur 3 - Groov dimnsion nomnclatur or V-blts α go lp b Ectiv diamtr Datum diamtr d Tabl No. 1 - Groov dimnsions and tolrancs or Hi-Powr PowrBand according to
1. A fully continuous 20-payment years, 30-year term life insurance of 2000 is issued to (35). You are given n A 1
 Chapter 7: Exercises 1. A fully continuous 20-payment years, 30-year term life insurance of 2000 is issued to (35). You are given n A 1 35+n:30 n a 35+n:20 n 0 0.068727 11.395336 10 0.097101 7.351745 25
Chapter 7: Exercises 1. A fully continuous 20-payment years, 30-year term life insurance of 2000 is issued to (35). You are given n A 1 35+n:30 n a 35+n:20 n 0 0.068727 11.395336 10 0.097101 7.351745 25
General theorems of Optical Imaging systems
 Gnral thorms of Optcal Imagng sstms Tratonal Optcal Imagng Topcs Imagng qualt harp: mags a pont sourc to a pont Dstorton fr: mags a shap to a smlar shap tgmatc Imagng Imags a pont sourc to a nfntl sharp
Gnral thorms of Optcal Imagng sstms Tratonal Optcal Imagng Topcs Imagng qualt harp: mags a pont sourc to a pont Dstorton fr: mags a shap to a smlar shap tgmatc Imagng Imags a pont sourc to a nfntl sharp
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
Similarly, we may define hyperbolic functions cosh α and sinh α from the unit hyperbola
 Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
Universit of Hperbolic Functions The trigonometric functions cos α an cos α are efine using the unit circle + b measuring the istance α in the counter-clockwise irection along the circumference of the
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PLATE BENDING
 Rad: Chaptr 7 NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PLATE BENDING CONTENTS Govrning Equations of th First-Ordr Shar Dformation thor (FSDT) Finit lmnt modls of FSDT Shar and mmbran locking Computr implmntation
Rad: Chaptr 7 NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PLATE BENDING CONTENTS Govrning Equations of th First-Ordr Shar Dformation thor (FSDT) Finit lmnt modls of FSDT Shar and mmbran locking Computr implmntation
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
5.4 The Poisson Distribution.
 The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
CHAPTER 101 FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD
 CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Relativsitic Quantum Mechanics. 3.1 Dirac Equation Summary and notation 3.1. DIRAC EQUATION SUMMARY AND NOTATION. April 22, 2015 Lecture XXXIII
 3.1. DIRAC EQUATION SUMMARY AND NOTATION April, 015 Lctur XXXIII Rlativsitic Quantum Mchanics 3.1 Dirac Equation Summary and notation W found that th two componnt spinors transform according to A = ± σ
3.1. DIRAC EQUATION SUMMARY AND NOTATION April, 015 Lctur XXXIII Rlativsitic Quantum Mchanics 3.1 Dirac Equation Summary and notation W found that th two componnt spinors transform according to A = ± σ
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C
 DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
Second Order RLC Filters
 ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
ECEN 60 Circuits/Electronics Spring 007-0-07 P. Mathys Second Order RLC Filters RLC Lowpass Filter A passive RLC lowpass filter (LPF) circuit is shown in the following schematic. R L C v O (t) Using phasor
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 651 APPENDIX B. BIBLIOGRAPHY 677 APPENDIX C. ANSWERS TO SELECTED EXERCISES 679
 APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
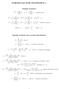 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Probability and Random Processes (Part II)
 Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Potential Dividers. 46 minutes. 46 marks. Page 1 of 11
 Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
Potential Dividers 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 11 Q1. In the circuit shown in the figure below, the battery, of negligible internal resistance, has an emf of 30 V. The pd across the lamp is 6.0 V and
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ
 ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Homework for 1/27 Due 2/5
 Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Modbus basic setup notes for IO-Link AL1xxx Master Block
 n Modbus has four tables/registers where data is stored along with their associated addresses. We will be using the holding registers from address 40001 to 49999 that are R/W 16 bit/word. Two tables that
n Modbus has four tables/registers where data is stored along with their associated addresses. We will be using the holding registers from address 40001 to 49999 that are R/W 16 bit/word. Two tables that
Differential equations
 Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
ΠΟΣΟΤΙΚΕΣ ΜΕΘΟΔΟΙ ΔΕΟ 13 ΤΟΜΟΣ Δ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ
 ΠΟΣΟΤΙΚΕΣ ΜΕΘΟΔΟΙ ΔΕΟ 13 ΤΟΜΟΣ Δ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ (5) ΑΘΗΝΑ ΜΑΡΤΙΟΣ 2013 1 ΕΠΕΞΗΓΗΣΗ ΤΥΠΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΩΝ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΤΑΝΟΜΕΣ Τυχαία μεταβλητή είναι μία συνάρτηση η οποία να αντιστοιχεί
ΠΟΣΟΤΙΚΕΣ ΜΕΘΟΔΟΙ ΔΕΟ 13 ΤΟΜΟΣ Δ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΣΗ ΕΠΙΧΕΙΡΗΣΕΩΝ (5) ΑΘΗΝΑ ΜΑΡΤΙΟΣ 2013 1 ΕΠΕΞΗΓΗΣΗ ΤΥΠΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΜΒΟΛΩΝ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗΣ ΚΑΤΑΝΟΜΕΣ Τυχαία μεταβλητή είναι μία συνάρτηση η οποία να αντιστοιχεί
Chapter 4 : Linear Wire Antenna
 Chapt 4 : Lina Wi Antnna nfinitsima Dipo Sma Dipo Finit Lngth Dipo Haf-Wavngth Dipo Lina mnts na o on nfinit Pfct Conductos nfinitsima Dipo Lngth
Chapt 4 : Lina Wi Antnna nfinitsima Dipo Sma Dipo Finit Lngth Dipo Haf-Wavngth Dipo Lina mnts na o on nfinit Pfct Conductos nfinitsima Dipo Lngth
( y) Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
An Inventory of Continuous Distributions
 Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals. Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz
 Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz ybridization Valence Bond Approach to bonding sp 3 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py + Ψ 2 pz) sp 2 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py)
Solutions to the Schrodinger equation atomic orbitals Ψ 1 s Ψ 2 s Ψ 2 px Ψ 2 py Ψ 2 pz ybridization Valence Bond Approach to bonding sp 3 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py + Ψ 2 pz) sp 2 (Ψ 2 s + Ψ 2 px + Ψ 2 py)
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Φυγόκεντρος αποθήκευσης Κανονική n 1k Αγωγή n 2k
 Άσκηση 3. Τα παρακάτω δεδομένα δίνουν το πλήθος y των φυτών που διατήρησαν μια ιδιότητα όταν n φυτά βρέθηκαν κάτω από διαφορετικές συνθήκες. Ένας ποιοτικός παράγοντας (αγωγή) ήταν η αποθήκευση σε θερμοκρασία
Άσκηση 3. Τα παρακάτω δεδομένα δίνουν το πλήθος y των φυτών που διατήρησαν μια ιδιότητα όταν n φυτά βρέθηκαν κάτω από διαφορετικές συνθήκες. Ένας ποιοτικός παράγοντας (αγωγή) ήταν η αποθήκευση σε θερμοκρασία
7 Present PERFECT Simple. 8 Present PERFECT Continuous. 9 Past PERFECT Simple. 10 Past PERFECT Continuous. 11 Future PERFECT Simple
 A/ Ονόματα και ένα παράδειγμα 1 Present Simple 7 Present PERFECT Simple 2 Present Continuous 8 Present PERFECT Continuous 3 Past Simple (+ used to) 9 Past PERFECT Simple she eats she is eating she ate
A/ Ονόματα και ένα παράδειγμα 1 Present Simple 7 Present PERFECT Simple 2 Present Continuous 8 Present PERFECT Continuous 3 Past Simple (+ used to) 9 Past PERFECT Simple she eats she is eating she ate
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΕΙΡΑΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΜΕΤΑΠΤΥΧΙΑΚΩΝ ΣΠΟΥΔΩΝ ΣΤΗΝ ΝΑΥΤΙΛΙΑ ΝΟΜΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΘΕΣΜΙΚΟ ΦΟΡΟΛΟΓΙΚΟ ΠΛΑΙΣΙΟ ΚΤΗΣΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΚΜΕΤΑΛΛΕΥΣΗΣ ΠΛΟΙΟΥ ΔΙΠΛΩΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΙΑ που υποβλήθηκε στο
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
Risk! " #$%&'() *!'+,'''## -. / # $
 Risk! " #$%&'(!'+,'''## -. / 0! " # $ +/ #%&''&(+(( &'',$ #-&''&$ #(./0&'',$( ( (! #( &''/$ #$ 3 #4&'',$ #- &'',$ #5&''6(&''&7&'',$ / ( /8 9 :&' " 4; < # $ 3 " ( #$ = = #$ #$ ( 3 - > # $ 3 = = " 3 3, 6?3
Risk! " #$%&'(!'+,'''## -. / 0! " # $ +/ #%&''&(+(( &'',$ #-&''&$ #(./0&'',$( ( (! #( &''/$ #$ 3 #4&'',$ #- &'',$ #5&''6(&''&7&'',$ / ( /8 9 :&' " 4; < # $ 3 " ( #$ = = #$ #$ ( 3 - > # $ 3 = = " 3 3, 6?3
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
CMPSCI 69GG Applied Information Theory Fall 006 Problem Set 3: Solutions. [Cover and Thomas 7.] a Define the following notation, C I p xx; Y max X; Y C I p xx; Ỹ max I X; Ỹ We would like to show that C
Bit Error Rate in Digital Photoreceivers
 Bit Eo Rat in Digital hotocivs In th pvious slids, w saw that th photociv aks a dcision as to whth th covd wavfo is abov ( o blow ( th thshold lvl. Whn nois is psnt, a wong dcision can b ad, i.. w hav
Bit Eo Rat in Digital hotocivs In th pvious slids, w saw that th photociv aks a dcision as to whth th covd wavfo is abov ( o blow ( th thshold lvl. Whn nois is psnt, a wong dcision can b ad, i.. w hav
ΕΦΑΡΜΟΣΜΕΝΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ I Παντελής Δημήτριος Τμήμα Μηχανολόγων Μηχανικών
 ΕΦΑΡΜΟΣΜΕΝΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ I Παντελής Δημήτριος Τμήμα Μηχανολόγων Μηχανικών ΤΥΧΑΙΕΣ ΜΕΤΑΒΛΗΤΕΣ Σε κάθε αποτέλεσμα του πειράματος αντιστοιχεί μία αριθμητική τιμή Μαθηματικός ορισμός: Τυχαία μεταβλητή X είναι
ΕΦΑΡΜΟΣΜΕΝΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ I Παντελής Δημήτριος Τμήμα Μηχανολόγων Μηχανικών ΤΥΧΑΙΕΣ ΜΕΤΑΒΛΗΤΕΣ Σε κάθε αποτέλεσμα του πειράματος αντιστοιχεί μία αριθμητική τιμή Μαθηματικός ορισμός: Τυχαία μεταβλητή X είναι
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ
 ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ Γηπισκαηηθή Δξγαζία ηνπ Φνηηεηή ηνπ ηκήκαηνο Ζιεθηξνιόγσλ Μεραληθώλ θαη Σερλνινγίαο Ζιεθηξνληθώλ
ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΠΑΣΡΩΝ ΣΜΖΜΑ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΖΥΑΝΗΚΩΝ ΚΑΗ ΣΔΥΝΟΛΟΓΗΑ ΤΠΟΛΟΓΗΣΩΝ ΣΟΜΔΑ ΤΣΖΜΑΣΩΝ ΖΛΔΚΣΡΗΚΖ ΔΝΔΡΓΔΗΑ Γηπισκαηηθή Δξγαζία ηνπ Φνηηεηή ηνπ ηκήκαηνο Ζιεθηξνιόγσλ Μεραληθώλ θαη Σερλνινγίαο Ζιεθηξνληθώλ
Section 9.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
Bayesian statistics. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
= λ 1 1 e. = λ 1 =12. has the properties e 1. e 3,V(Y
 Stat 50 Homework Solutions Spring 005. (a λ λ λ 44 (b trace( λ + λ + λ 0 (c V (e x e e λ e e λ e (λ e by definition, the eigenvector e has the properties e λ e and e e. (d λ e e + λ e e + λ e e 8 6 4 4
Stat 50 Homework Solutions Spring 005. (a λ λ λ 44 (b trace( λ + λ + λ 0 (c V (e x e e λ e e λ e (λ e by definition, the eigenvector e has the properties e λ e and e e. (d λ e e + λ e e + λ e e 8 6 4 4
ΕΝΙΣΧΥΣΗ ΠΛΑΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΟΚΩΝ ΣΕ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΜΕ ΜΑΝΔΥΕΣ Η ΕΛΑΣΜΑΤΑ ΣΥΝΘΕΤΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ.
 ΕΝΙΣΧΥΣΗ ΠΛΑΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΟΚΩΝ ΣΕ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΜΕ ΜΑΝΔΥΕΣ Η ΕΛΑΣΜΑΤΑ ΣΥΝΘΕΤΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ. Σύμφωνα με τον Κανονιμό Επεμβάεων, ο νέος οπλιμός υπολοίζεται έτι ώτε ε υνεραία με τον υφιτάμενο παλαιό οπλιμό να αναλαμβάνονται
ΕΝΙΣΧΥΣΗ ΠΛΑΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΔΟΚΩΝ ΣΕ ΚΑΜΨΗ ΜΕ ΜΑΝΔΥΕΣ Η ΕΛΑΣΜΑΤΑ ΣΥΝΘΕΤΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ. Σύμφωνα με τον Κανονιμό Επεμβάεων, ο νέος οπλιμός υπολοίζεται έτι ώτε ε υνεραία με τον υφιτάμενο παλαιό οπλιμό να αναλαμβάνονται
Answers - Worksheet A ALGEBRA PMT. 1 a = 7 b = 11 c = 1 3. e = 0.1 f = 0.3 g = 2 h = 10 i = 3 j = d = k = 3 1. = 1 or 0.5 l =
 C ALGEBRA Answers - Worksheet A a 7 b c d e 0. f 0. g h 0 i j k 6 8 or 0. l or 8 a 7 b 0 c 7 d 6 e f g 6 h 8 8 i 6 j k 6 l a 9 b c d 9 7 e 00 0 f 8 9 a b 7 7 c 6 d 9 e 6 6 f 6 8 g 9 h 0 0 i j 6 7 7 k 9
C ALGEBRA Answers - Worksheet A a 7 b c d e 0. f 0. g h 0 i j k 6 8 or 0. l or 8 a 7 b 0 c 7 d 6 e f g 6 h 8 8 i 6 j k 6 l a 9 b c d 9 7 e 00 0 f 8 9 a b 7 7 c 6 d 9 e 6 6 f 6 8 g 9 h 0 0 i j 6 7 7 k 9
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data
 Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Strain gauge and rosettes
 Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Strain gauge and rosettes Introduction A strain gauge is a device which is used to measure strain (deformation) on an object subjected to forces. Strain can be measured using various types of devices classified
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model
 Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
ss rt çã r s t Pr r Pós r çã ê t çã st t t ê s 1 t s r s r s r s r q s t r r t çã r str ê t çã r t r r r t r s
 P P P P ss rt çã r s t Pr r Pós r çã ê t çã st t t ê s 1 t s r s r s r s r q s t r r t çã r str ê t çã r t r r r t r s r t r 3 2 r r r 3 t r ér t r s s r t s r s r s ér t r r t t q s t s sã s s s ér t
P P P P ss rt çã r s t Pr r Pós r çã ê t çã st t t ê s 1 t s r s r s r s r q s t r r t çã r str ê t çã r t r r r t r s r t r 3 2 r r r 3 t r ér t r s s r t s r s r s ér t r r t t q s t s sã s s s ér t
Module 5. February 14, h 0min
 Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Notes on the Open Economy
 Notes on the Open Econom Ben J. Heijdra Universit of Groningen April 24 Introduction In this note we stud the two-countr model of Table.4 in more detail. restated here for convenience. The model is Table.4.
Notes on the Open Econom Ben J. Heijdra Universit of Groningen April 24 Introduction In this note we stud the two-countr model of Table.4 in more detail. restated here for convenience. The model is Table.4.
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet
 Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
