Kul Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 02/2016
|
|
|
- Ζηνόβιος Κανακάρης-Ρούφος
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Kul Models fo beam, plate and shell stuctues, /16 Demo poblems 1. Given the Catesian stain components ε ij ij, {, xy}, deive the coesponding stain components ε αβ αβ, {, φ } of the pola coodinate system (in tems of the Catesian components). Use the invaiance of dyad quantities and elationship e cosφ sinφ i =. eφ sinφ cosφ j Answe cos φ cosφsinφ cosφsinφ sin φ ε xx ε xy ε εφ cosφsinφ cos φ sin φ cosφsinφ = εφ cosφsinφ sin φ cos φ cosφsinφ ε yx εφφ sin cos sin cos sin cos yy φ φ φ φ φ φ ε. Deive the gadient expession of the spheical coodinate system, when the mapping is given by = xi + yj + zk = (sinθcosφi + sinθsinφ j + cos θ k ). Use the geneic ecipe { e e e }[ F] T [ H] 1 α = α β γ β γ αβγ,, θφ,,. and ( ) ( ), whee [ ] x, y, z α α, α e α i H = x, β y, β z, β, eβ = [ F] j x, γ y, γ z, γ eγ k Answe 1 1 = eθ + eφ + e θ sinθ φ 3. In the intinsic coodinate system and XY-plane case, the displacement assumption of a cuved Timoshenko beam model is u = u + θ ρ, whee u = use () s + vse () n, () θ = ψ se b, and ρ = ne n. Deive the small stain component expessions ε ij αβ, {, sn} by using 1 ε = + [ u ( u) ] c, 1 = es + en, 1 n/ R s n es 1 en es = s e R, and = n es n. en Assume that cuvatue 1/ R is constant. R v 1 R 1 Answe εss = ( u, s ψ, sn ) εsn ns ( u v, s ) R n R = ε = R n R + ψ
2 The demo poblems ae published in the couse homepage on Fidays. The poblems ae elated to the topic of the next weeks lectue (Wed hall K3 118). Solutions to the poblems ae explained in the weekly execise sessions (Thu hall K3 118) and will also be available in the home page of the couse. Please, notice that the poblems of the midtems and the final exam ae of this type.
3 Lectue poblem Be pepaed to deive the small stain components in a specified system, when displacement, gadient expession, and deivatives of the basis vectos ae given. Lectue poblems ae specified and solved duing the lectue (Wed hall K3 118). The time allocated fo this is 3 min.
4 Home poblem Deive the small stain expessions in the cylindical coodinate system, when displacement, gadient opeato and non-zeo deives of the basis vectos ae u (,, z) = ue + u e + uze 1 φ φ φ z, = e + eφ + ez φ z Solution template e eφ = eφ, and = e. φ φ, In manipulation of vecto expession containing vectos and dyads, it is impotant to emembe that tenso ( ), coss ( ), inne ( ) poducts ae non-commutative (ode mattes). The basis vectos of a cuvilinea coodinate system ae not constants which should be taken into account if gadient opeato is pat of expession. Othewise, simplifying an expession o finding a specific fom in a given coodinate system is a staightfowad (sometimes tedious) execise. 1. Conside the tems of displacements sepaately to keep expessions shot enough. Substitute the epesentations in the specified system, expand, use the poduct ule fo deivatives, and substitute the deivatives of the basis vectos. ( u 1 e ) = e ( ue ) + e ( ue ) + e z ( ue φ ) φ z u e 1 u 1 e u e = e e + eu + eφ e + eφ u + ez e + ezu φ φ z z u 1 u 1 u = ee + ee φ + ee φ φ u+ ee z φ z ( ue φ φ ) = = = ( ue ) = z z = =
5 . Combine the tems to get the displacement gadient u. Afte that, swap the basis vectos of each tem of u and e-aange to get the conjugate expession ( u ) (in the same ode of the tems as u ) u = ee + ee + ee + φ z c ee + ee + ee φ φ φ φ z + ee + ee + ee z z φ z z ( u) = ee + ee φ + ee z + c ee + ee + ee φ φ φ φ z + ee + ee + ee z z φ z z 3. Use the small stain definition ε = 1 [ u + ( u )] c (symmetic pat of displacement gadient!) ε = ee + ee + ee + φ z ee φ + ee φ φ + ee + φ z ee + ee + ee z z φ z z 4. Wite down the component expessions ε ε = ε z = = φ ε ε = ε z = φ = φφ φ ε z 1 u ( z u = + ) z 1 1 u u ( z φ φ = + ) φ z ε z zz u ε = z z
6 The compulsoy home poblems ae published in the couse homepage on Fidays and the deadline fo answes is the next weeks Fiday Retun you homewok answes into the geen couse mailbox that can be found fom the coido of the K3 building lobby (Puumiehenkuja 5A). Please, use the solution templates given.
7 Kul Models fo beam, plate and shell stuctues INDEX NOTATION (Othonomal basis) ab i i= ab i i= ab 11+ ab+ + anbn i I ai/ xj aij, δ ij ei ej {,1} ( e i e j = δ ij ) ε e ( e e ) { 1,,1} ( e i e j = ε ijk e k ) ijk i j k εijkεimn = δ jmδkn δ jnδ km ε det( a) = ε a a a ijk lmn il jm kn GENERAL a = ae i i a= a ij ee i j a = aijklee i je ke l... I a = a I = a a ( I = ii + jj + kk ) I : a = a: I = a a ( I = iiii + jjjj + kkkk + ijji + jiij + ikki + kiik + kjjk + jkkj ) a= aijee i j ac = aee ij j i a = a c a b = a b b IDENTITIES a ( b c) = ( a b) c a ( b c) = bac ( ) cab ( ) a:( b) = ( a b) ( a) b c CYLINDRICAL φ z SYSTEM = cosφi + sinφ j + zk e cφ sφ i e 1 e eφ = sφ cφ j eφ= 1 eφ φ ez 1 k ez ez 1 = e + eφ + ez φ z SPHERICAL θφ SYSTEM
8 ( θφ,, ) = (s θ c φ i + s θ s φ j + c θ k) eθ cθφ c cθφ s sθ i eθ cθ eφ eφ = sφ cφ j eφ= sθe cθeθ φ e sθφ c sθφ s cθ k e sθeφ eθ e eφ =, θ e eθ 1 1 = eθ + eφ + e θ sinθ φ THIN BODY snb SYSTEM FOR PLANAR BEAMS (, s n) = () s + ne () s n es, s /, s, s es en / R = = = e n ess, / ess, ess, R s en es / R R = es + en R n s n ORTHONORMAL CURVILINEAR COORDINATES eα eα eα 1 i e = ( i[ F])[ F] e = [ D] () i e e = D e en en en β β β i j ijk k T T eα α eα α = e F H = e D e e T 1 β [ ] [ ] β β [ ] β = ed i ij j = ed i i n n n n Γ = e e e = e = ( e e ) D D ( e e ) ijk i j k k i s s jl l k a= ( dae ) i a= ( da + a Γ ) ee i i j k ikj i j a= da +Γ a i i iji j a= ( da +Γ a +Γ a ) e i ij kik ij ikj ik j Γ ijk = D i D jk a= ( a) = dda i i +Γjijda i PLATE GEOMETRY ( φ n)
9 (, φ, n) = [ i cosφ+ j sin φ ] + nen e cosφ sinφ i eφ = sinφ cosφ j en 1 k e eφ eφ = e φ e n d = d 1 = d = φ φ n n Γ = Γ = φφ φφ 1 dv = dndω BEAM GEOMETRY ( snb ) ( s, n, b) = [ ( s)] + ne n + be b es, s es κb es κben en= ess, / ess, en= κb κs en= κseb κbes s eb es en eb κs eb κsen d 1 s = 1 n b) ( s + sb n sn b ( κ κ κ ) d n = n d b = b 1 ssn sns (1 n b) b Γ = Γ = κ κ dv = (1 nκ ) dads b 1 snb Γ sbn = (1 nκb ) κs Γ = CYLINDRICAL SHELL GEOMETRY ( zφ n) ( z, φ, n) = [ ir cosφ+ jrsin φ + kz] + nen ez 1 i ez eφ = sinφ cosφ j eφ = en φ en cos φ sinφ k en eφ d = z z 1 φ = ( ) φ d n = n d R n Γ φφn = Γ φnφ = ( R n) dv = (1 nr ) dn( Rdφ ) dz = (1 nr ) dndω LINEAR ISOTROPIC ELASTICITY σ = E : ε ε = 1 [ u + ( u )] c
10 E ν σ = [ I( I : ε) + ε] 1+ ν 1 ν E ν E = ( II + I ) 1+ ν 1 ν 3 Et D = 1(1 ν ) 1 ε= [(1 + νσ ) ν I( I : σ )] E PRINCIPLE OF VIRTUAL WORK ext int δw = δw + δw = δ u U (a function set) δw = ( σ : δε ) dv + ( f δu) dv + ( t δ u) da V c V A BEAM EQUATIONS F + b F σ = = da M + i F + c M ρ σ F σ E E ρ u + i θ = da = da M ρ σ ρ E ρ E ρ θ E = Eii + Gjj + Gkk TIMOSHENKO BEAM ( xyz ) N + bx Q y + by= Qz + bz T + cx M y Qz + cy= Mz + Qy + cz N EAu ES yψ + ESzθ Qy= GA( v ψ) GSzφ Q z GA( w + θ) + GS yφ T GSz ( v ψ) + GSy ( w + θ) + G( I yy + Izz ) φ M y = ESzu EIzyψ + EIzzθ M z ES yu + EI yyψ EI yzθ TIMOSHENKO BEAM ( snb ) N Qnκb + Qbκn + bs Qn + Nκb Qbκs + bn= Qb Nκn + Qnκs + bb T Mnκb + Mbκn + cs Mn + Tκb Mbκs Qb + cn= Mb Tκn + Mnκs + Qn + cb
11 N EA( u + wκ n vκ b) + ESb( θ + φκb ψκs) ESn( ψ φκn + θκs) Qn= GA( v + uκb wκ s ψ ) GSb( φ + ψκn θκb) Q b GA( w uκn + vκ s + θ ) + GSn( φ + ψκn θκb) T GSn( w uκn + vκ s + θ ) + GI ( φ + ψκn θκb) GSb( v + uκb wκ s ψ ) M n = ESb( u + wκ n vκ b) + EIbb( θ + φκb ψκs ) EIbn( ψ φκn + θκs ) M b ESn( u + wκ n vκ b) EInb( θ + φκb ψκs ) + EInn( ψ φκn + θκs ) PLATE EQUATIONS F + b = ( M Q+ c) k = F = σ dz = iin + ijn + jin + jjn + ( ki + ik ) Q + ( kj + jk ) Q xx xy yx yy x y M = σ zdz = iim + ijm + jim + jjm + ( ki + ik ) R + ( kj + jk ) R xx xy yx yy x y REISSNER-MINDLIN PLATE ( xyz ) Nxx, x + Nyx, y + b x = Nyy, y + Nxy, x + by Qxx, + Qyy, + bz Mxx, x + Myx, y Qx + cx = Myy, y + Mxy, x Qy + cy Qx w, x + θ = Gtk Q w φ y, y Nxx u, x + ν v, y Et Nyy = v, y + νu, x 1 ν N (1 ν )( u + v ) / xy, y, x M xx θ, x νφ, y Myy = D φ, y + νθ, x M (1 ν)( θ φ ) / xy, y, x Qn Q o w w n Nnn Nn o un un = M ns M s o θn θn = N ns Ns o us u s M nn M n o θs θs KIRCHHOFF PLATE ( xyz ) Nxx, x + Nyx, y + b x = Nyy, y + Nxy, x + by Mxx, xx + Mxy, xy + Myy, yy + bz ( Mxx, x + Myx, y Qx + cx ) = ( Myy, y + Mxy, x Qy + cy ) Nxx u, x + ν v, y Et Nyy = v, y + νu, x 1 ν N (1 ν )( u + v ) / xy, y, x Mxx w, xx + ν w, yy Myy = D w, yy + ν w, xx M (1 ν ) w xy, xy
12 Nnn Nn o un un = N ns Ns o us us Q + M Q M o w w M nn M n o w, n + θ s n nss, ss, = REISSNER-MINDLIN PLATE ( φ z) [( N ) + N N ] / + b [( Nφ ), + Nφφ, φ + Nφ] / + bφ, φ, φ φφ = N u, + ν ( u + uφφ, )/ Et Nφφ = u ν, + ( u+ uφ, φ )/ 1 ν N (1 ν )[( u u ) / + u ] / φ, φ φ φ, [( Q), + Qφφ, ] / + bz [( M ), + Mφ, φ Mφφ ] / Q + c = [( Mφ ), + Mφφ, φ + Mφ] / Qφ + cφ Q w, + θφ = Gt Q w θ φ, φ / M θφ, + νθ ( φ θ, φ)/ Mφφ = D νθφ, + ( θφ θ, φ )/ M (1 ν)[( θ + θ ) / θ ] / φ φφ,, ROTATION SYMMETRIC KIRCHHOFF PLATE D w+ b z = 1 d d = ( ) d d MEMBRANE EQUATIONS IN CYLINDRICAL GEOMETRY ( zφ n) 1 Nφz, φ + Nzz, z R bz 1 Nzφ, z + Nφφ, φ + bφ = R b 1 n Nφφ R te 1 [ u zz, + ν ( u φφ, u n)] 1 R Nzz ν te 1 Nφφ = [ ( u φ, φ un) + νuzz, ] 1 ν R Nzφ 1 tg( uz, φ + uφ, z) R MEMBRANE EQUATIONS IN SPHERICAL GEOMETRY ( φθ n ) cscθnφφ, φ + Nθφ, θ + cot θ( Nθφ + Nφθ ) bφ 1 csc θnφθ, φ + Nθθ, θ + cot θ ( Nθθ Nφφ ) + bθ = R Nφφ + Nθθ b n
13 te [ csc θ(cosθu θ + ν sin θuθθ, + uφφ, ) (1 + ν) un] N 1 φφ ν 1 te Nθθ = [ csc θ ( ν cosθu sin u θ + θ θθ, + νuφφ, ) ( 1 + ν) un] R 1 ν Nφθ tg( cscθuθφ, co tθuφ + uφθ, ) SHELL EQUATIONS IN CYLINDRICAL GEOMETRY ( zφ n) κ Nφz, φ + Nzz, z + bz Nzφ, z + κnφφ, φ κqφ + bφ = κqφ, φ + Qzz, + κnφφ + bn Mzφ, z + κmφφ, φ κmφn Qφ + cφ M + κm Q + c = zz, z φz, φ z z Nzz uz, z + νκ( uφφ, un) Et Nφφ = u ν z, z + κ( uφφ, un) 1 ν Nzφ (1 ν)( uφ, z + κuz, φ) / Mzz ωzz, + κνωφφ, κuzz, Mφφ νω zz, + κωφφ, + κ ( uφφ, un) M zφ D (1 ν )( ωφ, z κωz, φ κuφ, z) / = + Mφz (1 ν)( ωφ, z + κωz, φ + κ uz, φ) / M (1 νκκ ) ( u + κu + ω) / φn n, φ φ φ Qz unz, + ωz = tg Q ω + κ( u + u ) φ φ n, φ φ ωz θ φ = ωφ θz
Kul Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 08/2016
 Kul-49.45 Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 8/6 Demo problems. Spring geometry is defined by the mapping s s s r ( s) = ( ir cos + jrsin + kε ), R + ε R + ε + ε where R and ε are constants and
Kul-49.45 Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 8/6 Demo problems. Spring geometry is defined by the mapping s s s r ( s) = ( ir cos + jrsin + kε ), R + ε R + ε + ε where R and ε are constants and
Kul Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 10/2016
 Kul-49.45 Models fo beam, plate and shell stuctues, /6 Demo poblems. Conside mapping (, φ, n) = [ cos( φ) i + sin( φ) j] + nen. Compute the expession of the basis vecto deivatives, gadient opeato, and
Kul-49.45 Models fo beam, plate and shell stuctues, /6 Demo poblems. Conside mapping (, φ, n) = [ cos( φ) i + sin( φ) j] + nen. Compute the expession of the basis vecto deivatives, gadient opeato, and
Kul Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 09/2016
 Kul-49.45 Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 9/6 Demo problems. Derive the component forms of the membrane equations in spherical φθ n coordinate system and geometry. Use the component form N
Kul-49.45 Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 9/6 Demo problems. Derive the component forms of the membrane equations in spherical φθ n coordinate system and geometry. Use the component form N
Kul Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 07/2016
 Kul-9.5 Models fo beam, plate and shell stuctues, 7/6 Demo poblems. Deive the component foms of the elastic isotopic Kichhoff plate constitutive equations (just bending) in the pola coodinate system. Use
Kul-9.5 Models fo beam, plate and shell stuctues, 7/6 Demo poblems. Deive the component foms of the elastic isotopic Kichhoff plate constitutive equations (just bending) in the pola coodinate system. Use
Kul Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 09/2016
 Kul-49.45 Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 9/6 Demo problems. Derive the component forms of the membrane equations in spherical φθ n coordinate system and geometry. Use the component form N
Kul-49.45 Models for beam, plate and shell structures, 9/6 Demo problems. Derive the component forms of the membrane equations in spherical φθ n coordinate system and geometry. Use the component form N
Kul Models for beam, plate and shell structures, MT
 Kul-49.45 Models fo eam, plate and shell stuctues, MT- 4. Mapping (, φ, z) = cosφi + sinφ j + zk (in detail) the geneic fomula defines the cylindical φ z coodinate system. Use e e eφ= ( [ F])[ F] eφ α
Kul-49.45 Models fo eam, plate and shell stuctues, MT- 4. Mapping (, φ, z) = cosφi + sinφ j + zk (in detail) the geneic fomula defines the cylindical φ z coodinate system. Use e e eφ= ( [ F])[ F] eφ α
Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines
![Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines Space Physics (I) [AP-3044] Lecture 1 by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct Lecture 1. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines](/thumbs/51/28406191.jpg) Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
Space Physics (I) [AP-344] Lectue by Ling-Hsiao Lyu Oct. 2 Lectue. Dipole Magnetic Field and Equations of Magnetic Field Lines.. Dipole Magnetic Field Since = we can define = A (.) whee A is called the
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Curvilinear Systems of Coordinates
 A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
A Cuvilinea Systems of Coodinates A.1 Geneal Fomulas Given a nonlinea tansfomation between Catesian coodinates x i, i 1,..., 3 and geneal cuvilinea coodinates u j, j 1,..., 3, x i x i (u j ), we intoduce
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics
 Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Analytical Expression for Hessian
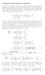 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) λ = 1 + t t. θ = t ε t. Continuum Mechanics. Chapter 1. Description of Motion dt t. Chapter 2. Deformation and Strain
 Continm Mechanics. Official Fom Chapte. Desciption of Motion χ (,) t χ (,) t (,) t χ (,) t t Chapte. Defomation an Stain s S X E X e i ij j i ij j F X X U F J T T T U U i j Uk U k E ( F F ) ( J J J J)
Continm Mechanics. Official Fom Chapte. Desciption of Motion χ (,) t χ (,) t (,) t χ (,) t t Chapte. Defomation an Stain s S X E X e i ij j i ij j F X X U F J T T T U U i j Uk U k E ( F F ) ( J J J J)
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION. Solution Manual
 ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
ANTENNAS and WAVE PROPAGATION Solution Manual A.R. Haish and M. Sachidananda Depatment of Electical Engineeing Indian Institute of Technolog Kanpu Kanpu - 208 06, India OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 2 Contents
21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) 21. Stresses Around a Hole (I) I Main Topics
 I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
I Main Topics A Intoducon to stess fields and stess concentaons B An axisymmetic poblem B Stesses in a pola (cylindical) efeence fame C quaons of equilibium D Soluon of bounday value poblem fo a pessuized
VEKTORANALYS. CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (kroklinjiga koordinatsytem) Kursvecka 4. Kapitel 10 Sidor
 VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
VEKTORANALYS Kusvecka 4 CURVILINEAR COORDINATES (koklinjiga koodinatstem) Kapitel 10 Sido 99-11 TARGET PROBLEM An athlete is otating a hamme Calculate the foce on the ams. F ams F F ma dv a v dt d v dt
r = x 2 + y 2 and h = z y = r sin sin ϕ
 Homewok 4. Solutions Calculate the Chistoffel symbols of the canonical flat connection in E 3 in a cylindical coodinates x cos ϕ, y sin ϕ, z h, b spheical coodinates. Fo the case of sphee ty to make calculations
Homewok 4. Solutions Calculate the Chistoffel symbols of the canonical flat connection in E 3 in a cylindical coodinates x cos ϕ, y sin ϕ, z h, b spheical coodinates. Fo the case of sphee ty to make calculations
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
4.2 Differential Equations in Polar Coordinates
 Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Course Reader for CHEN 7100/7106. Transport Phenomena I
 Couse Reade fo CHEN 7100/7106 Tanspot Phenomena I Pof. W. R. Ashust Aubun Univesity Depatment of Chemical Engineeing c 2012 Name: Contents Peface i 0.1 Nomenclatue........................................
Couse Reade fo CHEN 7100/7106 Tanspot Phenomena I Pof. W. R. Ashust Aubun Univesity Depatment of Chemical Engineeing c 2012 Name: Contents Peface i 0.1 Nomenclatue........................................
Problems in curvilinear coordinates
 Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Poblems in cuvilinea coodinates Lectue Notes by D K M Udayanandan Cylindical coodinates. Show that ˆ φ ˆφ, ˆφ φ ˆ and that all othe fist deivatives of the cicula cylindical unit vectos with espect to the
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
Kul Finite element method I, Exercise 08/2016
 Kul-49.3300 Finite element metod I, Eercise 08/016 Demo problems 1. A square tin slab (1) is loaded by a po force () as sown in te figure. Derive te relationsip between te force magnitude F and displacement
Kul-49.3300 Finite element metod I, Eercise 08/016 Demo problems 1. A square tin slab (1) is loaded by a po force () as sown in te figure. Derive te relationsip between te force magnitude F and displacement
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
The Laplacian in Spherical Polar Coordinates
 Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
dx x ψ, we should find a similar expression for rθφ L ψ. From L = R P and our knowledge of momentum operators, it follows that + e y z d
 PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
PHYS851 Quantum Mechanics I, Fall 2009 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 11 Topics Coveed: Obital angula momentum, cente-of-mass coodinates Some Key Concepts: angula degees of feedom, spheical hamonics 1. [20 pts] In
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Mock Exam 7. 1 Hong Kong Educational Publishing Company. Section A 1. Reference: HKDSE Math M Q2 (a) (1 + kx) n 1M + 1A = (1) =
 Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
Mock Eam 7 Mock Eam 7 Section A. Reference: HKDSE Math M 0 Q (a) ( + k) n nn ( )( k) + nk ( ) + + nn ( ) k + nk + + + A nk... () nn ( ) k... () From (), k...() n Substituting () into (), nn ( ) n 76n 76n
Chapter 7a. Elements of Elasticity, Thermal Stresses
 Chapte 7a lements of lasticit, Themal Stesses Mechanics of mateials method: 1. Defomation; guesswok, intuition, smmet, pio knowledge, epeiment, etc.. Stain; eact o appoimate solution fom defomation. Stess;
Chapte 7a lements of lasticit, Themal Stesses Mechanics of mateials method: 1. Defomation; guesswok, intuition, smmet, pio knowledge, epeiment, etc.. Stain; eact o appoimate solution fom defomation. Stess;
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small spheres separated by a distance s. The charge on one sphere changes with time and is described by
 5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
Appendix A. Curvilinear coordinates. A.1 Lamé coefficients. Consider set of equations. ξ i = ξ i (x 1,x 2,x 3 ), i = 1,2,3
 Appendix A Curvilinear coordinates A. Lamé coefficients Consider set of equations ξ i = ξ i x,x 2,x 3, i =,2,3 where ξ,ξ 2,ξ 3 independent, single-valued and continuous x,x 2,x 3 : coordinates of point
Appendix A Curvilinear coordinates A. Lamé coefficients Consider set of equations ξ i = ξ i x,x 2,x 3, i =,2,3 where ξ,ξ 2,ξ 3 independent, single-valued and continuous x,x 2,x 3 : coordinates of point
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Equations. BSU Math 275 sec 002,003 Fall 2018 (Ultman) Final Exam Notes 1. du dv. FTLI : f (B) f (A) = f dr. F dr = Green s Theorem : y da
 BSU Math 275 sec 002,003 Fall 2018 (Ultman) Final Exam Notes 1 Equations r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) k r = r (t) t s = r = r (t) t r(u, v) = x(u, v) î + y(u, v) ĵ + z(u, v) k S = ( ( ) r r u r v = u
BSU Math 275 sec 002,003 Fall 2018 (Ultman) Final Exam Notes 1 Equations r(t) = x(t) î + y(t) ĵ + z(t) k r = r (t) t s = r = r (t) t r(u, v) = x(u, v) î + y(u, v) ĵ + z(u, v) k S = ( ( ) r r u r v = u
Lifting Entry (continued)
 ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Strain and stress tensors in spherical coordinates
 Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Saeanifolds.0 Stain and stess tensos in spheical coodinates This woksheet demonstates a few capabilities of Saeanifolds (vesion.0, as included in Saeath 7.5) in computations eadin elasticity theoy in Catesian
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2
 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Page 1 of 13 Solutions Ph 236a Week 2 Kevin Bakett, Jonas Lippune, and Mak Scheel Octobe 6, 2015 Contents Poblem 1................................... 2 Pat (a...................................
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (2, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = 1+9 = 3.
 Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = ˆx( 1)+ŷ( 1 ( 1))+ẑ(0 ( 3)) = ˆx+ẑ3, A = 1+9 = 3.16, â = A A = ˆx+ẑ3 3.16
Problem 3.1 Vector A starts at point (1, 1, 3) and ends at point (, 1,0). Find a unit vector in the direction of A. Solution: A = ˆx( 1)+ŷ( 1 ( 1))+ẑ(0 ( 3)) = ˆx+ẑ3, A = 1+9 = 3.16, â = A A = ˆx+ẑ3 3.16
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Kul Finite element method I, Exercise 07/2016
 Kul-49.3300 Finite element metod I, Eercise 07/016 Demo problems y 1. Determine stress components at te midpo of element sown if u y = a and te oter nodal displacements are zeros. e approimations to te
Kul-49.3300 Finite element metod I, Eercise 07/016 Demo problems y 1. Determine stress components at te midpo of element sown if u y = a and te oter nodal displacements are zeros. e approimations to te
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Written Examination. Antennas and Propagation (AA ) April 26, 2017.
 Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Written Examination Antennas and Propagation (AA. 6-7) April 6, 7. Problem ( points) Let us consider a wire antenna as in Fig. characterized by a z-oriented linear filamentary current I(z) = I cos(kz)ẑ
Exercise 1.1. Verify that if we apply GS to the coordinate basis Gauss form ds 2 = E(u, v)du 2 + 2F (u, v)dudv + G(u, v)dv 2
 Math 209 Riemannian Geometry Jeongmin Shon Problem. Let M 2 R 3 be embedded surface. Then the induced metric on M 2 is obtained by taking the standard inner product on R 3 and restricting it to the tangent
Math 209 Riemannian Geometry Jeongmin Shon Problem. Let M 2 R 3 be embedded surface. Then the induced metric on M 2 is obtained by taking the standard inner product on R 3 and restricting it to the tangent
 J J l 2 J T l 1 J T J T l 2 l 1 J J l 1 c 0 J J J J J l 2 l 2 J J J T J T l 1 J J T J T J T J {e n } n N {e n } n N x X {λ n } n N R x = λ n e n {e n } n N {e n : n N} e n 0 n N k 1, k 2,..., k n N λ
J J l 2 J T l 1 J T J T l 2 l 1 J J l 1 c 0 J J J J J l 2 l 2 J J J T J T l 1 J J T J T J T J {e n } n N {e n } n N x X {λ n } n N R x = λ n e n {e n } n N {e n : n N} e n 0 n N k 1, k 2,..., k n N λ
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2
![If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2 If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2](/thumbs/53/31933086.jpg) Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
Physics 401 Final Exam Cheat Sheet, 17 April t = 0 = 1 c 2 ε 0. = 4π 10 7 c = SI (mks) units. = SI (mks) units H + M
 Maxwell' s Equations in vauum E ρ ε Physis 4 Final Exam Cheat Sheet, 7 Apil E B t B Loent Foe Law: F q E + v B B µ J + µ ε E t Consevation of hage: J + ρ t µ ε ε 8.85 µ 4π 7 3. 8 SI ms) units q eleton.6
Maxwell' s Equations in vauum E ρ ε Physis 4 Final Exam Cheat Sheet, 7 Apil E B t B Loent Foe Law: F q E + v B B µ J + µ ε E t Consevation of hage: J + ρ t µ ε ε 8.85 µ 4π 7 3. 8 SI ms) units q eleton.6
Problem 3.16 Given B = ˆx(z 3y) +ŷ(2x 3z) ẑ(x+y), find a unit vector parallel. Solution: At P = (1,0, 1), ˆb = B
 Problem 3.6 Given B = ˆxz 3y) +ŷx 3z) ẑx+y), find a unit vector parallel to B at point P =,0, ). Solution: At P =,0, ), B = ˆx )+ŷ+3) ẑ) = ˆx+ŷ5 ẑ, ˆb = B B = ˆx+ŷ5 ẑ = ˆx+ŷ5 ẑ. +5+ 7 Problem 3.4 Convert
Problem 3.6 Given B = ˆxz 3y) +ŷx 3z) ẑx+y), find a unit vector parallel to B at point P =,0, ). Solution: At P =,0, ), B = ˆx )+ŷ+3) ẑ) = ˆx+ŷ5 ẑ, ˆb = B B = ˆx+ŷ5 ẑ = ˆx+ŷ5 ẑ. +5+ 7 Problem 3.4 Convert
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π 2, π 2
 Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Orbital angular momentum and the spherical harmonics
 Obital angula momentum and the spheical hamonics Apil 2, 207 Obital angula momentum We compae ou esult on epesentations of otations with ou pevious expeience of angula momentum, defined fo a point paticle
Obital angula momentum and the spheical hamonics Apil 2, 207 Obital angula momentum We compae ou esult on epesentations of otations with ou pevious expeience of angula momentum, defined fo a point paticle
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Formulario Básico ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( 1) ( 1) ( 2) ( 2) λ = 1 + t t. θ = t ε t. Mecánica de Medios Continuos. Grado en Ingeniería Civil.
 Mecánica e Meios Continos. Gao en Ingenieía Ciil. Fomlaio Básico Tema. Descipción el moimiento χ (,) t χ (,) t (,) t χ (,) t t t Tema. Defomación s S X E X e i ij j i ij j F X X U F J T T T U U i j Uk
Mecánica e Meios Continos. Gao en Ingenieía Ciil. Fomlaio Básico Tema. Descipción el moimiento χ (,) t χ (,) t (,) t χ (,) t t t Tema. Defomación s S X E X e i ij j i ij j F X X U F J T T T U U i j Uk
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 2
 ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
ECE 634 Spring 6 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes Fields in a Source-Free Region Example: Radiation from an aperture y PEC E t x Aperture Assume the following choice of vector potentials: A F = =
C 1 D 1. AB = a, AD = b, AA1 = c. a, b, c : (1) AC 1 ; : (1) AB + BC + CC1, AC 1 = BC = AD, CC1 = AA 1, AC 1 = a + b + c. (2) BD 1 = BD + DD 1,
 1 1., BD 1 B 1 1 D 1, E F B 1 D 1. B = a, D = b, 1 = c. a, b, c : (1) 1 ; () BD 1 ; () F; D 1 F 1 (4) EF. : (1) B = D, D c b 1 E a B 1 1 = 1, B1 1 = B + B + 1, 1 = a + b + c. () BD 1 = BD + DD 1, BD =
1 1., BD 1 B 1 1 D 1, E F B 1 D 1. B = a, D = b, 1 = c. a, b, c : (1) 1 ; () BD 1 ; () F; D 1 F 1 (4) EF. : (1) B = D, D c b 1 E a B 1 1 = 1, B1 1 = B + B + 1, 1 = a + b + c. () BD 1 = BD + DD 1, BD =
Spherical Coordinates
 Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
Spherical Coordinates MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Spherical Coordinates Another means of locating points in three-dimensional space is known as the spherical
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Lifting Entry 2. Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYLAND U N I V E R S I T Y O F
 ifting Entry Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYAN 1 010 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu ifting Atmospheric
ifting Entry Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYAN 1 010 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu ifting Atmospheric
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Module 5. February 14, h 0min
 Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Reminders: linear functions
 Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Reminders: linear functions Let U and V be vector spaces over the same field F. Definition A function f : U V is linear if for every u 1, u 2 U, f (u 1 + u 2 ) = f (u 1 ) + f (u 2 ), and for every u U
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Tutorial problem set 6,
 GENERAL RELATIVITY Tutorial problem set 6, 01.11.2013. SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1 Killing vectors. a Show that the commutator of two Killing vectors is a Killing vector. Show that a linear combination with constant
GENERAL RELATIVITY Tutorial problem set 6, 01.11.2013. SOLUTIONS PROBLEM 1 Killing vectors. a Show that the commutator of two Killing vectors is a Killing vector. Show that a linear combination with constant
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations
 Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Appendix C Derivation of Optical-Bloch Equations In this appendix the optical-bloch equations that give the populations and coherences for an idealized three-level Λ system, Fig. 3. on page 47, will be
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Lecture VI: Tensor calculus
 Lectue VI: Tenso calculus Chistophe M. Hiata Caltech M/C 350-7, Pasadena CA 925, USA (Dated: Octobe 4, 20) I. OVERVIEW In this lectue, we will begin with some examples fom vecto calculus, and then continue
Lectue VI: Tenso calculus Chistophe M. Hiata Caltech M/C 350-7, Pasadena CA 925, USA (Dated: Octobe 4, 20) I. OVERVIEW In this lectue, we will begin with some examples fom vecto calculus, and then continue
DiracDelta. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
( ) 2 and compare to M.
 Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
Problems and Solutions for Section 4.2 4.9 through 4.33) 4.9 Calculate the square root of the matrix 3!0 M!0 8 Hint: Let M / 2 a!b ; calculate M / 2!b c ) 2 and compare to M. Solution: Given: 3!0 M!0 8
Physics 505 Fall 2005 Practice Midterm Solutions. The midterm will be a 120 minute open book, open notes exam. Do all three problems.
 Physics 55 Fll 25 Pctice Midtem Solutions The midtem will e 2 minute open ook, open notes exm. Do ll thee polems.. A two-dimensionl polem is defined y semi-cicul wedge with φ nd ρ. Fo the Diichlet polem,
Physics 55 Fll 25 Pctice Midtem Solutions The midtem will e 2 minute open ook, open notes exm. Do ll thee polems.. A two-dimensionl polem is defined y semi-cicul wedge with φ nd ρ. Fo the Diichlet polem,
ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS
 VSB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS Lecture 1 Jiří Brožovský Office: LP H 406/3 Phone: 597 321 321 E-mail: jiri.brozovsky@vsb.cz WWW: http://fast10.vsb.cz/brozovsky/
VSB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF OSTRAVA FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING ADVANCED STRUCTURAL MECHANICS Lecture 1 Jiří Brožovský Office: LP H 406/3 Phone: 597 321 321 E-mail: jiri.brozovsky@vsb.cz WWW: http://fast10.vsb.cz/brozovsky/
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Exercise, May 23, 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1
 Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
28.3. Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates 28.3 Introduction The derivatives div, grad and curl from Section 29.2 can be carried out using coordinate systems other than the rectangular cartesian coordinates. This
Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates 28.3 Introduction The derivatives div, grad and curl from Section 29.2 can be carried out using coordinate systems other than the rectangular cartesian coordinates. This
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most /BCJ BIOCHEMICAL JOURNAL
 Biochemical Journal: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Biochemical Journal: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
MÉTHODES ET EXERCICES
 J.-M. MONIER I G. HABERER I C. LARDON MATHS PCSI PTSI MÉTHODES ET EXERCICES 4 e édition Création graphique de la couverture : Hokus Pokus Créations Dunod, 2018 11 rue Paul Bert, 92240 Malakoff www.dunod.com
J.-M. MONIER I G. HABERER I C. LARDON MATHS PCSI PTSI MÉTHODES ET EXERCICES 4 e édition Création graphique de la couverture : Hokus Pokus Créations Dunod, 2018 11 rue Paul Bert, 92240 Malakoff www.dunod.com
