6.642 Continuum Electromechanics
|
|
|
- Χλωρίς Γεωργίου
- 8 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 MIT OpenCourseWre Continuum Electromechnics Fll 8 For informtion out citing these mterils or our Terms of Use, visit:
2 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics rof. Mrkus Zhn Lecture 5: Lws, Approximtions, n Reltions of Flui Mechnics Continuum Electromechnics (Melcher) Sections I. Useful Vector Opertions n Ientities Grient χi l = χ - χ Guss s Lw (Divergence Theorem) V i A V = S A in Stokes Theorem S A in = A i l C Some useful Vector Ientities ( f ) = i ( A ) = ( A B ) C=A ( i i B C) (Dot n Cross cn e interchnge in the sclr triple prouct) 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
3 II. Time Derivtive of Flui Volume Integrl ζ = ny sclr quntity such s ensity ρ ( t ) V = lim t ζ V( t) Δt ζ t + Δt V - ζ t V V( t+ Δt) V( t) Δt Linerize ll terms to first orer in ζ ζ( t + Δt ) = ζ( t ) + Δt +... Δ t t ζ V( t) t V = lim Δt ζ ζ ( t ) V - ζ ( t ) V + Δt V V( t+ t) V( t) V( t+ t) Δ Δ Δt s =lim Δ t ΔV ζ t V+ V t Δt ζ Δt V ( s ) ΔV = v Δt i v = flui surfce velocity t V() t ζ () t V = lim Δt S ζ ζ () t v i Δt + Δt V s Δt V() t t ζ() ζ i s V() t ζ t V = V + v V S 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
4 S s V ( ζ ) ζ v i = i v V Divergence Theorem ζ ( t ) V= + v V t ζ i ζ V( t) V III. Conservtion of Mss ( ρ = ζ ) t ρ V = = V + v n ρ ρ s i V V S V i ρ v V ( ρ ) ρ + i v = Volume is ritrry ρ + v i ρ+ ρ i v = D ρ + ρ i v = Dt Incompressile D ρ = i v= Dt IV. Conservtion of Momentum ( ρ v = ) t V ρ v V = F V = ( v ) V + v v n ρ ρ i i i i i s V V V S v + v v V = F V ( ρ i) ( ρ i ) i i i V ρ v + ρ v v = F i i i ρ ρ ρ ( i ) i ( ρ ) v i + v v i + v i i ( i ) v i + v v i = F i ( i ) v ρ + v v = F + v = F i ζ, i th component where i=x, y, or z (Conservtion of mss) 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 3 of 4
5 V. Equtions of Motion for n Invisci Flui ( i ) ex v ρ + v v = - p+f VI. Eulerin Description of the Flui Interfce ξ F x, y, z, t = = y, z, t - x n= F F Courtesy of MIT ress. Use with permission. ( i ) ξ DF F = + v F = on F = = y, z, t - x Dt ξ F F F +v x +v y +v z = x y z - ξ y ξ z ξ ξ ξ v x = + v y + vz y z 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 4 of 4
6 VII. Surfce Tension A. Surfce Force Density δw = γ A s δw s + Τ sa δξ = γ A + Τ sa δξ = Increse of surfce energy Work one on interfce Courtesy of MIT ress. Use with permission. Α + δa = x + δx y + δy xy + yδx + xδ y x+ δx x x = δx = δξ R + δξ R R y+ δy y y = δy = R + δξ R R δξ δa=yδx+xδ y 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 5 of 4
7 xy xy = + δξ R R =xy + δξ R R =A δξ + R R γ A δξ + + Τ sa δξ = R R Τ =- γ + n s [Young n Lplce surfce force ensity] R R B. Interfcil Deformtion V i C V = s C i n (Divergent Theorem) S C=n Courtesy of MIT ress. Use with permission. n=n on top s n = -n on ottom s n n on sie V s i i i ( i ) C V n δξα = n n s A n Α δξ = δα S = A - A = δα top ottom 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 6 of 4
8 - γδα - γ Αδξ i n T s = = Αδξ Αδξ s = - γ in in = + R R Τ =- γ i n n VIII. Bounry Conitions A. Rigi Wll ni v = (norml velocity component is zero) n v = (Viscous flow) (tngentil velocity component is zero) B. Interfce n i v = ; v = v - v ove elow Force Equilirium i ( s) i V F V + T = A m F=F +F e mechnicl electricl T e F e = ij i x j m m T p p F =- p= it =- =-δ m ij ij xj xi xj T = -p δ m ij ij 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 7 of 4
9 T sr Courtesy of MIT ress. Use with permission. m e V F V = T + T i i ij ij n S j T + T n + T = m e ij ij j s i p n = T n - γ i n n e i ij j i 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 8 of 4
10 IX. Bernoulli s Lw g i, r = Xi + yi = zi F = ρ g = ρ g r if ρ = constnt x y z e F = [Specil cse when electricl force is written s grient of sclr] ex ( i ) ( i ) v ρ + v v + p = F = ρ g r - ( v i ) v= ( v ) v+ ( v i v ) v ρ + ω v + p + ρ v v - ρg r + = t i i ω = v vorticity l v v ρ i l+ p + ρ v v - ρg r + = i i Irrottionl Flows ( v= ω = ) v=- θ θ - ρ +p + ρ v i v - ρg i r+ = 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 9 of 4
11 X. Bernoulli Lw rolems A. Cpillry Rise Courtesy of MIT ress. Use with permission. θ =, v=, g =-g i, = z = + ρgξ c = = c - + γ + = R R= αr 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
12 ρ ξ ρ ξ γ = + g - = g = α r ξ = γ ρgαr B. Electriclly Driven Rocket e pld + f x = LD e C V LD C=, f x = V =- x x x e -fx V LD V p= = = LD x LD x Another Wy: p - T e = ; T e = V xx xx x e V p=t xx = x p + ρ v = p + ρ v vld=vd V p = = ρ v - x L 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
13 V v = V p = ρx - L M Thrust=V p =Vp ρ D t C. Mgneticlly Driven Rocket e +p + T yy = μ μ T yy = - H = - z I w μ p= I w p + ρ v = p + ρ v I μ p =, vdw = v w w ρ w D μ I = v - μ I ρ ( w ) v = V = - D 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
14 M t Thrust = V = V Vw = V w ρ ρ D. Dielectric Liqui Rise. Kelvin olriztion Force Density ( i ) ij i j δij k k F= E, T =ED - EE ( ) = - E ( i ) ( )( i ) E = - E E ( ) ( E ) E= ( E i ) E- ( E i E ) ( E i ) E = ( E i E ) ( ) - i E = E i E = - E i E if constnt F=- = ( - ) E i E =- - E E ( ) i + ρgz - ( - ) E i E = constnt 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 3 of 4
15 Courtesy of MIT ress. Use with permission. V E= i αr θ = ( - ) V + ρgξ- = α r c - + T = γ = (negligile surfce tension) - = c T = - E θ = E θ continuous cross interfce = = c = ( - ) V ξ = α r ρ g 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 4 of 4
16 . Korteweg-Helmholtz Force Density F=- E i E, T = EE - δ EE ij i j ij K K =constnt, F=- = = In flui + ρ gz=constnt T = - E = - - ( ) θ V αr = - + T = - = c + ρg ξ = c V V - = ρg ξ = T = - ( - ) = + ( - ) αr αr ( - ) V ξ = α r ρ g E. Mgnetic Flui Rise in Tngentil Mgnetic Fiel Courtesy of MIT ress. Use with permission. 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 5 of 4
17 I H= iθ πr F = μ ( M i ) H, T = HB - μ δ H H ij i j ij K K. Linerly Mgnetizle ( μ ) B= H+M = H M= - H μ μ μ μ F= ( μ -μ)( H i ) H= ( μ - μ) ( H) H+ ( H i H) μ - μ μ - μ i i μ =- F = H H = H H if = constnt =- - H H μ μ i + ρgz - ( μ - μ ) H i H = constnt = = c - + T = T = - H θ = μ = = c = + g - ( - ) I ρ ξ μ μ = πr ( - ) μ μ I ξ = ρ g π r c 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 6 of 4
18 . Nonliner Mgnetiztion Chrcteristics H ( ) M = M H M H H M ( i ) ( i ) F= μ M H= μ H H H H i H = H H + H i H μ M μ μ H F= H = M H= M( H) H=- H H H μ μ = - M H H = - M H; M = M( H) H H Specil cse: Liner Mteril: μ M= μ -μ H =- ( μ -μ) H =- μmh Sturte Mteril: μ M = constnt =-μ MH + ρgz- =constnt 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 7 of 4
19 = = c - + T = + ρg ξ+ = + c c T = HB - H H δμ ij i j ij K K T = - Hθ T = μ = = c = H μm H H - μm H ξ = = = ρg ρg ρg Liner Mteril: =- ( - ) I μ μ π r ( μ μ ) ( π ) - I ξ = r ρg Sturte Mteril: =-μ MH μmh μmi ξ = = ρg πρgr 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 8 of 4
20 F. Mgnetic Flui Rise in Norml Fiel = + ρgδh+ = + ρgδh- μm H = - + T = T = H B - H μ x x x μ T = H - μ H ( H +M ) + μ H μ μ H = H +M μ T = ( H +M) - H ( H +M ) + H μ μ 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 9 of 4
21 μ = M μm = - = μm - = = ρgδh-μ M H μ M h= +M Δ H ρg Liner Mteril: M μ M MB ρg ρg M= Δh= M+ H = Sturte Mteril: μ M M=M Δh= M+ H ρg G. Mgnetic Nozzle 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
22 + ρv + = + ρv - μ M H = = μ v - v = M H ρ π π v = v = v 4 4 v μ μ v = v + M H = v + M H ρ ρv μ = + M H ρv H. Mgnetic Flui Rotry Shft Sel μm H 3 = - μm H T = 3, T =, Assume H tngentil to interfce T = - Ht T = μ, 3,4 = 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
23 4 = = 4 - = Δ = μ ( M H 3 3 -M H ) H3 = μ MH H In well esigne sel H Δ μ M H Typicl numers: μ M = 7 G =.7T μ H = 8, G =.8T ( μ M)( μ H ).7 (.8 ) H 3 Δ= = = Nm 5-7 μ 4 π = kscls = Atmosphere XI. Force on Boy in Mgnetic Flui p+ ρgz-μ M H=constnt=C p= μ M H-ρ gz+c f = - p p n = - μm H n + ρgz n + C n S S S S uoyncy effect Mgneticlly Sturte: M= M=constnt S C n = f = - μ M H n = - μ M H n = - μ M HV M S S Mgneticlly Liner: ( μ - μ ) M= M= H μ ( μ - μ ) V C V f M =- μm H n =- μ H n =- μ -μ H V μ S S V 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge of 4
24 A. Non-mgnetic Boy f oy =uoynt weight + f M f M opposite to irection of incresing H Non-mgnetic oy moves towrs wek fiel region (Sink-Flot Seprtion) 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 3 of 4
25 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics Lecture 5 rof. Mrkus Zhn ge 4 of 4
6.642 Continuum Electromechanics
 MIT OpenCourseWre http://ocw.mit.edu 6.64 Continuum Electromechnics Fll 8 For informtion out citing these mterils or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics,
MIT OpenCourseWre http://ocw.mit.edu 6.64 Continuum Electromechnics Fll 8 For informtion out citing these mterils or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics,
6.642, Continuum Electromechanics, Fall 2004 Prof. Markus Zahn Lecture 8: Electrohydrodynamic and Ferrohydrodynamic Instabilities
 6.64, Continuum Electromechnics, Fll 4 Prof. Mrus Zhn Lecture 8: Electrohydrodynmic nd Ferrohydrodynmic Instilities I. Mgnetic Field Norml Instility Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with permission. A. Equilirium
6.64, Continuum Electromechnics, Fll 4 Prof. Mrus Zhn Lecture 8: Electrohydrodynmic nd Ferrohydrodynmic Instilities I. Mgnetic Field Norml Instility Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with permission. A. Equilirium
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Prof. Markus Zahn Lecture 7: Polarization and Conduction
 6.641, Electromgnetic Fiels, Forces, n Motion Prof. Mrkus Zhn Lecture 7: Polriztion n Conuction I. Experimentl Oservtion A. Fixe oltge - Switch Close ( v= o ) As n insulting mteril enters free-spce cpcitor
6.641, Electromgnetic Fiels, Forces, n Motion Prof. Mrkus Zhn Lecture 7: Polriztion n Conuction I. Experimentl Oservtion A. Fixe oltge - Switch Close ( v= o ) As n insulting mteril enters free-spce cpcitor
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
 MIT OpenCourseWre http://ocw.mit.edu 6.013/ESD.013J Electromgnetics nd Applictions, Fll 005 Plese use the following cittion formt: Mrkus Zhn, Erich Ippen, nd Dvid Stelin, 6.013/ESD.013J Electromgnetics
MIT OpenCourseWre http://ocw.mit.edu 6.013/ESD.013J Electromgnetics nd Applictions, Fll 005 Plese use the following cittion formt: Mrkus Zhn, Erich Ippen, nd Dvid Stelin, 6.013/ESD.013J Electromgnetics
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
 MIT OpenCourseWre http://ocw.mit.edu 6.641 Electromgnetic Fields, Forces, nd Motion, Spring 005 Plese use the following cittion formt: Mrkus Zhn, 6.641 Electromgnetic Fields, Forces, nd Motion, Spring
MIT OpenCourseWre http://ocw.mit.edu 6.641 Electromgnetic Fields, Forces, nd Motion, Spring 005 Plese use the following cittion formt: Mrkus Zhn, 6.641 Electromgnetic Fields, Forces, nd Motion, Spring
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation format: Markus Zahn, 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation format: Markus Zahn, 6.03/ESD.03J Electromagnetics and Applications, Fall
Σχολή Εφαρμοσμένων Μαθηματικών και Φυσικών Επιστημών. Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο. Thales Workshop, 1-3 July 2015.
 Σχολή Εφαρμοσμένων Μαθηματικών και Φυσικών Επιστημών Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Thles Worksho, 1-3 July 015 The isomorhism function from S3(L(,1)) to the free module Boštjn Gbrovšek Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν
Σχολή Εφαρμοσμένων Μαθηματικών και Φυσικών Επιστημών Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Thles Worksho, 1-3 July 015 The isomorhism function from S3(L(,1)) to the free module Boštjn Gbrovšek Άδεια Χρήσης Το παρόν
To find the relationships between the coefficients in the original equation and the roots, we have to use a different technique.
 Further Conepts for Avne Mthemtis - FP1 Unit Ientities n Roots of Equtions Cui, Qurti n Quinti Equtions Cui Equtions The three roots of the ui eqution x + x + x + 0 re lle α, β n γ (lph, et n gmm). The
Further Conepts for Avne Mthemtis - FP1 Unit Ientities n Roots of Equtions Cui, Qurti n Quinti Equtions Cui Equtions The three roots of the ui eqution x + x + x + 0 re lle α, β n γ (lph, et n gmm). The
MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3)
![MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3) MATH423 String Theory Solutions 4. = 0 τ = f(s). (1) dτ ds = dxµ dτ f (s) (2) dτ 2 [f (s)] 2 + dxµ. dτ f (s) (3)](/thumbs/81/84712331.jpg) 1. MATH43 String Theory Solutions 4 x = 0 τ = fs). 1) = = f s) ) x = x [f s)] + f s) 3) equation of motion is x = 0 if an only if f s) = 0 i.e. fs) = As + B with A, B constants. i.e. allowe reparametrisations
1. MATH43 String Theory Solutions 4 x = 0 τ = fs). 1) = = f s) ) x = x [f s)] + f s) 3) equation of motion is x = 0 if an only if f s) = 0 i.e. fs) = As + B with A, B constants. i.e. allowe reparametrisations
CHAPTER (2) Electric Charges, Electric Charge Densities and Electric Field Intensity
 CHAPTE () Electric Chrges, Electric Chrge Densities nd Electric Field Intensity Chrge Configurtion ) Point Chrge: The concept of the point chrge is used when the dimensions of n electric chrge distriution
CHAPTE () Electric Chrges, Electric Chrge Densities nd Electric Field Intensity Chrge Configurtion ) Point Chrge: The concept of the point chrge is used when the dimensions of n electric chrge distriution
Space-Time Symmetries
 Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Chapter Space-Time Symmetries In classical fiel theory any continuous symmetry of the action generates a conserve current by Noether's proceure. If the Lagrangian is not invariant but only shifts by a
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
Oscillatory Gap Damping
 Oscillatory Gap Damping Find the damping due to the linear motion of a viscous gas in in a gap with an oscillating size: ) Find the motion in a gap due to an oscillating external force; ) Recast the solution
Oscillatory Gap Damping Find the damping due to the linear motion of a viscous gas in in a gap with an oscillating size: ) Find the motion in a gap due to an oscillating external force; ) Recast the solution
Review-2 and Practice problems. sin 2 (x) cos 2 (x)(sin(x)dx) (1 cos 2 (x)) cos 2 (x)(sin(x)dx) let u = cos(x), du = sin(x)dx. = (1 u 2 )u 2 ( du)
 . Trigonometric Integrls. ( sin m (x cos n (x Cse-: m is odd let u cos(x Exmple: sin 3 (x cos (x Review- nd Prctice problems sin 3 (x cos (x Cse-: n is odd let u sin(x Exmple: cos 5 (x cos 5 (x sin (x
. Trigonometric Integrls. ( sin m (x cos n (x Cse-: m is odd let u cos(x Exmple: sin 3 (x cos (x Review- nd Prctice problems sin 3 (x cos (x Cse-: n is odd let u sin(x Exmple: cos 5 (x cos 5 (x sin (x
Oscillatory integrals
 Oscilltory integrls Jordn Bell jordn.bell@gmil.com Deprtment of Mthemtics, University of Toronto August, 0 Oscilltory integrls Suppose tht Φ C R d ), ψ DR d ), nd tht Φ is rel-vlued. I : 0, ) C by Iλ)
Oscilltory integrls Jordn Bell jordn.bell@gmil.com Deprtment of Mthemtics, University of Toronto August, 0 Oscilltory integrls Suppose tht Φ C R d ), ψ DR d ), nd tht Φ is rel-vlued. I : 0, ) C by Iλ)
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Chapter 5-Old. Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability
 Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics (I) [SS-841] Chapter 5-Ol by Ling-Hsiao Lyu 008 Fall Chapter 5-Ol. Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability Exercise 5.1 Rea section 11.4.3 in the following textboo an erive symmetric
Nonlinear Space Plasma Physics (I) [SS-841] Chapter 5-Ol by Ling-Hsiao Lyu 008 Fall Chapter 5-Ol. Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability Exercise 5.1 Rea section 11.4.3 in the following textboo an erive symmetric
F19MC2 Solutions 9 Complex Analysis
 F9MC Solutions 9 Complex Analysis. (i) Let f(z) = eaz +z. Then f is ifferentiable except at z = ±i an so by Cauchy s Resiue Theorem e az z = πi[res(f,i)+res(f, i)]. +z C(,) Since + has zeros of orer at
F9MC Solutions 9 Complex Analysis. (i) Let f(z) = eaz +z. Then f is ifferentiable except at z = ±i an so by Cauchy s Resiue Theorem e az z = πi[res(f,i)+res(f, i)]. +z C(,) Since + has zeros of orer at
What happens when two or more waves overlap in a certain region of space at the same time?
 Wave Superposition What happens when two or more waves overlap in a certain region of space at the same time? To find the resulting wave according to the principle of superposition we should sum the fields
Wave Superposition What happens when two or more waves overlap in a certain region of space at the same time? To find the resulting wave according to the principle of superposition we should sum the fields
STEAM TABLES. Mollier Diagram
 STEAM TABLES and Mollier Diagram (S.I. Units) dharm \M-therm\C-steam.pm5 CONTENTS Table No. Page No. 1. Saturated Water and Steam (Temperature) Tables I (ii) 2. Saturated Water and Steam (Pressure) Tables
STEAM TABLES and Mollier Diagram (S.I. Units) dharm \M-therm\C-steam.pm5 CONTENTS Table No. Page No. 1. Saturated Water and Steam (Temperature) Tables I (ii) 2. Saturated Water and Steam (Pressure) Tables
CT Correlation (2B) Young Won Lim 8/15/14
 CT Correlation (2B) 8/5/4 Copyright (c) 2-24 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version.2 or any
CT Correlation (2B) 8/5/4 Copyright (c) 2-24 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version.2 or any
6. ΙΑΦΟΡΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΡΟΗΣ
 6.1 ΚΙΝΗΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΡΟΪΚΟΥ ΣΤΟΙΧΕΙΟΥ 6. ΙΑΦΟΡΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΡΟΗΣ -Λεπτοµέρειες της ροής Απειροστός όγκος ελέγχου - ιαφορική Ανάλυση Περιγραφή πεδίων ταχύτητας και επιτάχυνσης Euleian, Lagangian U U(x,y,,t)
6.1 ΚΙΝΗΜΑΤΙΚΗ ΡΟΪΚΟΥ ΣΤΟΙΧΕΙΟΥ 6. ΙΑΦΟΡΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΡΟΗΣ -Λεπτοµέρειες της ροής Απειροστός όγκος ελέγχου - ιαφορική Ανάλυση Περιγραφή πεδίων ταχύτητας και επιτάχυνσης Euleian, Lagangian U U(x,y,,t)
Solutions_3. 1 Exercise Exercise January 26, 2017
 s_3 Jnury 26, 217 1 Exercise 5.2.3 Apply composite Simpson s rule with m = 1, 2, 4 pnels to pproximte the integrls: () x 2 dx = 1 π/2 3, (b) cos(x) dx = 1, (c) e x dx = e 1, nd report the errors. () f(x)
s_3 Jnury 26, 217 1 Exercise 5.2.3 Apply composite Simpson s rule with m = 1, 2, 4 pnels to pproximte the integrls: () x 2 dx = 1 π/2 3, (b) cos(x) dx = 1, (c) e x dx = e 1, nd report the errors. () f(x)
Περιεχόμενα. Εξίσωση Συνέχειας Αστρόβιλη Ροή Εξισώσεις Κίνησης. Σειρά ΙΙ 2
 Περιεχόμενα Εξίσωση Συνέχειας Αστρόβιλη Ροή Εξισώσεις Κίνησης Σειρά ΙΙ 2 Πεδίο ταχύτητας Όγκος Ελέγχου Καρτεσιανές Συντεταγμένες w+(/)dz z y u dz u+(/ x)dx x dy dx w Σειρά ΙΙ 3 1. Εισαγωγή 1.1 Εξίσωση
Περιεχόμενα Εξίσωση Συνέχειας Αστρόβιλη Ροή Εξισώσεις Κίνησης Σειρά ΙΙ 2 Πεδίο ταχύτητας Όγκος Ελέγχου Καρτεσιανές Συντεταγμένες w+(/)dz z y u dz u+(/ x)dx x dy dx w Σειρά ΙΙ 3 1. Εισαγωγή 1.1 Εξίσωση
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
ω ω ω ω ω ω+2 ω ω+2 + ω ω ω ω+2 + ω ω+1 ω ω+2 2 ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ω+1 ω ω2 ω ω2 + ω ω ω2 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω ω+1 ω ω2 + ω ω+1 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω
 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Tridiagonal matrices. Gérard MEURANT. October, 2008
 Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
(ii) x[y (x)] 4 + 2y(x) = 2x. (vi) y (x) = x 2 sin x
![(ii) x[y (x)] 4 + 2y(x) = 2x. (vi) y (x) = x 2 sin x (ii) x[y (x)] 4 + 2y(x) = 2x. (vi) y (x) = x 2 sin x](/thumbs/62/47493101.jpg) ΕΥΓΕΝΙΑ Ν. ΠΕΤΡΟΠΟΥΛΟΥ ΕΠΙΚ. ΚΑΘΗΓΗΤΡΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ ΓΙΑ ΤΟ ΜΑΘΗΜΑ «ΕΦΑΡΜΟΣΜΕΝΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΙΚΑ ΙΙΙ» ΠΑΤΡΑ 2015 1 Ασκήσεις 1η ομάδα ασκήσεων 1. Να χαρακτηρισθούν πλήρως
ΕΥΓΕΝΙΑ Ν. ΠΕΤΡΟΠΟΥΛΟΥ ΕΠΙΚ. ΚΑΘΗΓΗΤΡΙΑ ΤΜΗΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΠΑΤΡΩΝ ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ ΓΙΑ ΤΟ ΜΑΘΗΜΑ «ΕΦΑΡΜΟΣΜΕΝΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΙΚΑ ΙΙΙ» ΠΑΤΡΑ 2015 1 Ασκήσεις 1η ομάδα ασκήσεων 1. Να χαρακτηρισθούν πλήρως
Eulerian Simulation of Large Deformations
 Eulerian Simulation of Large Deformations Shayan Hoshyari April, 2018 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 / 11 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 Muscle Animation 2 / 11 Some Applications
Eulerian Simulation of Large Deformations Shayan Hoshyari April, 2018 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 / 11 Some Applications 1 Biomechanical Engineering 2 Muscle Animation 2 / 11 Some Applications
Integrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 15.7)
 Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Integrals in clindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect. 5.7 Integration in spherical coordinates. Review: Clindrical coordinates. Spherical coordinates in space. Triple integral in spherical coordinates.
Treatment of Boundary Conditions. Advanced CFD 03
 Treatment of Boundary Conditions Advanced CFD 03 Momentum BCs ( ρv) ( ρvv) = τ p B t semi-discretized form ( ρv) ( ρv) t discretization type element discretization ( ρv) ρv ( ) t oundary terms Ω Ω ( m
Treatment of Boundary Conditions Advanced CFD 03 Momentum BCs ( ρv) ( ρvv) = τ p B t semi-discretized form ( ρv) ( ρv) t discretization type element discretization ( ρv) ρv ( ) t oundary terms Ω Ω ( m
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
ΠΡΟΣΚΛΗΣΗ ΕΚΔΗΛΩΣΗΣ ΕΝΔΙΑΦΕΡΟΝΤΟΣ
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΥΠΟΥΡΓΕΙΟ ΑΓΡΟΤΙΚΗΣ ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΚΟΙΝΟΤΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΥΠΟΔΟΜΩΝ ΕΙΔΙΚΗ ΥΠΗΡΕΣΙΑ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗΣ ΠΑΑ ΑΝΤΑΓΩΝΙΣΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΗ ΕΝΩΣΗ ΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΟ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΟ ΤΑΜΕΙΟ
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΥΠΟΥΡΓΕΙΟ ΑΓΡΟΤΙΚΗΣ ΑΝΑΠΤΥΞΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΡΟΦΙΜΩΝ ΔΙΟΙΚΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΤΟΜΕΑΣ ΚΟΙΝΟΤΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΥΠΟΔΟΜΩΝ ΕΙΔΙΚΗ ΥΠΗΡΕΣΙΑ ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΗΣ ΠΑΑ ΑΝΤΑΓΩΝΙΣΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑ ΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΗ ΕΝΩΣΗ ΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΟ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΟ ΤΑΜΕΙΟ
2.019 Design of Ocean Systems. Lecture 6. Seakeeping (II) February 21, 2011
 2.019 Design of Ocean Systems Lecture 6 Seakeeping (II) February 21, 2011 ω, λ,v p,v g Wave adiation Problem z ζ 3 (t) = ζ 3 cos(ωt) ζ 3 (t) = ω ζ 3 sin(ωt) ζ 3 (t) = ω 2 ζ3 cos(ωt) x 2a ~n Total: P (t)
2.019 Design of Ocean Systems Lecture 6 Seakeeping (II) February 21, 2011 ω, λ,v p,v g Wave adiation Problem z ζ 3 (t) = ζ 3 cos(ωt) ζ 3 (t) = ω ζ 3 sin(ωt) ζ 3 (t) = ω 2 ζ3 cos(ωt) x 2a ~n Total: P (t)
 K K 1 2 1 K M N M(2 N 1) K K K K K f f(x 1, x 2,..., x K ) = K f xk (x k ), x 1, x 2,..., x K K K K f Yk (y k x 1, x 2,..., x k ) k=1 M i, i = 1, 2 Xi n n Yi n Xn 1 Xn 2 ˆM i P (n) e = {( ˆM 1, ˆM2 )
K K 1 2 1 K M N M(2 N 1) K K K K K f f(x 1, x 2,..., x K ) = K f xk (x k ), x 1, x 2,..., x K K K K f Yk (y k x 1, x 2,..., x k ) k=1 M i, i = 1, 2 Xi n n Yi n Xn 1 Xn 2 ˆM i P (n) e = {( ˆM 1, ˆM2 )
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
ΚΑΝΟΝΙΣΜΟΣ (EE) 2019/1238 ΤΟΥ ΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΟΥ ΚΟΙΝΟΒΟΥΛΙΟΥ ΚΑΙ ΤΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΥΛΙΟΥ
 198/1 L I ( (EE) 2019/1238 20 2019 (PEPP) ( ), 114,,, ( 1 ), ( 2 ), : (1),.. (2),., 25, :. (3),,.,,,. ( 1 ) C 81 2.3.2018,. 139. ( 2 ) 4 2019 ( ) 14 2019. EL L 198/2 25.7.2019 (4).,,. H,, ( ). (5) 2015,
198/1 L I ( (EE) 2019/1238 20 2019 (PEPP) ( ), 114,,, ( 1 ), ( 2 ), : (1),.. (2),., 25, :. (3),,.,,,. ( 1 ) C 81 2.3.2018,. 139. ( 2 ) 4 2019 ( ) 14 2019. EL L 198/2 25.7.2019 (4).,,. H,, ( ). (5) 2015,
Chapter 7b, Torsion. τ = 0. τ T. T τ D'' A'' C'' B'' 180 -rotation around axis C'' B'' D'' A'' A'' D'' 180 -rotation upside-down C'' B''
 Chpter 7b, orsion τ τ τ ' D' B' C' '' B'' B'' D'' C'' 18 -rottion round xis C'' B'' '' D'' C'' '' 18 -rottion upside-down D'' stright lines in the cross section (cross sectionl projection) remin stright
Chpter 7b, orsion τ τ τ ' D' B' C' '' B'' B'' D'' C'' 18 -rottion round xis C'' B'' '' D'' C'' '' 18 -rottion upside-down D'' stright lines in the cross section (cross sectionl projection) remin stright
Rectangular Polar Parametric
 Hrold s AP Clculus BC Rectngulr Polr Prmetric Chet Sheet 15 Octoer 2017 Point Line Rectngulr Polr Prmetric f(x) = y (x, y) (, ) Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + Point-Slope Form: y y 0 = m (x x 0 ) Generl
Hrold s AP Clculus BC Rectngulr Polr Prmetric Chet Sheet 15 Octoer 2017 Point Line Rectngulr Polr Prmetric f(x) = y (x, y) (, ) Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + Point-Slope Form: y y 0 = m (x x 0 ) Generl
 φ(t) TE 0 φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) η(λ) G(z,λ) λ φ(z) η(λ) η(λ) = t CIGS 0 G(z,λ)φ(z)dz t CIGS η(λ) φ(z) 0 z
φ(t) TE 0 φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) η(λ) G(z,λ) λ φ(z) η(λ) η(λ) = t CIGS 0 G(z,λ)φ(z)dz t CIGS η(λ) φ(z) 0 z
BSL Transport Phenomena 2e Revised: Chapter 2 - Problem 2C.4 Page 1 of 9
 BSL Transport Phenomena e Revised: Chapter - Problem C.4 Page 1 of 9 Problem C.4 Falling-cylinder viscometer see Fig. C.4. 6 A falling-cylinder viscometer consists of a long vertical cylindrical container
BSL Transport Phenomena e Revised: Chapter - Problem C.4 Page 1 of 9 Problem C.4 Falling-cylinder viscometer see Fig. C.4. 6 A falling-cylinder viscometer consists of a long vertical cylindrical container
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
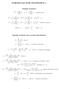 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
On the summability of divergent power series solutions for certain first-order linear PDEs Masaki HIBINO (Meijo University)
 On the summability of divergent power series solutions for certain first-order linear PDEs Masaki HIBINO (Meijo University) 1 1 Introduction (E) {1+x 2 +β(x,y)}y u x (x,y)+{x+b(x,y)}y2 u y (x,y) +u(x,y)=f(x,y)
On the summability of divergent power series solutions for certain first-order linear PDEs Masaki HIBINO (Meijo University) 1 1 Introduction (E) {1+x 2 +β(x,y)}y u x (x,y)+{x+b(x,y)}y2 u y (x,y) +u(x,y)=f(x,y)
Mechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapter 5 Plasticity Theory
 Mechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapter 5 Plasticity Theory Dr.-Ing. 郭瑞昭 Yield criteria Question: For what combinations of loads will the cylinder begin to yield plastically? The criteria for deciding
Mechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapter 5 Plasticity Theory Dr.-Ing. 郭瑞昭 Yield criteria Question: For what combinations of loads will the cylinder begin to yield plastically? The criteria for deciding
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS
 SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
ITU-R P (2012/02)
 ITU-R P.56- (0/0 P ITU-R P.56- ii.. (IPR (ITU-T/ITU-R/ISO/IEC.ITU-R ttp://www.itu.int/itu-r/go/patents/en. (ttp://www.itu.int/publ/r-rec/en ( ( BO BR BS BT F M P RA RS S SA SF SM SNG TF V 0.ITU-R ITU 0..(ITU
ITU-R P.56- (0/0 P ITU-R P.56- ii.. (IPR (ITU-T/ITU-R/ISO/IEC.ITU-R ttp://www.itu.int/itu-r/go/patents/en. (ttp://www.itu.int/publ/r-rec/en ( ( BO BR BS BT F M P RA RS S SA SF SM SNG TF V 0.ITU-R ITU 0..(ITU
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations
 On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) λ = 1 + t t. θ = t ε t. Continuum Mechanics. Chapter 1. Description of Motion dt t. Chapter 2. Deformation and Strain
 Continm Mechanics. Official Fom Chapte. Desciption of Motion χ (,) t χ (,) t (,) t χ (,) t t Chapte. Defomation an Stain s S X E X e i ij j i ij j F X X U F J T T T U U i j Uk U k E ( F F ) ( J J J J)
Continm Mechanics. Official Fom Chapte. Desciption of Motion χ (,) t χ (,) t (,) t χ (,) t t Chapte. Defomation an Stain s S X E X e i ij j i ij j F X X U F J T T T U U i j Uk U k E ( F F ) ( J J J J)
Chapter 2. Stress, Principal Stresses, Strain Energy
 Chapter Stress, Principal Stresses, Strain nergy Traction vector, stress tensor z z σz τ zy ΔA ΔF A ΔA ΔF x ΔF z ΔF y y τ zx τ xz τxy σx τ yx τ yz σy y A x x F i j k is the traction force acting on the
Chapter Stress, Principal Stresses, Strain nergy Traction vector, stress tensor z z σz τ zy ΔA ΔF A ΔA ΔF x ΔF z ΔF y y τ zx τ xz τxy σx τ yx τ yz σy y A x x F i j k is the traction force acting on the
Κεφάλαιο 1 Πραγματικοί Αριθμοί 1.1 Σύνολα
 x + = 0 N = {,, 3....}, Z Q, b, b N c, d c, d N + b = c, b = d. N = =. < > P n P (n) P () n = P (n) P (n + ) n n + P (n) n P (n) n P n P (n) P (m) P (n) n m P (n + ) P (n) n m P n P (n) P () P (), P (),...,
x + = 0 N = {,, 3....}, Z Q, b, b N c, d c, d N + b = c, b = d. N = =. < > P n P (n) P () n = P (n) P (n + ) n n + P (n) n P (n) n P n P (n) P (m) P (n) n m P (n + ) P (n) n m P n P (n) P () P (), P (),...,
Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α
 Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
wave energy Superposition of linear plane progressive waves Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture Oblique Plane Waves:
 3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
Κεφάλαιο 1 Πραγματικοί Αριθμοί 1.1 Σύνολα
 x 2 + 1 = 0 N = {1, 2, 3....}, Z Q a, b a, b N c, d c, d N a + b = c, a b = d. a a N 1 a = a 1 = a. < > P n P (n) P (1) n = 1 P (n) P (n + 1) n n + 1 P (n) n P (n) n P n P (n) P (m) P (n) n m P (n + 1)
x 2 + 1 = 0 N = {1, 2, 3....}, Z Q a, b a, b N c, d c, d N a + b = c, a b = d. a a N 1 a = a 1 = a. < > P n P (n) P (1) n = 1 P (n) P (n + 1) n n + 1 P (n) n P (n) n P n P (n) P (m) P (n) n m P (n + 1)
Part III - Pricing A Down-And-Out Call Option
 Part III - Pricing A Down-And-Out Call Option Gary Schurman MBE, CFA March 202 In Part I we examined the reflection principle and a scaled random walk in discrete time and then extended the reflection
Part III - Pricing A Down-And-Out Call Option Gary Schurman MBE, CFA March 202 In Part I we examined the reflection principle and a scaled random walk in discrete time and then extended the reflection
Electromagnetic Waves I
 Electromgnetic Wves I Jnury, 03. Derivtion of wve eqution of string. Derivtion of EM wve Eqution in time domin 3. Derivtion of the EM wve Eqution in phsor domin 4. The complex propgtion constnt 5. The
Electromgnetic Wves I Jnury, 03. Derivtion of wve eqution of string. Derivtion of EM wve Eqution in time domin 3. Derivtion of the EM wve Eqution in phsor domin 4. The complex propgtion constnt 5. The
Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 8, 24, no. 5, 239-246 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/.2988/ija.24.422 Congruence Classes of Invertible Matrices of Order 3 over F 2 Ligong An and
4.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves
 .0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 08 Lecture 6 Copyright c 08 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved..0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6 4.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive
.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 08 Lecture 6 Copyright c 08 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved..0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6 4.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive
6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves
 .0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
Lifting Entry (continued)
 ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
P AND P. P : actual probability. P : risk neutral probability. Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P. For example:
 (B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
(B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
The kinetic and potential energies as T = 1 2. (m i η2 i k(η i+1 η i ) 2 ). (3) The Hooke s law F = Y ξ, (6) with a discrete analog
 Lecture 12: Introduction to Analytical Mechanics of Continuous Systems Lagrangian Density for Continuous Systems The kinetic and potential energies as T = 1 2 i η2 i (1 and V = 1 2 i+1 η i 2, i (2 where
Lecture 12: Introduction to Analytical Mechanics of Continuous Systems Lagrangian Density for Continuous Systems The kinetic and potential energies as T = 1 2 i η2 i (1 and V = 1 2 i+1 η i 2, i (2 where
Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation
 Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation Praveen. C praveen@math.tifrbng.res.in Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Center for Applicable Mathematics Bangalore 560065 http://math.tifrbng.res.in/~praveen
Finite difference method for 2-D heat equation Praveen. C praveen@math.tifrbng.res.in Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Center for Applicable Mathematics Bangalore 560065 http://math.tifrbng.res.in/~praveen
Theoretical Competition: 12 July 2011 Question 2 Page 1 of 2
 Theoretcl Competton: July Queston ge of. Ηλεκτρισμένη Σαπουνόφουσκα Θεωρήστε μια σφαιρική σαπουνόφουσκα ακτίνας. Ο αέρας στο εσωτερικό της σαπουνόφουσκας έχει πυκνότητα ρ και θερμοκρασία T. Η σαπουνόφουσκα
Theoretcl Competton: July Queston ge of. Ηλεκτρισμένη Σαπουνόφουσκα Θεωρήστε μια σφαιρική σαπουνόφουσκα ακτίνας. Ο αέρας στο εσωτερικό της σαπουνόφουσκας έχει πυκνότητα ρ και θερμοκρασία T. Η σαπουνόφουσκα
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Lecture 5: Numerical Integration
 Lecture notes on Vritionl nd Approximte Metods in Applied Mtemtics - A Peirce UBC 1 Lecture 5: Numericl Integrtion Compiled 15 September 1 In tis lecture we introduce tecniques for numericl integrtion,
Lecture notes on Vritionl nd Approximte Metods in Applied Mtemtics - A Peirce UBC 1 Lecture 5: Numericl Integrtion Compiled 15 September 1 In tis lecture we introduce tecniques for numericl integrtion,
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl
 Around Vortices: from Cont. to Quantum Mech. Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl Maicon José Benvenutti (UNICAMP)
Around Vortices: from Cont. to Quantum Mech. Global nonlinear stability of steady solutions of the 3-D incompressible Euler equations with helical symmetry and with no swirl Maicon José Benvenutti (UNICAMP)
m i N 1 F i = j i F ij + F x
 N m i i = 1,..., N m i Fi x N 1 F ij, j = 1, 2,... i 1, i + 1,..., N m i F i = j i F ij + F x i mi Fi j Fj i mj O P i = F i = j i F ij + F x i, i = 1,..., N P = i F i = N F ij + i j i N i F x i, i = 1,...,
N m i i = 1,..., N m i Fi x N 1 F ij, j = 1, 2,... i 1, i + 1,..., N m i F i = j i F ij + F x i mi Fi j Fj i mj O P i = F i = j i F ij + F x i, i = 1,..., N P = i F i = N F ij + i j i N i F x i, i = 1,...,
Lifting Entry 2. Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYLAND U N I V E R S I T Y O F
 ifting Entry Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYAN 1 010 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu ifting Atmospheric
ifting Entry Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYAN 1 010 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu ifting Atmospheric
Q π (/) ^ ^ ^ Η φ. <f) c>o. ^ ο. ö ê ω Q. Ο. o 'c. _o _) o U 03. ,,, ω ^ ^ -g'^ ο 0) f ο. Ε. ιη ο Φ. ο 0) κ. ο 03.,Ο. g 2< οο"" ο φ.
 II 4»» «i p û»7'' s V -Ζ G -7 y 1 X s? ' (/) Ζ L. - =! i- Ζ ) Η f) " i L. Û - 1 1 Ι û ( - " - ' t - ' t/î " ι-8. Ι -. : wî ' j 1 Τ J en " il-' - - ö ê., t= ' -; '9 ',,, ) Τ '.,/,. - ϊζ L - (- - s.1 ai
II 4»» «i p û»7'' s V -Ζ G -7 y 1 X s? ' (/) Ζ L. - =! i- Ζ ) Η f) " i L. Û - 1 1 Ι û ( - " - ' t - ' t/î " ι-8. Ι -. : wî ' j 1 Τ J en " il-' - - ö ê., t= ' -; '9 ',,, ) Τ '.,/,. - ϊζ L - (- - s.1 ai
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Solutions 3. February 2, Apply composite Simpson s rule with m = 1, 2, 4 panels to approximate the integrals:
 s Februry 2, 216 1 Exercise 5.2. Apply composite Simpson s rule with m = 1, 2, 4 pnels to pproximte the integrls: () x 2 dx = 1 π/2, (b) cos(x) dx = 1, (c) e x dx = e 1, nd report the errors. () f(x) =
s Februry 2, 216 1 Exercise 5.2. Apply composite Simpson s rule with m = 1, 2, 4 pnels to pproximte the integrls: () x 2 dx = 1 π/2, (b) cos(x) dx = 1, (c) e x dx = e 1, nd report the errors. () f(x) =
Appendix to On the stability of a compressible axisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe. By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee
 Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
Appendi to On the stability of a compressible aisymmetric rotating flow in a pipe By Z. Rusak & J. H. Lee Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 5 4, pp. 5 4 This material has not been copy-edited or typeset
10.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response)
 Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
Lecture Notes on Control Systems/D. Ghose/0 57 0.7 Performance of Second-Order System (Unit Step Response) Consider the second order system a ÿ + a ẏ + a 0 y = b 0 r So, Y (s) R(s) = b 0 a s + a s + a
Kul Finite element method I, Exercise 04/2016. Demo problems
 Kul-49 Finite element method I, Eercise 4/6 Demo problems Determine displcement u Z = nd rottion θ Y = t the mid-po of the Bernoulli bem of the figure Use two bem elements of equl length () nd () Po moment
Kul-49 Finite element method I, Eercise 4/6 Demo problems Determine displcement u Z = nd rottion θ Y = t the mid-po of the Bernoulli bem of the figure Use two bem elements of equl length () nd () Po moment
Econ Spring 2004 Instructor: Prof. Kiefer Solution to Problem set # 5. γ (0)
 Cornell University Department of Economics Econ 60 - Spring 004 Instructor: Prof. Kiefer Solution to Problem set # 5. Autocorrelation function is defined as ρ h = γ h γ 0 where γ h =Cov X t,x t h =E[X
Cornell University Department of Economics Econ 60 - Spring 004 Instructor: Prof. Kiefer Solution to Problem set # 5. Autocorrelation function is defined as ρ h = γ h γ 0 where γ h =Cov X t,x t h =E[X
 k k ΚΕΦΑΛΑΙΟ 1 G = (V, E) V E V V V G E G e = {v, u} E v u e v u G G V (G) E(G) n(g) = V (G) m(g) = E(G) G S V (G) S G N G (S) = {u V (G)\S v S : {v, u} E(G)} G v S v V (G) N G (v) = N G ({v}) x V (G)
k k ΚΕΦΑΛΑΙΟ 1 G = (V, E) V E V V V G E G e = {v, u} E v u e v u G G V (G) E(G) n(g) = V (G) m(g) = E(G) G S V (G) S G N G (S) = {u V (G)\S v S : {v, u} E(G)} G v S v V (G) N G (v) = N G ({v}) x V (G)
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
6.003: Signals and Systems. Modulation
 6.003: Signals and Systems Modulation May 6, 200 Communications Systems Signals are not always well matched to the media through which we wish to transmit them. signal audio video internet applications
6.003: Signals and Systems Modulation May 6, 200 Communications Systems Signals are not always well matched to the media through which we wish to transmit them. signal audio video internet applications
ΕΛΤΙΟ ΤΥΠΟΥ. ΕΙΚΤΗΣ ΤΙΜΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΗΣ ΝΕΩΝ ΚΤΙΡΙΩΝ ΚΑΤΟΙΚΙΩΝ: εκέµβριος 2015 (2010=100,0)
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΡΧΗ Πειραιάς, 22 Ιανουαρίου 2016 ΕΛΤΙΟ ΤΥΠΟΥ ΕΙΚΤΗΣ ΤΙΜΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΗΣ ΝΕΩΝ ΚΤΙΡΙΩΝ ΚΑΤΟΙΚΙΩΝ: εκέµβριος 2015 (2010=100,0) Ο Γενικός είκτης Τιµών Υλικών Κατασκευής
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΡΧΗ Πειραιάς, 22 Ιανουαρίου 2016 ΕΛΤΙΟ ΤΥΠΟΥ ΕΙΚΤΗΣ ΤΙΜΩΝ ΥΛΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΤΑΣΚΕΥΗΣ ΝΕΩΝ ΚΤΙΡΙΩΝ ΚΑΤΟΙΚΙΩΝ: εκέµβριος 2015 (2010=100,0) Ο Γενικός είκτης Τιµών Υλικών Κατασκευής
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
( ) Sine wave travelling to the right side
 SOUND WAVES (1) Sound wave: Varia2on of density of air Change in density at posi2on x and 2me t: Δρ(x,t) = Δρ m sin kx ωt (2) Sound wave: Varia2on of pressure Bulk modulus B is defined as: B = V dp dv
SOUND WAVES (1) Sound wave: Varia2on of density of air Change in density at posi2on x and 2me t: Δρ(x,t) = Δρ m sin kx ωt (2) Sound wave: Varia2on of pressure Bulk modulus B is defined as: B = V dp dv
A Hierarchy of Theta Bodies for Polynomial Systems
 A Hierarchy of Theta Bodies for Polynomial Systems Rekha Thomas, U Washington, Seattle Joint work with João Gouveia (U Washington) Monique Laurent (CWI) Pablo Parrilo (MIT) The Theta Body of a Graph G
A Hierarchy of Theta Bodies for Polynomial Systems Rekha Thomas, U Washington, Seattle Joint work with João Gouveia (U Washington) Monique Laurent (CWI) Pablo Parrilo (MIT) The Theta Body of a Graph G
Model Description. 1.1 Governing equations. The vertical coordinate (eta) is defined by: p re f. z s p T 0 p T. p p T p s p T. η s
 Model Description. Governing equations The vertical coordinate (eta) is defined by: η p p T p s p T η s ; η s p re f z s p T p re f 0 p T The horizontal equations of motion in the η system may be expressed
Model Description. Governing equations The vertical coordinate (eta) is defined by: η p p T p s p T η s ; η s p re f z s p T p re f 0 p T The horizontal equations of motion in the η system may be expressed
Math 248 Homework 1. Edward Burkard. Exercise 1. Prove the following Fourier Transforms where a > 0 and c R: f (x) = b. f(x c) = e.
 Math 48 Homework Ewar Burkar Exercise. Prove the following Fourier Transforms where a > an c : a. f(x) f(ξ) b. f(x c) e πicξ f(ξ) c. eπixc f(x) f(ξ c). f(ax) f(ξ) a e. f (x) πiξ f(ξ) f. xf(x) f(ξ) πi ξ
Math 48 Homework Ewar Burkar Exercise. Prove the following Fourier Transforms where a > an c : a. f(x) f(ξ) b. f(x c) e πicξ f(ξ) c. eπixc f(x) f(ξ c). f(ax) f(ξ) a e. f (x) πiξ f(ξ) f. xf(x) f(ξ) πi ξ
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 651 APPENDIX B. BIBLIOGRAPHY 677 APPENDIX C. ANSWERS TO SELECTED EXERCISES 679
 APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
 k k ΚΕΦΑΛΑΙΟ 1 G = (V, E) V E V V V G E G e = {v, u} E v u e v u G G V (G) E(G) n(g) = V (G) m(g) = E(G) G S V (G) S G N G (S) = {u V (G)\S v S : {v, u} E(G)} G v S v V (G) N G (v) = N G ({v}) x V (G)
k k ΚΕΦΑΛΑΙΟ 1 G = (V, E) V E V V V G E G e = {v, u} E v u e v u G G V (G) E(G) n(g) = V (G) m(g) = E(G) G S V (G) S G N G (S) = {u V (G)\S v S : {v, u} E(G)} G v S v V (G) N G (v) = N G ({v}) x V (G)
ΕΝΝΟΙΑ ΤΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΟΥ - ΟΡΙΣΜΟΣ
 ΕΝΝΟΙΑ ΤΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΟΥ - ΟΡΙΣΜΟΣ 3.1. Να αποδείξετε ότι η συνάρτηση: f x = { x e 1/ x,αν x 0 x ημx,αν x 0} είναι παραγωγίσιμη στο 0. 3.2. Δίνεται η συνάρτηση f x = { x 2 αx 1,αν x 1 2x 2, αν x 1 } η οποία
ΕΝΝΟΙΑ ΤΗΣ ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΟΥ - ΟΡΙΣΜΟΣ 3.1. Να αποδείξετε ότι η συνάρτηση: f x = { x e 1/ x,αν x 0 x ημx,αν x 0} είναι παραγωγίσιμη στο 0. 3.2. Δίνεται η συνάρτηση f x = { x 2 αx 1,αν x 1 2x 2, αν x 1 } η οποία
3.5 - Boundary Conditions for Potential Flow
 13.021 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 10 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. 13.021 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 10 3.5 - Boundary Conditions for Potential
13.021 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 10 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. 13.021 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 10 3.5 - Boundary Conditions for Potential
Μάρω Ευαγγελίδου, Αμαλιάδος 17, 11523. Τηλ. 2106475171. m.evangelidou@prv.ypeka.gr
 & 1 2012 1 2013 & Μάρω Ευαγγελίδου, Αμαλιάδος 17, 11523. Τηλ. 2106475171. m.evangelidou@prv.ypeka.gr ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 3 1.
& 1 2012 1 2013 & Μάρω Ευαγγελίδου, Αμαλιάδος 17, 11523. Τηλ. 2106475171. m.evangelidou@prv.ypeka.gr ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 3 1.
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
ΚΑΝΟΝΙΣΜΟΣ (ΕΕ) 2019/1243 ΤΟΥ ΕΥΡΩΠΑΪΚΟΥ ΚΟΙΝΟΒΟΥΛΙΟΥ ΚΑΙ ΤΟΥ ΣΥΜΒΟΥΛΙΟΥ
 25.7.2019 EL 198/241 L ( ) 2019/1243 20 2019 290 291 ( ),, 33, 43 2, 53 1, 62, 91, 100 2, 114, 153 2 ), 168 4 ), 172, 192 1, 207 2, 214 3 338 1,,, ( 1 ), ( 2 ), ( 3 ), : (1), ( ) ( ). (2) 5 1999/468/ (
25.7.2019 EL 198/241 L ( ) 2019/1243 20 2019 290 291 ( ),, 33, 43 2, 53 1, 62, 91, 100 2, 114, 153 2 ), 168 4 ), 172, 192 1, 207 2, 214 3 338 1,,, ( 1 ), ( 2 ), ( 3 ), : (1), ( ) ( ). (2) 5 1999/468/ (
Phase-Field Force Convergence
 Phase-Field Force Convergence Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Quantitative Biology Graduate Program UC San Diego Collaborators: Shibin Dai and Jianfeng Lu Funding: NSF School of Mathematical Sciences
Phase-Field Force Convergence Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Quantitative Biology Graduate Program UC San Diego Collaborators: Shibin Dai and Jianfeng Lu Funding: NSF School of Mathematical Sciences
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
