Quantitative Finance and Investments Advanced Formula Sheet. Fall 2013/Spring 2014
|
|
|
- Ἀδάμ Τρικούπη
- 7 χρόνια πριν
- Προβολές:
Transcript
1 Quaniaive Finance and Invesmens Advanced Formula Shee Fall 013/Spring 014 ThisishesamesheeusedforFall013.Theonlychangeisonhiscoverpage. Morning and afernoon exam bookles will include a formula package idenical o he one aached o his sudy noe. The exam commiee believes ha by providing many key formulas, candidaes will be able o focus more of heir exam preparaion ime on he applicaion of he formulas and conceps o demonsrae heir undersanding of he syllabus maerial and less ime on he memorizaion of he formulas. The formula shee was developed sequenially by reviewing he syllabus maerial for each major syllabus opic. Candidaes should be able o follow he flow of he formula package easily. We recommend ha candidaes use he formula package concurrenly wih he syllabus maerial. No every formula in he syllabus is in he formula package. Candidaes are responsible for all formulas on he syllabus, including hose no on he formula shee. Candidaes should carefully observe he someimes suble differences in formulas and heir applicaion o slighly differen siuaions. Candidaes will be expeced o recognize he correc formula o apply in a specific siuaion of an exam quesion. Candidaes will noe ha he formula package does no generally provide names or definiions of he formula or symbols used in he formula. Wih he wide variey of references and auhors of he syllabus, candidaes should recognize ha he leer convenions and use of symbols may vary from one par of he syllabus o anoher and hus from one formula o anoher. Werushayouwillfindheinclusionofheformulapackageobeavaluablesudyaide ha will allow for more of your preparaion ime o be spen on masering he learning objecives and learning oucomes. 1
2 Ineres Rae Models - Theory and racice, Brigo and Mercurio Chaper 3 Table 3.1 Summary of insananeous shor rae models Model Dynamics r > 0 r AB AO V dr = k[θ r ]d + σdw N N Y Y CIR dr = k[θ r ]d + σ r dw Y NCχ Y Y D dr = ar d + σr dw Y LN Y N EV dr = r [η a ln r ]d + σr dw Y LN N N HW dr = k[θ r ]d + σdw N N Y Y BK dr = r [η ³ a ln r ]d + i σr dw Y LN N N MM dr = r hη λ ln r d + σr dw Y LN N N γ 1+γ CIR++ r = x + ϕ, dx = k[θ x ]d + σ x dw Y* SNCχ Y Y EEV r = x + ϕ, dx = x [η a ln x ]d + σx dw Y* SLN N N *raes are posiive under suiable condiions for he deerminisic funcion ϕ. (3.5) dr() =k[θ r()]d + σdw(), r(0) = r 0 (3.6) r() =r(s)e k( s) + θ 1 e k( s) + σ R s e k( u) dw (u) (3.7) E {r() F s } = r(s)e k( s) + θ 1 e k( s) Var{r() F s } = σ 1 e k( s) k (3.8) B(,T )r() (, T )=A(, T )e (3.9) dr() =[kθ B(, T )σ kr()]d + σdw T () (3.11) dr() =[kθ (k + λσ)r()]d + σdw 0 (), r(0) = r 0 (3.1) dr() =[b ar()]d + σdw 0 () (3.13) r() =r(s)e a( s) + b 1 e a( s) + σ R s a dw 0 (u) (3.14) ˆα = n n r ir i 1 n r n i r i 1 n n r i 1 ( n r i 1) n (3.15) ˆβ = [r i ˆαr i 1 ] n(1 ˆα) (3.16) V c = 1 h n r i ˆαr i 1 n ˆβ(1 i ˆα) (3.19) E {r() F s } = r(s)e a( s) and Var{r() F s } = r (s)e ³e a( s) σ ( s) 1 (3.0) (, T )= rp R sin( r sinh y) R f(z)sin(yz)dzdy + π 0 0 Γ(p) rp K p ( r) (3.1) dr() =k(θ r())d + σ p r()dw (), r(0) = r 0 (3.) dr() =[kθ (k + λσ)r()]d + σ p r()dw 0 (), r(0) = r 0
3 (3.3) E {r() F s } = r(s)e k( s) + θ 1 e k( s) Var{r() F s } = r(s) σ e k( s) e k( s) + θ σ 1 e k( s) k k (3.4) B(,T )r() (, T )=A(, T )e (3.5) kθ/σ h exp {(k + h)(t )/} A(, T )= h +(k + h)(exp {(T )h} 1) B(, T )= (exp{(t )h} 1) h +(k + h)(exp {(T )h} 1), h = k +σ (3.7) dr() =[kθ (k + B(, T )σ )r()]d + σ p r()dw T () (3.8) p T r() r(s) (x) =p χ (υ,δ(,s))/q(,s)(x) =q(, s)p χ (υ,δ(,s))(q(, s)x) q(, s) =[ρ( s)+ψ + B(, T )] and δ(, s) = 4ρ( s) r(s)e h( s) q(, s) age 68 R(, T )=α(, T )+β(, T )r(), B(,T )r() (, T )=A(, T )e (3.9) σ f (, T )= B(, T ) σ(, r()) T age 69 dr() = b(, r())d + σ(, r())dw () b(, x) =λ()x + η(), σ (, x) =γ()x + δ() B(, T )+λ()b(, T ) 1 γ()b(, T ) +1=0, B(T,T)=0 [ln A(, T )] η()b(, T )+1 δ()b(, T ) =0, A(T,T)=1 age 69/70 Vasicek λ() = k, η() =kθ, γ() =0, δ() =σ age 70 CIR λ() = k, η() =kθ, γ() =σ, δ() =0 b(x) =λx + η, σ (x) =γx + δ µ θ age 71 lim E{r() F s } =exp a + σ 4a µ µ θ (3.31) lim Var{r() F s } =exp a + σ σ exp 1 a a (3.3) dr() =[ϑ() a()r()]d + σ()dw () (3.33) dr() =[ϑ() ar()]d + σdw() (3.34) ϑ() = fm (0,) + af M (0,)+ σ T a (1 e a ) (3.35) r() =r(s)e a( s) + R s e a( u) ϑ(u)du + σ R s e a( u) dw (u) = r(s)e a( s) + α() α(s)e a( s) + σ R s e a( u) dw (u) (3.36) where α() =f M (0,)+ σ a (1 e a ) 3
4 (3.37) E{r() F s } = r(s)e a( s) + α() α(s)e a( s) Var{r() F s } = σ 1 e a( s) a (3.38) dx() = ax()d + σdw(), x(0) = 0 age 74 x() =x(s)e a( s) + σ R s e a( u) dw (u) (3.47) E{x( i+1 ) x( i )=x i,j } = x i,j e a i =: M i,j Var{x( i+1 ) x( i )=x i,j } = σ 1 e a i =: V a i r 3 (3.48) x i = V i 1 3=σ a [1 e a i 1 µ Mi,j (3.49) k =round x i+1 (3.50) p u = η j,k + η j,k 6Vi,p m = 3V i 3 η j,k,p 3Vi d = η j,k 6Vi 3V i (3.64) dx α = μ(x α ; α)d + σ(x α ; α)dw x (3.65) x (, T )=Π x (, T, x α ; α) (3.66) r = x + ϕ(; α), 0 h (3.67) (, T )=exp R i T ϕ(s; α)ds Π x (, T, r ϕ(; α); α) (3.68) ϕ(; α) =ϕ (; α) :=f M (o, ) f x (0,; α) (3.69) h exp R i T ϕ(s; α)ds = Φ (, T, x 0 ; α) := M (0,T) Π x (0,,x 0 ; α) Π x (0,T,x 0 ; α) M (0,) (3.70) Π(, T, r ; α) =Φ (, T, x 0 ; α)π (, T, r ϕ (; α); α) (3.71) V x (, T, τ, K) =Ψ x (, T, τ, K, x α ; α) dϕ(; α) (3.74) dr = kθ + kϕ(; α)+ kr d + σdw d age 100 ϕ VAS (; α) =f M (0,)+(e k 1) k θ σ / k η j,k σ k e k (1 e k ) x 0 e k age 101 (, T )= M (0,T)A(0,)exp{ B(0,)x 0 } M (0,)A(0,T)exp{ B(0,T)x 0 } A(, T )exp{ B(, T )[r ϕ VAS (; α)]} (3.76) dx() =k(θ x())d + σ p x()dw (), x(0) = x 0, r() =x()+ϕ() (3.77) ϕ CIR (; α) =f M (0,) f CIR (0,; α) f CIR kθ(exp{h} 1) (0,; α) = h +(k + h)(exp{h} 1) + x 4h exp{h} 0 [h +(k + h)(exp{h} 1)] h = k +σ 4
5 Chaper 4 (4.4) r = x()+y()+ϕ(), r(0) = r 0 (4.5) dx() = ax()d + σdw 1 (), x(0) = 0 dy() = by()d + ηdw (), y(0) = 0 (4.6) E{r() F s } = x(s)e a( s) + y(s)e b( s) + ϕ() Var{r() F s } = σ 1 e a( s) + η 1 e b( s) +ρ ση 1 e (a+b)( s) a b a + b (4.7) r() =σ R 0 e a( u) dw 1 (u)+η R 0 e b( u) dw (u)+ϕ() (4.8) dx() = ax()d + σdfw 1 () dy() = by()d + ηρdfw 1 ()+η p 1 ρ dfw () where dw 1 () =ddfw 1 () and dw () =ρdfw 1 ()+ p 1 ρ dfw () ) ) 1 e a(t 1 e b(t (4.9) M(, T )= x()+ y() a b (4.10) V (, T )= σ T + a a e a(t ) 1 a e a(t ) 3 a + η T + b b e b(t ) 1 b e b(t ) 3 b +ρ ση ab (4.11) (, T )=exp T + e a(t ) 1 a ½ R T + e b(t ) 1 b ϕ(u)du 1 e a(t ) x() a e (a+b)(t ) 1 a + b ) 1 e b(t y()+ 1 ¾ b V (, T ) (4.1) ϕ() =f M (0,T)+ σ 1 e at + η 1 e bt + ρ ση a b ab (1 e at )(1 e bt ) n (4.13) exp R o T ϕ(u)du = M (0,T) ½ M (0,) exp 1 ¾ [V (0,T) V (0,)] (4.14) (, T )= M (0,T) exp {A(, T )} M (0,) A(, T ):= 1 ) ) 1 e a(t 1 e b(t [V (, T ) V (0,T)+V(0,)] x() y() a b (4.15) (, T )=A(, T )exp{ B(a,, T )x() B(b,, T )y()} (4.16) σ f (, T )= p σ e a(t ) + η e b(t ) +ρσηe (a+b)(t ) 5
6 age 15 Cov(df (, T 1 ),df(, T )) d = σ B T (a,, T 1) B T (a,, T )+η B T (b,, T 1) B T (b,, T ) B +ρση T (a,, T 1) B T (b,, T )+ B T (a,, T ) B T (b,, T 1) = σ e a(t 1+T ) + η e b(t 1+T ) +ρση e at 1 bt +(a+b) + e at bt 1 +(a+b) Corr(df (, T 1 ),df(, T )) = σ e a(t 1+T ) + η e b(t 1+T ) σ f (, T 1 )σ f (, T ) + ρση e at 1 bt +(a+b) + e at bt 1 +(a+b) σ f (, T 1 )σ f (, T ) age 153 f(, T 1 T )= ln (, T 1) ln (, T ) T T 1 df (, T 1,T )=...d + B(a,, T ) B(a,, T 1 ) σdw 1 () T T 1 + B(b,, T ) B(b,, T 1 ) ηdw () T T 1 σ f (, T 1,T )= p σ β(a,, T 1,T ) + η β(b,, T 1,T ) +ρσηβ(a,, T 1,T )β(b,, T 1,T ) where β(z,, T 1,T )= B(z,, T ) B(z,,T 1 ) T T 1 Cov(df (, T 1,T ),df(, T 3,T 4 )) d σ B(a,, T ) B(a,, T 1 ) B(a,, T 4 ) B(a,, T 3 ) T T 1 T 4 T 3 +η B(b,, T ) B(b,, T 1 ) B(b,, T 4 ) B(b,, T 3 ) T T 1 T 4 T 3 B(a,, T ) B(a,, T 1 ) B(b,, T 4 ) B(b,, T 3 ) +ρση T T 1 T 4 T 3 + B(a,, T 4) B(a,, T 3 ) B(b,, T ) B(b,, T 1 ) T 4 T 3 T T 1 s age 160 σ 3 = dz 3 () = σ 1 + σ (ā b) + ρ σ 1σ b ā σ 1 dz 1 () σ ā b dz (), σ 4 = σ σ 3 ā b age 161 a =ā, b = b, σ = σ 3, η = σ 4, ρ = σ 1 ρ σ 4 σ 3 6
7 ϕ() =r 0 e ā + R 0 θ(v)e ā( v) dv ā = a, b = b, σ1 = p σ + η +ρση, σ = η(a b) ρ = σρ + η p σ + η +ρση, θ() =dϕ() + aϕ() d Managing Credi Risk: The Grea Challenge for Global Financial Markes, Caouee, e. al. Chaper 0 (0.) R p = N X i EAR (0.3) V p = N j=1 (0.5) UAL p = N age 403 N X i X j σ i σ j ρ ij j=1 N X i X j σ i σ j ρ ij 1 CV ar(cl)=ead LGD µ µ ρφ 1 (CL)+Φ 1 (D) Φ D 1 ρ 1+(M.5) b(d) 1 1.5b(D) Liquidiy Risk Measuremen and Managemen: Guide o Global Bes racices, Maz and Neu A racioner s Chaper age 33 age 33 log V () =α + β + σε log V q () =α + β σφ 1 (q) Bond-CDS Basis Handbook: Measuring, Trading and Analysing Basis Trades, Elizalde, Docor, and Saluk age 13, Equaion 1 S = D (1 R) age 15, Equaion FR = U AI RA + FC age 18, Equaion 3 V[c + p] B SS = RF A age 5, Equaion 4 BT1 =CN (100 R U C F C)+BN (R+CR B FC) age 5, Equaion 5 BT =BN (100 + CR B FC) CN (U + C + FC) age 43, Equaion 7 CN = B R 100 R U BN 7
8 A Survey of Behavioral Finance, Barberis and Thaler (1) (x, p : y,q) =π(p)v(x) +π(q)v(y) () i π i v(x i ) where v = xα if x 0 λ( x) α if x<0 and π i = w( i ) w(i ), w( )= γ ( γ +(1 ) γ ) 1/γ (3) D +1 D = e g D+σ D ε +1 (4) (5) C +1 = e g C+σ C η +1 C µ µµ µ ε 0 1 w N, η 0 w 1 (6) E 0 ρ C1 γ =0 1 γ " µc+1 γ (7) 1 = ρe R +1# C, i.i.d.over ime (8) R +1 = D = 1+ +1/D +1 D +1 /D D (9) r +1 = d +1 +cons. d +1 d +cons. (10) E π v[(1 w)r f,+1 + wr +1 1] (11) E 0 ρ C1 γ 1 γ + b 0C γ ˆv(X +1 ) =0 (13) R +1 = +1 + D +1 (14) p d = E ρ d +1+j E (15) E 0 =0 j=0 j=0 ρ C1 γ 1 γ + b 0C γ ṽ(x +1,z ) ρ r +1+j + E lim ρ j (p +j d +j )+cons. j (16) r i r f = β i.1 (F 1 r f )+...+ β i,k (F K r f ) (17) r i, r f, = α i + β i,1 (F 1, r f, )+...+ β i,k (F K, r f, )+ε i, (18) R f = 1 ρ eγg C+0.5γ σ C (19) 1 = ρ 1+f e g D γg C +0.5(σD +γ σc γσ Cσ D w) f (0) R +1 = D = 1+ +1/D +1 D +1 = 1+f /D D f e g D+σ D ε +1 8
9 CAIA Level II: Advanced Core Topics in Alernaive Invesmens, Black, Chambers, Kazemi Chaper 16 (16.1) repored (16.) repored (16.3) rue (16.4) rue = α + β 0 rue = α rue =(1/α) repored = repored 1 + β 1 rue 1 + β rue + + α(1 α) rue 1 + α(1 α) rue + [(1 α)/α] repored 1 +[(1/α) ( repored repored 1 )] (16.5) R,repored β 0 R,rue + β 1 R 1,rue + β R,rue + (16.6) repored (16.7) repored =(1 ρ) rue =(1 ρ) rue + ρ repored 1 + ρ repored 1 (16.8) R,repored (1 ρ)r,rue + ρr 1,repored (16.9) R,rue =(R,repored ρr 1,repored )/(1 ρ) (16.10) ˆρ = corr(r,repored R 1,repored ) (16.11) ρ i,j = σ ij /(σ i σ j ) (16.1) R repored Chaper 1 age 6 = α + β 1 R repored 1 + β R repored + + β k R repored k + ε Y = S I E H where Y = yield, S = oal solar radiaion over he area per period, I = fracion of solar radiaion capured by he crop canopy, E = phoosynheic efficiency of he crop (oal plan dry maer per uni of solar radiaion), H = harves index (fracion of oal dry maer ha is harvesable) Managing Invesmen orfolio: A Dynamic rocess, Maginn, Tule, ino, McLeavey Chaper 8 age 53 TRCI = CR + RR + SR age 553 RR n, =(R + R 1 + R R n )/n age 554 r n DD = i r, 0)] n 1 age 555 ARR rf SR = SD age 556 ARR rf SR = DD 9
10 The Secular and Cyclic Deerminans of Capializaion Raes: The Role of ropery Fundamenals, Macroeconic Facors, and "Srucural Changes," Chervachidze, Cosello, Wheaon (1) Log(C j, )=a 0 + a 1 log(c j, 1 )+a log(c j, 4 )+a 3 log(rri j, )+a 4 RTB + a 7 Q (1.1) RRI j, s = RR j, /M RR j +a 8 Q3 + a 9 Q4 + a 10 D j () Log(C j, )=a 0 + a 1 log(c j, 1 )+a log(c j, 4 )+a 3 log(rri j, s )+a 4 RTB (.1) DEBTFLOW = TNBL /GD +a 5 SREAD + a 6 DEBTFLOW + a 7 Q + a 8 Q3 + a 9 Q4 + a 10 D j (3) Log(C j, )=a 0 + a 1 log(c j, 1 )+a log(c j, 4 )+a 3 log(rri j, s )+a 4 RTB +a 5 SREAD + a 6 DEBTFLOW + a 7 Q + a 8 Q3 + a 9 Q4 (4) Log(C j, )=a 0 + a 1 yearq + a log(c j, 1 )+a 3 log(c j, 4 )+a 4 log(rri j, s )+a 5 RT B +a 6 SREAD + a 7 DEBTFLOW + a 7 Q + a 8 Q3 + a 9 Q4 + a 10 D j Analysis of Financial Time Series, Tsay Chaper 3 µ (v+1)/ Γ[(v +1)/] (3.7) f( v) = Γ(v/) p 1+, v > (v )π v µ (3.8) (a m+1,...,a T α, A m )= T v +1 a ln 1+ =m+1 (v )σ ξ + 1 f[ξ( + ω) v] if < ω/ ξ (3.9) g( ξ,v) = ξ + 1 f[( + ω)/ξ v] if ω/ ξ (3.10) f(x) = v exp 1 x/λ v, <x<, 0 <v λ (1+1/v) Γ(1/v) (3.14) GARCH(m, s): a = σ, σ = α 0 + m α i a i + s β j σ j j=1 + 1 ln(σ ) (3.3) GARCH(1, 1)-M: r = μ + cσ + a, a = σ, σ = α 0 + α 1 a 1 + β 1 σ 1 (3.8) EGARCH(m, s): ln(σ )=α 0 + s a i + γ i a i α i + m β j ln(σ σ j) i Chaper 8 (8.1) μ = E(r ), Γ 0 = E[(r μ)(r μ) 0 ] (8.) Γ [Γ ij ( )] = E[(r μ)(r μ) 0 ] (8.3) ρ [ρ ij ( )] = D 1 Γ D 1 j=1 10
11 (8.4) Γ ij ( ) ρ ij ( ) = p Γii (0)Γ jj (0) = Cov(r i,r j, ) sd(r i )sd(r j ) (8.5) ˆΓ = 1 T (r r)(r r) 0, 0 T = +1 (8.6) ˆρ = ˆD 1ˆΓ ˆD 1, 0 (8.7) Q k (m) =T m 1 =1 T r(ˆγ 0 ˆΓ 1ˆΓ 0 ˆΓ 1 0 ) (8.11) r = a + Φa 1 + Φ a + Φ 3 a 3 + (8.13) r = φ 0 + Φr Φ p r p + a, p > 0 (8.3) r = θ 0 + a Θ 1 a 1 Θ q a q or r = θ 0 + Θ(B)a (8.33) x = αβ 0 x 1 + p 1 (8.34) Φ j = p i=j+1 Φ i x i + a q Θ j a j j=1 Φ i, j =1,...,p 1, αβ 0 = Φ p + Φ p Φ 1 I = Φ(1) (8.35) x = μ + Φ 1 x Φ p x p + a (8.39) x = μd + αβ 0 x 1 + Φ 1 x Φ p 1 x p+1 + a Chaper 9 (9.1) r i = α i + β i1 f β im f m + i, =1,...,T,,...,k (9.) r = α + βf +, =1,...,T (9.3) R i = α i 1 T + Fβ 0 i + E i (9.4) R = Gξ 0 + E (9.5) r i = α i + β i r m + i, i =1,...,k =1,...,T (9.11) Var(y i )=wiσ 0 r w i, i =1,...,k (9.1) Cov(y i,y j )=wiσ 0 r w j, i, j =1,...,k (9.13) k Var(r i )=r(σ r )= k λ i = k Var(y i ) (9.14) ˆΣ r [ˆσ ij,r ]= 1 T 1 (9.15) ˆρ r = Ŝ 1 ˆΣ r Ŝ 1 T =1(r r)(r r) 0, r = 1 T T r =1 (9.16) r μ = βf + (9.17) Σr = Cov(r )=E[(r μ)(r μ) 0 ]=E[(βf + )(βf + ) 0 ]=ββ 0 + D (9.18) Cov(r, f )=E[(r μ)f]=βe(f 0 f)+e( 0 f)=β 0 (9.19) ˆβ [ ˆβ i ij ]= hpˆλ1 ê 1 pˆλ ê pˆλm ê m 11
12 (9.0) LR(m) = T 1 16 (k +5) 3 m ³ ln ˆΣ r ln ˆβ ˆβ 0 + ˆD Handbook of Fixed Income Securiies, Fabozzi Chaper 70 (70 1) Asse Allocaion w µ w s s w wb s (TR B w B s TR B ) (70 ) Secor Managemen ws (TRs TRs B ) s (70 3) Top-Level Exposure (w w B ) TR B (70 4) Asse Allocaion w µ w s s w wb s (ER B w B s ER B ) (70 5) Secor Managemen ws (ERs ERs B ) s (70 6) Top-Level Exposure (w w B ) ER B 1
Quantitative Finance and Investments Advanced Formula Sheet. Fall 2014/Spring 2015
 Quaniaive Finance and Invemen Advanced Formula Shee Fall 2014/Spring 2015 Morning and afernoon exam bookle will include a formula package idenical o he one aached o hi udy noe. The exam commiee believe
Quaniaive Finance and Invemen Advanced Formula Shee Fall 2014/Spring 2015 Morning and afernoon exam bookle will include a formula package idenical o he one aached o hi udy noe. The exam commiee believe
Quantitative Finance and Investments Advanced Formula Sheet. Fall 2016/Spring 2017
 Quanave Fnance and Invesmens Advanced Formula Shee Fall 2016/Sprng 2017 Mornng and afernoon exam bookles wll nclude a formula package dencal o he one aached o hs sudy noe. The exam commee beleves ha by
Quanave Fnance and Invesmens Advanced Formula Shee Fall 2016/Sprng 2017 Mornng and afernoon exam bookles wll nclude a formula package dencal o he one aached o hs sudy noe. The exam commee beleves ha by
Quantitative Finance and Investments Advanced Formula Sheet. Fall 2017/Spring 2018
 Quanave Fnance and Invesmens Advanced Formula Shee Fall 2017/Sprng 2018 Mornng and afernoon exam bookles wll nclude a formula package dencal o he one aached o hs sudy noe. The exam commee beleves ha by
Quanave Fnance and Invesmens Advanced Formula Shee Fall 2017/Sprng 2018 Mornng and afernoon exam bookles wll nclude a formula package dencal o he one aached o hs sudy noe. The exam commee beleves ha by
Quantitative Finance and Investment Core Formula Sheet. Spring 2017
 Quaniaive Finance and Invesmen Core Formula Shee Spring 7 Morning and afernoon exam bookles will include a formula package idenical o he one aached o his sudy noe. The exam commiee believe ha by providing
Quaniaive Finance and Invesmen Core Formula Shee Spring 7 Morning and afernoon exam bookles will include a formula package idenical o he one aached o his sudy noe. The exam commiee believe ha by providing
Quantitative Finance and Investments Core Formula Sheet. Spring 2016
 Quaniaive Finance and Invesmens Core Formula Shee Spring 6 Morning and afernoon exam bookles will include a formula package idenical o he one aached o his sudy noe. The exam commiee believe ha by providing
Quaniaive Finance and Invesmens Core Formula Shee Spring 6 Morning and afernoon exam bookles will include a formula package idenical o he one aached o his sudy noe. The exam commiee believe ha by providing
9.1 Introduction 9.2 Lags in the Error Term: Autocorrelation 9.3 Estimating an AR(1) Error Model 9.4 Testing for Autocorrelation 9.
 9.1 Inroducion 9.2 Lags in he Error Term: Auocorrelaion 9.3 Esimaing an AR(1) Error Model 9.4 Tesing for Auocorrelaion 9.5 An Inroducion o Forecasing: Auoregressive Models 9.6 Finie Disribued Lags 9.7
9.1 Inroducion 9.2 Lags in he Error Term: Auocorrelaion 9.3 Esimaing an AR(1) Error Model 9.4 Tesing for Auocorrelaion 9.5 An Inroducion o Forecasing: Auoregressive Models 9.6 Finie Disribued Lags 9.7
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr (T t N n) Pr (max (X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr (max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
SOLUTIONS TO MATH38181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question 1 a) The cumulative distribution function of T conditional on N n is Pr T t N n) Pr max X 1,..., X N ) t N n) Pr max
( ) ( t) ( 0) ( ) dw w. = = β. Then the solution of (1.1) is easily found to. wt = t+ t. We generalize this to the following nonlinear differential
 Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
Periodic oluion of van der Pol differenial equaion. by A. Arimoo Deparmen of Mahemaic Muahi Iniue of Technology Tokyo Japan in Seminar a Kiami Iniue of Technology January 8 9. Inroducion Le u conider a
ITU-R P (2009/10)
 ITU-R.45-4 (9/) % # GHz,!"# $$ # ITU-R.45-4.. (IR) (ITU-T/ITU-R/ISO/IEC).ITU-R http://www.tu.t/itu-r/go/patets/e. (http://www.tu.t/publ/r-rec/e ) () ( ) BO BR BS BT F M RA S RS SA SF SM SNG TF V.ITU-R
ITU-R.45-4 (9/) % # GHz,!"# $$ # ITU-R.45-4.. (IR) (ITU-T/ITU-R/ISO/IEC).ITU-R http://www.tu.t/itu-r/go/patets/e. (http://www.tu.t/publ/r-rec/e ) () ( ) BO BR BS BT F M RA S RS SA SF SM SNG TF V.ITU-R
Math221: HW# 1 solutions
 Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Math: HW# solutions Andy Royston October, 5 7.5.7, 3 rd Ed. We have a n = b n = a = fxdx = xdx =, x cos nxdx = x sin nx n sin nxdx n = cos nx n = n n, x sin nxdx = x cos nx n + cos nxdx n cos n = + sin
Teor imov r. ta matem. statist. Vip. 94, 2016, stor
 eor imov r. ta matem. statist. Vip. 94, 6, stor. 93 5 Abstract. e article is devoted to models of financial markets wit stocastic volatility, wic is defined by a functional of Ornstein-Ulenbeck process
eor imov r. ta matem. statist. Vip. 94, 6, stor. 93 5 Abstract. e article is devoted to models of financial markets wit stocastic volatility, wic is defined by a functional of Ornstein-Ulenbeck process
r r t r r t t r t P s r t r P s r s r r rs tr t r r t s ss r P s s t r t t tr r r t t r t r r t t s r t rr t Ü rs t 3 r r r 3 rträ 3 röÿ r t
 r t t r t ts r3 s r r t r r t t r t P s r t r P s r s r P s r 1 s r rs tr t r r t s ss r P s s t r t t tr r 2s s r t t r t r r t t s r t rr t Ü rs t 3 r t r 3 s3 Ü rs t 3 r r r 3 rträ 3 röÿ r t r r r rs
r t t r t ts r3 s r r t r r t t r t P s r t r P s r s r P s r 1 s r rs tr t r r t s ss r P s s t r t t tr r 2s s r t t r t r r t t s r t rr t Ü rs t 3 r t r 3 s3 Ü rs t 3 r r r 3 rträ 3 röÿ r t r r r rs
Parts Manual. Trio Mobile Surgery Platform. Model 1033
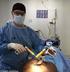 Trio Mobile Surgery Platform Model 1033 Parts Manual For parts or technical assistance: Pour pièces de service ou assistance technique : Für Teile oder technische Unterstützung Anruf: Voor delen of technische
Trio Mobile Surgery Platform Model 1033 Parts Manual For parts or technical assistance: Pour pièces de service ou assistance technique : Für Teile oder technische Unterstützung Anruf: Voor delen of technische
HW 3 Solutions 1. a) I use the auto.arima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA(3,1)
 HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
HW 3 Solutions a) I use the autoarima R function to search over models using AIC and decide on an ARMA3,) b) I compare the ARMA3,) to ARMA,0) ARMA3,) does better in all three criteria c) The plot of the
Geodesic Equations for the Wormhole Metric
 Geodesic Equations for the Wormhole Metric Dr R Herman Physics & Physical Oceanography, UNCW February 14, 2018 The Wormhole Metric Morris and Thorne wormhole metric: [M S Morris, K S Thorne, Wormholes
Geodesic Equations for the Wormhole Metric Dr R Herman Physics & Physical Oceanography, UNCW February 14, 2018 The Wormhole Metric Morris and Thorne wormhole metric: [M S Morris, K S Thorne, Wormholes
P P Ó P. r r t r r r s 1. r r ó t t ó rr r rr r rí st s t s. Pr s t P r s rr. r t r s s s é 3 ñ
 P P Ó P r r t r r r s 1 r r ó t t ó rr r rr r rí st s t s Pr s t P r s rr r t r s s s é 3 ñ í sé 3 ñ 3 é1 r P P Ó P str r r r t é t r r r s 1 t r P r s rr 1 1 s t r r ó s r s st rr t s r t s rr s r q s
P P Ó P r r t r r r s 1 r r ó t t ó rr r rr r rí st s t s Pr s t P r s rr r t r s s s é 3 ñ í sé 3 ñ 3 é1 r P P Ó P str r r r t é t r r r s 1 t r P r s rr 1 1 s t r r ó s r s st rr t s r t s rr s r q s
Jeux d inondation dans les graphes
 Jeux d inondation dans les graphes Aurélie Lagoutte To cite this version: Aurélie Lagoutte. Jeux d inondation dans les graphes. 2010. HAL Id: hal-00509488 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00509488
Jeux d inondation dans les graphes Aurélie Lagoutte To cite this version: Aurélie Lagoutte. Jeux d inondation dans les graphes. 2010. HAL Id: hal-00509488 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00509488
Χρονοσειρές Μάθημα 3
 Χρονοσειρές Μάθημα 3 Ασυσχέτιστες (λευκός θόρυβος) και ανεξάρτητες (iid) παρατηρήσεις Chafield C., The Analysis of Time Series, An Inroducion, 6 h ediion,. 38 (Chaer 3): Some auhors refer o make he weaker
Χρονοσειρές Μάθημα 3 Ασυσχέτιστες (λευκός θόρυβος) και ανεξάρτητες (iid) παρατηρήσεις Chafield C., The Analysis of Time Series, An Inroducion, 6 h ediion,. 38 (Chaer 3): Some auhors refer o make he weaker
Appendix. The solution begins with Eq. (2.15) from the text, which we repeat here for 1, (A.1)
 Aenix Aenix A: The equaion o he sock rice. The soluion egins wih Eq..5 rom he ex, which we reea here or convenience as Eq.A.: [ [ E E X, A. c α where X u ε, α γ, an c α y AR. Take execaions o Eq. A. as
Aenix Aenix A: The equaion o he sock rice. The soluion egins wih Eq..5 rom he ex, which we reea here or convenience as Eq.A.: [ [ E E X, A. c α where X u ε, α γ, an c α y AR. Take execaions o Eq. A. as
Homework 8 Model Solution Section
 MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
MATH 004 Homework Solution Homework 8 Model Solution Section 14.5 14.6. 14.5. Use the Chain Rule to find dz where z cosx + 4y), x 5t 4, y 1 t. dz dx + dy y sinx + 4y)0t + 4) sinx + 4y) 1t ) 0t + 4t ) sinx
HONDA. Έτος κατασκευής
 Accord + Coupe IV 2.0 16V (CB3) F20A2-A3 81 110 01/90-09/93 0800-0175 11,00 2.0 16V (CB3) F20A6 66 90 01/90-09/93 0800-0175 11,00 2.0i 16V (CB3-CC9) F20A8 98 133 01/90-09/93 0802-9205M 237,40 2.0i 16V
Accord + Coupe IV 2.0 16V (CB3) F20A2-A3 81 110 01/90-09/93 0800-0175 11,00 2.0 16V (CB3) F20A6 66 90 01/90-09/93 0800-0175 11,00 2.0i 16V (CB3-CC9) F20A8 98 133 01/90-09/93 0802-9205M 237,40 2.0i 16V
m 1, m 2 F 12, F 21 F12 = F 21
 m 1, m 2 F 12, F 21 F12 = F 21 r 1, r 2 r = r 1 r 2 = r 1 r 2 ê r = rê r F 12 = f(r)ê r F 21 = f(r)ê r f(r) f(r) < 0 f(r) > 0 m 1 r1 = f(r)ê r m 2 r2 = f(r)ê r r = r 1 r 2 r 1 = 1 m 1 f(r)ê r r 2 = 1 m
m 1, m 2 F 12, F 21 F12 = F 21 r 1, r 2 r = r 1 r 2 = r 1 r 2 ê r = rê r F 12 = f(r)ê r F 21 = f(r)ê r f(r) f(r) < 0 f(r) > 0 m 1 r1 = f(r)ê r m 2 r2 = f(r)ê r r = r 1 r 2 r 1 = 1 m 1 f(r)ê r r 2 = 1 m
Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α
 Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
Α Ρ Χ Α Ι Α Ι Σ Τ Ο Ρ Ι Α Π Ο Λ Ι Τ Ι Κ Α Κ Α Ι Σ Τ Ρ Α Τ Ι Ω Τ Ι Κ Α Γ Ε Γ Ο Ν Ο Τ Α Σ η µ ε ί ω σ η : σ υ ν ά δ ε λ φ ο ι, ν α µ ο υ σ υ γ χ ω ρ ή σ ε τ ε τ ο γ ρ ή γ ο ρ ο κ α ι α τ η µ έ λ η τ ο ύ
Physique des réacteurs à eau lourde ou légère en cycle thorium : étude par simulation des performances de conversion et de sûreté
 Physique des réacteurs à eau lourde ou légère en cycle thorium : étude par simulation des performances de conversion et de sûreté Alexis Nuttin To cite this version: Alexis Nuttin. Physique des réacteurs
Physique des réacteurs à eau lourde ou légère en cycle thorium : étude par simulation des performances de conversion et de sûreté Alexis Nuttin To cite this version: Alexis Nuttin. Physique des réacteurs
Econ 2110: Fall 2008 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 questions or comments to Dan Fetter 1
 Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Eon : Fall 8 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Email questions or omments to Dan Fetter Problem. Let X be a salar with density f(x, θ) (θx + θ) [ x ] with θ. (a) Find the most powerful level α test
Radio détection des rayons cosmiques d ultra-haute énergie : mise en oeuvre et analyse des données d un réseau de stations autonomes.
 Radio détection des rayons cosmiques d ultra-haute énergie : mise en oeuvre et analyse des données d un réseau de stations autonomes. Diego Torres Machado To cite this version: Diego Torres Machado. Radio
Radio détection des rayons cosmiques d ultra-haute énergie : mise en oeuvre et analyse des données d un réseau de stations autonomes. Diego Torres Machado To cite this version: Diego Torres Machado. Radio
Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st & 2 nd reprint)
 Wedesday, May 5, 3 Erraa (Icludes criical correcios oly for he s & d repri) Advaced Egieerig Mahemaics, 7e Peer V O eil ISB: 978474 Page # Descripio 38 ie 4: chage "w v a v " "w v a v " 46 ie : chage "y
Wedesday, May 5, 3 Erraa (Icludes criical correcios oly for he s & d repri) Advaced Egieerig Mahemaics, 7e Peer V O eil ISB: 978474 Page # Descripio 38 ie 4: chage "w v a v " "w v a v " 46 ie : chage "y
Appendix A. Curvilinear coordinates. A.1 Lamé coefficients. Consider set of equations. ξ i = ξ i (x 1,x 2,x 3 ), i = 1,2,3
 Appendix A Curvilinear coordinates A. Lamé coefficients Consider set of equations ξ i = ξ i x,x 2,x 3, i =,2,3 where ξ,ξ 2,ξ 3 independent, single-valued and continuous x,x 2,x 3 : coordinates of point
Appendix A Curvilinear coordinates A. Lamé coefficients Consider set of equations ξ i = ξ i x,x 2,x 3, i =,2,3 where ξ,ξ 2,ξ 3 independent, single-valued and continuous x,x 2,x 3 : coordinates of point
Empirical best prediction under area-level Poisson mixed models
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor Empirical best prediction under area-level Poisson mixed models Miguel Boubeta María José Lombardía Domingo Morales eceived: date / Accepted: date
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor Empirical best prediction under area-level Poisson mixed models Miguel Boubeta María José Lombardía Domingo Morales eceived: date / Accepted: date
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations
 On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
On the Galois Group of Linear Difference-Differential Equations Ruyong Feng KLMM, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Ruyong Feng (KLMM, CAS) Galois Group 1 / 19 Contents 1 Basic Notations and Concepts
 Z = 1.2 X 1 + 1, 4 X 2 + 3, 3 X 3 + 0, 6 X 4 + 0, 999 X 5. X 1 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 4 X 4 X 5 X 4 X 4 Z = 0.717 X 1 + 0.847 X 2 + 3.107 X 3 + 0.420 X 4 + 0.998 X 5. X 5 X 4 Z = 6.56 X 1 + 3.26 X 2 + 6.72 X 3
Z = 1.2 X 1 + 1, 4 X 2 + 3, 3 X 3 + 0, 6 X 4 + 0, 999 X 5. X 1 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 4 X 4 X 5 X 4 X 4 Z = 0.717 X 1 + 0.847 X 2 + 3.107 X 3 + 0.420 X 4 + 0.998 X 5. X 5 X 4 Z = 6.56 X 1 + 3.26 X 2 + 6.72 X 3
Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence MRI in Multiple Sclerosis
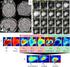 Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence MRI in Multiple Sclerosis Daniel García-Lorenzo To cite this version: Daniel García-Lorenzo. Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence
Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence MRI in Multiple Sclerosis Daniel García-Lorenzo To cite this version: Daniel García-Lorenzo. Robust Segmentation of Focal Lesions on Multi-Sequence
Fourier Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
Fourier Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction Not all functions can be represented by Taylor series. f (k) (c) A Taylor series f (x) = (x c)
(... )..!, ".. (! ) # - $ % % $ & % 2007
 (! ), "! ( ) # $ % & % $ % 007 500 ' 67905:5394!33 : (! ) $, -, * +,'; ), -, *! ' - " #!, $ & % $ ( % %): /!, " ; - : - +', 007 5 ISBN 978-5-7596-0766-3 % % - $, $ &- % $ % %, * $ % - % % # $ $,, % % #-
(! ), "! ( ) # $ % & % $ % 007 500 ' 67905:5394!33 : (! ) $, -, * +,'; ), -, *! ' - " #!, $ & % $ ( % %): /!, " ; - : - +', 007 5 ISBN 978-5-7596-0766-3 % % - $, $ &- % $ % %, * $ % - % % # $ $,, % % #-
= e 6t. = t 1 = t. 5 t 8L 1[ 1 = 3L 1 [ 1. L 1 [ π. = 3 π. = L 1 3s = L. = 3L 1 s t. = 3 cos(5t) sin(5t).
 Worked Soluion 95 Chaper 25: The Invere Laplace Tranform 25 a From he able: L ] e 6 6 25 c L 2 ] ] L! + 25 e L 5 2 + 25] ] L 5 2 + 5 2 in(5) 252 a L 6 + 2] L 6 ( 2)] 6L ( 2)] 6e 2 252 c L 3 8 4] 3L ] 8L
Worked Soluion 95 Chaper 25: The Invere Laplace Tranform 25 a From he able: L ] e 6 6 25 c L 2 ] ] L! + 25 e L 5 2 + 25] ] L 5 2 + 5 2 in(5) 252 a L 6 + 2] L 6 ( 2)] 6L ( 2)] 6e 2 252 c L 3 8 4] 3L ] 8L
ω = radians per sec, t = 3 sec
 Secion. Linear and Angular Speed 7. From exercise, =. A= r A = ( 00 ) (. ) = 7,00 in 7. Since 7 is in quadran IV, he reference 7 8 7 angle is = =. In quadran IV, he cosine is posiive. Thus, 7 cos = cos
Secion. Linear and Angular Speed 7. From exercise, =. A= r A = ( 00 ) (. ) = 7,00 in 7. Since 7 is in quadran IV, he reference 7 8 7 angle is = =. In quadran IV, he cosine is posiive. Thus, 7 cos = cos
Homework for 1/27 Due 2/5
 Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Name: ID: Homework for /7 Due /5. [ 8-3] I Example D of Sectio 8.4, the pdf of the populatio distributio is + αx x f(x α) =, α, otherwise ad the method of momets estimate was foud to be ˆα = 3X (where
Lecture 12 Modulation and Sampling
 EE 2 spring 2-22 Handou #25 Lecure 2 Modulaion and Sampling The Fourier ransform of he produc of wo signals Modulaion of a signal wih a sinusoid Sampling wih an impulse rain The sampling heorem 2 Convoluion
EE 2 spring 2-22 Handou #25 Lecure 2 Modulaion and Sampling The Fourier ransform of he produc of wo signals Modulaion of a signal wih a sinusoid Sampling wih an impulse rain The sampling heorem 2 Convoluion
m i N 1 F i = j i F ij + F x
 N m i i = 1,..., N m i Fi x N 1 F ij, j = 1, 2,... i 1, i + 1,..., N m i F i = j i F ij + F x i mi Fi j Fj i mj O P i = F i = j i F ij + F x i, i = 1,..., N P = i F i = N F ij + i j i N i F x i, i = 1,...,
N m i i = 1,..., N m i Fi x N 1 F ij, j = 1, 2,... i 1, i + 1,..., N m i F i = j i F ij + F x i mi Fi j Fj i mj O P i = F i = j i F ij + F x i, i = 1,..., N P = i F i = N F ij + i j i N i F x i, i = 1,...,
Ax = b. 7x = 21. x = 21 7 = 3.
 3 s st 3 r 3 t r 3 3 t s st t 3t s 3 3 r 3 3 st t t r 3 s t t r r r t st t rr 3t r t 3 3 rt3 3 t 3 3 r st 3 t 3 tr 3 r t3 t 3 s st t Ax = b. s t 3 t 3 3 r r t n r A tr 3 rr t 3 t n ts b 3 t t r r t x 3
3 s st 3 r 3 t r 3 3 t s st t 3t s 3 3 r 3 3 st t t r 3 s t t r r r t st t rr 3t r t 3 3 rt3 3 t 3 3 r st 3 t 3 tr 3 r t3 t 3 s st t Ax = b. s t 3 t 3 3 r r t n r A tr 3 rr t 3 t n ts b 3 t t r r t x 3
Solutions - Chapter 4
 Solutions - Chapter Kevin S. Huang Problem.1 Unitary: Ût = 1 ī hĥt Û tût = 1 Neglect t term: 1 + hĥ ī t 1 īhĥt = 1 + hĥ ī t ī hĥt = 1 Ĥ = Ĥ Problem. Ût = lim 1 ī ] n hĥ1t 1 ī ] hĥt... 1 ī ] hĥnt 1 ī ]
Solutions - Chapter Kevin S. Huang Problem.1 Unitary: Ût = 1 ī hĥt Û tût = 1 Neglect t term: 1 + hĥ ī t 1 īhĥt = 1 + hĥ ī t ī hĥt = 1 Ĥ = Ĥ Problem. Ût = lim 1 ī ] n hĥ1t 1 ī ] hĥt... 1 ī ] hĥnt 1 ī ]
6.003: Signals and Systems. Modulation
 6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Subjec Evaluaions Your feedback is imporan o us! Please give feedback o he saff and fuure 6.3 sudens: hp://web.mi.edu/subjecevaluaion Evaluaions are open
6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Subjec Evaluaions Your feedback is imporan o us! Please give feedback o he saff and fuure 6.3 sudens: hp://web.mi.edu/subjecevaluaion Evaluaions are open
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS
 SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS and POLYNOMIALS Gerard t Hooft Stefan Nobbenhuis Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University, Leuvenlaan 4 3584 CC Utrecht, the Netherlands and Spinoza Institute Postbox 8.195
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix
 The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 () The ε-pseudospectrum of a Matrix Feb 16, 2015 1 / 18 1 Preliminaries 2 Definitions 3 Basic Properties 4 Computation of Pseudospectrum of 2 2 5 Problems
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Answer sheet: Third Midterm for Math 339 November 3, Problem. Calculate the iterated integrals (Simplify as much as possible) (a) e sin(x) dydx y e sin(x) dydx y sin(x) ln y ( cos(x)) ye y dx sin(x)(lne
Matrices and Determinants
 Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Matrices and Determinants SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. For what value of k do the following system of equations possess a non-trivial (i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q? x + ky + 3z
Second Order Partial Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
Chapter 7 Second Order Partial Differential Equations 7.1 Introduction A second order linear PDE in two independent variables (x, y Ω can be written as A(x, y u x + B(x, y u xy + C(x, y u u u + D(x, y
4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(1,1)
 84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
84 CHAPTER 4. STATIONARY TS MODELS 4.6 Autoregressive Moving Average Model ARMA(,) This section is an introduction to a wide class of models ARMA(p,q) which we will consider in more detail later in this
d dt S = (t)si d dt R = (t)i d dt I = (t)si (t)i
 d d S = ()SI d d I = ()SI ()I d d R = ()I d d S = ()SI μs + fi + hr d d I = + ()SI (μ + + f + ())I d d R = ()I (μ + h)r d d P(S,I,) = ()(S +1)(I 1)P(S +1, I 1, ) +()(I +1)P(S,I +1, ) (()SI + ()I)P(S,I,)
d d S = ()SI d d I = ()SI ()I d d R = ()I d d S = ()SI μs + fi + hr d d I = + ()SI (μ + + f + ())I d d R = ()I (μ + h)r d d P(S,I,) = ()(S +1)(I 1)P(S +1, I 1, ) +()(I +1)P(S,I +1, ) (()SI + ()I)P(S,I,)
TeSys contactors a.c. coils for 3-pole contactors LC1-D
 References a.c. coils for 3-pole contactors LC1-D Control circuit voltage Average resistance Inductance of Reference (1) Weight Uc at 0 C ± 10 % closed circuit For 3-pole " contactors LC1-D09...D38 and
References a.c. coils for 3-pole contactors LC1-D Control circuit voltage Average resistance Inductance of Reference (1) Weight Uc at 0 C ± 10 % closed circuit For 3-pole " contactors LC1-D09...D38 and
 φ(t) TE 0 φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) η(λ) G(z,λ) λ φ(z) η(λ) η(λ) = t CIGS 0 G(z,λ)φ(z)dz t CIGS η(λ) φ(z) 0 z
φ(t) TE 0 φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) φ(z) η(λ) G(z,λ) λ φ(z) η(λ) η(λ) = t CIGS 0 G(z,λ)φ(z)dz t CIGS η(λ) φ(z) 0 z
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude
 Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
Approximation of distance between locations on earth given by latitude and longitude Jan Behrens 2012-12-31 In this paper we shall provide a method to approximate distances between two points on earth
: Ω F F 0 t T P F 0 t T F 0 P Q. Merton 1974 XT T X T XT. T t. V t t X d T = XT [V t/t ]. τ 0 < τ < X d T = XT I {V τ T } δt XT I {V τ<t } I A
![: Ω F F 0 t T P F 0 t T F 0 P Q. Merton 1974 XT T X T XT. T t. V t t X d T = XT [V t/t ]. τ 0 < τ < X d T = XT I {V τ T } δt XT I {V τ<t } I A : Ω F F 0 t T P F 0 t T F 0 P Q. Merton 1974 XT T X T XT. T t. V t t X d T = XT [V t/t ]. τ 0 < τ < X d T = XT I {V τ T } δt XT I {V τ<t } I A](/thumbs/91/105433318.jpg) 2012 4 Chinese Journal of Applied Probability and Statistics Vol.28 No.2 Apr. 2012 730000. :. : O211.9. 1..... Johnson Stulz [3] 1987. Merton 1974 Johnson Stulz 1987. Hull White 1995 Klein 1996 2008 Klein
2012 4 Chinese Journal of Applied Probability and Statistics Vol.28 No.2 Apr. 2012 730000. :. : O211.9. 1..... Johnson Stulz [3] 1987. Merton 1974 Johnson Stulz 1987. Hull White 1995 Klein 1996 2008 Klein
r t t r t t à ré ér t é r t st é é t r s s2stè s t rs ts t s
 r t r r é té tr q tr t q t t q t r t t rrêté stér ût Prés té r ré ér ès r é r r st P t ré r t érô t 2r ré ré s r t r tr q t s s r t t s t r tr q tr t q t t q t r t t r t t r t t à ré ér t é r t st é é
r t r r é té tr q tr t q t t q t r t t rrêté stér ût Prés té r ré ér ès r é r r st P t ré r t érô t 2r ré ré s r t r tr q t s s r t t s t r tr q tr t q t t q t r t t r t t r t t à ré ér t é r t st é é
C 1 D 1. AB = a, AD = b, AA1 = c. a, b, c : (1) AC 1 ; : (1) AB + BC + CC1, AC 1 = BC = AD, CC1 = AA 1, AC 1 = a + b + c. (2) BD 1 = BD + DD 1,
 1 1., BD 1 B 1 1 D 1, E F B 1 D 1. B = a, D = b, 1 = c. a, b, c : (1) 1 ; () BD 1 ; () F; D 1 F 1 (4) EF. : (1) B = D, D c b 1 E a B 1 1 = 1, B1 1 = B + B + 1, 1 = a + b + c. () BD 1 = BD + DD 1, BD =
1 1., BD 1 B 1 1 D 1, E F B 1 D 1. B = a, D = b, 1 = c. a, b, c : (1) 1 ; () BD 1 ; () F; D 1 F 1 (4) EF. : (1) B = D, D c b 1 E a B 1 1 = 1, B1 1 = B + B + 1, 1 = a + b + c. () BD 1 = BD + DD 1, BD =
 Molekulare Ebene (biochemische Messungen) Zelluläre Ebene (Elektrophysiologie, Imaging-Verfahren) Netzwerk Ebene (Multielektrodensysteme) Areale (MRT, EEG...) Gene Neuronen Synaptische Kopplung kleine
Molekulare Ebene (biochemische Messungen) Zelluläre Ebene (Elektrophysiologie, Imaging-Verfahren) Netzwerk Ebene (Multielektrodensysteme) Areale (MRT, EEG...) Gene Neuronen Synaptische Kopplung kleine
6.003: Signals and Systems
 6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Communicaions Sysems Signals are no always well mached o he media hrough which we wish o ransmi hem. signal audio video inerne applicaions elephone, radio,
6.3: Signals and Sysems Modulaion December 6, 2 Communicaions Sysems Signals are no always well mached o he media hrough which we wish o ransmi hem. signal audio video inerne applicaions elephone, radio,
16. 17. r t te 2t i t 1. 18 19 Find the derivative of the vector function. 19. r t e t cos t i e t sin t j ln t k. 31 33 Evaluate the integral.
 SECTION.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES A Click here for answers. S Click here for soluions. Copyrigh Cengage Learning. All righs reserved.. Find he domain of he
SECTION.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES.7 VECTOR FUNCTIONS AND SPACE CURVES A Click here for answers. S Click here for soluions. Copyrigh Cengage Learning. All righs reserved.. Find he domain of he
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set
 Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
Every set of first-order formulas is equivalent to an independent set May 6, 2008 Abstract A set of first-order formulas, whatever the cardinality of the set of symbols, is equivalent to an independent
 γ n ϑ n n ψ T 8 Q 6 j, k, m, n, p, r, r t, x, y f m (x) (f(x)) m / a/b (f g)(x) = f(g(x)) n f f n I J α β I = α + βj N, Z, Q ϕ Εὐκλείδης ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς Στοιχεῖα ἄκρος καὶ μέσος λόγος ὕδωρ αἰθήρ ϕ φ Φ τ
γ n ϑ n n ψ T 8 Q 6 j, k, m, n, p, r, r t, x, y f m (x) (f(x)) m / a/b (f g)(x) = f(g(x)) n f f n I J α β I = α + βj N, Z, Q ϕ Εὐκλείδης ὁ Ἀλεξανδρεύς Στοιχεῖα ἄκρος καὶ μέσος λόγος ὕδωρ αἰθήρ ϕ φ Φ τ
Lifting Entry (continued)
 ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
ifting Entry (continued) Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion Planar state equations MARYAN 1 01 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu
Vol. 37 ( 2017 ) No. 3. J. of Math. (PRC) : A : (2017) k=1. ,, f. f + u = f φ, x 1. x n : ( ).
 Vol. 37 ( 2017 ) No. 3 J. of Math. (PRC) R N - R N - 1, 2 (1., 100029) (2., 430072) : R N., R N, R N -. : ; ; R N ; MR(2010) : 58K40 : O192 : A : 0255-7797(2017)03-0467-07 1. [6], Mather f : (R n, 0) R
Vol. 37 ( 2017 ) No. 3 J. of Math. (PRC) R N - R N - 1, 2 (1., 100029) (2., 430072) : R N., R N, R N -. : ; ; R N ; MR(2010) : 58K40 : O192 : A : 0255-7797(2017)03-0467-07 1. [6], Mather f : (R n, 0) R
Το άτομο του Υδρογόνου
 Το άτομο του Υδρογόνου Δυναμικό Coulomb Εξίσωση Schrödinger h e (, r, ) (, r, ) E (, r, ) m ψ θφ r ψ θφ = ψ θφ Συνθήκες ψ(, r θφ, ) = πεπερασμένη ψ( r ) = 0 ψ(, r θφ, ) =ψ(, r θφ+, ) π Επιτρεπτές ενέργειες
Το άτομο του Υδρογόνου Δυναμικό Coulomb Εξίσωση Schrödinger h e (, r, ) (, r, ) E (, r, ) m ψ θφ r ψ θφ = ψ θφ Συνθήκες ψ(, r θφ, ) = πεπερασμένη ψ( r ) = 0 ψ(, r θφ, ) =ψ(, r θφ+, ) π Επιτρεπτές ενέργειες
d dx x 2 = 2x d dx x 3 = 3x 2 d dx x n = nx n 1
 d dx x 2 = 2x d dx x 3 = 3x 2 d dx x n = nx n1 x dx = 1 2 b2 1 2 a2 a b b x 2 dx = 1 a 3 b3 1 3 a3 b x n dx = 1 a n +1 bn +1 1 n +1 an +1 d dx d dx f (x) = 0 f (ax) = a f (ax) lim d dx f (ax) = lim 0 =
d dx x 2 = 2x d dx x 3 = 3x 2 d dx x n = nx n1 x dx = 1 2 b2 1 2 a2 a b b x 2 dx = 1 a 3 b3 1 3 a3 b x n dx = 1 a n +1 bn +1 1 n +1 an +1 d dx d dx f (x) = 0 f (ax) = a f (ax) lim d dx f (ax) = lim 0 =
P AND P. P : actual probability. P : risk neutral probability. Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P. For example:
 (B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
(B t, S (t) t P AND P,..., S (p) t ): securities P : actual probability P : risk neutral probability Realtionship: mutual absolute continuity P P For example: P : ds t = µ t S t dt + σ t S t dw t P : ds
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions
 C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
C.S. 430 Assignment 6, Sample Solutions Paul Liu November 15, 2007 Note that these are sample solutions only; in many cases there were many acceptable answers. 1 Reynolds Problem 10.1 1.1 Normal-order
A Probabilistic Numerical Method for Fully Non-linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equations
 A Probabilistic Numerical Metod for Fully Non-linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equations Aras Faim To cite tis version: Aras Faim. A Probabilistic Numerical Metod for Fully Non-linear Parabolic Partial
A Probabilistic Numerical Metod for Fully Non-linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equations Aras Faim To cite tis version: Aras Faim. A Probabilistic Numerical Metod for Fully Non-linear Parabolic Partial
wave energy Superposition of linear plane progressive waves Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture Oblique Plane Waves:
 3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
3.0 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 004 Lecture 0 Copyriht c 004 MIT - Department of Ocean Enineerin, All rihts reserved. 3.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 0 Free-surface waves: wave enery linear superposition,
.. ntsets ofa.. d ffeom.. orp ism.. na s.. m ooth.. man iod period I n open square. n t s e t s ofa \quad d ffeom \quad orp ism \quad na s \quad m o
 G G - - -- - W - - - R S - q k RS ˆ W q q k M G W R S L [ RS - q k M S 4 R q k S [ RS [ M L ˆ L [M O S 4] L ˆ ˆ L ˆ [ M ˆ S 4 ] ˆ - O - ˆ q k ˆ RS q k q k M - j [ RS ] [ M - j - L ˆ ˆ ˆ O ˆ [ RS ] [ M
G G - - -- - W - - - R S - q k RS ˆ W q q k M G W R S L [ RS - q k M S 4 R q k S [ RS [ M L ˆ L [M O S 4] L ˆ ˆ L ˆ [ M ˆ S 4 ] ˆ - O - ˆ q k ˆ RS q k q k M - j [ RS ] [ M - j - L ˆ ˆ ˆ O ˆ [ RS ] [ M
Aquinas College. Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET
 Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Aquinas College Edexcel Mathematical formulae and statistics tables DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced GCE in Mathematics and Further Mathematics Mathematical
Assessment of otoacoustic emission probe fit at the workfloor
 Assessment of otoacoustic emission probe fit at the workfloor t s st tt r st s s r r t rs t2 t P t rs str t t r 1 t s ér r tr st tr r2 t r r t s t t t r t s r ss r rr t 2 s r r 1 s r r t s s s r t s t
Assessment of otoacoustic emission probe fit at the workfloor t s st tt r st s s r r t rs t2 t P t rs str t t r 1 t s ér r tr st tr r2 t r r t s t t t r t s r ss r rr t 2 s r r 1 s r r t s s s r t s t
Points de torsion des courbes elliptiques et équations diophantiennes
 Points de torsion des courbes elliptiques et équations diophantiennes Nicolas Billerey To cite this version: Nicolas Billerey. Points de torsion des courbes elliptiques et équations diophantiennes. Mathématiques
Points de torsion des courbes elliptiques et équations diophantiennes Nicolas Billerey To cite this version: Nicolas Billerey. Points de torsion des courbes elliptiques et équations diophantiennes. Mathématiques
Cable Systems - Postive/Negative Seq Impedance
 Cable Systems - Postive/Negative Seq Impedance Nomenclature: GMD GMR - geometrical mead distance between conductors; depends on construction of the T-line or cable feeder - geometric mean raduius of conductor
Cable Systems - Postive/Negative Seq Impedance Nomenclature: GMD GMR - geometrical mead distance between conductors; depends on construction of the T-line or cable feeder - geometric mean raduius of conductor
ITU-R P (2012/02)
 ITU-R P.56- (0/0 P ITU-R P.56- ii.. (IPR (ITU-T/ITU-R/ISO/IEC.ITU-R ttp://www.itu.int/itu-r/go/patents/en. (ttp://www.itu.int/publ/r-rec/en ( ( BO BR BS BT F M P RA RS S SA SF SM SNG TF V 0.ITU-R ITU 0..(ITU
ITU-R P.56- (0/0 P ITU-R P.56- ii.. (IPR (ITU-T/ITU-R/ISO/IEC.ITU-R ttp://www.itu.int/itu-r/go/patents/en. (ttp://www.itu.int/publ/r-rec/en ( ( BO BR BS BT F M P RA RS S SA SF SM SNG TF V 0.ITU-R ITU 0..(ITU
6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves
 .0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 005 Lecture.0 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 6.4 Superposition of Linear Plane Progressive Waves. Oblique Plane Waves z v k k k z v k = ( k, k z ) θ (Looking up the y-ais
Mean-Variance Analysis
 Mean-Variance Analysis Jan Schneider McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin Jan Schneider Mean-Variance Analysis Beta Representation of the Risk Premium risk premium E t [Rt t+τ ] R1
Mean-Variance Analysis Jan Schneider McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin Jan Schneider Mean-Variance Analysis Beta Representation of the Risk Premium risk premium E t [Rt t+τ ] R1
Vers un assistant à la preuve en langue naturelle
 Vers un assistant à la preuve en langue naturelle Thévenon Patrick To cite this version: Thévenon Patrick. Vers un assistant à la preuve en langue naturelle. Autre [cs.oh]. Université de Savoie, 2006.
Vers un assistant à la preuve en langue naturelle Thévenon Patrick To cite this version: Thévenon Patrick. Vers un assistant à la preuve en langue naturelle. Autre [cs.oh]. Université de Savoie, 2006.
#%" )*& ##+," $ -,!./" %#/%0! %,!
 -!"#$% -&!'"$ & #("$$, #%" )*& ##+," $ -,!./" %#/%0! %,! %!$"#" %!#0&!/" /+#0& 0.00.04. - 3 3,43 5 -, 4 $ $.. 04 ... 3. 6... 6.. #3 7 8... 6.. %9: 3 3 7....3. % 44 8... 6.4. 37; 3,, 443 8... 8.5. $; 3
-!"#$% -&!'"$ & #("$$, #%" )*& ##+," $ -,!./" %#/%0! %,! %!$"#" %!#0&!/" /+#0& 0.00.04. - 3 3,43 5 -, 4 $ $.. 04 ... 3. 6... 6.. #3 7 8... 6.. %9: 3 3 7....3. % 44 8... 6.4. 37; 3,, 443 8... 8.5. $; 3
Fourier Analysis of Waves
 Exercises for the Feynman Lectures on Physics by Richard Feynman, Et Al. Chapter 36 Fourier Analysis of Waves Detailed Work by James Pate Williams, Jr. BA, BS, MSwE, PhD From Exercises for the Feynman
Exercises for the Feynman Lectures on Physics by Richard Feynman, Et Al. Chapter 36 Fourier Analysis of Waves Detailed Work by James Pate Williams, Jr. BA, BS, MSwE, PhD From Exercises for the Feynman
Ó³ Ÿ , º 2(131).. 105Ä ƒ. ± Ï,.. ÊÉ ±μ,.. Šμ ² ±μ,.. Œ Ì ²μ. Ñ Ò É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ, Ê
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2006.. 3, º 2(131).. 105Ä110 Š 537.311.5; 538.945 Œ ƒ ˆ ƒ Ÿ ˆŠ ˆ ƒ Ÿ ƒ ˆ œ ƒ Œ ƒ ˆ ˆ Š ˆ 4 ². ƒ. ± Ï,.. ÊÉ ±μ,.. Šμ ² ±μ,.. Œ Ì ²μ Ñ Ò É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ, Ê ³ É É Ö μ ² ³ μ É ³ Í ² Ö Ê³ μ μ ³ É μ μ μ²ö
Ó³ Ÿ. 2006.. 3, º 2(131).. 105Ä110 Š 537.311.5; 538.945 Œ ƒ ˆ ƒ Ÿ ˆŠ ˆ ƒ Ÿ ƒ ˆ œ ƒ Œ ƒ ˆ ˆ Š ˆ 4 ². ƒ. ± Ï,.. ÊÉ ±μ,.. Šμ ² ±μ,.. Œ Ì ²μ Ñ Ò É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ, Ê ³ É É Ö μ ² ³ μ É ³ Í ² Ö Ê³ μ μ ³ É μ μ μ²ö
Ó³ Ÿ , º 1(130).. 7Ä ±μ. Ñ Ò É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ, Ê
 Ó³ Ÿ. 006.. 3, º 1(130).. 7Ä16 Š 530.145 ˆ ƒ ˆ ˆŒ ˆŸ Š ƒ.. ±μ Ñ Ò É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ, Ê É μ ² Ö Ó μ μ Ö μ μ²õ μ É μ ÌÉ ±ÊÎ É ² ³ É μ - Î ±μ μ ÊÌ ±μ Ëμ ³ μ- ±² μ ÒÌ ³μ ²ÖÌ Ê ±. ³ É ÔÉμ μ μ μ Ö, Ö ²ÖÖ Ó ±μ³
Ó³ Ÿ. 006.. 3, º 1(130).. 7Ä16 Š 530.145 ˆ ƒ ˆ ˆŒ ˆŸ Š ƒ.. ±μ Ñ Ò É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ, Ê É μ ² Ö Ó μ μ Ö μ μ²õ μ É μ ÌÉ ±ÊÎ É ² ³ É μ - Î ±μ μ ÊÌ ±μ Ëμ ³ μ- ±² μ ÒÌ ³μ ²ÖÌ Ê ±. ³ É ÔÉμ μ μ μ Ö, Ö ²ÖÖ Ó ±μ³
Example Sheet 3 Solutions
 Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Example Sheet 3 Solutions. i Regular Sturm-Liouville. ii Singular Sturm-Liouville mixed boundary conditions. iii Not Sturm-Liouville ODE is not in Sturm-Liouville form. iv Regular Sturm-Liouville note
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix Measuring crisis risk using conditional copulas: An empirical analysis of the 2008 shipping crisis Sebastian Opitz, Henry Seidel and Alexander Szimayer Model specification Table
Supplementary Appendix Measuring crisis risk using conditional copulas: An empirical analysis of the 2008 shipping crisis Sebastian Opitz, Henry Seidel and Alexander Szimayer Model specification Table
6.1. Dirac Equation. Hamiltonian. Dirac Eq.
 6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
6.1. Dirac Equation Ref: M.Kaku, Quantum Field Theory, Oxford Univ Press (1993) η μν = η μν = diag(1, -1, -1, -1) p 0 = p 0 p = p i = -p i p μ p μ = p 0 p 0 + p i p i = E c 2 - p 2 = (m c) 2 H = c p 2
 γ 1 6 M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F 2 2 λ τ M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 1 6 τ = 36 1 6 τ = 102 1 6 M = 5000
γ 1 6 M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.05 F M = 0.2 F M = 0.05 F 2 2 λ τ M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 M = 6000 M = 10000 M = 15000 1 6 τ = 36 1 6 τ = 102 1 6 M = 5000
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian
 The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
The Pohozaev identity for the fractional Laplacian Xavier Ros-Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (joint work with Joaquim Serra) Xavier Ros-Oton (UPC) The Pohozaev
Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
 Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
Kiryl Tsishchanka Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates In this section we develop the formula for the area of a region whose boundary is given by a polar equation. We need to use the formula for the
26 28 Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve at the given point Discuss the curve under the guidelines of Section
 SECTION 5. THE NATURAL LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION 5. THE NATURAL LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 4 Use the Laws of Logarithms to epand the quantit.. ln ab. ln c. ln
SECTION 5. THE NATURAL LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION 5. THE NATURAL LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION A Click here for answers. S Click here for solutions. 4 Use the Laws of Logarithms to epand the quantit.. ln ab. ln c. ln
Laplace Expansion. Peter McCullagh. WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, Department of Statistics University of Chicago
 Laplace Expansion Peter McCullagh Department of Statistics University of Chicago WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, 2017 Outline Laplace approximation in 1D Laplace expansion in 1D Laplace expansion in R p Formal
Laplace Expansion Peter McCullagh Department of Statistics University of Chicago WHOA-PSI, St Louis August, 2017 Outline Laplace approximation in 1D Laplace expansion in 1D Laplace expansion in R p Formal
= df. f (n) (x) = dn f dx n
 Παράγωγος Συνάρτησης Ορισμός Παραγώγου σε ένα σημείο ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΟΣ ΣΥΝΑΡΤΗΣΗΣ σε ένα σημείο ξ είναι το όριο (αν υπάρχει!) Ορισμός Cauchy: f (ξ) = lim x ξ g(x, ξ), g(x, ξ) = f(x) f(ξ) x ξ ɛ > 0 δ(ɛ, ξ) > 0
Παράγωγος Συνάρτησης Ορισμός Παραγώγου σε ένα σημείο ΠΑΡΑΓΩΓΟΣ ΣΥΝΑΡΤΗΣΗΣ σε ένα σημείο ξ είναι το όριο (αν υπάρχει!) Ορισμός Cauchy: f (ξ) = lim x ξ g(x, ξ), g(x, ξ) = f(x) f(ξ) x ξ ɛ > 0 δ(ɛ, ξ) > 0
DiracDelta. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. General characteristics. Traditional name. Traditional notation
 DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
DiracDelta Notations Traditional name Dirac delta function Traditional notation x Mathematica StandardForm notation DiracDeltax Primary definition 4.03.02.000.0 x Π lim ε ; x ε0 x 2 2 ε Specific values
= f(0) + f dt. = f. O 2 (x, u) x=(x 1,x 2,,x n ) T, f(x) =(f 1 (x), f 2 (x),, f n (x)) T. f x = A = f
 2 n dx (x)+g(x)u () x n u (x), g(x) x n () +2 -a -b -b -a 3 () x,u dx x () dx () + x x + g()u + O 2 (x, u) x x x + g()u + O 2 (x, u) (2) x O 2 (x, u) x u 2 x(x,x 2,,x n ) T, (x) ( (x), 2 (x),, n (x)) T
2 n dx (x)+g(x)u () x n u (x), g(x) x n () +2 -a -b -b -a 3 () x,u dx x () dx () + x x + g()u + O 2 (x, u) x x x + g()u + O 2 (x, u) (2) x O 2 (x, u) x u 2 x(x,x 2,,x n ) T, (x) ( (x), 2 (x),, n (x)) T
The mass and anisotropy profiles of nearby galaxy clusters from the projected phase-space density
 The mass and anisotropy profiles of nearby galaxy clusters from the projected phase-space density 5..29 Radek Wojtak Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center collaboration: Ewa Łokas, Gary Mamon, Stefan
The mass and anisotropy profiles of nearby galaxy clusters from the projected phase-space density 5..29 Radek Wojtak Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center collaboration: Ewa Łokas, Gary Mamon, Stefan
Alterazioni del sistema cardiovascolare nel volo spaziale
 POLITECNICO DI TORINO Corso di Laurea in Ingegneria Aerospaziale Alterazioni del sistema cardiovascolare nel volo spaziale Relatore Ing. Stefania Scarsoglio Studente Marco Enea Anno accademico 2015 2016
POLITECNICO DI TORINO Corso di Laurea in Ingegneria Aerospaziale Alterazioni del sistema cardiovascolare nel volo spaziale Relatore Ing. Stefania Scarsoglio Studente Marco Enea Anno accademico 2015 2016
Lifting Entry 2. Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYLAND U N I V E R S I T Y O F
 ifting Entry Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYAN 1 010 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu ifting Atmospheric
ifting Entry Basic planar dynamics of motion, again Yet another equilibrium glide Hypersonic phugoid motion MARYAN 1 010 avid. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu ifting Atmospheric
m r = F m r = F ( r) m r = F ( v) F = F (x) m dv dt = F (x) vdv = F (x)dx d dt = dx dv dt dx = v dv dx
 m r = F m r = F ( r) m r = F ( v) x F = F (x) m dv dt = F (x) d dt = dx dv dt dx = v dv dx vdv = F (x)dx 2 mv2 x 2 mv2 0 = F (x )dx x 0 K = 2 mv2 W x0 x = x x 0 F (x)dx K K 0 = W x0 x x, x 2 x K 2 K =
m r = F m r = F ( r) m r = F ( v) x F = F (x) m dv dt = F (x) d dt = dx dv dt dx = v dv dx vdv = F (x)dx 2 mv2 x 2 mv2 0 = F (x )dx x 0 K = 2 mv2 W x0 x = x x 0 F (x)dx K K 0 = W x0 x x, x 2 x K 2 K =
Arbitrage Analysis of Futures Market with Frictions
 2007 1 1 :100026788 (2007) 0120033206, (, 200052) : Vignola2Dale (1980) Kawaller2Koch(1984) (cost of carry),.,, ;,, : ;,;,. : ;;; : F83019 : A Arbitrage Analysis of Futures Market with Frictions LIU Hai2long,
2007 1 1 :100026788 (2007) 0120033206, (, 200052) : Vignola2Dale (1980) Kawaller2Koch(1984) (cost of carry),.,, ;,, : ;,;,. : ;;; : F83019 : A Arbitrage Analysis of Futures Market with Frictions LIU Hai2long,
Durbin-Levinson recursive method
 Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
Durbin-Levinson recursive method A recursive method for computing ϕ n is useful because it avoids inverting large matrices; when new data are acquired, one can update predictions, instead of starting again
The Simply Typed Lambda Calculus
 Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
Type Inference Instead of writing type annotations, can we use an algorithm to infer what the type annotations should be? That depends on the type system. For simple type systems the answer is yes, and
