Stationary Stochastic Processes Table of Formulas, 2016
|
|
|
- Σωτηρία Μεταξάς
- 8 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 Stationary Stochastic Processes Table of Formulas, 06 Basics of probability theory The following is valid for probabilities: P(Ω), where Ω is all possible outcomes 0 P(A), where A is some event P(A c ) P(A), where A c is the complement of A P(A B) P(A) + P(B), if the events A and B are mutually exclusive The addition law of probability: P(A B) P(A) + P(B) P(A B) The conditional probability: P(B A) P(A B) P(A) A and B are independent P(A B) P(A) P(B) Stochastic variables p X (k) k x Distribution functions: F X (x 0 ) P(X x 0 ) 0 x0 f X (x) dx k p X (k) k Expected value: E[X] m X x f X (x) dx (X discrete) (X continuous) (X discrete) (X continuous) (k m X ) p X (k) (X discrete) Variance: V[X] E[X ] m X k (x m X ) f X (x) dx (X continuous) Rules for expected value and variance (a and b constants): E[aX + b] ae[x] + b V[aX] a V[X] V[X + b] V[X] E[X + Y] E[X] + E[Y] V[X + Y] V[X] + V[Y] + C[X, Y]
2 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 Covariance: C[X, Y] E[(X m X )(Y m Y )] E[XY] m X m Y Correlation coefficient: ρ[x, Y] C[X, Y] V[X] V[Y] Taylor series expansions ("Gauss approximations"): E[g(X,..., X n )] g(e[x ],..., E[X n ]) V[g(X,..., X n )] c i V[X i ] + c i c j C[X i, X j ] i<j where c i g (x,..., x n ) x i xk E[X k ], k i The two-dimensional probability density function of a jointly Gaussian random variable, (X, Y), with E[X] E[Y] 0, V[X] V[Y] and C[X, Y] ρ is { } f X,Y (x, y) π ρ exp ( ρ ) (x ρxy + y ) Stationary stochastic processes Estimation of expected value: ˆm n n t X t V [ ˆm n ] n n nv [ ˆm n ] τ τ n+ r X (τ) (n τ )r X (τ) If ˆm n N(m, V[ ˆm n ]), the confidence interval for m is for large n I m : { ˆm n λ α/ V[ ˆmn ], ˆm n + λ α/ V[ ˆmn ]} with confidence level α. For confidence level 0.95, α 0.05 and λ α/ λ Estimation of covariance function: ˆr n (τ) n τ (X t m X )(X t+τ m X ) for τ 0 n t
3 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 3 where m X is replaced by ˆm n if m X is unknown. If X t is Gaussian, with mean m X and covariance function r X (τ), such that τ0 r X(τ) <, then for t s + τ, nc [ˆr n (s),ˆr n (t)] u The Poisson process and the Wiener process {r X (u)r X (u + τ) + r X (u s)r X (u + t)} when n A simply increasing process {X(t), t 0} is a homogeneous Poisson process, if X(0) 0 and X(t) has stationary, independent increments. If the intensity is λ, E[X(t)] λt V[X(t)] λt r X (s, t) λ min(s, t) The interarrival times are independent and exponentially distributed with mean value /λ. A Gaussian process {X(t), t 0} is a Wiener process, if X(0) 0, and X(t) has independent increments, where X(t) X(t + h) N(0, σ h), E[X(t)] 0 V[X(t)] σ t r X (s, t) σ min(s, t) Spectral representations Relations between covariance function r X (τ) and spectral density R X (f): Continuous time Discrete time r X (τ) R X(f)e iπfτ df r X (τ) / / R X(f)e iπfτ df R X (f) r X(τ)e iπfτ dτ R X (f) τ r X(τ)e iπfτ Folding (aliasing): Let {Z t, t 0, ±d, ±d,... } be the continuous time process Y(t) sampled with time interval d and sampling frequency f s /d: R Z (f) R Y (f + kf s ) for f s / < f f s / k
4 4 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 Sum of harmonic components with random phase and amplitude: X(t) A 0 + A k cos(πf k t + φ k ) where φ k Rect(0, π), A k, k 0,..., n, are independent and E[A 0 ] 0. Covariance function: k r X (τ) σ 0 + where σ 0 E [A 0] and σ k E [A k ] /. Spectral density: σ k cos πf k τ k R X (f) k n b k δ fk (f), where b 0 σ 0 E [A 0], and b k σ k / E [A k ] /4. Linear filters - general theory Impulse response h(u): Y(t) h(u)x(t u) du u h(u)x(t u) (continuous time) (discrete time) Relation between covariance functions: h(u)h(v) r X(τ + u v) du dv r Y (τ) v h(u)h(v) r X(τ + u v) u (continuous time) (discrete time) Relation between spectral densities: R Y (f) H(f) R X (f) where H(f) is the frequency function corresponding to the impulse response h(n). Differentiation: X (t) exists (in quadratic mean) if r X (t) exists. This is equivalent
5 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 5 to (πf) R(f)df <. If X (t) exists, the following relations hold: r X (τ) r X(τ) R X (f) (πf) R X (f) V [X (t)] (πf) R X (f) df r X,X (τ) r X(τ) r X (j),x (k)(τ) ( )j r (j+k) X (τ) Integration: [ E ] g(s)x(s) ds g(s)e[x(s)] ds [ C g(s)x(s) ds, ] h(t)y(t) dt g(s)h(t) C[X(s), Y(t)] ds dt Cross-covariance and cross-spectrum: r X,Y (τ) C[X(t), Y(t + τ)] e iπfτ R X,Y (f) df R X,Y (f) H(f)R X (f) A X,Y (f)e iφ X,Y(f) where A X,Y (f) is the amplitude spectrum and Φ X,Y (f) the phase spectrum. The squared coherence spectrum is κ X,Y(f) A X,Y (f) R X (f)r Y (f) AR- MA- and ARMA-models White noise in discrete time: {e t, t 0, ±,...}, E[e t ] 0 and V[e t ] σ : R e (f) σ for / f / AR(p)-process: (a 0 ) X t + a X t + a X t a p X t p e t
6 6 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 Yule-Walker equations for covariance function: r X (k) + a r X (k ) a p r X (k p) Spectral density: { σ for k 0 0 for k,,... MA(q)-process: (b 0 ) R X (f) σ p k0 a ke iπfk Covariance function: Spectral density: X t e t + b e t + b e t b q e t q r X (τ) Matched filter and Wiener filter Matched filter: with white noise: with colored noise: s(t u) c { σ j kτ b jb k for τ q 0 for τ > q q R X (f) σ b k e iπfk k0 h(u) c s(t u) SNR N 0 s(t u) du SNR c h(v)r N (u v) dv h(u)h(v)r N (u v) du dv Wiener filter: H(f) SNR R S (f) R S (f) + R N (f) RS (f) df RS (f)r N (f) R S (f)+r N (f) df
7 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 7 Spectral estimation Periodogram of the sequence {x(t), t 0,,,... n }, where X (f) n t0 x(t)e iπft. ] E [ˆRx (f) ˆR x (f) X (f) n τ / / k n (τ)r X (τ)e iπfτ K n (f u)r X (u)du where k n (τ) τ for n + τ n and K n n(f) n τ n+ k n(τ)e iπfτ. ] { R V [ˆRx (f) X (f) for 0 < f < / R X (f) for f 0, ±/ The distribution of the periodogram estimate is ˆR x (f) R X (f) χ () for 0 < f < / Modified periodogram ˆR w (f) n x(t)w(t)e iπft n t0 / X (ν)w(f ν)dν n Lag-windowing Averaging of spectrum ˆR lw (f) / τ / / ˆR av (f) K k Ln (τ)ˆr x (τ)e iπfτ K Ln (f ν)ˆr x (ν)dν K ˆR x,j (f) where K different spectrum estimates, ˆR x,j (f), j... K, are used. The distribution is ˆR av (f) R X (f) χ (K) for 0 < f < / K j
8 8 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 Fourier transforms g(τ) (α > 0) G(f) e iπfτ g(τ) dτ e α τ α α +(πf) α +τ π α e πα f τ e α τ (α (πf) ) (α +(πf) ) τ k e α τ k! {(α + iπf) k+ + (α iπf) k+ } (α +(πf) ) k+ e ατ π/α exp( (πf) 4α ) e α τ cos(πf 0 τ) e α τ sin(πf 0 τ) { α if τ 0 sin(πατ) πτ if τ 0 { α τ if τ α 0 if τ > α g(τ)h(τ) g(τ) h(τ) g(t)h(τ t)dt g (τ) α α α +(πf 0 + πf) α +(πf 0 +πf) πf 0 πf α +(πf 0 + πf 0+πf πf) α +(πf 0 +πf) { / if f α 0 if f > α { α ( ( if f 0 α (πf) cos πf )) α if f 0 G(f) H(f) G(ν)H(f ν)dν G(f)H(f) iπf G(f) g(ατ) α G( f α ) α g( τ α ) G(αf) g(τ τ 0 ) G(f)e iπfτ 0 g(τ)e iπf 0τ G(f f 0 )
9 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 06 9 Gaussian distribution table F(x) Φ(x) x
Stationary Stochastic Processes Table of Formulas, 2017
 Stationary Stochastic Processes, 07 Stationary Stochastic Processes Table of Formulas, 07 Basics of probability theory The following is valid for probabilities: P(Ω), where Ω is all possible outcomes 0
Stationary Stochastic Processes, 07 Stationary Stochastic Processes Table of Formulas, 07 Basics of probability theory The following is valid for probabilities: P(Ω), where Ω is all possible outcomes 0
Probability and Random Processes (Part II)
 Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
Probability and Random Processes (Part II) 1. If the variance σ x of d(n) = x(n) x(n 1) is one-tenth the variance σ x of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 2
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 5.4: Στατιστικοί Μέσοι Όροι 5.5 Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις (Stochastic Processes)
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 5.4: Στατιστικοί Μέσοι Όροι 5.5 Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις (Stochastic Processes)
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 4
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 4 5.9 Η Στοχαστική Ανέλιξη Gauss (οι διαφάνειες ακολουθούν διαφορετική
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 4 5.9 Η Στοχαστική Ανέλιξη Gauss (οι διαφάνειες ακολουθούν διαφορετική
Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review
 Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
Harvard College Statistics 104: Quantitative Methods for Economics Formula and Theorem Review Tommy MacWilliam, 13 tmacwilliam@college.harvard.edu March 10, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction to Data 5 1.1 Sample
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 3
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 3 5.6: Μέση Τιμή, Συναρτήσεις Συσχέτισης (Correlation) & Συνδιασποράς (Covariance)
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 3 5.6: Μέση Τιμή, Συναρτήσεις Συσχέτισης (Correlation) & Συνδιασποράς (Covariance)
Introduction to the ML Estimation of ARMA processes
 Introduction to the ML Estimation of ARMA processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi ARMA Estimation Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 1 We consider the AR(p) model: Y t = c + φ 1 Y
Introduction to the ML Estimation of ARMA processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi ARMA Estimation Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 1 We consider the AR(p) model: Y t = c + φ 1 Y
Solution Series 9. i=1 x i and i=1 x i.
 Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Mete SONER Coordinator: Yilin WANG Solution Series 9 Q1. Let α, β >, the p.d.f. of a beta distribution with parameters α and β is { Γ(α+β) Γ(α)Γ(β) f(x α, β) xα 1 (1 x) β 1 for < x
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
HW 3 Solutions 1. a) I use the auto.arima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA(3,1)
 HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
Chapter 5, 6 Multiple Random Variables ENCS Probability and Stochastic Processes
 Chapter 5, 6 Multiple Random Variables ENCS6161 - Probability and Stochastic Processes Concordia University ENCS6161 p.1/47 Vector Random Variables A vector r.v. X is a function X : S R n, where S is the
Chapter 5, 6 Multiple Random Variables ENCS6161 - Probability and Stochastic Processes Concordia University ENCS6161 p.1/47 Vector Random Variables A vector r.v. X is a function X : S R n, where S is the
Solutions to Exercise Sheet 5
 Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
Solutions to Eercise Sheet 5 jacques@ucsd.edu. Let X and Y be random variables with joint pdf f(, y) = 3y( + y) where and y. Determine each of the following probabilities. Solutions. a. P (X ). b. P (X
6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes
 122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
122 CHAPTER 6. ARMA MODELS 6.3 Forecasting ARMA processes The purpose of forecasting is to predict future values of a TS based on the data collected to the present. In this section we will discuss a linear
HMY 799 1: Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων
 HMY 799 : Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων Διάλεξη Στοχαστικές Τυχαίες Μεταβλητές/ Στοχαστικά Σήματα Πειραματικά δεδομένα >Επιλογή τύπου μοντέλου >Επιλογή κριτηρίου >Υπολογισμός >Επικύρωση Προσαρμογή καμπύλης (Curve
HMY 799 : Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων Διάλεξη Στοχαστικές Τυχαίες Μεταβλητές/ Στοχαστικά Σήματα Πειραματικά δεδομένα >Επιλογή τύπου μοντέλου >Επιλογή κριτηρίου >Υπολογισμός >Επικύρωση Προσαρμογή καμπύλης (Curve
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 3
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 3 5.6: Μέση Τιμή, Συναρτήσεις Συσχέτισης & Συνδιασποράς 5.7: Μετάδοση Στοχαστικής
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 3 5.6: Μέση Τιμή, Συναρτήσεις Συσχέτισης & Συνδιασποράς 5.7: Μετάδοση Στοχαστικής
5.4 The Poisson Distribution.
 The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
The worst thing you can do about a situation is nothing. Sr. O Shea Jackson 5.4 The Poisson Distribution. Description of the Poisson Distribution Discrete probability distribution. The random variable
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 5
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 5 5.10: Θόρυβος (Πηγές Θορύβου, Κατανομή Poisson, Λευκός Θόρυβος, Ισοδύναμο
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 5 5.10: Θόρυβος (Πηγές Θορύβου, Κατανομή Poisson, Λευκός Θόρυβος, Ισοδύναμο
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
HOMEWORK#1. t E(x) = 1 λ = (b) Find the median lifetime of a randomly selected light bulb. Answer:
 HOMEWORK# 52258 李亞晟 Eercise 2. The lifetime of light bulbs follows an eponential distribution with a hazard rate of. failures per hour of use (a) Find the mean lifetime of a randomly selected light bulb.
HOMEWORK# 52258 李亞晟 Eercise 2. The lifetime of light bulbs follows an eponential distribution with a hazard rate of. failures per hour of use (a) Find the mean lifetime of a randomly selected light bulb.
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 1
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 1 5.1: Εισαγωγή 5.2: Πιθανότητες 5.3: Τυχαίες Μεταβλητές καθ. Βασίλης Μάγκλαρης
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Θεωρία Πιθανοτήτων & Στοχαστικές Ανελίξεις - 1 5.1: Εισαγωγή 5.2: Πιθανότητες 5.3: Τυχαίες Μεταβλητές καθ. Βασίλης Μάγκλαρης
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1
 Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Main source: "Discrete-time systems and computer control" by Α. ΣΚΟΔΡΑΣ ΨΗΦΙΑΚΟΣ ΕΛΕΓΧΟΣ ΔΙΑΛΕΞΗ 4 ΔΙΑΦΑΝΕΙΑ 1 A Brief History of Sampling Research 1915 - Edmund Taylor Whittaker (1873-1956) devised a
Linear System Response to Random Inputs. M. Sami Fadali Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Nevada
 Linear System Response to Random Inputs M. Sami Fadali Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Nevada 1 Outline Linear System Response to deterministic input. Response to stochastic input. Characterize
Linear System Response to Random Inputs M. Sami Fadali Professor of Electrical Engineering University of Nevada 1 Outline Linear System Response to deterministic input. Response to stochastic input. Characterize
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Introduction to Time Series Analysis. Lecture 16.
 Introduction to Time Series Analysis. Lecture 16. 1. Review: Spectral density 2. Examples 3. Spectral distribution function. 4. Autocovariance generating function and spectral density. 1 Review: Spectral
Introduction to Time Series Analysis. Lecture 16. 1. Review: Spectral density 2. Examples 3. Spectral distribution function. 4. Autocovariance generating function and spectral density. 1 Review: Spectral
List MF20. List of Formulae and Statistical Tables. Cambridge Pre-U Mathematics (9794) and Further Mathematics (9795)
 List MF0 List of Formulae and Statistical Tables Cambridge Pre-U Mathematics (979) and Further Mathematics (979) For use from 07 in all aers for the above syllabuses. CST7 Mensuration Surface area of shere
List MF0 List of Formulae and Statistical Tables Cambridge Pre-U Mathematics (979) and Further Mathematics (979) For use from 07 in all aers for the above syllabuses. CST7 Mensuration Surface area of shere
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise. Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University
 Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
Estimation for ARMA Processes with Stable Noise Matt Calder & Richard A. Davis Colorado State University rdavis@stat.colostate.edu 1 ARMA processes with stable noise Review of M-estimation Examples of
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet
 Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Biostatistics for Health Sciences Review Sheet http://mathvault.ca June 1, 2017 Contents 1 Descriptive Statistics 2 1.1 Variables.............................................. 2 1.1.1 Qualitative........................................
Asymptotic distribution of MLE
 Asymptotic distribution of MLE Theorem Let {X t } be a causal and invertible ARMA(p,q) process satisfying Φ(B)X = Θ(B)Z, {Z t } IID(0, σ 2 ). Let ( ˆφ, ˆϑ) the values that minimize LL n (φ, ϑ) among those
Asymptotic distribution of MLE Theorem Let {X t } be a causal and invertible ARMA(p,q) process satisfying Φ(B)X = Θ(B)Z, {Z t } IID(0, σ 2 ). Let ( ˆφ, ˆϑ) the values that minimize LL n (φ, ϑ) among those
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
CT Correlation (2B) Young Won Lim 8/15/14
 CT Correlation (2B) 8/5/4 Copyright (c) 2-24 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version.2 or any
CT Correlation (2B) 8/5/4 Copyright (c) 2-24 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version.2 or any
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Limit theorems under sublinear expectations and probabilities
 Limit theorems under sublinear expectations and probabilities Xinpeng LI Shandong University & Université Paris 1 Young Researchers Meeting on BSDEs, Numerics and Finance 4 July, Oxford 1 / 25 Outline
Limit theorems under sublinear expectations and probabilities Xinpeng LI Shandong University & Université Paris 1 Young Researchers Meeting on BSDEs, Numerics and Finance 4 July, Oxford 1 / 25 Outline
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
Fundamentals of Signals, Systems and Filtering
 Fundamentals of Signals, Systems and Filtering Brett Ninness c 2000-2005, Brett Ninness, School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science The University of Newcastle, Australia. 2 c Brett Ninness
Fundamentals of Signals, Systems and Filtering Brett Ninness c 2000-2005, Brett Ninness, School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science The University of Newcastle, Australia. 2 c Brett Ninness
P AND P. P : actual probability. P : risk neutral probability. Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P. For example:
 (B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
(B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1
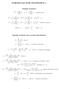 FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
FORMULAS FOR STATISTICS 1 X = 1 n Sample statistics X i or x = 1 n x i (sample mean) S 2 = 1 n 1 s 2 = 1 n 1 (X i X) 2 = 1 n 1 (x i x) 2 = 1 n 1 Xi 2 n n 1 X 2 x 2 i n n 1 x 2 or (sample variance) E(X)
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS
 SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
HMY 799 1: Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων
 HMY 799 : Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων Διαλέξεις 3 4 Στοχαστικά/τυχαία / χ διανύσματα Ντετερμινιστικά και στοχαστικά σήματα στο πεδίο της συχνότητας Στοχαστικά σήματα και γραμμικά συστήματα Deterministic and
HMY 799 : Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων Διαλέξεις 3 4 Στοχαστικά/τυχαία / χ διανύσματα Ντετερμινιστικά και στοχαστικά σήματα στο πεδίο της συχνότητας Στοχαστικά σήματα και γραμμικά συστήματα Deterministic and
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
Nachrichtentechnik I WS 2005/2006
 Nachrichtentechnik I WS 2005/2006 1 Signals & Systems wt 10/2005 1 Overview (Signals & Systems) Signals: definition & classification properties basic signals Signal transformations Fourier transformation
Nachrichtentechnik I WS 2005/2006 1 Signals & Systems wt 10/2005 1 Overview (Signals & Systems) Signals: definition & classification properties basic signals Signal transformations Fourier transformation
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 651 APPENDIX B. BIBLIOGRAPHY 677 APPENDIX C. ANSWERS TO SELECTED EXERCISES 679
 APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
APPENDICES APPENDIX A. STATISTICAL TABLES AND CHARTS 1 Table I Summary of Common Probability Distributions 2 Table II Cumulative Standard Normal Distribution Table III Percentage Points, 2 of the Chi-Squared
Outline Analog Communications. Lecture 05 Angle Modulation. Instantaneous Frequency and Frequency Deviation. Angle Modulation. Pierluigi SALVO ROSSI
 Outline Analog Communications Lecture 05 Angle Modulation 1 PM and FM Pierluigi SALVO ROSSI Department of Industrial and Information Engineering Second University of Naples Via Roma 9, 81031 Aversa (CE),
Outline Analog Communications Lecture 05 Angle Modulation 1 PM and FM Pierluigi SALVO ROSSI Department of Industrial and Information Engineering Second University of Naples Via Roma 9, 81031 Aversa (CE),
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential. be continuous functions on the interval
 Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Differential Equations Let a (t), a 2 (t),..., a nn (t), b (t), b 2 (t),..., b n (t) be continuous functions on the interval I. The system of n first-order differential equations
w o = R 1 p. (1) R = p =. = 1
 Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
Πανεπιστήµιο Κρήτης - Τµήµα Επιστήµης Υπολογιστών ΗΥ-570: Στατιστική Επεξεργασία Σήµατος 205 ιδάσκων : Α. Μουχτάρης Τριτη Σειρά Ασκήσεων Λύσεις Ασκηση 3. 5.2 (a) From the Wiener-Hopf equation we have:
2. THEORY OF EQUATIONS. PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits.
 EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
EAMCET-. THEORY OF EQUATIONS PREVIOUS EAMCET Bits. Each of the roots of the equation x 6x + 6x 5= are increased by k so that the new transformed equation does not contain term. Then k =... - 4. - Sol.
Bayesian statistics. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
Bayesian statistics DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Frequentist vs Bayesian statistics In frequentist
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation
 D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
D Alembert s Solution to the Wave Equation MATH 467 Partial Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives In this lesson we will learn: a change of variable technique
MOTORCAR INSURANCE I
 MOTORCAR INSURANCE I I Acc. II Acc. III Acc. Sex Year Month Day 19970602 0 0 M 1966 4 11 19820101 19840801 0 M 1926 3 25 19820801 19840712 0 F 1952 2 19 19781222 19810507 0 M 1952 3 23 19821110 19870614
MOTORCAR INSURANCE I I Acc. II Acc. III Acc. Sex Year Month Day 19970602 0 0 M 1966 4 11 19820101 19840801 0 M 1926 3 25 19820801 19840712 0 F 1952 2 19 19781222 19810507 0 M 1952 3 23 19821110 19870614
Module 5. February 14, h 0min
 Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
Module 5 Stationary Time Series Models Part 2 AR and ARMA Models and Their Properties Class notes for Statistics 451: Applied Time Series Iowa State University Copyright 2015 W. Q. Meeker. February 14,
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain. Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics
 A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
A Bonus-Malus System as a Markov Set-Chain Małgorzata Niemiec Warsaw School of Economics Institute of Econometrics Contents 1. Markov set-chain 2. Model of bonus-malus system 3. Example 4. Conclusions
Ηλεκτρονικοί Υπολογιστές IV
 ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ηλεκτρονικοί Υπολογιστές IV Μοντέλα χρονολογικών σειρών Διδάσκων: Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Αθανάσιος Σταυρακούδης Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό
ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΙΩΑΝΝΙΝΩΝ ΑΝΟΙΚΤΑ ΑΚΑΔΗΜΑΪΚΑ ΜΑΘΗΜΑΤΑ Ηλεκτρονικοί Υπολογιστές IV Μοντέλα χρονολογικών σειρών Διδάσκων: Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Αθανάσιος Σταυρακούδης Άδειες Χρήσης Το παρόν εκπαιδευτικό υλικό
 γ 1 6 M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F 2 2 λ τ M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 1 6 τ = 36 1 6 τ = 102 1 6 M = 5000
γ 1 6 M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F 2 2 λ τ M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 1 6 τ = 36 1 6 τ = 102 1 6 M = 5000
Lecture 7: Overdispersion in Poisson regression
 Lecture 7: Overdispersion in Poisson regression Claudia Czado TU München c (Claudia Czado, TU Munich) ZFS/IMS Göttingen 2004 0 Overview Introduction Modeling overdispersion through mixing Score test for
Lecture 7: Overdispersion in Poisson regression Claudia Czado TU München c (Claudia Czado, TU Munich) ZFS/IMS Göttingen 2004 0 Overview Introduction Modeling overdispersion through mixing Score test for
6. MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATION
 6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
6 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESIMAION [1] Maximum Likelihood Estimator (1) Cases in which θ (unknown parameter) is scalar Notational Clarification: From now on, we denote the true value of θ as θ o hen, view θ
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II
 ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
ST5224: Advanced Statistical Theory II 2014/2015: Semester II Tutorial 7 1. Let X be a sample from a population P and consider testing hypotheses H 0 : P = P 0 versus H 1 : P = P 1, where P j is a known
Fundamentals of Probability: A First Course. Anirban DasGupta
 Fundamentals of Probability: A First Course Anirban DasGupta Contents 1 Introducing Probability 5 1.1 ExperimentsandSampleSpaces... 6 1.2 Set Theory Notation and Axioms of Probability........... 7 1.3
Fundamentals of Probability: A First Course Anirban DasGupta Contents 1 Introducing Probability 5 1.1 ExperimentsandSampleSpaces... 6 1.2 Set Theory Notation and Axioms of Probability........... 7 1.3
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C
 DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
DERIVATION OF MILES EQUATION FOR AN APPLIED FORCE Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com August 6, 8 Introduction The obective is to derive a Miles equation which gives the overall response
Ψηφιακές Επικοινωνίες
 Ψηφιακές Επικοινωνίες Βασικές Έννοιες Θεωρία Σηµάτων: ανάλυση στο χρονικό και φασµατικό πεδίο Continuous Fourier Transform Σειρές Fourier Σήµατα βασικής ζώνης (Baseband) και ιέλευσης ζώνης (Bandpass) Θεωρία
Ψηφιακές Επικοινωνίες Βασικές Έννοιες Θεωρία Σηµάτων: ανάλυση στο χρονικό και φασµατικό πεδίο Continuous Fourier Transform Σειρές Fourier Σήµατα βασικής ζώνης (Baseband) και ιέλευσης ζώνης (Bandpass) Θεωρία
Διάλεξη 6. Fourier Ανάλυση Σημάτων. (Επανάληψη Κεφ. 10.0-10.2 Κεφ. 10.3, 10.5-7) Ανάλυση σημάτων. Τι πρέπει να προσέξουμε
 University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics Διάλεξη (Επανάληψη Κεφ. 10.0-10. Κεφ. 10.3, 10.5-7) Ανάλυση σημάτων Τι πρέπει να προσέξουμε Επαρκής ψηφιοποίηση στο χρόνο (Nyquist) Αναδίπλωση (aliasing)
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics Διάλεξη (Επανάληψη Κεφ. 10.0-10. Κεφ. 10.3, 10.5-7) Ανάλυση σημάτων Τι πρέπει να προσέξουμε Επαρκής ψηφιοποίηση στο χρόνο (Nyquist) Αναδίπλωση (aliasing)
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data
 Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
Web-based supplementary materials for Bayesian Quantile Regression for Ordinal Longitudinal Data Rahim Alhamzawi, Haithem Taha Mohammad Ali Department of Statistics, College of Administration and Economics,
CHAPTER 101 FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD
 CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
CHAPTER FOURIER SERIES FOR PERIODIC FUNCTIONS OF PERIOD EXERCISE 36 Page 66. Determine the Fourier series for the periodic function: f(x), when x +, when x which is periodic outside this rge of period.
Probability theory STATISTICAL METHODS FOR SAFETY ANALYSIS FMS065 TABLE OF FORMULÆ (2016) Basic probability theory. One-dimensional random variables
 Lund University Centre for Mthemticl Sciences Mthemticl Sttistics STATISTICAL METHODS FOR SAFETY ANALYSIS FMS065 TABLE OF FORMULÆ (06) Probbility theory Bsic probbility theory Let S be smple spce, nd let
Lund University Centre for Mthemticl Sciences Mthemticl Sttistics STATISTICAL METHODS FOR SAFETY ANALYSIS FMS065 TABLE OF FORMULÆ (06) Probbility theory Bsic probbility theory Let S be smple spce, nd let
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Ανάλυση Επικοινωνιακών Σημάτων κατά Fourier
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Ανάλυση Επικοινωνιακών Σημάτων κατά Fourier 2.2: Μετασχηματισμός Fourier (Fourier Transform, FT) 2.3: Ιδιότητες του
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 3, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Ανάλυση Επικοινωνιακών Σημάτων κατά Fourier 2.2: Μετασχηματισμός Fourier (Fourier Transform, FT) 2.3: Ιδιότητες του
 l 0 l 2 l 1 l 1 l 1 l 2 l 2 l 1 l p λ λ µ R N l 2 R N l 2 2 = N x i l p p R N l p N p = ( x i p ) 1 p i=1 l 2 l p p = 2 l p l 1 R N l 1 i=1 x 2 i 1 = N x i i=1 l p p p R N l 0 0 = {i x i 0} R
l 0 l 2 l 1 l 1 l 1 l 2 l 2 l 1 l p λ λ µ R N l 2 R N l 2 2 = N x i l p p R N l p N p = ( x i p ) 1 p i=1 l 2 l p p = 2 l p l 1 R N l 1 i=1 x 2 i 1 = N x i i=1 l p p p R N l 0 0 = {i x i 0} R
Section 8.3 Trigonometric Equations
 99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
99 Section 8. Trigonometric Equations Objective 1: Solve Equations Involving One Trigonometric Function. In this section and the next, we will exple how to solving equations involving trigonometric functions.
Gaussian related distributions
 Gaussian related distributions Santiago Aja-Fernández June 19, 009 1 Gaussian related distributions 1. Gaussian: ormal PDF: MGF: Main moments:. Rayleigh: PDF: MGF: Raw moments: Main moments: px = 1 σ π
Gaussian related distributions Santiago Aja-Fernández June 19, 009 1 Gaussian related distributions 1. Gaussian: ormal PDF: MGF: Main moments:. Rayleigh: PDF: MGF: Raw moments: Main moments: px = 1 σ π
The circle theorem and related theorems for Gauss-type quadrature rules
 OP.circle p. / The circle theorem and related theorems for Gauss-type quadrature rules Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University OP.circle p. 2/ Web Site http : //www.cs.purdue.edu/ archives/22/wxg/codes
OP.circle p. / The circle theorem and related theorems for Gauss-type quadrature rules Walter Gautschi wxg@cs.purdue.edu Purdue University OP.circle p. 2/ Web Site http : //www.cs.purdue.edu/ archives/22/wxg/codes
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model
 Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
Additional Results for the Pareto/NBD Model Peter S. Fader www.petefader.com Bruce G. S. Hardie www.brucehardie.com January 24 Abstract This note derives expressions for i) the raw moments of the posterior
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
A Two-Sided Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bounds and Its Applications in Financial Engineering
 Electronic Companion A Two-Sie Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bouns an Its Applications in Financial Engineering Ning Cai, S. G. Kou, Zongjian Liu HKUST an Columbia University Appenix
Electronic Companion A Two-Sie Laplace Inversion Algorithm with Computable Error Bouns an Its Applications in Financial Engineering Ning Cai, S. G. Kou, Zongjian Liu HKUST an Columbia University Appenix
Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE
 Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE BLUE: Robustness of LSE against normality We now study properties of l τ β and σ 2 under assumption A2, i.e., without the normality assumption on ε. From Theorem
Lecture 21: Properties and robustness of LSE BLUE: Robustness of LSE against normality We now study properties of l τ β and σ 2 under assumption A2, i.e., without the normality assumption on ε. From Theorem
Stationary ARMA Processes
 University of Pavia 2007 Stationary ARMA Processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia Moving Average of order 1 (MA(1)) Y t = µ + ǫ t + θǫ t 1 t = 1,...,T ǫ t WN(0, σ 2 ) E(ǫ t ) = 0 E(ǫ 2 t) = σ 2 E(ǫ
University of Pavia 2007 Stationary ARMA Processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia Moving Average of order 1 (MA(1)) Y t = µ + ǫ t + θǫ t 1 t = 1,...,T ǫ t WN(0, σ 2 ) E(ǫ t ) = 0 E(ǫ 2 t) = σ 2 E(ǫ
HMY 429: Εισαγωγή στην Επεξεργασία Ψηφιακών. Χρόνου (Ι)
 HMY 429: Εισαγωγή στην Επεξεργασία Ψηφιακών Σημάτων Διάλεξη 5: Στοχαστικά/Τυχαία Σήματα Διακριτού Διάλεξη 5: Στοχαστικά/Τυχαία Σήματα Διακριτού Χρόνου (Ι) Στοχαστικά σήματα Στα προηγούμενα: Ντετερμινιστικά
HMY 429: Εισαγωγή στην Επεξεργασία Ψηφιακών Σημάτων Διάλεξη 5: Στοχαστικά/Τυχαία Σήματα Διακριτού Διάλεξη 5: Στοχαστικά/Τυχαία Σήματα Διακριτού Χρόνου (Ι) Στοχαστικά σήματα Στα προηγούμενα: Ντετερμινιστικά
ON NEGATIVE MOMENTS OF CERTAIN DISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONS
 Pa J Statist 2009 Vol 25(2), 135-140 ON NEGTIVE MOMENTS OF CERTIN DISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONS Masood nwar 1 and Munir hmad 2 1 Department of Maematics, COMSTS Institute of Information Technology, Islamabad,
Pa J Statist 2009 Vol 25(2), 135-140 ON NEGTIVE MOMENTS OF CERTIN DISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONS Masood nwar 1 and Munir hmad 2 1 Department of Maematics, COMSTS Institute of Information Technology, Islamabad,
 1.8 Paul Mother Wavelet Real Part Imaginary Part Magnitude.6.4 Amplitude.2.2.4.6.8 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 t .8.6 Real Part of Three Scaled Wavelets a = 1 a = 5 a = 1 1.2 1 Imaginary Part of Three Scaled Wavelets
1.8 Paul Mother Wavelet Real Part Imaginary Part Magnitude.6.4 Amplitude.2.2.4.6.8 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 t .8.6 Real Part of Three Scaled Wavelets a = 1 a = 5 a = 1 1.2 1 Imaginary Part of Three Scaled Wavelets
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Ανάλυση Επικοινωνιακών Σημάτων κατά Fourier
 ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Ανάλυση Επικοινωνιακών Σημάτων κατά Fourier 2.2: Μετασχηματισμός Fourier (Fourier Transform, FT) 2.3: Ιδιότητες του
ΣΤΟΧΑΣΤΙΚΑ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ & ΕΠΙΚΟΙΝΩΝΙΕΣ 1o Τμήμα (Α - Κ): Αμφιθέατρο 4, Νέα Κτίρια ΣΗΜΜΥ Ανάλυση Επικοινωνιακών Σημάτων κατά Fourier 2.2: Μετασχηματισμός Fourier (Fourier Transform, FT) 2.3: Ιδιότητες του
Using Long-Run Consumption-Return Correlations to Test Asset Pricing Models : Internet Appendix
 Using Long-Run Consumption-Return Correlations to Test Asset Pricing Models : Internet Appendix Jianfeng Yu University of Minnesota April 0, 0 Proof. [For Equation 6]: To derive the log-linear approximation
Using Long-Run Consumption-Return Correlations to Test Asset Pricing Models : Internet Appendix Jianfeng Yu University of Minnesota April 0, 0 Proof. [For Equation 6]: To derive the log-linear approximation
k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +
[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R + k A = [k, k]( )[a 1, a 2 ] = [ka 1,ka 2 ] 4For the division of two intervals of confidence in R +](/thumbs/73/69566903.jpg) Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Chapter 3. Fuzzy Arithmetic 3- Fuzzy arithmetic: ~Addition(+) and subtraction (-): Let A = [a and B = [b, b in R If x [a and y [b, b than x+y [a +b +b Symbolically,we write A(+)B = [a (+)[b, b = [a +b
Fourier Analysis of Waves
 Exercises for the Feynman Lectures on Physics by Richard Feynman, Et Al. Chapter 36 Fourier Analysis of Waves Detailed Work by James Pate Williams, Jr. BA, BS, MSwE, PhD From Exercises for the Feynman
Exercises for the Feynman Lectures on Physics by Richard Feynman, Et Al. Chapter 36 Fourier Analysis of Waves Detailed Work by James Pate Williams, Jr. BA, BS, MSwE, PhD From Exercises for the Feynman
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor
 Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
Uniform Convergence of Fourier Series Michael Taylor Given f L 1 T 1 ), we consider the partial sums of the Fourier series of f: N 1) S N fθ) = ˆfk)e ikθ. k= N A calculation gives the Dirichlet formula
5. Choice under Uncertainty
 5. Choice under Uncertainty Daisuke Oyama Microeconomics I May 23, 2018 Formulations von Neumann-Morgenstern (1944/1947) X: Set of prizes Π: Set of probability distributions on X : Preference relation
5. Choice under Uncertainty Daisuke Oyama Microeconomics I May 23, 2018 Formulations von Neumann-Morgenstern (1944/1947) X: Set of prizes Π: Set of probability distributions on X : Preference relation
Stationary ARMA Processes
 Stationary ARMA Processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi Stationary ARMA Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 45 Moving Average of order 1 (MA(1)) Y t = µ + ɛ t + θɛ t 1 t = 1,..., T
Stationary ARMA Processes Eduardo Rossi University of Pavia October 2013 Rossi Stationary ARMA Financial Econometrics - 2013 1 / 45 Moving Average of order 1 (MA(1)) Y t = µ + ɛ t + θɛ t 1 t = 1,..., T
Jesse Maassen and Mark Lundstrom Purdue University November 25, 2013
 Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
Notes on Average Scattering imes and Hall Factors Jesse Maassen and Mar Lundstrom Purdue University November 5, 13 I. Introduction 1 II. Solution of the BE 1 III. Exercises: Woring out average scattering
HMY 799 1: Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων
 HMY 799 : Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων Διάλεξη 5 Εκτίμηση φάσματος ισχύος Συνάφεια Παραδείγματα Στοχαστικά Διανύσματα Autoregressive model with exogenous inputs (ARX y( t + a y( t +... + a y( t n = bu( t +...
HMY 799 : Αναγνώριση Συστημάτων Διάλεξη 5 Εκτίμηση φάσματος ισχύος Συνάφεια Παραδείγματα Στοχαστικά Διανύσματα Autoregressive model with exogenous inputs (ARX y( t + a y( t +... + a y( t n = bu( t +...
Ανάλυση Θορύβου Σε Γραμμικά Κυκλώματα
 AO Ηλεκτρονική ΙΙΙ Παύλος - Πέτρος Σωτηριάδης Ανάλυση Θορύβου Σε Γραμμικά Κυκλώματα Θεωρία, Εξαρτήματα και ιατάξεις Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών - Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Άδεια
AO Ηλεκτρονική ΙΙΙ Παύλος - Πέτρος Σωτηριάδης Ανάλυση Θορύβου Σε Γραμμικά Κυκλώματα Θεωρία, Εξαρτήματα και ιατάξεις Εθνικό Μετσόβιο Πολυτεχνείο Σχολή Ηλεκτρολόγων Μηχανικών - Μηχανικών Υπολογιστών Άδεια
Exercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5
 Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Prof. Dr. Christine Müller Dipl.-Math. Christoph Kustosz Eercises to Statistics of Material Fatigue No. 5 E. 9 (5 a Show, that a Fisher information matri for a two dimensional parameter θ (θ,θ 2 R 2, can
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals
 Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
Lecture 34 Bootstrap confidence intervals Confidence Intervals θ: an unknown parameter of interest We want to find limits θ and θ such that Gt = P nˆθ θ t If G 1 1 α is known, then P θ θ = P θ θ = 1 α
2. ARMA 1. 1 This part is based on H and BD.
 2. ARMA 1 1 This part is based on H and BD. 1 1 MA 1.1 MA(1) Let ε t be WN with variance σ 2 and consider the zero mean 2 process Y t = ε t + θε t 1 (1) where θ is a constant. MA(1). This time series is
2. ARMA 1 1 This part is based on H and BD. 1 1 MA 1.1 MA(1) Let ε t be WN with variance σ 2 and consider the zero mean 2 process Y t = ε t + θε t 1 (1) where θ is a constant. MA(1). This time series is
EE512: Error Control Coding
 EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
EE512: Error Control Coding Solution for Assignment on Finite Fields February 16, 2007 1. (a) Addition and Multiplication tables for GF (5) and GF (7) are shown in Tables 1 and 2. + 0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 2 3
Srednicki Chapter 55
 Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
Srednicki Chapter 55 QFT Problems & Solutions A. George August 3, 03 Srednicki 55.. Use equations 55.3-55.0 and A i, A j ] = Π i, Π j ] = 0 (at equal times) to verify equations 55.-55.3. This is our third
ESTIMATION OF SYSTEM RELIABILITY IN A TWO COMPONENT STRESS-STRENGTH MODELS DAVID D. HANAGAL
 ESTIMATION OF SYSTEM RELIABILITY IN A TWO COMPONENT STRESS-STRENGTH MODELS DAVID D. HANAGAL Department of Statistics, University of Poona, Pune-411007, India. Abstract In this paper, we estimate the reliability
ESTIMATION OF SYSTEM RELIABILITY IN A TWO COMPONENT STRESS-STRENGTH MODELS DAVID D. HANAGAL Department of Statistics, University of Poona, Pune-411007, India. Abstract In this paper, we estimate the reliability
ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2
 ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος 2007-08 -- Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2 Ημερομηνία Παραδόσεως: Παρασκευή
ΤΜΗΜΑ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΛΟΓΩΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΩΝ ΥΠΟΛΟΓΙΣΤΩΝ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΚΥΠΡΟΥ ΗΜΥ 220: ΣΗΜΑΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΣΥΣΤΗΜΑΤΑ Ι Ακαδημαϊκό έτος 2007-08 -- Εαρινό Εξάμηνο Κατ οίκον εργασία αρ. 2 Ημερομηνία Παραδόσεως: Παρασκευή
Anti-Final CS/SE 3341 SOLUTIONS
 CS/SE 3341 SOLUTIONS Anti-Final 1. Users call help desk every 15 minutes, on the average. There is one help desk specialist on duty, and her average service time is 9 minutes. Modeling the help desk as
CS/SE 3341 SOLUTIONS Anti-Final 1. Users call help desk every 15 minutes, on the average. There is one help desk specialist on duty, and her average service time is 9 minutes. Modeling the help desk as
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit
 Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
Ordinal Arithmetic: Addition, Multiplication, Exponentiation and Limit Ting Zhang Stanford May 11, 2001 Stanford, 5/11/2001 1 Outline Ordinal Classification Ordinal Addition Ordinal Multiplication Ordinal
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve. r(t) = 3cost, 4t, 3sint
 1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
1. a) 5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve at the point P, π, rt) cost, t, sint ). b) 5 points) Find curvature of the curve at the point P. Solution: a) r t) sint,,
ECE598: Information-theoretic methods in high-dimensional statistics Spring 2016
 ECE598: Information-theoretic methods in high-dimensional statistics Spring 06 Lecture 7: Information bound Lecturer: Yihong Wu Scribe: Shiyu Liang, Feb 6, 06 [Ed. Mar 9] Recall the Chi-squared divergence
ECE598: Information-theoretic methods in high-dimensional statistics Spring 06 Lecture 7: Information bound Lecturer: Yihong Wu Scribe: Shiyu Liang, Feb 6, 06 [Ed. Mar 9] Recall the Chi-squared divergence
Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Series representations. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 Pi Notations Traditional name Π Traditional notation Π Mathematica StandardForm notation Pi Primary definition.3... Π Specific values.3.3.. Π 3.5965358979338663383795889769399375589795937866868998683853
Pi Notations Traditional name Π Traditional notation Π Mathematica StandardForm notation Pi Primary definition.3... Π Specific values.3.3.. Π 3.5965358979338663383795889769399375589795937866868998683853
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES G11LMA Linear Mathematics Examination Solutions
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES GLMA Linear Mathematics 00- Examination Solutions. (a) i. ( + 5i)( i) = (6 + 5) + (5 )i = + i. Real part is, imaginary part is. (b) ii. + 5i i ( + 5i)( + i) = ( i)( + i)
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests
 Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
Other Test Constructions: Likelihood Ratio & Bayes Tests Side-Note: So far we have seen a few approaches for creating tests such as Neyman-Pearson Lemma ( most powerful tests of H 0 : θ = θ 0 vs H 1 :
