Generalized additive models in R
|
|
|
- Ζώνα Μαρής
- 6 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Generalized additive models in R Magne Aldrin, Norwegian Computing Center and the University of Oslo Sharp workshop, Copenhagen, October 2012
2 Generalized Linear Models - GLM y Distributed with mean µ and perhaps an additional parameter h(µ) = η η = β 0 + β 1 x 1 + β 2 x β p x p η: linear predictor h: link fuction 1
3 Generalized Additive Models - GAM η is additive, but each term can be non-linear η = β 0 + s 1 (x 1 ) + s 2 (x 2 ) + + s p (x p ) η: additive predictor s i ( ) is a smooth function, estimated from the data 2
4 Estimation of s Find s such that fit to data is as best as possible and s is as smooth as possible Can for instance be formulated as Minimize likelihood + i x λ is i (x)dx where s (x) = d 2 s(x)/d 2 x is the second derivative of s and λ s are constants that control the degree of smoothing 3
5 Effective number of parameters Very high λ i gives maximal smoothness a straight line described by 1 parameter (per explanatory variable) Smaller values of λ i gives more flexible functions effective number of parameters > 1 4
6 Choice of smoothness in the mgcv package Default is to estimate the smoothness of each s-function, controlled by λ i or a corresponding sp[i] by generalized cross-validation, minimizing - 2 log likelihood n/(n p) 2 where n = number of observations p = effective number of parameters This tends to give too unsmooth curves 5
7 Ex: Ozone data y = log(no 3 ) Gaussian > require(faraway) > data(ozone) > > require(mgcv) > gamobj<-gam(log(o3)~s(vh)+s(wind)+s(humidity)+s(temp)+s(ibh)+ s(dpg)+s(ibt)+s(vis)+s(doy), family=gaussian(link=identity),data=ozone) > summary(gamobj) Family: gaussian Link function: identity Formula: log(o3) ~ s(vh) + s(wind) + s(humidity) + s(temp) + s(ibh) + s(dpg) + s(ibt) + s(vis) + s(doy) Parametric coefficients: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(> t ) (Intercept) <2e-16 *** 6
8 Approximate significance of smooth terms: edf Ref.df F p-value s(vh) ** s(wind) ** s(humidity) s(temp) ** s(ibh) *** s(dpg) e-11 *** s(ibt) s(vis) e-06 *** s(doy) < 2e-16 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 * R-sq.(adj) = Deviance explained = 84% GCV score = Scale est. = n = 330 7
9 Plot results > pdf("gamozone.pdf") > par(mfrow=c(3,3)) > plot(gamobj) > dev.off() null device 1 8
10 s(vh,1) s(wind,1.02) vh wind humidity s(temp,3.8) s(ibh,2.77) s(humidity,2.41) temp ibh dpg s(ibt,1) s(vis,5.48) s(doy,4.61) s(dpg,3.29) ibt vis doy 9
11 Ex: Precipitation - binary logistic regression > Tryvann.dat<-read.table("/nr/user/aldrin/Sharp/data/Tryvann.dat") > > ### load the mgcv library > require(mgcv) > > gamobj<-gam(p01~p01.l1+p01.l2+p01.l3+ s(prep.l1)+s(prep.l2)+s(prep.l3), data=tryvann.dat,family=binomial(link=logit)) > summary(gamobj) Family: binomial Link function: logit Formula: P01 ~ P01.L1 + P01.L2 + P01.L3 + s(prep.l1) + s(prep.l2) + s(prep.l3) 10
12 Parametric coefficients: Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(> z ) (Intercept) e-15 *** P01.L < 2e-16 *** P01.L e-04 *** P01.L e-06 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 *
13 Approximate significance of smooth terms: edf Ref.df Chi.sq p-value s(prep.l1) e-07 *** s(prep.l2) s(prep.l3) Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 * R-sq.(adj) = Deviance explained = 9.81% UBRE score = Scale est. = 1 n = 3420 > 12
14 Plot results > pdf("gamlogistic.pdf") > par(mfrow=c(2,2)) > plot(gamobj) > dev.off() null device 1 13
15 s(prep.l1,2.53) Prep.L Prep.L2 s(prep.l3,1.11) s(prep.l2,1.01) Prep.L3 14
16 Ex: Simulated data y Poisson > n<-200 > x1<-rnorm(n) # N(0,1) > x2<-runif(n,-10,10) # Uniform(-10,10) > x3<-rnorm(n) > > eta< *x1-0.2*x2^2 + 0*x3 > mu<-exp(eta) > > y<-rpois(n=n,lambda=mu) > > data.obj<-data.frame(y=y,x1=x1,x2=x2,x3=x3) > > gamobj<-gam(y~s(x1)+s(x2)+s(x3),family=poisson(link=log), data=data.obj) 15
17 Results > summary(gamobj) Family: poisson Link function: log Formula: y ~ s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3) Parametric coefficients: Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(> z ) (Intercept) e-13 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 *
18 Approximate significance of smooth terms: edf Ref.df Chi.sq p-value s(x1) <2e-16 *** s(x2) <2e-16 *** s(x3) Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 * R-sq.(adj) = Deviance explained = 97.4% UBRE score = Scale est. = 1 n =
19 Plot results > pdf("gampoisson.pdf") > par(mfrow=c(2,2)) > plot(gamobj) > dev.off() null device 1 18
20 s(x1,1.51) x x2 s(x3,1) s(x2,4.36) x3 19
21 Option: Terms can be forced to be linear > ### The terms can be forced to be linear > gamobj<-gam(log(o3)~vh+wind+s(humidity)+s(temp)+s(ibh)+ s(dpg)+ibt+s(vis)+s(doy), family=gaussian(link=identity),data=ozone) > summary(gamobj) Family: gaussian Link function: identity Formula: log(o3) ~ vh + wind + s(humidity) + s(temp) + s(ibh) + s(dpg) + ibt + s(vis) + s(doy) Parametric coefficients: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(> t ) (Intercept) * vh ** wind ** ibt
22 Approximate significance of smooth terms: edf Ref.df F p-value s(humidity) s(temp) ** s(ibh) *** s(dpg) e-11 *** s(vis) e-06 *** s(doy) < 2e-16 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 * R-sq.(adj) = Deviance explained = 83.9% GCV score = Scale est. = n =
23 Controlling the smoothness by the sp option > gamobj<-gam(log(o3)~s(vh)+s(wind)+s(humidity)+s(temp)+s(ibh)+ s(dpg)+s(ibt)+s(vis)+s(doy),sp=rep(0.5,9), family=gaussian(link=identity),data=ozone) > summary(gamobj) Family: gaussian Link function: identity Formula: log(o3) ~ s(vh) + s(wind) + s(humidity) + s(temp) + s(ibh) + s(dpg) + s(ibt) + s(vis) + s(doy) Parametric coefficients: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(> t ) (Intercept) <2e-16 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 *
24 Approximate significance of smooth terms: edf Ref.df F p-value s(vh) s(wind) s(humidity) s(temp) e-07 *** s(ibh) * s(dpg) e-06 *** s(ibt) s(vis) *** s(doy) e-06 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 * R-sq.(adj) = Deviance explained = 78.6% GCV score = Scale est. = n =
25 Plot results > pdf("gamsmoothozone.pdf") > par(mfrow=c(3,3)) > plot(gamobj) > dev.off() null device 1 24
26 s(vh,1.63) s(wind,2.56) vh wind humidity s(temp,1.85) s(ibh,1.47) s(humidity,1.56) temp ibh dpg s(ibt,1.71) s(vis,2.04) s(doy,1.41) s(dpg,1.96) ibt vis doy 25
27 AIC or BIC to choose degree of smoothness > gamobj<-gam(log(o3)~s(vh)+s(wind)+s(humidity)+s(temp)+s(ibh)+ s(dpg)+s(ibt)+s(vis)+s(doy), family=gaussian(link=identity),data=ozone) > sp<-gamobj$sp > > tuning.scale<-c(1e-5,1e-4,1e-3,1e-2,1e-1,1e0,1e1,1e2,1e3,1e4,1e5) > ###tuning.scale<-c( ,0.0001,0.001,0.01,0.1,1,10,100,1000,10000 > scale.exponent<-log10(tuning.scale) > n.tuning<-length(tuning.scale) > edf<-rep(na,n.tuning) > min2ll<-rep(na,n.tuning) > aic<-rep(na,n.tuning) > bic<-rep(na,n.tuning) 26
28 > for (i in 1:n.tuning) { + gamobj<-gam(log(o3)~s(vh)+s(wind)+s(humidity)+s(temp)+s(ibh)+ s(dpg)+s(ibt)+s(vis)+s(doy), family=gaussian(link=identity),data=ozone, sp=tuning.scale[i]*sp) + min2ll[i]<--2*loglik(gamobj) + edf[i]<-sum(gamobj$edf)+1 + aic[i]<-aic(gamobj) + bic[i]<-bic(gamobj) + } 27
29 Plot results > pdf("aicbicozone.pdf") > par(mfrow=c(2,2)) > plot(scale.exponent,min2ll,type="b",main="-2 log likelihood") > plot(scale.exponent,edf,ylim=c(0,70),type="b",main="effective number > plot(scale.exponent,aic,type="b",main="aic") > plot(scale.exponent,bic,type="b",main="bic") > dev.off() null device 1 28
30 2 log likelihood effective number of parameters min2ll edf scale.exponent scale.exponent AIC BIC aic bic scale.exponent scale.exponent 29
31 Scaling corresponding to minimum BIC > min.bic<-1e100 > opt.tuning.scale<-null > for (i in 1:n.tuning) { + if (bic[i]<min.bic) { + min.bic<-bic[i] + opt.tuning.scale<-tuning.scale[i] + } + } > opt.sp<-opt.tuning.scale*sp 30
32 Estimate final model with optimal value of sp > gamobj<-gam(log(o3)~s(vh)+s(wind)+s(humidity)+s(temp)+s(ibh)+ s(dpg)+s(ibt)+s(vis)+s(doy), family=gaussian(link=identity),data=ozone,sp=opt.sp) > summary(gamobj) Family: gaussian Link function: identity Formula: log(o3) ~ s(vh) + s(wind) + s(humidity) + s(temp) + s(ibh) + s(dpg) + s(ibt) + s(vis) + s(doy) Parametric coefficients: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(> t ) (Intercept) <2e-16 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 *
33 Approximate significance of smooth terms: edf Ref.df F p-value s(vh) s(wind) * s(humidity) s(temp) e-05 *** s(ibh) ** s(dpg) e-07 *** s(ibt) s(vis) e-05 *** s(doy) < 2e-16 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 *** ** 0.01 * R-sq.(adj) = Deviance explained = 81% GCV score = Scale est. = n =
34 Plot results > pdf("gamoptsmoothozone.pdf") > par(mfrow=c(3,3)) > plot(gamobj) > dev.off() null device 1 33
35 s(vh,1) s(wind,1) vh wind humidity s(temp,2.1) s(ibh,1.66) s(humidity,1.37) temp ibh dpg s(ibt,1) s(vis,3.17) s(doy,2.46) s(dpg,1.73) ibt vis doy 34
5.1 logistic regresssion Chris Parrish July 3, 2016
 5.1 logistic regresssion Chris Parrish July 3, 2016 Contents logistic regression model 1 1992 vote 1 data..................................................... 1 model....................................................
5.1 logistic regresssion Chris Parrish July 3, 2016 Contents logistic regression model 1 1992 vote 1 data..................................................... 1 model....................................................
Wan Nor Arifin under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 1 Introduction 1
 Poisson Regression A Short Course on Data Analysis Using R Software (2017) Wan Nor Arifin (wnarifin@usm.my), Universiti Sains Malaysia Website: sites.google.com/site/wnarifin Wan Nor Arifin under the Creative
Poisson Regression A Short Course on Data Analysis Using R Software (2017) Wan Nor Arifin (wnarifin@usm.my), Universiti Sains Malaysia Website: sites.google.com/site/wnarifin Wan Nor Arifin under the Creative
Λογαριθμικά Γραμμικά Μοντέλα Poisson Παλινδρόμηση Παράδειγμα στο SPSS
 Λογαριθμικά Γραμμικά Μοντέλα Poisson Παλινδρόμηση Παράδειγμα στο SPSS Ο παρακάτω πίνακας παρουσιάζει θανάτους από καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια ανάμεσα σε άνδρες γιατρούς οι οποίοι έχουν κατηγοριοποιηθεί κατά ηλικία
Λογαριθμικά Γραμμικά Μοντέλα Poisson Παλινδρόμηση Παράδειγμα στο SPSS Ο παρακάτω πίνακας παρουσιάζει θανάτους από καρδιακή ανεπάρκεια ανάμεσα σε άνδρες γιατρούς οι οποίοι έχουν κατηγοριοποιηθεί κατά ηλικία
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Queensland University of Technology Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies
 Queensland University of Technology Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies Lab Session #7 Example 5.2 (with 3SLS Extensions) Seemingly Unrelated Regression Estimation and 3SLS A survey of 206
Queensland University of Technology Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies Lab Session #7 Example 5.2 (with 3SLS Extensions) Seemingly Unrelated Regression Estimation and 3SLS A survey of 206
Supplementary figures
 A Supplementary figures a) DMT.BG2 0.87 0.87 0.72 20 40 60 80 100 DMT.EG2 0.93 0.85 20 40 60 80 EMT.MG3 0.85 0 20 40 60 80 20 40 60 80 100 20 40 60 80 100 20 40 60 80 EMT.G6 DMT/EMT b) EG2 0.92 0.85 5
A Supplementary figures a) DMT.BG2 0.87 0.87 0.72 20 40 60 80 100 DMT.EG2 0.93 0.85 20 40 60 80 EMT.MG3 0.85 0 20 40 60 80 20 40 60 80 100 20 40 60 80 100 20 40 60 80 EMT.G6 DMT/EMT b) EG2 0.92 0.85 5
Bayesian statistics. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise. Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University
 Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
 η π 2 /3 χ 2 χ 2 t k Y 0/0, 0/1,..., 3/3 π 1, π 2,..., π k k k 1 β ij Y I i = 1,..., I p (X i = x i1,..., x ip ) Y i J (j = 1,..., J) x i Y i = j π j (x i ) x i π j (x i ) x (n 1 (x),..., n J (x))
η π 2 /3 χ 2 χ 2 t k Y 0/0, 0/1,..., 3/3 π 1, π 2,..., π k k k 1 β ij Y I i = 1,..., I p (X i = x i1,..., x ip ) Y i J (j = 1,..., J) x i Y i = j π j (x i ) x i π j (x i ) x (n 1 (x),..., n J (x))
Λογιστική Παλινδρόµηση
 Κεφάλαιο 10 Λογιστική Παλινδρόµηση Στο κεφάλαιο αυτό ϑα δούµε την µέθοδο της λογιστικής παλινδρόµησης η οποία χρησιµεύει στο να αναπτύξουµε σχέση µίας δίτιµης ανεξάρτητης τυχαίας µετα- ϐλητής και συνεχών
Κεφάλαιο 10 Λογιστική Παλινδρόµηση Στο κεφάλαιο αυτό ϑα δούµε την µέθοδο της λογιστικής παλινδρόµησης η οποία χρησιµεύει στο να αναπτύξουµε σχέση µίας δίτιµης ανεξάρτητης τυχαίας µετα- ϐλητής και συνεχών
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Solution Series 9. i=1 x i and i=1 x i.
 Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Wan Nor Arifin under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 1 Introduction 1
 Linear Regression A Short Course on Data Analysis Using R Software (2017) Wan Nor Arifin (wnarifin@usm.my), Universiti Sains Malaysia Website: sites.google.com/site/wnarifin Wan Nor Arifin under the Creative
Linear Regression A Short Course on Data Analysis Using R Software (2017) Wan Nor Arifin (wnarifin@usm.my), Universiti Sains Malaysia Website: sites.google.com/site/wnarifin Wan Nor Arifin under the Creative
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 1 43 123 5 122 3 1 312 1 1 122 1 1 1 1 6 1 7 1 6 1 7 1 3 4 2 312 43 4 3 3 1 1 4 1 1 52 122 54 124 8 1 3 1 1 1 1 1 152 1 1 1 1 1 1 152 1 5 1 152 152 1 1 3 9 1 159 9 13 4 5 1 122 1 4 122 5
1 1 1 2 1 2 2 1 43 123 5 122 3 1 312 1 1 122 1 1 1 1 6 1 7 1 6 1 7 1 3 4 2 312 43 4 3 3 1 1 4 1 1 52 122 54 124 8 1 3 1 1 1 1 1 152 1 1 1 1 1 1 152 1 5 1 152 152 1 1 3 9 1 159 9 13 4 5 1 122 1 4 122 5
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
«ΑΝΑΠΣΤΞΖ ΓΠ ΚΑΗ ΥΩΡΗΚΖ ΑΝΑΛΤΖ ΜΔΣΔΩΡΟΛΟΓΗΚΩΝ ΓΔΓΟΜΔΝΩΝ ΣΟΝ ΔΛΛΑΓΗΚΟ ΥΩΡΟ»
 ΓΔΩΠΟΝΗΚΟ ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΑΘΖΝΩΝ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΑΞΙΟΠΟΙΗΗ ΦΤΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ & ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΗ ΜΗΥΑΝΙΚΗ ΣΟΜΕΑ ΕΔΑΦΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΗ ΥΗΜΕΙΑ ΕΙΔΙΚΕΤΗ: ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΕ ΣΗ ΓΕΩΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗ ΣΟΤ ΦΤΙΚΟΤ ΠΟΡΟΤ «ΑΝΑΠΣΤΞΖ ΓΠ ΚΑΗ ΥΩΡΗΚΖ ΑΝΑΛΤΖ ΜΔΣΔΩΡΟΛΟΓΗΚΩΝ
ΓΔΩΠΟΝΗΚΟ ΠΑΝΔΠΗΣΖΜΗΟ ΑΘΖΝΩΝ ΣΜΗΜΑ ΑΞΙΟΠΟΙΗΗ ΦΤΙΚΩΝ ΠΟΡΩΝ & ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΗ ΜΗΥΑΝΙΚΗ ΣΟΜΕΑ ΕΔΑΦΟΛΟΓΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΚΗ ΥΗΜΕΙΑ ΕΙΔΙΚΕΤΗ: ΕΦΑΡΜΟΓΕ ΣΗ ΓΕΩΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗ ΣΟΤ ΦΤΙΚΟΤ ΠΟΡΟΤ «ΑΝΑΠΣΤΞΖ ΓΠ ΚΑΗ ΥΩΡΗΚΖ ΑΝΑΛΤΖ ΜΔΣΔΩΡΟΛΟΓΗΚΩΝ
Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review
 Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Εργασία. στα. Γενικευμένα Γραμμικά Μοντέλα
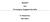 Εργασία στα Γενικευμένα Γραμμικά Μοντέλα Μ. Παρζακώνης ΜΕΣ/ 06015 Ο παρακάτω πίνακας δίνει τα αποτελέσματα 800 αιτήσεων για δάνειο σε μία τράπεζα. Ο πίνακας παρουσιάζει τον αριθμό των δανείων που εγκρίθηκαν,
Εργασία στα Γενικευμένα Γραμμικά Μοντέλα Μ. Παρζακώνης ΜΕΣ/ 06015 Ο παρακάτω πίνακας δίνει τα αποτελέσματα 800 αιτήσεων για δάνειο σε μία τράπεζα. Ο πίνακας παρουσιάζει τον αριθμό των δανείων που εγκρίθηκαν,
Γενικευµένα Γραµµικά Μοντέλα
 Σηµειώσεις για το εργαστήριο υπολογιστών για το µάθηµα Γενικευµένα Γραµµικά Μοντέλα. Μέρος δεύτερο: Γενικευµένα Γραµµικά Μοντέλα στην SPLUS Οι σηµειώσεις γράφτηκαν από το Γιώργο Τζουγά, υποψήφιο διδάκτορα
Σηµειώσεις για το εργαστήριο υπολογιστών για το µάθηµα Γενικευµένα Γραµµικά Μοντέλα. Μέρος δεύτερο: Γενικευµένα Γραµµικά Μοντέλα στην SPLUS Οι σηµειώσεις γράφτηκαν από το Γιώργο Τζουγά, υποψήφιο διδάκτορα
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Asymptotic distribution of MLE
 Asymptotic distribution of MLE Theorem Let {X t } be a causal and invertible ARMA(p,q) process satisfying Φ(B)X = Θ(B)Z, {Z t } IID(0, σ 2 ). Let ( ˆφ, ˆϑ) the values that minimize LL n (φ, ϑ) among those
Asymptotic distribution of MLE Theorem Let {X t } be a causal and invertible ARMA(p,q) process satisfying Φ(B)X = Θ(B)Z, {Z t } IID(0, σ 2 ). Let ( ˆφ, ˆϑ) the values that minimize LL n (φ, ϑ) among those
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix Measuring crisis risk using conditional copulas: An empirical analysis of the 2008 shipping crisis Sebastian Opitz, Henry Seidel and Alexander Szimayer Model specification Table
Supplementary Appendix Measuring crisis risk using conditional copulas: An empirical analysis of the 2008 shipping crisis Sebastian Opitz, Henry Seidel and Alexander Szimayer Model specification Table
Numerical Analysis FMN011
 Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Numerical Analysis FMN011 Carmen Arévalo Lund University carmen@maths.lth.se Lecture 12 Periodic data A function g has period P if g(x + P ) = g(x) Model: Trigonometric polynomial of order M T M (x) =
Introduction to the ML Estimation of ARMA processes
 Introduction to the ML Estimation of ARMA processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi ARMA Estimation Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 1 We consider the AR(p) model: Y t = c + φ 1 Y
Introduction to the ML Estimation of ARMA processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi ARMA Estimation Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 1 We consider the AR(p) model: Y t = c + φ 1 Y
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme
 Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
Math 6 SL Probability Distributions Practice Test Mark Scheme. (a) Note: Award A for vertical line to right of mean, A for shading to right of their vertical line. AA N (b) evidence of recognizing symmetry
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Άσκηση 10, σελ. 119. Για τη μεταβλητή x (άτυπος όγκος) έχουμε: x censored_x 1 F 3 F 3 F 4 F 10 F 13 F 13 F 16 F 16 F 24 F 26 F 27 F 28 F
 Άσκηση 0, σελ. 9 από το βιβλίο «Μοντέλα Αξιοπιστίας και Επιβίωσης» της Χ. Καρώνη (i) Αρχικά, εισάγουμε τα δεδομένα στο minitab δημιουργώντας δύο μεταβλητές: τη x για τον άτυπο όγκο και την y για τον τυπικό
Άσκηση 0, σελ. 9 από το βιβλίο «Μοντέλα Αξιοπιστίας και Επιβίωσης» της Χ. Καρώνη (i) Αρχικά, εισάγουμε τα δεδομένα στο minitab δημιουργώντας δύο μεταβλητές: τη x για τον άτυπο όγκο και την y για τον τυπικό
[2] T.S.G. Peiris and R.O. Thattil, An Alternative Model to Estimate Solar Radiation
![[2] T.S.G. Peiris and R.O. Thattil, An Alternative Model to Estimate Solar Radiation [2] T.S.G. Peiris and R.O. Thattil, An Alternative Model to Estimate Solar Radiation](/thumbs/74/71129035.jpg) References [1] B.V.R. Punyawardena and Don Kulasiri, Stochastic Simulation of Solar Radiation from Sunshine Duration in Srilanka [2] T.S.G. Peiris and R.O. Thattil, An Alternative Model to Estimate Solar
References [1] B.V.R. Punyawardena and Don Kulasiri, Stochastic Simulation of Solar Radiation from Sunshine Duration in Srilanka [2] T.S.G. Peiris and R.O. Thattil, An Alternative Model to Estimate Solar
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Interpretation of linear, logistic and Poisson regression models with transformed variables and its implementation in the R package tlm
 Interpretation of linear, logistic and Poisson regression models with transformed variables and its implementation in the R package tlm Jose Barrera-Gómez a jbarrera@creal.cat a Centre for Research in
Interpretation of linear, logistic and Poisson regression models with transformed variables and its implementation in the R package tlm Jose Barrera-Gómez a jbarrera@creal.cat a Centre for Research in
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
Μη Παραµετρική Παλινδρόµηση
 Κεφάλαιο 18 Μη Παραµετρική Παλινδρόµηση Το παραδοσιακό παραµετρικό µοντέλο δίνεται από την εξίσωση y i = f(β, x i ) + ε i, όπου β = (β 1,..., β p ) το διάνυσµα των παραµέτρων που ϑα εκτιµηθούν, και x i
Κεφάλαιο 18 Μη Παραµετρική Παλινδρόµηση Το παραδοσιακό παραµετρικό µοντέλο δίνεται από την εξίσωση y i = f(β, x i ) + ε i, όπου β = (β 1,..., β p ) το διάνυσµα των παραµέτρων που ϑα εκτιµηθούν, και x i
An Introduction to Splines
 An Introduction to Splines Trinity River Restoration Program Workshop on Outmigration: Population Estimation October 6 8, 2009 An Introduction to Splines 1 Linear Regression Simple Regression and the Least
An Introduction to Splines Trinity River Restoration Program Workshop on Outmigration: Population Estimation October 6 8, 2009 An Introduction to Splines 1 Linear Regression Simple Regression and the Least
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Module 5. February 14, h 0min
 Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
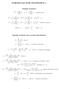 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
SCITECH Volume 13, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION Published online: March 29, 2018
 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics(JRM) ISSN: 2395-028 SCITECH Volume 3, Issue 2 RESEARCH ORGANISATION ublished online: March 29, 208 Journal of rogressive Research in Mathematics www.scitecresearch.com/journals
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
HW 3 Solutions 1. a) I use the auto.arima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA(3,1)
 HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
Review Test 3. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact value of the expression. 1) sin - 11π 1 1) + - + - - ) sin 11π 1 ) ( -
Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact value of the expression. 1) sin - 11π 1 1) + - + - - ) sin 11π 1 ) ( -
MATHACHij = γ00 + u0j + rij
 Stata output for Hierarchical Linear Models. ***************************************. * Unconditional Random Intercept Model. *************************************** MATHACHij = γ00 + u0j + rij. mixed
Stata output for Hierarchical Linear Models. ***************************************. * Unconditional Random Intercept Model. *************************************** MATHACHij = γ00 + u0j + rij. mixed
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ
 ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
ΕΙΣΑΓΩΓΗ ΣΤΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΛΥΣΗ ΕΛΕΝΑ ΦΛΟΚΑ Επίκουρος Καθηγήτρια Τµήµα Φυσικής, Τοµέας Φυσικής Περιβάλλοντος- Μετεωρολογίας ΓΕΝΙΚΟΙ ΟΡΙΣΜΟΙ Πληθυσµός Σύνολο ατόµων ή αντικειµένων στα οποία αναφέρονται
6. MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATION
 6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2
![If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2 If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π, π ], the restrict function. y = sin x, π 2 x π 2](/thumbs/53/31933086.jpg) Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 651 APPENDIX B. BIBLIOGRAPHY 677 APPENDIX C. ANSWERS TO SELECTED EXERCISES 679
 APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ. Ψηφιακή Οικονομία. Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Διάλεξη 7η: Consumer Behavior Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Τέλος Ενότητας Χρηματοδότηση Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό έχει αναπτυχθεί
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet
 Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
SECTION II: PROBABILITY MODELS
 SECTION II: PROBABILITY MODELS 1 SECTION II: Aggregate Data. Fraction of births with low birth weight per province. Model A: OLS, using observations 1 260 Heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors, variant
SECTION II: PROBABILITY MODELS 1 SECTION II: Aggregate Data. Fraction of births with low birth weight per province. Model A: OLS, using observations 1 260 Heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors, variant
If we restrict the domain of y = sin x to [ π 2, π 2
 Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Chapter 3. Analytic Trigonometry 3.1 The inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions 1. Review: Inverse function (1) f 1 (f(x)) = x for every x in the domain of f and f(f 1 (x)) = x for every x in the
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Tutorial on Multinomial Logistic Regression
 Tutorial on Multinomial Logistic Regression Javier R Movellan June 19, 2013 1 1 General Model The inputs are n-dimensional vectors the outputs are c-dimensional vectors The training sample consist of m
Tutorial on Multinomial Logistic Regression Javier R Movellan June 19, 2013 1 1 General Model The inputs are n-dimensional vectors the outputs are c-dimensional vectors The training sample consist of m
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
Γενικευμένα Γραμμικά Μοντέλα (GLM) Επισκόπηση
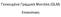 Γενικευμένα Γραμμικά Μοντέλα (GLM) Επισκόπηση Γενική μορφή g( E[ Y X ]) Xb Κατανομή της Υ στην εκθετική οικογένεια Ανεξάρτητες παρατηρήσεις Ενας όρος για το σφάλμα g(.) Συνδετική συνάρτηση (link function)
Γενικευμένα Γραμμικά Μοντέλα (GLM) Επισκόπηση Γενική μορφή g( E[ Y X ]) Xb Κατανομή της Υ στην εκθετική οικογένεια Ανεξάρτητες παρατηρήσεις Ενας όρος για το σφάλμα g(.) Συνδετική συνάρτηση (link function)
Εργαστήριο Ανάπτυξης Εφαρμογών Βάσεων Δεδομένων. Εξάμηνο 7 ο
 Εργαστήριο Ανάπτυξης Εφαρμογών Βάσεων Δεδομένων Εξάμηνο 7 ο Procedures and Functions Stored procedures and functions are named blocks of code that enable you to group and organize a series of SQL and PL/SQL
Εργαστήριο Ανάπτυξης Εφαρμογών Βάσεων Δεδομένων Εξάμηνο 7 ο Procedures and Functions Stored procedures and functions are named blocks of code that enable you to group and organize a series of SQL and PL/SQL
Partial Differential Equations in Biology The boundary element method. March 26, 2013
 The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
The boundary element method March 26, 203 Introduction and notation The problem: u = f in D R d u = ϕ in Γ D u n = g on Γ N, where D = Γ D Γ N, Γ D Γ N = (possibly, Γ D = [Neumann problem] or Γ N = [Dirichlet
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
DirichletReg: Dirichlet Regression for Compositional Data in R
 DirichletReg: Dirichlet Regression for Compositional Data in R Marco J. Maier Wirtschaftsuniversität Wien Abstract Full R Code for Maier, M. J. (2014). DirichletReg: Dirichlet Regression for Compositional
DirichletReg: Dirichlet Regression for Compositional Data in R Marco J. Maier Wirtschaftsuniversität Wien Abstract Full R Code for Maier, M. J. (2014). DirichletReg: Dirichlet Regression for Compositional
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 01, Brooks/Cole Chapter
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 19/5/2007
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Αν κάπου κάνετε κάποιες υποθέσεις να αναφερθούν στη σχετική ερώτηση. Όλα τα αρχεία που αναφέρονται στα προβλήματα βρίσκονται στον ίδιο φάκελο με το εκτελέσιμο
Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης, Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Άνοιξη 2009. HΥ463 - Συστήματα Ανάκτησης Πληροφοριών Information Retrieval (IR) Systems
 Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης, Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Άνοιξη 2009 HΥ463 - Συστήματα Ανάκτησης Πληροφοριών Information Retrieval (IR) Systems Στατιστικά Κειμένου Text Statistics Γιάννης Τζίτζικας άλ ιάλεξη :
Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης, Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Άνοιξη 2009 HΥ463 - Συστήματα Ανάκτησης Πληροφοριών Information Retrieval (IR) Systems Στατιστικά Κειμένου Text Statistics Γιάννης Τζίτζικας άλ ιάλεξη :
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Lecture 7: Overdispersion in Poisson regression
 Lecture 7: Overdispersion in Poisson regression Claudia Czado TU München c (Claudia Czado, TU Munich) ZFS/IMS Göttingen 2004 0 Overview Introduction Modeling overdispersion through mixing Score test for
Lecture 7: Overdispersion in Poisson regression Claudia Czado TU München c (Claudia Czado, TU Munich) ZFS/IMS Göttingen 2004 0 Overview Introduction Modeling overdispersion through mixing Score test for
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data
 Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
5.4 The Poisson Distribution.
 The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
An Inventory of Continuous Distributions
 Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Summary of the model specified
 Program: HLM 7 Hierarchical Linear and Nonlinear Modeling Authors: Stephen Raudenbush, Tony Bryk, & Richard Congdon Publisher: Scientific Software International, Inc. (c) 2010 techsupport@ssicentral.com
Program: HLM 7 Hierarchical Linear and Nonlinear Modeling Authors: Stephen Raudenbush, Tony Bryk, & Richard Congdon Publisher: Scientific Software International, Inc. (c) 2010 techsupport@ssicentral.com
Section 9.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
Elements of Information Theory
 Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Elements of Information Theory Model of Digital Communications System A Logarithmic Measure for Information Mutual Information Units of Information Self-Information News... Example Information Measure
Differential equations
 Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
Differential equations Differential equations: An equation inoling one dependent ariable and its deriaties w. r. t one or more independent ariables is called a differential equation. Order of differential
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
Does anemia contribute to end-organ dysfunction in ICU patients Statistical Analysis
 Does anemia contribute to end-organ dysfunction in ICU patients Statistical Analysis Xue Han, MPH and Matt Shotwell, PhD Department of Biostatistics Vanderbilt University School of Medicine March 14, 2014
Does anemia contribute to end-organ dysfunction in ICU patients Statistical Analysis Xue Han, MPH and Matt Shotwell, PhD Department of Biostatistics Vanderbilt University School of Medicine March 14, 2014
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Supplementary Material for The Cusp Catastrophe Model as Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Mixture Structural Equation Models
 Supplementary Material for The Cusp Catastrophe Model as Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Mixture Structural Equation Models Sy-Miin Chow Pennsylvania State University Katie Witkiewitz University of New
Supplementary Material for The Cusp Catastrophe Model as Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Mixture Structural Equation Models Sy-Miin Chow Pennsylvania State University Katie Witkiewitz University of New
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Άσκηση αυτοαξιολόγησης 4 Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών CS-593 Game Theory 1. For the game depicted below, find the mixed strategy
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Ψηφιακή Οικονομία Άσκηση αυτοαξιολόγησης 4 Mαρίνα Μπιτσάκη Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών CS-593 Game Theory 1. For the game depicted below, find the mixed strategy
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in
 Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Tridiagonal matrices. Gérard MEURANT. October, 2008
 Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
Tridiagonal matrices Gérard MEURANT October, 2008 1 Similarity 2 Cholesy factorizations 3 Eigenvalues 4 Inverse Similarity Let α 1 ω 1 β 1 α 2 ω 2 T =......... β 2 α 1 ω 1 β 1 α and β i ω i, i = 1,...,
forms This gives Remark 1. How to remember the above formulas: Substituting these into the equation we obtain with
 Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
Week 03: C lassification of S econd- Order L inear Equations In last week s lectures we have illustrated how to obtain the general solutions of first order PDEs using the method of characteristics. We
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Laplace Expansion. Peter McCullagh. WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, Department of Statistics University of Chicago
 Laplace Expansion Peter McCullagh Department of Statistics University of Chicago WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, 2017 Outline Laplace approximation in 1D Laplace expansion in 1D Laplace expansion in R p Formal
Laplace Expansion Peter McCullagh Department of Statistics University of Chicago WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, 2017 Outline Laplace approximation in 1D Laplace expansion in 1D Laplace expansion in R p Formal
