Technical Appendix (Not for publication) Generic and Brand Advertising Strategies in a Dynamic Duopoly
|
|
|
- É Παππάς
- 5 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Tehnal Appendx (Not fo publaton Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly Ths Tehnal Appendx povdes supplementay nfomaton to the pape Gene and Band Advetsng Stateges n a Dynam Duopoly. It s dvded nto the followng setons: A. Poofs n geate detal than n the Appendx. B. Poofs of ompaatve stats esults fo asymmet fms. C. Poofs of ompaatve stats esults fo symmet fms. D. Devatons fo the Extenson seton. A. Poofs n Geate Detal than n the Appendx. Poof of Poposton The Hamlton-Jaob-Bellman (HJB equaton fo fm { } s gven by V ps( bp dp3 ( a u ( u S3 3u3 S θ( a a S V max (A u a p V ( 3u3 S u S3 θ3( a a. S3 Fom ths the fst-ode ondtons fo u and a { } yeld espetvely V V V V u ( S a ( θ θ. 3 3 S S3 S S3 (A The fst-ode ondtons fo p and p yeld bp dp 0 d p bp 0. (A3 Solvng the two smultaneous equatons n (A3 we obtan the optmal pe of fm to be p d b 3 4bb dd We an theefoe smplfy the pe tems n (A so that. (A4
2 d b p ( bp dp b( m. Fom ths pont fowad we wll use 3 3 4bb dd m b denote the equlbum magns of the two fms. Substtutng (A and (A5 nto (A yelds d b ( 4bb dd V V V V V m S S and m d b b( 4bb dd ( θ θ3 ( 3 S S3 S S3 3 V V V V 3 V V V V S θ θ θ θ 3 S S S S 3 S S S S ( ( ( (. The lnea value funton V α βs γs3 { } satsfes (A6. The optmal band and gene advetsng desons n (A an now be ewtten as 3 3 (A5 to (A6 u ( β γ S a ( θ β θ γ. (A7 Substtutng V α βs γs3 nto (A6 and smplfyng we have α βs γs3 ms ( θβ θ3γ ( β γ S3 (A8 ( ( ( (. 3 3 β γ β γ S θβ θγ θβ θγ 3 3 Equatng the oeffents of S S3 and the onstant n equaton (A8 esults n the followng smultaneous equatons to solve fo α β and γ : ( ( ( (A9 α 3 3 θ β θ γ θ β θ γ θ β θγ 3 3 β m ( β γ ( β γ (A0 3 γ β γ (. (A Wtng out these equatons expltly fo { } we get ( ( ( (A α θ β θ γ θ β θ γ θ β θ γ
3 β β γ β γ m ( ( (A3 ( (A4 γ β γ ( ( ( (A5 α θ β θ γ θ β θ γ θ β θ γ ( ( (A6 β m β γ β γ (. (A7 γ β γ To solve subtat (A4 fom (A3 and (A7 fom (A6. Let y β γ and z β γ. Upon smplfyng we have the followng smultaneous quadat equatons n y and z : y yz y m 0 (A8 z yz z m 0. (A9 Substtutng fo z n tems of y n equaton (A9 afte solvng fo z n (A8 yelds the followng quat equaton n y : η η η η η (A0 4 3 y y 3y 4y whee η 3 η 4 ( η 4 ( ( m m 4 η 8 m( and η 4 m. 5 3 The oots of equaton (A0 an be omputed usng Mathemata v4.0. Of the fou solutons fo y two ae magnay one s negatve and only one s always eal and postve. Ths s the unque Nash equlbum of the dffeental game. That soluton s gven by η ω y 4η 4 ω ω ω ( 7 ω ω5 ω6 ω ω5 ω6 5 6 (A 3
4 η 3 whee η ω 4η 3 ω η3 3ηη 4 ηη 5 ω3 η3 9ηηη 3 4 7ηη 4 7ηη 5 7 ηηη 3 5 3η ω ( ω ω 4 ω ω 3 ω ω 4 5 ω6 3η ω Knowng y we an ompute the followng: 3 4ηη 3 η 8η 4 and ω7. 3 η η η η γ y β y y z ( m y y γ z β z z. (A y One an see fom (A that β > 0 γ > 0 and β > γ esultng n postve values fo the ontols. Poof of Coollay To solve the smultaneous equatons: 3 α ( β γ (A3 8 β m ( β γ (A4 γ ( β γ (A5 m multply (A5 by and add to (A4. Ths yelds β γ. Substtutng ths nto (A5 esults n the followng quadat equaton n γ : m γ γ γ m γ m (A6 ( (3 0. The two solutons of ths quadat equaton ae 3 m ± ( 6 m γ. (A7 9 To fnd out whh of the two oots to hoose we use the test that γ 0 when m 0. Ths s beause the value funton should be dentally equal to zeo when the goss magn s zeo sne the fm maes zeo poft n ths ase. Cheng wth (A7 t an be seen that 4
5 3 m ( 6 m γ (A8 9 s the only oot that satsfes ths ondton. m Knowng γ we an ompute β and α usng β γ and (A3 espetvely to be 3m ( 6 m β (A ( 3m 8 m (6 m ( 6 m α 3 4. (A30 08 An examnaton of equatons (A8-30 eveals that α > 0 β > 0 γ > 0 and β > γ so the ontols and the value funtons ae postve. Poof of Poposton To deve the optmal sales paths we substtute the esults fom Poposton nto the two state equatons to obtan the followng system of dffeental equatons: S S S S S (A3 S ( S ( S ( ( S (0 S. ( βγ ( β γ θ( ( θβ θγ ( θγ θβ (0 0 β γ β γ θ( θβ θγ θγ θβ 0 Fo expostonal ease denote ψ ( β γ ψ ( β γ ψ ( θβ θγ ( θ γ θβ. (A3 3 The dffeental equatons an now be ewtten as S ψs ψs θψ 3 S(0 S0 S ψ S ψ S θ ψ S (0 S. 3 0 Note fom (A33 that thee s no long-un equlbum n sales.e. S and S need not go to (A33 zeo. Solvng the smultaneous dffeental equatons n (A33 usng Mathemata v4.0 yelds 5
6 e S ( t ( ( S ( e ( S ( e (A34 ( ψ ψ t ( ψ ψ t ( ψ ψ t ψ ψ ψ 0 ψ ψ 0 ψ ψ ( ψ ψ ψ ( θψ θψ ( ψ ψ θ ψ ψ θ t t e ( ψ ψ t 3 ( ( e S ( t ( ( S ( e ( S ( e (A35 ( ψ ψ t ( ψ ψ t ( ψ ψ t ψ ψ ψ 0 ψ ψ 0 ψ ψ ( ψ ψ ψ ( θψ θ ψ ( ψ ψ θ ψ ψ θ t t e ( ψ ψ t 3 ( (. The long-un equlbum maet shaes ae gven by S( t S( t x lm x lm. t S( t S( t t S( t S( t Smplfyng and tang the lmts we have (A36 x. (A37 ( ( ( ( ( βγ ( β γ x β γ β γ β γ β γ Poof of Poposton 3 If the fm owns both bands ts deson poblem s max u( t a( t u( t a( t p( t p( t ( t e p( t S(( t bp( t dp( t p( t S(( t dp( t bp( t V (A38 0 ( a( t u( t ( a( t u( t dt s.t. S ( t u( t S( t u( t S( t θ( a( t a( t S(0 S0 (A39 S ( t u ( t S ( t u ( t S ( t θ ( a ( t a ( t S (0 S 0 whee V s the value funton of the fm a and u ae the gene and band advetsng desons espetvely of band S s the sales of band s the advetsng ost paamete and m the magn of band and s the fm s dsount ate. The HJB equaton s 6
7 p S( bp dp ps( dpbp ( u a ( u a V V max ( u S u S θ( a a u a p u a p S V ( u S u S θ( a a. S The fst-ode ondtons fo the optmal advetsng desons yeld V V V V u ( S a ( θ θ S S S S (A40 (A4 V V V V u ( S a ( θ θ. S S S S As befoe substtutng the solutons fom (A4-4 nto (A40 suggests a lnea value funton V α β S γ S wll solve the esultng patal dffeental equaton. The optmal m m m advetsng desons an now be ewtten as 0 Note fom (A43-44 that ethe m m m m (A4 u max{0 ( β γ S } a ( θ β θ γ (A43 u max{0 ( γ β S } a ( θ β θ γ. (A44 m m m m u o u s always postve. If β > γ m m > 0 u and u sne band s moe poftable. If β < γ the opposte s tue. Theefoe n a m monopoly total band advetsng need not be zeo. The monopolst an hoose the optmal advetsng desons to ensue the value funton n the monopoly ase s neve less than that n the ase of ompetton.e. V V V whee V and V ae the pofts n the ompettve ase. We theefoe have m α β γ α β γ α γ β (A45. m ms ms S S S S Equaton (A45 an be ewtten to yeld α ( α α ( β ( β γ S ( γ ( β γ S 0. (A46 m m m Sne equaton (A46 holds S 0 S 0 t must be the ase that α ( α α β β γ γ β γ (A47 m m m whee eah of the above oeffents s non-negatve. 7
8 Fom equaton (A7 the total gene advetsng n the ompettve ase s ( θ β θ γ ( θ γ θ β (A48 whle that n the monopoly ase s fom equatons (A43-44 ( θ β θ γ ( θ β θ γ. (A49 m m m m Subtatng equaton (A48 fom (A49 the dffeene between the total gene advetsng n the monopoly ase and that n the ompettve ase s ( θ ( β β θ ( γ γ ( θ ( β γ θ ( γ β (A50 m m m m whh fom equaton (A47 s geate than zeo. Theefoe the monopolst s total gene advetsng s geate than that unde ompetton. B. Poofs of Compaatve Stats Results fo Asymmet Fms. We epodue the ompaatve stats table fo onvenene. Table : Compaatve Stats Results fo the Asymmet Case Vaables 3 m m θ α????????? β?? γ u a? V????????? x Legend: nease; deease; unhanged;? ambguous. 8
9 To obtan the ompaatve stats fo γ and β we fst ty to obtan the esults fo y and z. Defne F( y z m y yz y 0 F ( y z m z yz z 0. Fo any paamete φ we an use the mplt funton theoem y F F F F F F φ y z φ z z φ z F F F F F F φ y z φ y y φ to detemne the ompaatve stats esult. Afte some smplfaton ths an be ewtten as y F y z y φ φ z F z y z φ φ (B (B (B3 whee the detemnant y z y > 0. z y z We now detemne the ompaatve stats wth espet to eah of the model paametes. y y z y y z m z 0 (B4 z y z z m y y z y y m 0 z (B5 z y z y z m 9
10 y y z y y( y z y z 0 (B6 z y z yz y y z y yz 0 z z (B7 z y z z( y z y y z y y z z y z yz y ( y z? yz( y z y y z y yz z z y z z? yz( y z z ( y z y y z y y z z y z yz y ( y z? yz( y z (B8 (B9 (B0 0
11 Theefoe y y z y yz z z y z z yz( y z.? z ( y z y z y z y z > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 < 0 > 0 m m m m y z z y z y > 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 > 0. (B (B The ompaatve stats esults fo y on and and fo z on and ae ambguous. Note that y and z ae ndependent of and θ { }. To ompute the ompaatve stats fo γ β γ and β we use γ y β y y γ z β z z. (B3 Theefoe γ ( y y y y y 0 β ( y y ( > > 0 m m m m m m γ ( z z z z z 0 β ( z z ( < < 0 m m m m m m (B4 (B5 γ ( y y y y y 0 β ( y y ( < < 0 (B6 m m m m m m γ ( z z z z z 0 β ( z z ( > > 0 (B7 m m m m m m γ ( y y y 0 β ( y ( y y < < 0 (B8 y y y γ ( z z z z z 0 β ( z z ( > > 0 (B9
12 γ ( y y y y y 0 β ( y y ( > > 0 (B0 γ ( z z z 0 β ( z ( z z < < 0 (B z z z γ ( y y y ( y ( y y y β y y (B γ ( z z z z z 0 β ( z z ( < < 0 (B3 γ ( y y y y y 0 β ( y y ( < < 0 (B4 γ ( z z z ( z ( z z z β z z (B5 γ ( y y y β ( y ( y y (B6 y y y γ ( z z z z z 0 β ( z z ( > > 0 (B7 γ ( y y y y y 0 β ( y y ( > > 0 (B8 γ ( z z z β ( z ( z z. z z z (B9 Although the ompaatve stats fo γ on and n (B and fo γ on and n (B5 ae ambguous one an sgn these devatves by tansfomng the mplt equatons n (B n tems of γ and γ. Rewtng the equatons n (B usng z γ yelds the followng: y γ and J ( γ γ m γ γ γ γ 0 J ( γ γ m γ γ γ γ 0. (B30
13 Fo any paamete φ we have γ J J J J J J φ γ γ φ γ γ φ γ J J J J J J φ γ γ φ γ γ φ Afte some smplfaton ths an be ewtten as. (B3 γ γ γ J φ γ γ γ φ (B3 γ γ γ J φ γ γ γ φ whee the detemnant > 0. as follows: We an now ompute the ompaatve stats fo γ on and and fo γ on and γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ (B33 γγ γ γγ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ (B34 γγ γγ γ 3
14 γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ (B35 γγ γ γγ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ γ (B36 γγ. γγ γ Howeve the ompaatve stats of β on and and of β on and ae stll ambguous. Moeove note that γ β γ and β ae ndependent of and θ { }. We an now wte γ β γ β γ β γ β γ > 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 m m m m m m m m β γ β γ β γ β γ γ < 0 > 0 > 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 < 0 (B37 β γ γ β γ γ β γ γ β < 0 < 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 > 0. Fo the ompaatve stats esults fo α { } on the model paametes we note that ( ( ( (B38 α θ β θ γ θ β θ γ θ β θ γ ( ( ( (B39 α θ β θ γ θ β θ γ θ β θ γ α ( y θ y ( y θ y( z θ z (B40 4
15 α ( z θ z ( y θ y( z θ z. (B4 The ompaatve stats esults fo α { } on and ae easy to obtan. We have α α α α > 0 > 0 > 0 > 0. (B4 The ompaatve stats fo α { } on the othe model paametes ae ambguous gven the esults fo β and γ { }. The ompaatve stats fo y and z have the opposte sgns fo most of the model paametes so the devatves of the seond tem n equatons (B40 and (B4 ( y y( z z and θ θ ( y y( z z θ θ espetvely ae not easy to sgn. Fo the ompaatve stats fo the optmal band and gene advetsng desons we an see that sne u a and ( β γ S u ( β γ S a ( θ β θ γ and ( θ γ θ β most of the esults ae staghtfowad gven the ompaatve stats fo γ β { }. Fo the ompaatve stats of we ewte the optmal band advetsng desons as u w..t. and and of u w..t. and u ( β γ S y S u ( β γ S z S.(B43 Substtutng fo y n tems of mplt equatons: u and fo z n tems of S SS S S SS S u we have the followng G ( u u m u uu u 0 G ( u u m u uu u 0. (B44 The mplt funton theoem yelds 5
16 whee the detemnant > 0. Theefoe u G G G G G G u u u u u G G G G G G u u u u (B45 u u u u S SS S SS u u u u S SS SS S (B46 uu u SS S uu SS u u u u S SS S SS u u u u S SS SS S (B47 uu SS uu u SS S u u u u S SS S SS u u u u S SS SS S (B48 u uu u S SS S 0 6
17 The ompaatve stats of u u u u S SS S SS u u u u S SS SS S (B49 a and fashon. The esults ae summazed below. 0. u uu u S SS S a w..t. and espetvely an be obtaned n a smla u u u u u u u u u > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 > 0 m m m m u u u u u u u a a < 0 > 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 < 0 m m a a a a a a a a a < 0 > 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 m m a a a a a a a a a > 0 > 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0. θ θ θ θ (B50 Gven the ambguous ompaatve stats esults fo α most of the esults fo V ae also ambguous. Howeve t s possble to sgn the ompaatve stats of V fo the paametes n equaton (B4. The esults ae as follows: V V V V > 0 > 0 > 0 > 0. We now ty to obtan the ompaatve stats esults fo the steady-state maet shaes. The long-un equlbum maet shaes ae gven by x ( βγ ( β γ x β γ β γ β γ β γ (B5. (B5 ( ( ( ( Fo all the paametes exept and the ompaatve stats of x and x ae staghtfowad to obtan gven the ompaatve stats fo y and z. Fo and we ewte equaton (B5 as 7
18 y z x x. y z y z (B53 Defne l y l z. Theefoe l l x x. l l l l l Fo the ompaatve stats of x w..t. any paamete φ note that x l l theefoe l x φ l l l (. φ φ φ l l ( l l (B54 (B55 Rewtng the mplt equatons n tems of l and l yelds H ( l l m l ll l 0 H ( l l m l ll l 0. (B56 As befoe one an obtan the ompaatve stats of l and l w..t. and usng whee φ s any paamete. l H H H φ l l φ l H H H φ l l φ (B57 Pefomng the ompaatve stats of l and l fo any paamete φ yelds whee the detemnant > 0. l H l l l φ φ l H l l l φ φ (B58 8
19 Pefomng the ompaatve stats of l and l w..t. we have l ( l l l 3 l ( l l. l (B59 l ( l l 0 l l Theefoe > 0 and < 0. Moeove l l ( l 3 ( l l ( l l ll 3 ( l l (B60 ( l ( l ( l l > 0. x Fom (B55 and (B60 one an see that > 0 3. The ompaatve stats of x on and an also be obtaned usng the mplt equatons n (B56. These esults ae summazed below. x x x x > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0. (B6 Fo all the othe paametes the esults fo y also hold fo x. Sne x x the ompaatve stats esults fo x an be obtaned by flppng the esults fo x. C. Poofs of Compaatve Stats Results fo Symmet Fms. Fo onvenene we epodue the ompaatve stats esults n Table. We now 4 4 ( 3m 8 m (6 m ( 6 m α (C m ( 6 m β (C 9 9
20 3 m ( 6 m γ. (C3 9 Table : Compaatve Stats Results fo the Symmet Case Vaables m α? β γ u a V?? x Legend: nease; deease; unhanged;? ambguous. Tang the fst devatves of β and γ n equatons (C-3 wth espet to eah of the paametes yelds the followng ompaatve stats: β γ β γ β γ β γ > 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 < 0. (C4 m m The esults n (C4 follow n a staghtfowad manne. The ompaatve stats fo the optmal advetsng expendtues u and a { } ae easy to obtan wheneve the esults fo β and γ ae n the same deton. The ompaatve stats β and γ wth espet to and ae not of the same sgn. Howeve even n these ases the sgns of the devatves an be obtaned as n the asymmet ase usng the mplt equatons. The ompaatve stats esults of V and x { } on the model paametes an also be obtaned as fo asymmet fms. We obtan the followng ompaatve stats fo the optmal advetsng desons: 0
21 u u u u u u u u a > 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 > 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 m m m a a a a a a a a a > 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 < 0 > 0 > 0. m (C5 D. Devatons fo the Extenson Seton. a. Maet Potental The Hamlton-Jaob-Bellman (HJB equaton fo fm { } s gven by V ps( bp dp3 ( a u ( u S3 3u3 S θ( a a QSS S V max (D u a p V ( 3u3 S u S3 θ3( a a Q S S. S3 Fom ths the fst-ode ondtons fo u and a yeld espetvely V V V V u ( S a ( θ θ QS S. 3 3 S S3 S S3 As befoe one an solve fo the optmal pes and vefy that the solutons ae the same as those n equaton (A4. Substtutng equatons (A4 and (D nto (D yelds V V V V V m S Q S S S ( θ θ j ( ( 3 S S3 S S3 3 V V V V 3 V V V V S θ θ θ θ QSS 3 S S S S 3 S S S S ( ( ( ( (. The lnea value funton V α β S γ S3 satsfes (D3. The optmal band and gene advetsng desons n (D an now be ewtten as u ( β γ S a ( θ β θ γ QS S. (D4 3 3 Substtutng V α β S γ S3 nto (D3 and smplfyng we have S S ms Q S S S (D5 ( ( ( ( (. α β γ 3 ( θβ θ3 γ ( ( β γ βγ β γ S θβ θγ θβ θγ QSS 3 3 (D (D3
22 Equatng the oeffents of S S3 and the onstant n equaton (D5 esults n the followng smultaneous equatons to solve fo α β and γ { } : ( Q ( ( Q (D6 3 α θβ θ3γ θβ θγ θβ θγ 3 ( ( ( ( ( (D7 3 3 β m θβ θ3γ β γ β γ θβ θγ θβ θγ 3 3 ( ( ( (.(D8 3 γ θβ θ3γ β γ θβ θγ θβ θγ 3 Wtng out these equatons expltly fo { } we get ( Q ( ( Q (D9 α θβ θγ θβ θγ θβ θγ ( ( ( ( ( (D0 β m θβ θγ β γ β γ θβ θγ θβ θγ ( ( ( ( (D γ θβ θγ β γ θβ θγ θβ θγ ( Q ( ( Q (D α θβ θγ θβ θγ θβ θγ ( ( ( ( ( (D3 β m θβ θγ β γ β γ θβ θγ θβ θγ ( ( ( (. (D4 γ θβ θγ β γ θβ θγ θβ θγ To solve subtat (D fom (D0 and (D4 fom (D3. Let y β γ and z β γ Smplfyng esults n the followng smultaneous quadat equatons n y and z :. y yz y m 0 (D5 z yz z m 0. (D6 Substtutng fo z n tems of y n equaton (D6 afte solvng fo z n (D5 yelds the followng quat equaton n y : η η η η η (D7 4 3 y y 3y 4y 5 0
23 4 whee η 3 η 4 ( η 4 ( ( m m 4 η 8 m( and η 4 m. 5 3 The oots of equaton (D7 an be omputed usng Mathemata v4.0. Of the fou solutons fo y two ae magnay one s negatve and only one s always eal and postve. Ths s the unque Nash equlbum of the dffeental game. That soluton s gven by η ω y 4η 4 ω ω ω ( 7 ω ω5 ω6 ω ω5 ω6 5 6 (D8 η 3 whee η ω 4η 3 ω η3 3ηη 4 ηη 5 ω3 η3 9ηηη 3 4 7ηη 4 7ηη 5 7 ηηη 3 5 3η ω ( ω ω 4 ω ω 3 ω ω 4 5 ω6 3η ω ηη 3 η 8η 4 and ω7. 3 η η η η Knowng y we an ompute z ( m y y. Knowng y and z γ and γ y an be obtaned by solvng the followng smultaneous quadat equatons: ( y y ( y (( z (D9 γ θ γ θ γ θ γ (( z z ( y(( z. (D0 γ θ γ γ θ θ γ Afte γ and γ ae obtaned one an obtan β and β usng β y γ and β z γ espetvely. These solutons fo γ γ β and β an be used n equatons (D9 and (D to solve fo α and α. b. Othe Extensons The uent-value Hamltonan fo fm { } s H ps ( bp dp3 ( a u S λ( ω ( ω ω ( ω ( (D u( S3 S 3u3( 3 S 3 S3 S S a a S3 ( 3u3( 3 S ( 3 S3 u( S3 ( S a a S S µ ω ω ω ω (. 3
24 The optmal pes ae the same as those obtaned n equaton (A4. Fo the optmal advetsng desons the fst-ode ondtons fo fm ae H u ( ( u λ ( ω S ( ω S µ ( ω S ( ω S 0 (D 3 3 H λ S µ S 0. a S S S S 3 a (D3 Solvng the fst-ode ondtons fo the two fms yelds the optmal advetsng desons to be λ S µ S u ( S ( S ( a ( ω ω λ µ S S S S (D4 λ S µ S u ( S ( S ( a (. ω ω µ λ S S S S The adjont equatons fo the shadow pes λ ( t and µ ( t fo fm ae H H u H a λ λ S u S a S ( ω u ω u ( a a S λ p ( b p d p ( λ µ 3 ( S S ( S S ω (( ω S ( ω S ( λ µ ( S λ S µ S S ( ( ( µ 3 λ3 S S S S S S S ( H H u H a µ µ S u S a S ( µ λ 3 3 ωu ( ω u ( a a S µ ( λ µ ( S S 3 3 ( S S ( ω (( ω S ( ω S ( λ µ ( ( µ 3 λ S3 λ S µ S S ( ( ( µ 3 λ3. S S S S S S S ( (D5 (D6 One an now substtute the optmal pes and advetsng desons nto the state equatons and the adjont equatons. Sne these dffeental equatons do not pemt losed-fom solutons we use numeal methods to solve fo λ ( t and µ ( t { }. These solutons an then be used n (D4 to obtan the optmal band and gene advetsng desons fo the two fms. 4
α & β spatial orbitals in
 The atrx Hartree-Fock equatons The most common method of solvng the Hartree-Fock equatons f the spatal btals s to expand them n terms of known functons, { χ µ } µ= consder the spn-unrestrcted case. We
The atrx Hartree-Fock equatons The most common method of solvng the Hartree-Fock equatons f the spatal btals s to expand them n terms of known functons, { χ µ } µ= consder the spn-unrestrcted case. We
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών. ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος. ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης. εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων.
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 2015 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 1. 1. Consder the gven expresson for R 1/2 : R 1/2
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 2015 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης εύτερη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 1. 1. Consder the gven expresson for R 1/2 : R 1/2
One and two particle density matrices for single determinant HF wavefunctions. (1) = φ 2. )β(1) ( ) ) + β(1)β * β. (1)ρ RHF
 One and two partcle densty matrces for sngle determnant HF wavefunctons One partcle densty matrx Gven the Hartree-Fock wavefuncton ψ (,,3,!, = Âϕ (ϕ (ϕ (3!ϕ ( 3 The electronc energy s ψ H ψ = ϕ ( f ( ϕ
One and two partcle densty matrces for sngle determnant HF wavefunctons One partcle densty matrx Gven the Hartree-Fock wavefuncton ψ (,,3,!, = Âϕ (ϕ (ϕ (3!ϕ ( 3 The electronc energy s ψ H ψ = ϕ ( f ( ϕ
(a,b) Let s review the general definitions of trig functions first. (See back cover of your book) sin θ = b/r cos θ = a/r tan θ = b/a, a 0
 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES (a,b) Let s eview the geneal definitions of tig functions fist. (See back cove of you book) θ b/ θ a/ tan θ b/a, a 0 θ csc θ /b, b 0 sec θ /a, a 0 cot θ a/b, b 0 By doing some
The following are appendices A, B1 and B2 of our paper, Integrated Process Modeling
 he followng ae appendes A, B1 and B2 of ou pape, Integated Poess Modelng and Podut Desgn of Bodesel Manufatung, that appeas n the Industal and Engneeng Chemsty Reseah, Deembe (2009). Appendx A. An Illustaton
he followng ae appendes A, B1 and B2 of ou pape, Integated Poess Modelng and Podut Desgn of Bodesel Manufatung, that appeas n the Industal and Engneeng Chemsty Reseah, Deembe (2009). Appendx A. An Illustaton
Analytical Expression for Hessian
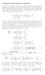 Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Analytical Expession fo Hessian We deive the expession of Hessian fo a binay potential the coesponding expessions wee deived in [] fo a multibody potential. In what follows, we use the convention that
Variance of Trait in an Inbred Population. Variance of Trait in an Inbred Population
 Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Revew of Mean Trat Value n Inbred Populatons We showed n the last lecture that for a populaton
Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Varance of Trat n an Inbred Populaton Revew of Mean Trat Value n Inbred Populatons We showed n the last lecture that for a populaton
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE
 Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Example 1: THE ELECTRIC DIPOLE 1 The Electic Dipole: z + P + θ d _ Φ = Q 4πε + Q = Q 4πε 4πε 1 + 1 2 The Electic Dipole: d + _ z + Law of Cosines: θ A B α C A 2 = B 2 + C 2 2ABcosα P ± = 2 ( + d ) 2 2
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
A Class of Orthohomological Triangles
 A Class of Orthohomologcal Trangles Prof. Claudu Coandă Natonal College Carol I Craova Romana. Prof. Florentn Smarandache Unversty of New Mexco Gallup USA Prof. Ion Pătraşcu Natonal College Fraţ Buzeşt
A Class of Orthohomologcal Trangles Prof. Claudu Coandă Natonal College Carol I Craova Romana. Prof. Florentn Smarandache Unversty of New Mexco Gallup USA Prof. Ion Pătraşcu Natonal College Fraţ Buzeşt
Phys460.nb Solution for the t-dependent Schrodinger s equation How did we find the solution? (not required)
 Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Phys460.nb 81 ψ n (t) is still the (same) eigenstate of H But for tdependent H. The answer is NO. 5.5.5. Solution for the tdependent Schrodinger s equation If we assume that at time t 0, the electron starts
Multi-dimensional Central Limit Theorem
 Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t tme
Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t tme
CHAPTER 25 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS
 CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
CHAPTER 5 SOLVING EQUATIONS BY ITERATIVE METHODS EXERCISE 104 Page 8 1. Find the positive root of the equation x + 3x 5 = 0, correct to 3 significant figures, using the method of bisection. Let f(x) =
Finite Field Problems: Solutions
 Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Finite Field Problems: Solutions 1. Let f = x 2 +1 Z 11 [x] and let F = Z 11 [x]/(f), a field. Let Solution: F =11 2 = 121, so F = 121 1 = 120. The possible orders are the divisors of 120. Solution: The
Laplace s Equation in Spherical Polar Coördinates
 Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
Laplace s Equation in Spheical Pola Coödinates C. W. David Dated: Januay 3, 001 We stat with the pimitive definitions I. x = sin θ cos φ y = sin θ sin φ z = cos θ thei inveses = x y z θ = cos 1 z = z cos1
HOMEWORK 4 = G. In order to plot the stress versus the stretch we define a normalized stretch:
 HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
HOMEWORK 4 Problem a For the fast loading case, we want to derive the relationship between P zz and λ z. We know that the nominal stress is expressed as: P zz = ψ λ z where λ z = λ λ z. Therefore, applying
2 Composition. Invertible Mappings
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 4033: Elementary Modern Algebra Dr. Marcel B. Finan Composition. Invertible Mappings In this section we discuss two procedures for creating new mappings from old ones, namely,
Some Theorems on Multiple. A-Function Transform
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 202, no. 20, 995-004 Some Theoems on Multple A-Functon Tansfom Pathma J SCSVMV Deemed Unvesty,Kanchpuam, Tamlnadu, Inda & Dept.of Mathematcs, Manpal Insttute of
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 202, no. 20, 995-004 Some Theoems on Multple A-Functon Tansfom Pathma J SCSVMV Deemed Unvesty,Kanchpuam, Tamlnadu, Inda & Dept.of Mathematcs, Manpal Insttute of
Matrix Hartree-Fock Equations for a Closed Shell System
 atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
atix Hatee-Fock Equations fo a Closed Shell System A single deteminant wavefunction fo a system containing an even numbe of electon N) consists of N/ spatial obitals, each occupied with an α & β spin has
Multi-dimensional Central Limit Theorem
 Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t ();
Mult-dmensonal Central Lmt heorem Outlne () () () t as () + () + + () () () Consder a sequence of ndependent random proceses t, t, dentcal to some ( t). Assume t 0. Defne the sum process t t t t () t ();
Exercise, May 23, 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1
 Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Monetay Policy Henik Jensen Depatment of Economics Univesity of Copenhagen Execise May 23 2016: Inflation stabilization with noisy data 1 Suggested answes We have the basic model x t E t x t+1 σ 1 ît E
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing
 ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΔΗΜΟΚΡΑΤΙΑ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΡΗΤΗΣ Μηχανική Μάθηση Hypothesis Testing Γιώργος Μπορμπουδάκης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Procedure 1. Form the null (H 0 ) and alternative (H 1 ) hypothesis 2. Consider
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Solution Set #2
 . For the followng two harmon waves: (a) Show on a phasor dagram: 05-55-007 Soluton Set # phasor s the omplex vetor evaluated at t 0: f [t] os[ω 0 t] h f [t] 7os ω 0 t π f [t] exp[ 0] + 0 h f [t] 7exp
. For the followng two harmon waves: (a) Show on a phasor dagram: 05-55-007 Soluton Set # phasor s the omplex vetor evaluated at t 0: f [t] os[ω 0 t] h f [t] 7os ω 0 t π f [t] exp[ 0] + 0 h f [t] 7exp
Section 7.6 Double and Half Angle Formulas
 09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
09 Section 7. Double and Half Angle Fmulas To derive the double-angles fmulas, we will use the sum of two angles fmulas that we developed in the last section. We will let α θ and β θ: cos(θ) cos(θ + θ)
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutions to Problems on Matrix Algebra
 MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
MATH 38061/MATH48061/MATH68061: MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS Solutios to Poblems o Matix Algeba 1 Let A be a squae diagoal matix takig the fom a 11 0 0 0 a 22 0 A 0 0 a pp The ad So, log det A t log A t log
1 Complete Set of Grassmann States
 Physcs 610 Homework 8 Solutons 1 Complete Set of Grassmann States For Θ, Θ, Θ, Θ each ndependent n-member sets of Grassmann varables, and usng the summaton conventon ΘΘ Θ Θ Θ Θ, prove the dentty e ΘΘ dθ
Physcs 610 Homework 8 Solutons 1 Complete Set of Grassmann States For Θ, Θ, Θ, Θ each ndependent n-member sets of Grassmann varables, and usng the summaton conventon ΘΘ Θ Θ Θ Θ, prove the dentty e ΘΘ dθ
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
8.324 Relativistic Quantum Field Theory II
 Lecture 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II Fall 00 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II MIT OpenCourseWare Lecture Notes Hon Lu, Fall 00 Lecture 5.: RENORMALIZATION GROUP FLOW Consder the bare acton
Lecture 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II Fall 00 8.3 Relatvstc Quantum Feld Theory II MIT OpenCourseWare Lecture Notes Hon Lu, Fall 00 Lecture 5.: RENORMALIZATION GROUP FLOW Consder the bare acton
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS. NOTE: cos(α+β) cos α + cos β cos(α-β) cos α -cos β
 3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
3.4 SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS Page Theorem cos(αβ cos α cos β -sin α cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α NOTE: cos(αβ cos α cos β cos(α-β cos α -cos β Proof of cos(α-β cos α cos β sin α Let s use a unit circle
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedasticity 8.2 Using the Least Squares Estimator 8.3 The Generalized Least Squares Estimator 8.
 8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedastcty 8. Usng the Least Squares Estmator 8.3 The Generalzed Least Squares Estmator 8.4 Detectng Heteroskedastcty E( y) = β+β 1 x e = y E( y ) = y β β x 1 y = β+β x + e 1 Fgure
8.1 The Nature of Heteroskedastcty 8. Usng the Least Squares Estmator 8.3 The Generalzed Least Squares Estmator 8.4 Detectng Heteroskedastcty E( y) = β+β 1 x e = y E( y ) = y β β x 1 y = β+β x + e 1 Fgure
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC = DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION #2. h 0 h h 0 h h 0 ( ) g k = g 0 + g 1 + g g 2009 =?
 Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Teko Classes IITJEE/AIEEE Maths by SUHAAG SIR, Bhopal, Ph (0755) 3 00 000 www.tekoclasses.com ANSWERSHEET (TOPIC DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS) COLLECTION # Question Type A.Single Correct Type Q. (A) Sol least
Exercises 10. Find a fundamental matrix of the given system of equations. Also find the fundamental matrix Φ(t) satisfying Φ(0) = I. 1.
 Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
Exercises 0 More exercises are available in Elementary Differential Equations. If you have a problem to solve any of them, feel free to come to office hour. Problem Find a fundamental matrix of the given
1 3D Helmholtz Equation
 Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
Deivation of the Geen s Funtions fo the Helmholtz and Wave Equations Alexande Miles Witten: Deembe 19th, 211 Last Edited: Deembe 19, 211 1 3D Helmholtz Equation A Geen s Funtion fo the 3D Helmholtz equation
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs
 Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Fractional Colorings and Zykov Products of graphs Who? Nichole Schimanski When? July 27, 2011 Graphs A graph, G, consists of a vertex set, V (G), and an edge set, E(G). V (G) is any finite set E(G) is
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
e t e r Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate Representation of grad, div, curl and 2
 Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Cylindical and Spheical Coodinate Repesentation of gad, div, cul and 2 Thus fa, we have descibed an abitay vecto in F as a linea combination of i, j and k, which ae unit vectos in the diection of inceasin,
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3
 Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
Lecture 2: Dirac notation and a review of linear algebra Read Sakurai chapter 1, Baym chatper 3 1 State vector space and the dual space Space of wavefunctions The space of wavefunctions is the set of all
ω ω ω ω ω ω+2 ω ω+2 + ω ω ω ω+2 + ω ω+1 ω ω+2 2 ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ω+1 ω ω2 ω ω2 + ω ω ω2 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω ω+1 ω ω2 + ω ω+1 + ω ω ω ω2 + ω
 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ω ω + 1 ω + 2 ω + 3 ω + 4 ω2 ω2 + 1 ω2 + 2 ω2 + 3 ω3 ω3 + 1 ω3 + 2 ω4 ω4 + 1 ω5 ω 2 ω 2 + 1 ω 2 + 2 ω 2 + ω ω 2 + ω + 1 ω 2 + ω2 ω 2 2 ω 2 2 + 1 ω 2 2 + ω ω 2 3 ω 3 ω 3 + 1 ω 3 + ω ω 3 +
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates
 derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
derivation of the Laplacian from rectangular to spherical coordinates swapnizzle 03-03- :5:43 We begin by recognizing the familiar conversion from rectangular to spherical coordinates (note that φ is used
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL h in h 4 0.
 DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
DESIGN OF MACHINERY SOLUTION MANUAL -7-1! PROBLEM -7 Statement: Design a double-dwell cam to move a follower from to 25 6, dwell for 12, fall 25 and dwell for the remader The total cycle must take 4 sec
Practice Exam 2. Conceptual Questions. 1. State a Basic identity and then verify it. (a) Identity: Solution: One identity is csc(θ) = 1
 Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
Conceptual Questions. State a Basic identity and then verify it. a) Identity: Solution: One identity is cscθ) = sinθ) Practice Exam b) Verification: Solution: Given the point of intersection x, y) of the
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. ------------------ ----------------------------- -----------------
 Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Inverse trigonometric functions & General Solution of Trigonometric Equations. 1. Sin ( ) = a) b) c) d) Ans b. Solution : Method 1. Ans a: 17 > 1 a) is rejected. w.k.t Sin ( sin ) = d is rejected. If sin
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests
 Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Statistical Inference I Locally most powerful tests Shirsendu Mukherjee Department of Statistics, Asutosh College, Kolkata, India. shirsendu st@yahoo.co.in So far we have treated the testing of one-sided
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Section 9.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
180 Section 9. Polar Equations and Graphs In this section, we will be graphing polar equations on a polar grid. In the first few examples, we will write the polar equation in rectangular form to help identify
Constant Elasticity of Substitution in Applied General Equilibrium
 Constant Elastct of Substtuton n Appled General Equlbru The choce of nput levels that nze the cost of producton for an set of nput prces and a fed level of producton can be epressed as n sty.. f Ltng for
Constant Elastct of Substtuton n Appled General Equlbru The choce of nput levels that nze the cost of producton for an set of nput prces and a fed level of producton can be epressed as n sty.. f Ltng for
4.2 Differential Equations in Polar Coordinates
 Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
Section 4. 4. Diffeential qations in Pola Coodinates Hee the two-dimensional Catesian elations of Chapte ae e-cast in pola coodinates. 4.. qilibim eqations in Pola Coodinates One wa of epesg the eqations
George S. A. Shaker ECE477 Understanding Reflections in Media. Reflection in Media
 Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
Geoge S. A. Shake C477 Udesadg Reflecos Meda Refleco Meda Ths hadou ages a smplfed appoach o udesad eflecos meda. As a sude C477, you ae o equed o kow hese seps by hea. I s jus o make you udesad how some
ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 2017 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations
 ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 07 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations Answers to problems on Midterm Examination #, Spring 009. x(t) = r(t + ) r(t ) u(t ) r(t ) + r(t 3) + u(t +
ECE 308 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS FALL 07 Answers to selected problems on prior years examinations Answers to problems on Midterm Examination #, Spring 009. x(t) = r(t + ) r(t ) u(t ) r(t ) + r(t 3) + u(t +
TMA4115 Matematikk 3
 TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
TMA4115 Matematikk 3 Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet Trondheim Spring 2010 Lecture 12: Mathematics Marvellous Matrices Andrew Stacey Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet
Symplecticity of the Störmer-Verlet algorithm for coupling between the shallow water equations and horizontal vehicle motion
 Symplectcty of the Störmer-Verlet algorthm for couplng between the shallow water equatons and horzontal vehcle moton by H. Alem Ardakan & T. J. Brdges Department of Mathematcs, Unversty of Surrey, Guldford
Symplectcty of the Störmer-Verlet algorthm for couplng between the shallow water equatons and horzontal vehcle moton by H. Alem Ardakan & T. J. Brdges Department of Mathematcs, Unversty of Surrey, Guldford
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016
 Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
Concrete Mathematics Exercises from 30 September 2016 Silvio Capobianco Exercise 1.7 Let H(n) = J(n + 1) J(n). Equation (1.8) tells us that H(2n) = 2, and H(2n+1) = J(2n+2) J(2n+1) = (2J(n+1) 1) (2J(n)+1)
A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy. Equivalence Relation
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no. 67, 3301-3307 A Note on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Equivalence Relation D. K. Basnet Dept. of Mathematics, Assam University Silchar-788011, Assam, India dkbasnet@rediffmail.com
8. ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΊΑ ΣΗΜΆΤΩΝ. ICA: συναρτήσεις κόστους & εφαρμογές
 8. ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΊΑ ΣΗΜΆΤΩΝ ICA: συναρτήσεις κόστους & εφαρμογές ΚΎΡΤΩΣΗ (KUROSIS) Αθροιστικό (cumulant) 4 ης τάξεως μίας τ.μ. x με μέσο όρο 0: kurt 4 [ x] = E[ x ] 3( E[ y ]) Υποθέτουμε διασπορά=: kurt[ x]
8. ΕΠΕΞΕΡΓΑΣΊΑ ΣΗΜΆΤΩΝ ICA: συναρτήσεις κόστους & εφαρμογές ΚΎΡΤΩΣΗ (KUROSIS) Αθροιστικό (cumulant) 4 ης τάξεως μίας τ.μ. x με μέσο όρο 0: kurt 4 [ x] = E[ x ] 3( E[ y ]) Υποθέτουμε διασπορά=: kurt[ x]
Generalized Fibonacci-Like Polynomial and its. Determinantal Identities
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 01, no. 9, 1415-140 Generalzed Fbonacc-Le Polynomal and ts Determnantal Identtes V. K. Gupta 1, Yashwant K. Panwar and Ompraash Shwal 3 1 Department of Mathematcs,
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Scences, Vol. 7, 01, no. 9, 1415-140 Generalzed Fbonacc-Le Polynomal and ts Determnantal Identtes V. K. Gupta 1, Yashwant K. Panwar and Ompraash Shwal 3 1 Department of Mathematcs,
Saigo-Maeda Fractional Differential Operators of the Multivariable H-Function
 Intenatonal Jounal of Computatonal Scence and athematcs. ISSN 0974-89 Volume 5, Numbe (0, pp. 4-54 Intenatonal Reseach ublcaton House http://www.phouse.com Sago-aeda Factonal Dffeental Opeatos of the ultvaable
Intenatonal Jounal of Computatonal Scence and athematcs. ISSN 0974-89 Volume 5, Numbe (0, pp. 4-54 Intenatonal Reseach ublcaton House http://www.phouse.com Sago-aeda Factonal Dffeental Opeatos of the ultvaable
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
On a four-dimensional hyperbolic manifold with finite volume
 BULETINUL ACADEMIEI DE ŞTIINŢE A REPUBLICII MOLDOVA. MATEMATICA Numbers 2(72) 3(73), 2013, Pages 80 89 ISSN 1024 7696 On a four-dimensional hyperbolic manifold with finite volume I.S.Gutsul Abstract. In
BULETINUL ACADEMIEI DE ŞTIINŢE A REPUBLICII MOLDOVA. MATEMATICA Numbers 2(72) 3(73), 2013, Pages 80 89 ISSN 1024 7696 On a four-dimensional hyperbolic manifold with finite volume I.S.Gutsul Abstract. In
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Tutorial Note - Week 09 - Solution
 Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Tutoial Note - Week 9 - Solution ouble Integals in Pola Coodinates. a Since + and + 5 ae cicles centeed at oigin with adius and 5, then {,θ 5, θ π } Figue. f, f cos θ, sin θ cos θ sin θ sin θ da 5 69 5
Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small spheres separated by a distance s. The charge on one sphere changes with time and is described by
 5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
5 Radiation (Chapte 11) 5.1 Electic dipole adiation Oscillating dipole system Suppose we have two small sphees sepaated by a distance s. The chage on one sphee changes with time and is descibed by q(t)
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Instruction Execution Times
 1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
1 C Execution Times InThisAppendix... Introduction DL330 Execution Times DL330P Execution Times DL340 Execution Times C-2 Execution Times Introduction Data Registers This appendix contains several tables
The Laplacian in Spherical Polar Coordinates
 Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Univesity of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Chemisty Education Mateials Depatment of Chemisty -6-007 The Laplacian in Spheical Pola Coodinates Cal W. David Univesity of Connecticut, Cal.David@uconn.edu
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Galatia SIL Keyboard Information
 Galatia SIL Keyboard Information Keyboard ssignments The main purpose of the keyboards is to provide a wide range of keying options, so many characters can be entered in multiple ways. If you are typing
Galatia SIL Keyboard Information Keyboard ssignments The main purpose of the keyboards is to provide a wide range of keying options, so many characters can be entered in multiple ways. If you are typing
The challenges of non-stable predicates
 The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
The challenges of non-stable predicates Consider a non-stable predicate Φ encoding, say, a safety property. We want to determine whether Φ holds for our program. The challenges of non-stable predicates
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
b. Use the parametrization from (a) to compute the area of S a as S a ds. Be sure to substitute for ds!
 MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
MTH U341 urface Integrals, tokes theorem, the divergence theorem To be turned in Wed., Dec. 1. 1. Let be the sphere of radius a, x 2 + y 2 + z 2 a 2. a. Use spherical coordinates (with ρ a) to parametrize.
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in
 Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
Nowhere-zero flows Let be a digraph, Abelian group. A Γ-circulation in is a mapping : such that, where, and : tail in X, head in : tail in X, head in A nowhere-zero Γ-flow is a Γ-circulation such that
1 String with massive end-points
 1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
1 String with massive end-points Πρόβλημα 5.11:Θεωρείστε μια χορδή μήκους, τάσης T, με δύο σημειακά σωματίδια στα άκρα της, το ένα μάζας m, και το άλλο μάζας m. α) Μελετώντας την κίνηση των άκρων βρείτε
( y) Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Partial Dierential Equations Linear P.D.Es. contains no owers roducts o the deendent variables / an o its derivatives can occasionall be solved. Consider eamle ( ) a (sometimes written as a ) we can integrate
Neutralino contributions to Dark Matter, LHC and future Linear Collider searches
 Neutralno contrbutons to Dark Matter, LHC and future Lnear Collder searches G.J. Gounars Unversty of Thessalonk, Collaboraton wth J. Layssac, P.I. Porfyrads, F.M. Renard and wth Th. Dakonds for the γz
Neutralno contrbutons to Dark Matter, LHC and future Lnear Collder searches G.J. Gounars Unversty of Thessalonk, Collaboraton wth J. Layssac, P.I. Porfyrads, F.M. Renard and wth Th. Dakonds for the γz
ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα,
 ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα Βασίλειος Σύρης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης Εαρινό εξάμηνο 2008 Economcs Contents The contet The basc model user utlty, rces and
ΗΥ537: Έλεγχος Πόρων και Επίδοση σε Ευρυζωνικά Δίκτυα Βασίλειος Σύρης Τμήμα Επιστήμης Υπολογιστών Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης Εαρινό εξάμηνο 2008 Economcs Contents The contet The basc model user utlty, rces and
ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER
 ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER Abstract. We define ordinal arithmetic and show laws of Left- Monotonicity, Associativity, Distributivity, some minor related properties and the Cantor Normal Form.
ORDINAL ARITHMETIC JULIAN J. SCHLÖDER Abstract. We define ordinal arithmetic and show laws of Left- Monotonicity, Associativity, Distributivity, some minor related properties and the Cantor Normal Form.
An Inventory of Continuous Distributions
 Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Appendi A An Inventory of Continuous Distributions A.1 Introduction The incomplete gamma function is given by Also, define Γ(α; ) = 1 with = G(α; ) = Z 0 Z 0 Z t α 1 e t dt, α > 0, >0 t α 1 e t dt, α >
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics
 Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Fundamental Equations of Fluid Mechanics 1 Calculus 1.1 Gadient of a scala s The gadient of a scala is a vecto quantit. The foms of the diffeential gadient opeato depend on the paticula geomet of inteest.
Homework 3 Solutions
 Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Homework 3 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151A TA) Problem 1: Compute the absolute error and relative error in approximations of p by p. (Use calculator!) a) p π, p 22/7; b) p π, p 3.141. Solution: For
Vidyamandir Classes. Solutions to Revision Test Series - 2/ ACEG / IITJEE (Mathematics) = 2 centre = r. a
 Per -.(D).() Vdymndr lsses Solutons to evson est Seres - / EG / JEE - (Mthemtcs) Let nd re dmetrcl ends of crcle Let nd D re dmetrcl ends of crcle Hence mnmum dstnce s. y + 4 + 4 6 Let verte (h, k) then
Per -.(D).() Vdymndr lsses Solutons to evson est Seres - / EG / JEE - (Mthemtcs) Let nd re dmetrcl ends of crcle Let nd D re dmetrcl ends of crcle Hence mnmum dstnce s. y + 4 + 4 6 Let verte (h, k) then
Forced Pendulum Numerical approach
 Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
Numerical approach UiO April 8, 2014 Physical problem and equation We have a pendulum of length l, with mass m. The pendulum is subject to gravitation as well as both a forcing and linear resistance force.
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
CHAPTER 48 APPLICATIONS OF MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXERCISE 01 Page 545 1. Use matrices to solve: 3x + 4y x + 5y + 7 3x + 4y x + 5y 7 Hence, 3 4 x 0 5 y 7 The inverse of 3 4 5 is: 1 5 4 1 5 4 15 8 3
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities
 PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
PARTIAL NOTES for 6.1 Trigonometric Identities tanθ = sinθ cosθ cotθ = cosθ sinθ BASIC IDENTITIES cscθ = 1 sinθ secθ = 1 cosθ cotθ = 1 tanθ PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES sin θ + cos θ =1 tan θ +1= sec θ 1 + cot
ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ CYPRUS COMPUTER SOCIETY ΠΑΓΚΥΠΡΙΟΣ ΜΑΘΗΤΙΚΟΣ ΔΙΑΓΩΝΙΣΜΟΣ ΠΛΗΡΟΦΟΡΙΚΗΣ 6/5/2006
 Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Οδηγίες: Να απαντηθούν όλες οι ερωτήσεις. Ολοι οι αριθμοί που αναφέρονται σε όλα τα ερωτήματα είναι μικρότεροι το 1000 εκτός αν ορίζεται διαφορετικά στη διατύπωση του προβλήματος. Διάρκεια: 3,5 ώρες Καλή
Problem Set 9 Solutions. θ + 1. θ 2 + cotθ ( ) sinθ e iφ is an eigenfunction of the ˆ L 2 operator. / θ 2. φ 2. sin 2 θ φ 2. ( ) = e iφ. = e iφ cosθ.
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 9 Solutions The ˆ L 2 operator is defined as Verify that the angular wavefunction Y θ,φ) Also verify that the eigenvalue is given by 2! 2 & L ˆ 2! 2 2 θ 2 +
